Android进阶——性能优化之进程提权与拉活原理及手段完全解析(九)
文章大纲
- 引言
- 一、系统账户同步机制拉活
- 1、继承Service并在内部继承实现用于返回Binder的AbstractAccountAuthenticator
- 2、在res/xml/文件夹下定义将要显示在Account列表的资源
- 3、在清单文件中配置AuthenticationService
- 4、创建App的账户
- 5、创建账户同步Service
- 6、告知系统我们的Account需要进行同步服务
- 7、完整的清单配置文件和MainActivity代码
- 二、JobSchedule 机制拉活
- 1、实现JobService
- 2、在清单中注册JobService
- 3、手动开启JobSchedule
- 三、双进程Service互相拉活
- 1、实现一个AIDL文件
- 2、实现运行在主进程的Service
- 3、定义子进程的Service
- 4、声明服务
- 5、开启双进程
- 6、再结合JobSchedule 进一步保活拉活
引言
上一篇文章Android进阶——性能优化之进程提权与保活原理及手段完全解析(八)总结了Android进程和线程的相关知识,主要介绍了几种提升进程优先级的手段,通常仅仅是提高优先级只能让你的进程存活时间久一点,但是真正的被杀死之后就不会自动拉活的,如果你的进程需要尽可能存在后台还需要拉活措施,在被杀死之后一段时间之内自动拉活。(如非绝对的需求,还是少浪费点用户的资源吧)以下是性能优化系列的链接地址列表(持续更新):
- Android进阶——性能优化之APP启动时黑白屏的根源解析及对应的优化措施小结(一)
- Android进阶——性能优化之APP启动过程相关源码解析(二)
- Android进阶——性能优化之APP启动速度优化实战总结(三)
- Android进阶——性能优化之布局渲染原理和底层机制详解(四)
- Android进阶——性能优化之布局优化实战经验小结(五)
- Android进阶——性能优化之内存管理机制和垃圾采集回收机制(六)
- Android进阶——性能优化之内存泄漏和内存抖动的检测及优化措施总结(七)
- Android进阶——性能优化之进程提权与保活原理及手段完全解析(八)
- Android进阶——性能优化之进程提权与拉活原理及手段完全解析(九
- Android进阶——性能优化之一种更高效更轻量的序列化方案Protocol Buffer完全攻略(十)
一、系统账户同步机制拉活
手机系统设置里会有Account帐户一项功能,任何第三方APP都可以通过此功能将我们自己的APP注册到这个Account帐户中,并且将数据在一定时间内同步到服务器中去。系统在将APP帐户同步时,自动将未启动的APP进程拉活,具体操作参见Google官方demo。
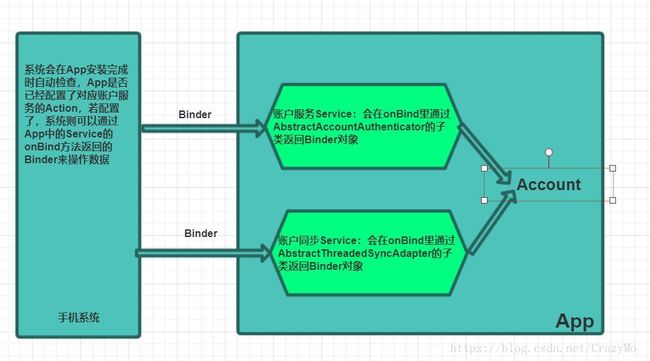
1、继承Service并在内部继承实现用于返回Binder的AbstractAccountAuthenticator
AuthenticationService继承自Service本质上是一个AIDL,提供给其他的进程使用的,主要我们实现并且声明了之后,android系统会通过android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator这个Action找到它,并通过它来把我们自己的账号注册到系统设置界面,其中Authenticator是一个继承自AbstractAccountAuthenticator的类,而AbstractAccountAuthenticator是用于实现对手机系统设置里“账号与同步”中Account的添加、删除和验证等一些基本功能。很明显AbstractAccountAuthenticator里面有个继承于IAccountAuthenticator.Stub的内部类,以用来对AbstractAccountAuthenticator的远程接口调用进行包装。所以可以通过AbstractAccountAuthenticator的getIBinder()方法,返回内部类的IBinder形式.
