java基础之反射机制
java基础之反射机制
一、反射机制的概述
1.java反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能成为java语言的反射机制。
2.反射机制是java的动态性之一;所谓动态语言是指在程序运行时,可以改变程序的结构或变量的类型;常见的动态语言有Python,ruby,JavaScript;java可以利用反射机制来实现类似动态的功能。
3.反射机制常见作用:动态加载类、动态的获取类的信息;动态构造对象;动态调用和处理属性;用来编写一些通用性较高的代码或者框架等;
二、反射机制常用的操作
创建一个简单的Student类用于辅助测试
public class Student {
private String name;
private String sex;
private int age;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, String sex, int age) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃东西");
}
private void run() {
System.out.println("跑步");
}
private void score(int m)
{
System.out.println("你的java成绩是:"+m);
}
}
1.获取class对象:
在已知类和对象的情况下:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.通过类名.class
Class c=Person.class;
System.out.println(c);
//2.通过getClass方法
Person p=new Person();
Class c2=p.getClass();
System.out.println(c2);
}
}
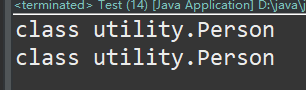
运行结果:返回包名加类名
在未知类和对象的情况下:(该方法是最常用的方法)
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//1.forName()方法,参数为类所在的包名加类名
Class c=Class.forName("fanshe.Student");
System.out.println(c);
}
}
该方法得到包名和类名的快捷方法:找到所在类的位置,右键选择
2.获得构造方法,并实例化对象
获得无参构造方法:使用getConstructor方法,不传入参数;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, SecurityException {
//获得无参构造方法
Class c=Class.forName("fanshe.Student");
Constructor con= c.getConstructor();
//调用newInstance方法实例化对象
Student stu=(Student) con.newInstance();
}
}
获得带参构造方法:
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, SecurityException {
//获得带参构造方法
Class c=Class.forName("fanshe.Student");
Constructor con= c.getConstructor(String.class,String.class,int.class);
//调用newInstance方法实例化对象
Student stu=(Student) con.newInstance("张三","男",18);//相当于Student stu=new Student("张三","男",18);
}
}
3.获得类的属性:
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, SecurityException {
Class c=Class.forName("fanshe.Student");
//获得公有属性,将Student类中的name属性改为公有public
Field f=c.getField("name");
Student stu=(Student) c.newInstance();
//通过set方法,传入两个参数,第一个为操作对象,第二个参数是传入的值
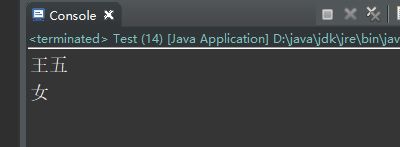
f.set(stu, "王五");
System.out.println(stu.getName());
//获得私有属性
Field field=c.getDeclaredField("sex");
//私有属性需要设置可访问的一个权限
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(stu, "女");
System.out.println(stu.getSex());
}
}
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, SecurityException {
Class c = Class.forName("fanshe.Student");
Student stu = (Student) c.newInstance();
// 测试公有方法,不带参数
Method method = c.getMethod("eat");
// 使用invoke执行方法
method.invoke(stu);// 相当于stu.eat()
System.out.println("******测试私有方法*******");
//测试私有方法,run方法
Method method2=c.getDeclaredMethod("run");
//设置私有属性权限
method2.setAccessible(true);
method2.invoke(stu);
System.out.println("******测试私有方法带参数******");
Method method3=c.getDeclaredMethod("score", int.class);
//设置私有属性权限
method3.setAccessible(true);
method3.invoke(stu, 90);
}
}
5.Accessable属性
作用是是否启用或禁用安全检查,值为 true 则指示反射的对象在使用时应该取消 Java 语言访问检查。值为 false 则指示反射的对象应该实施 Java 语言访问检查。禁止安全检查可以提高反射的运行速度
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test {
public static void test01(){
Object obj=new Object();
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<1000000000L;i++){
obj.hashCode();
}
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
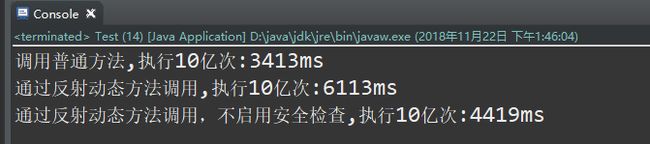
System.out.println("调用普通方法,执行10亿次:"+(endTime-startTime)+"ms");
}
public static void test02() throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException{
Object obj=new Object();
Class c=obj.getClass();
//获取指定的方法
Method m=c.getDeclaredMethod("hashCode", null);
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<1000000000L;i++){
//执行这个方法
m.invoke(obj, null);
}
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("通过反射动态方法调用,执行10亿次:"+(endTime-startTime)+"ms");
}
public static void test03() throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException{
Object obj=new Object();
Class c=obj.getClass();
//获取指定的方法
Method m=c.getDeclaredMethod("hashCode", null);
m.setAccessible(true);//不执行安全检查
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
for(int i=0;i<1000000000L;i++){
//执行这个方法
m.invoke(obj, null);
}
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("通过反射动态方法调用,不启用安全检查,执行10亿次:"+(endTime-startTime)+"ms");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, SecurityException, IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException {
test01();
test02();
test03();
}
}
作为一个初学者,还有很多地方不懂,如有错误,请大家指教。