C++ STL丨string 基本使用(一)
C++ STL丨string 基本使用(一)
文章目录
- C++ STL丨string 基本使用(一)
- 1 `string` 字符串
- 2 使用速查表(`点击函数名查看使用代码`)
- 3 详细使用
- 3.1 string 初始化
- 3.2 c_str()
- 3.3 data()
- 3.4 empty()
- 3.5 size() length()
- 3.6 shrink_to_fit()
- 3.7 earse()
- 3.8 append ()
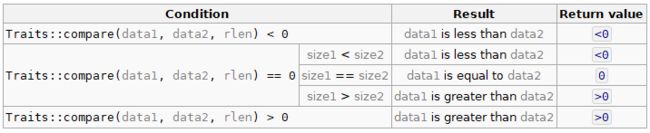
- 3.9 compare()
- 3.10 replace()
- 3.11 substr()
- 3.12 swap()
- 3.13 find()
- 3.14 string::npos()
1 string 字符串
string是C++标准库的一个重要的部分,主要用于字符串处理。可以使用输入输出流方式直接进行操作,也可以通过文件等手段进行操作。同时C++的算法库对string也有着很好的支持,而且string还和c语言的字符串之间有着良好的接口。虽然也有一些弊端,但是瑕不掩瑜。
以下是 C/C++ 中定义的字符串的内存表示:
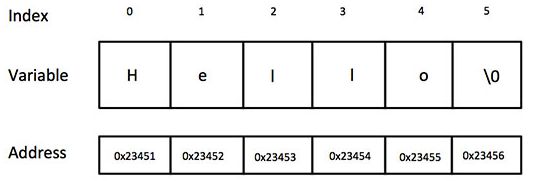
其实,您不需要把 null 字符放在字符串常量的末尾。C++ 编译器会在初始化数组时,自动把 ‘\0’ 放在字符串的末尾。
2 使用速查表(点击函数名查看使用代码)
| 函数 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| string s | 创建一个空的string |
| s.c_str() | 返回指向以null结尾的字符数组的指针,其数据与存储在字符串中的数据相同 |
| s.data() | 返回指向字符串第一个字符的指针 |
| s.begin(); s.cbegin() | 返回字符串第一个字符的迭代器 |
| s.end(); s.cend() | 返回字符串最后一个字符的迭代器 |
| s.empty() | true如果字符串为空, 否则返回false |
| s.size(); s.length() | 字符串中CharT元素的数量 |
| s.capacity() | 返回字符串当前为其分配空间的字符数 |
| s.shrink_to_fit() | 请求删除未使用的容量 |
| s.insert() | 迭代器,如果没有插入字符,则引用第一个插入字符或pos的副本 |
| s.clear() | 从字符串中删除所有字符 |
| s.earse(n, m) | 删除[n, m)之间的数据 |
| s.push_back(str); s.pop_back() | 在s尾插入str字符串;删除尾字符串 |
| s.append() | 在字符串中附加其他字符 |
| s.compare(str) | 比较两个字符串是否相等 |
| s.replaec | 用新字符串替换[pos,pos + count]或[first,last)中的字符串部分 |
| s.substr() | 返回子串[pos,pos + count)。如果请求的子字符串超出字符串的结尾,或者如果count == npos,则返回的子字符串为[pos,size()) |
| s.swap(str) | 将字符串的内容与其他内容交换。所有迭代器和引用都可能无效 |
| s.find(str) | 查找与给定字符序列相等的第一个子字符串。搜索从pos开始,即找到的子字符串不得在pos之前的位置开始 |
| string::npos | 相当于s.end() |
3 详细使用
3.1 string 初始化
string 初始化的多种方式:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
{
// string::string()
std::string s;
assert(s.empty() && (s.length() == 0) && (s.size() == 0));
}
{
// string::string(size_type count, charT ch)
std::string s(4, '=');
std::cout << s << '\n'; // "===="
}
{
std::string const other("Exemplary");
// string::string(string const& other, size_type pos, size_type count)
std::string s(other, 0, other.length()-1);
std::cout << s << '\n'; // "Exemplar"
}
{
// string::string(charT const* s, size_type count)
std::string s("C-style string", 7);
std::cout << s << '\n'; // "C-style"
}
{
// string::string(charT const* s)
std::string s("C-style\0string");
std::cout << s << '\n'; // "C-style"
}
{
char mutable_c_str[] = "another C-style string";
// string::string(InputIt first, InputIt last)
std::string s(std::begin(mutable_c_str)+8, std::end(mutable_c_str)-1);
std::cout << s << '\n'; // "C-style string"
}
{
std::string const other("Exemplar");
std::string s(other);
std::cout << s << '\n'; // "Exemplar"
}
{
// string::string(string&& str)
std::string s(std::string("C++ by ") + std::string("example"));
std::cout << s << '\n'; // "C++ by example"
}
{
// string(std::initializer_list ilist)