/**
* Created by cmo on 2018/8/19 14:17
*/
public class AuthenticationService extends Service {
private AccountAuthenticator mAuthenticator;
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mAuthenticator.getIBinder();//返回操作数据的Binder
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mAuthenticator = new AccountAuthenticator(this);
}
/**
* 账户操作的
*/
class AccountAuthenticator extends AbstractAccountAuthenticator{
public AccountAuthenticator(Context context) {
super(context);
}
@Override
public Bundle editProperties(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle addAccount(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType, String authTokenType, String[] requiredFeatures, Bundle options) throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle confirmCredentials(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, Bundle options) throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle getAuthToken(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, String authTokenType, Bundle options) throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
@Override
public String getAuthTokenLabel(String authTokenType) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle updateCredentials(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, String authTokenType, Bundle options) throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
@Override
public Bundle hasFeatures(AccountAuthenticatorResponse response, Account account, String[] features) throws NetworkErrorException {
return null;
}
}
}
2、在res/xml/文件夹下定义将要显示在Account列表的资源
以account-authenticator 为根节点的xml文件,其中icon、label分别是Account列表中的图标和显示名称,而accountType则是操作用户所必须的参数之一。
<account-authenticator xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:accountType="com.crazymo.guardback"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name" />
3、在清单文件中配置AuthenticationService
一定要配置上指定的Action:android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator和meta-data
<application>
<service android:name=".account.AuthenticationService" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator"/>
intent-filter>
<meta-data android:name="android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator"
android:resource="@xml/accountauthenticator"/>
service>
application>
经过以上三步之后,安装Apk,再次打开Account你会发现原来的Account列表多了一行数据,说明我们的App也可以支持这个Account系统了
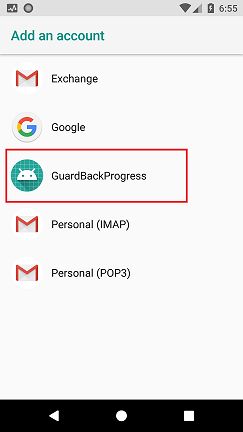
4、创建App的账户
接来还需要创建一个我们自己的Account和进行一些必要的配置。
public class AccountHelper {
//authenticator.xml 中配置 的accountType值
public static final String ACCOUNT_TYPE="com.crazymo.guardback";
/**
* 添加Account,需要"android.permission.GET_ACCOUNTS"权限
* @param context
*/
public static void addAccount(Context context){
AccountManager accountManager = (AccountManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE);
Account[] accountsType = accountManager.getAccountsByType(ACCOUNT_TYPE);
if(accountsType.length>0){
Log.e("cmo","账户已经存在");
return;
}
//给这个账户类型添加账户 crazymo cmo518
Account account=new Account("crazymo",ACCOUNT_TYPE);
//需要"android.permission.AUTHENTICATE_ACCOUNTS"权限
accountManager.addAccountExplicitly(account,"cmo518",new Bundle());
}
/**
* 设置账户同步,即告知系统我们需要系统为我们来进行账户同步,只有设置了之后系统才会自动去
* 触发SyncAdapter#onPerformSync方法
*/
public static void autoSyncAccount(){
Account account=new Account("crazymo",ACCOUNT_TYPE);
//设置可同步
ContentResolver.setIsSyncable(account,"com.crazymo.guardback.provider",2);
//设置自动同步
ContentResolver.setSyncAutomatically(account,"com.crazymo.guardback.provider",true);
//设置同步周期参考值,不受开发者控制完全由系统决定何时同步,测试下来最长等了差不多几十分钟才同步一次,不同系统表现不同
ContentResolver.addPeriodicSync(account,"com.crazymo.guardback.provider",new Bundle(),1);
}
}
调用addAccount这个方法之后就会在系统设置的Account界面多了一个Account
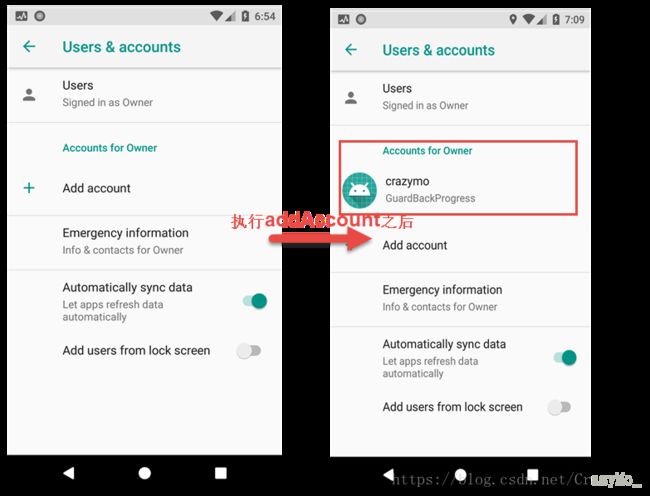
5、创建账户同步Service
创建一个Service作为同步Service,并且在onBind返回AbstractThreadedSyncAdapter的getSyncAdapterBinder
/**
* Created by cmo on 2018/8/19 22:35
* 用于执行账户同步,当系统执行账户同步时则会自动拉活所在的进程,不需要手动配置好之后,系统会自动绑定并调起
*/
public class SyncService extends Service {
private SyncAdapter mSyncAdapter;
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mSyncAdapter.getSyncAdapterBinder();
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mSyncAdapter = new SyncAdapter(getApplicationContext(), true);
}
static class SyncAdapter extends AbstractThreadedSyncAdapter{
public SyncAdapter(Context context, boolean autoInitialize) {
super(context, autoInitialize);
}
@Override
public void onPerformSync(Account account, Bundle extras, String authority, ContentProviderClient provider, SyncResult syncResult) {
//todo 账户同步 工作
Log.e("cmo","同步账户");
//与互联网 或者 本地数据库同步账户
}
}
}
contentAuthority属性是配置系统在进行账户同步的时候会查找此auth的ContentProvider,allowParallelSyncs 允许多个同步。
<sync-adapter xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:accountType="com.crazymo.guardback"
android:contentAuthority="com.crazymo.guardback.provider"
android:allowParallelSyncs="false"
android:isAlwaysSyncable="true"
android:userVisible="false"/>
账户同步还需要提供一个ContentProvider
public class SyncContentProvider extends ContentProvider {
@Override
public boolean onCreate() {
return false;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Cursor query(@NonNull Uri uri, @Nullable String[] projection, @Nullable String selection, @Nullable String[] selectionArgs, @Nullable String sortOrder) {
return null;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public String getType(@NonNull Uri uri) {
return null;
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Uri insert(@NonNull Uri uri, @Nullable ContentValues values) {
return null;
}
@Override
public int delete(@NonNull Uri uri, @Nullable String selection, @Nullable String[] selectionArgs) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public int update(@NonNull Uri uri, @Nullable ContentValues values, @Nullable String selection, @Nullable String[] selectionArgs) {
return 0;
}
}
6、告知系统我们的Account需要进行同步服务
经过以上几步,基本完成了账户同步的机制的搭建,但是还需要主动告知系统我们,即通过调用AccountHelper.autoSyncAccount();
7、完整的清单配置文件和MainActivity代码
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.crazymo.guardback">
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.AUTHENTICATE_ACCOUNTS"
android:maxSdkVersion="22" />
<uses-permission
android:name="android.permission.GET_ACCOUNTS"
android:maxSdkVersion="22" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_SYNC_SETTINGS" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
activity>
<service android:name=".account.AuthenticationService" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator"/>
intent-filter>
<meta-data android:name="android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator"
android:resource="@xml/accountauthenticator"/>
service>
<service android:name=".account.SyncService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.content.SyncAdapter" />
intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.content.SyncAdapter"
android:resource="@xml/sync_adapter" />
service>
<provider
android:authorities="com.crazymo.guardback.provider"
android:name=".account.SyncContentProvider"/>
application>
manifest>
MainActivity.java
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
AccountHelper.addAccount(this);//添加账户
AccountHelper.autoSyncAccount();//调用告知系统自动同步
}
}

以上就是利用账户同步进行拉活的主要核心思想(至于真正同步的代码不在此文章讨论),测试过程中发现(最高测试版本到Android 8.0),不同系统表现不同,至于同步周期完全是由系统进行控制的,虽然比较稳定但是周期不可控。
二、JobSchedule 机制拉活
JobScheduler允许在特定状态与特定时间间隔周期执行任务,所以我们也可以利用它的这个机制来完成拉活的功能,其效果就像是开启一个定时器,与普通定时器不同的是其调度由系统完成,也比较可靠稳定,但是会受到白名单等模式的影响,在某些ROM中甚至无法拉活。
1、实现JobService
package com.crazymo.guardback.jobschedule;
import android.app.job.JobInfo;
import android.app.job.JobParameters;
import android.app.job.JobScheduler;
import android.app.job.JobService;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Build;
import android.util.Log;
/**
* Created by cmo on 2018/8/21 21:06
*/
public class GuardJobService extends JobService {
@Override
public boolean onStartJob(JobParameters params) {
Log.e("cmo", "开启job");
//如果7.0以上 轮询
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {
startGuardJob(this);
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean onStopJob(JobParameters params) {
return false;
}
public static void startGuardJob(Context context) {
if(context!=null) {
JobScheduler jobScheduler = (JobScheduler) context.getSystemService(Context.JOB_SCHEDULER_SERVICE);
// setPersisted 在设备重启依然执行
JobInfo.Builder builder = new JobInfo.Builder(10, new ComponentName(context
.getPackageName(), GuardJobService.class
.getName())).setPersisted(true);
//小于7.0
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {
// 每隔1s 执行一次 job
builder.setPeriodic(1_000);
} else {
//延迟执行任务
builder.setMinimumLatency(1_000);
}
jobScheduler.schedule(builder.build());
}
}
}
2、在清单中注册JobService
<application>
...