std::string s({ 'C', '-', 's', 't', 'y', 'l', 'e' });
std::cout << s << '\n'; // "C-style"
}
{
// overload resolution selects string(InputIt first, InputIt last) [with InputIt = int]
// which behaves as if string(size_type count, charT ch) is called
std::string s(3, std::toupper('a'));
std::cout << s << '\n'; // "AAA"
}
}
====
Exemplar
C-style
C-style
C-style string
Exemplar
C++ by example
C-style
AAA
3.2 c_str()
c_str 使用方法:
std::string const s("Emplary");
assert(s.size() == std::strlen(s.c_str()));
assert(std::equal(s.begin(), s.end(), s.c_str()));
assert(std::equal(s.c_str(), s.c_str() + s.size(), s.begin()));
assert(0 == *(s.c_str() + s.size()));
3.3 data()
data 使用方法:
std::string const s("Emplary");
assert(s.size() == std::strlen(s.data()));
assert(std::equal(s.begin(), s.end(), s.data()));
assert(std::equal(s.data(), s.data() + s.size(), s.begin()));
assert(0 == *(s.data() + s.size()));
3.4 empty()
empty 使用代码:
std::string s;
std::boolalpha(std::cout);
std::cout << "s.empty():" << s.empty() << "\t s:'" << s << "'\n";
s = "Exemplar";
std::cout << "s.empty():" << s.empty() << "\t s:'" << s << "'\n";
s = "";
std::cout << "s.empty():" << s.empty() << "\t s:'" << s << "'\n";
s.empty():true s:’’
s.empty():false s:‘Exemplar’
s.empty():true s:’’
3.5 size() length()
size和length 使用代码:
std::string s("Exemplar");
assert(8 == s.size());
assert(s.size() == s.length());
assert(s.size() == static_cast(
std::distance(s.begin(), s.end())));
std::u32string a(U"ハロー・ワールド"); // 8 code points
assert(8 == a.size()); // 8 code units in UTF-32
std::u16string b(u"ハロー・ワールド"); // 8 code points
assert(8 == b.size()); // 8 code units in UTF-16
std::string c(u8"ハロー・ワールド"); // 8 code points
assert(24 == c.size()); // 24 code units in UTF-8
3.6 shrink_to_fit()
shrink_to_fit 使用代码:
std::string s;
std::cout << "Default-constructed capacity is " << s.capacity() << '\n';
s.resize(100);
std::cout << "Capacity of a 100-element string is " << s.capacity() << '\n';
s.clear();
std::cout << "Capacity after clear() is " << s.capacity() << '\n';
s.shrink_to_fit();
std::cout << "Capacity after shrink_to_fit() is " << s.capacity() << '\n';
Default-constructed capacity is 0
Capacity of a 100-element string is 100
Capacity after clear() is 100
Capacity after shrink_to_fit() is 0
3.7 earse()
earse 删除元素的方式:
std::string s = "This is an example";
std::cout << s << '\n';
s.erase(0, 5); // Erase "This "
std::cout << s << '\n';
s.erase(std::find(s.begin(), s.end(), ' ')); // Erase ' '
std::cout << s << '\n';
s.erase(s.find(' ')); // Trim from ' ' to the end of the string
std::cout << s << '\n';
输出:
This is an example
is an example
isan example
isan
3.8 append ()
append 追加元素的几种方式:
std::basic_string str = "string";
const char* cptr = "C-string";
const char carr[] = "Two and one";
std::string output;
// 1) Append a char 3 times.
// Notice, this is the only overload accepting chars.