<service
android:name=".jobschedule.GuardJobService"
android:permission="android.permission.BIND_JOB_SERVICE" />
application>
3、手动开启JobSchedule
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
GuardJobService.startGuardJob(this);//通过JobSchedule 拉活
}
}
三、双进程Service互相拉活
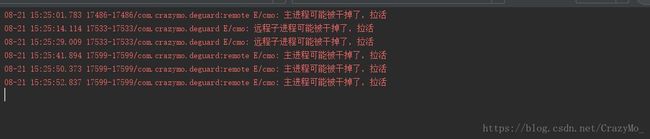
这里所讲的双进程守护并非是以前通过Native fork子进程用于观察当前app主进程的存亡状态,那种Native形式对于5.0以上成功率极低。
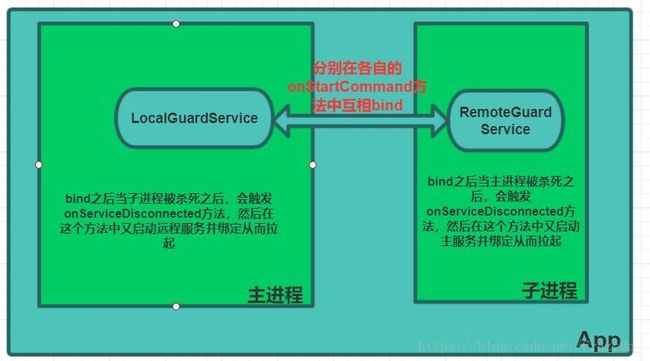
如上图所述,所谓双进程Service互相拉活,本质就是利用了系统Binder机制并结合前台服务提权,目前此种方式也是成功率很高的一种方式。
1、实现一个AIDL文件
此处如果仅仅是为了拉活,不需要远程调用某些功能的话,可以不用具体实现,但是不能缺少。
// IGuardService.aidl
package com.crazymo.deguard;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
interface IGuardService {
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat,
double aDouble, String aString);
}
2、实现运行在主进程的Service
package com.crazymo.deguard.service;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.Log;
import com.crazymo.deguard.IGuardService;
/**
* Created by cmo on 2018/8/21 22:12
* 提权Service
*/
public class LocalGuardService extends Service {
private final static int SERVICE_ID=10;
private GuardBinder mBinder;
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection;
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mBinder=new GuardBinder();
serviceConnection=new ServiceConnection();
startForeground(SERVICE_ID, new Notification());
//如果 18 以上的设备 启动一个Service startForeground给相同的id,然后结束这个Service
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR2) {
startService(new Intent(this, InnnerService.class));
}
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
//绑定本地守护Service,必须实现AIDL否则bindService在这没有作用
bindService(new Intent(this,RemoteGuardService.class),serviceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
class ServiceConnection implements android.content.ServiceConnection {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//服务连接后回调,即返回到GuardService的onBind方法中
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Log.e("cmo","远程子进程可能被干掉了,拉活");
//连接中断后回调,再启动子进程所在的Service,并进行绑定,通过启动主进程的服务强行拉活
startService(new Intent(LocalGuardService.this, RemoteGuardService.class));
bindService(new Intent(LocalGuardService.this, RemoteGuardService.class),serviceConnection,
BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
}
public static class InnnerService extends Service {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
startForeground(SERVICE_ID, new Notification());
stopSelf();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
}
class GuardBinder extends IGuardService.Stub{
@Override
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, String aString) throws RemoteException {
}
}
}
3、定义子进程的Service
package com.crazymo.deguard.service;
import android.app.Notification;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.util.Log;
import com.crazymo.deguard.IGuardService;
/**
* Created by cmo on 2018/8/21 22:12
* 提权Service
*/
public class RemoteGuardService extends Service {
private final static int SERVICE_ID=10;
private GuardBinder mBinder;
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection;
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mBinder=new GuardBinder();
serviceConnection=new ServiceConnection();
startForeground(SERVICE_ID, new Notification());
//如果 18 以上的设备 启动一个Service startForeground给相同的id,然后结束这个Service
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.JELLY_BEAN_MR2) {
startService(new Intent(this, InnnerService.class));
}
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
//绑定本地守护Service
bindService(new Intent(this,LocalGuardService.class),serviceConnection,BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
class ServiceConnection implements android.content.ServiceConnection {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//服务连接后回调,即返回到GuardService的onBind方法中
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
Log.e("cmo","主进程可能被干掉了,拉活");
//连接中断后回调,再启动主进程所在的Service,再进行绑定,通过启动主进程的服务强行拉活,另外先start再bind是为了确保,在其他地方调用unbind时候不被停止掉
startService(new Intent(RemoteGuardService.this, LocalGuardService.class));
bindService(new Intent(RemoteGuardService.this, LocalGuardService.class),serviceConnection,
BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
}
public static class InnnerService extends Service {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
startForeground(SERVICE_ID, new Notification());
stopSelf();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
}
class GuardBinder extends IGuardService.Stub{
@Override
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, String aString) throws RemoteException {
}
}
}
4、声明服务
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.crazymo.deguard">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service
android:name=".service.LocalGuardService"
android:exported="true"
android:process=":local" />
<service
android:name=".service.LocalGuardService$InnnerService"
android:exported="true"
android:process=":local" />
<service
android:name=".service.RemoteGuardService"
android:exported="true"
android:process=":remote" />
<service
android:name=".service.RemoteGuardService$InnnerService"
android:exported="true"
android:process=":remote" />
</application>
</manifest>
5、开启双进程
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//双进程Service守护
startService(new Intent(this, LocalGuardService.class));//启动主线程守护服务
startService(new Intent(this, RemoteGuardService.class));//启动主线程守护服务
GuardJobService.startGuardJob(this);
}
}
6、再结合JobSchedule 进一步保活拉活
package com.crazymo.deguard.service;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.app.job.JobInfo;
import android.app.job.JobParameters;
import android.app.job.JobScheduler;
import android.app.job.JobService;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Build;
import android.util.Log;
import com.crazymo.deguard.Utils;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2018/1/29 0029.
*/
@SuppressLint("NewApi")
public class GuardJobService extends JobService {
public static void startGuardJob(Context context) {
JobScheduler jobScheduler = (JobScheduler) context.getSystemService(Context
.JOB_SCHEDULER_SERVICE);
// setPersisted 在设备重启依然执行
JobInfo.Builder builder = new JobInfo.Builder(10, new ComponentName(context
.getPackageName(), GuardJobService.class
.getName())).setPersisted(true);
//小于7.0
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT < Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {
// 每隔1s 执行一次 job
builder.setPeriodic(1_000);
} else {
//延迟执行任务
builder.setMinimumLatency(1_000);
}
jobScheduler.schedule(builder.build());
}
private static final String TAG = "MyJobService";
@Override
public boolean onStartJob(JobParameters params) {
Log.e(TAG, "开启job");
//如果7.0以上 轮训
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {
startGuardJob(this);
}
boolean isLocalRun = Utils.isRunningService(this, LocalGuardService.class.getName());
boolean isRemoteRun = Utils.isRunningService(this, RemoteGuardService.class.getName());
if (!isLocalRun || !isRemoteRun) {
startService(new Intent(this, LocalGuardService.class));
startService(new Intent(this, RemoteGuardService.class));
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean onStopJob(JobParameters params) {
return false;
}
}