output.append(3, '*');
std::cout << "1) " << output << "\n";
// 2) Append a whole string
output.append(str);
std::cout << "2) " << output << "\n";
// 3) Append part of a string (last 3 letters, in this case)
output.append(str, 3, 3);
std::cout << "3) " << output << "\n";
// 4) Append part of a C-string
// Notice, because `append` returns *this, we can chain calls together
output.append(1, ' ').append(carr, 4);
std::cout << "4) " << output << "\n";
// 5) Append a whole C-string
output.append(cptr);
std::cout << "5) " << output << "\n";
// 6) Append range
output.append(&carr[3], std::end(carr));
std::cout << "6) " << output << "\n";
// 7) Append initializer list
output.append({ ' ', 'l', 'i', 's', 't' });
std::cout << "7) " << output << "\n";
输出:
1)***
2)***string
3)***stringing
4)***stringing Two
5)***stringing Two C-string
6)***stringing Two C-string and one
7)***stringing Two C-string and one list
3.9 compare()
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
// 1) Compare with other string
{
int compare_value{
std::string{"Batman"}.compare(std::string{"Superman"})
};
std::cout << (
compare_value < 0 ? "Batman comes before Superman\n" :
compare_value > 0 ? "Superman comes before Batman\n" :
"Superman and Batman are the same.\n"
);
}
// 2) Compare substring with other string
{
int compare_value{
std::string{"Batman"}.compare(3, 3, std::string{"Superman"})
};
std::cout << (
compare_value < 0 ? "man comes before Superman\n" :
compare_value > 0 ? "Superman comes before man\n" :
"man and Superman are the same.\n"
);
}
// 3) Compare substring with other substring
{
std::string a{"Batman"};
std::string b{"Superman"};
int compare_value{a.compare(3, 3, b, 5, 3)};
std::cout << (
compare_value < 0 ? "man comes before man\n" :
compare_value > 0 ? "man comes before man\n" :
"man and man are the same.\n"
);
// Compare substring with other substring
// defaulting to end of other string
assert(compare_value == a.compare(3, 3, b, 5));
}
// 4) Compare with char pointer
{
int compare_value{std::string{"Batman"}.compare("Superman")};
std::cout << (
compare_value < 0 ? "Batman comes before Superman\n" :
compare_value > 0 ? "Superman comes before Batman\n" :
"Superman and Batman are the same.\n"
);
}
// 5) Compare substring with char pointer
{
int compare_value{std::string{"Batman"}.compare(3, 3, "Superman")};
std::cout << (
compare_value < 0 ? "man comes before Superman\n" :
compare_value > 0 ? "Superman comes before man\n" :
"man and Superman are the same.\n"
);
}
// 6) Compare substring with char pointer substring
{
int compare_value{std::string{"Batman"}.compare(0, 3, "Superman", 5)};
std::cout << (
compare_value < 0 ? "Bat comes before Super\n" :
compare_value > 0 ? "Super comes before Bat\n" :
"Super and Bat are the same.\n"
);
}
}
Batman comes before Superman
Superman comes before man
man and man are the same.
Batman comes before Superman
Superman comes before man
Bat comes before Super
3.10 replace()
replace 的简单使用:
std::string str("The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.");
str.replace(10, 5, "red"); // (5)
str.replace(str.begin(), str.begin() + 3, 1, 'A'); // (6)
std::cout << str << '\n';
A quick red fox jumps over the lazy dog.
3.11 substr()
substr 的简单使用:
std::string a = "0123456789abcdefghij";
// count is npos, returns [pos, size())
std::string sub1 = a.substr(10);
std::cout << sub1 << '\n';
// both pos and pos+count are within bounds, returns [pos, pos+count)
std::string sub2 = a.substr(5, 3);
std::cout << sub2 << '\n';
// pos is within bounds, pos+count is not, returns [pos, size())
std::string sub4 = a.substr(a.size()-3, 50);
std::cout << sub4 << '\n';
try {
// pos is out of bounds, throws
std::string sub5 = a.substr(a.size()+3, 50);
std::cout << sub5 << '\n';
} catch(const std::out_of_range& e) {
std::cout << "pos exceeds string size\n";
}
abcdefghij
567
hij
pos exceeds string size
3.12 swap()
swap 的简单使用:
std::string a = "AAA";
std::string b = "BBB";
std::cout << "before swap" << '\n';
std::cout << "a: " << a << '\n';
std::cout << "b: " << b << '\n';
a.swap(b);
std::cout << "after swap" << '\n';
std::cout << "a: " << a << '\n';
std::cout << "b: " << b << '\n';
before swap
a: AAA
b: BBB
after swap
a: BBB
b: AAA
3.13 find()
swap 的简单使用:
#include
#include
void print(std::string::size_type n, std::string const &s)
{
if (n == std::string::npos) {
std::cout << "not found\n";
} else {
std::cout << "found: " << s.substr(n) << '\n';
}
}
int main()
{
std::string::size_type n;
std::string const s = "This is a string";
// search from beginning of string
n = s.find("is");
print(n, s);
// search from position 5
n = s.find("is", 5);
print(n, s);
// find a single character
n = s.find('a');
print(n, s);
// find a single character
n = s.find('q');
print(n, s);
}
found: is is a string
found: is a string
found: a string
not found
3.14 string::npos()
npos 的使用:
// string search functions return npos if nothing is found
std::string s = "test";
if(s.find('a') == std::string::npos)
std::cout << "no 'a' in 'test'\n";
// functions that take string subsets as arguments
// use npos as the "all the way to the end" indicator
std::string s2(s, 2, std::string::npos);
std::cout << s2 << '\n';
std::bitset<5> b("aaabb", std::string::npos, 'a', 'b');
std::cout << b << '\n';
no ‘a’ in ‘test’
st
00011