多光谱影像分类(双通道CNN实现)
1.介绍
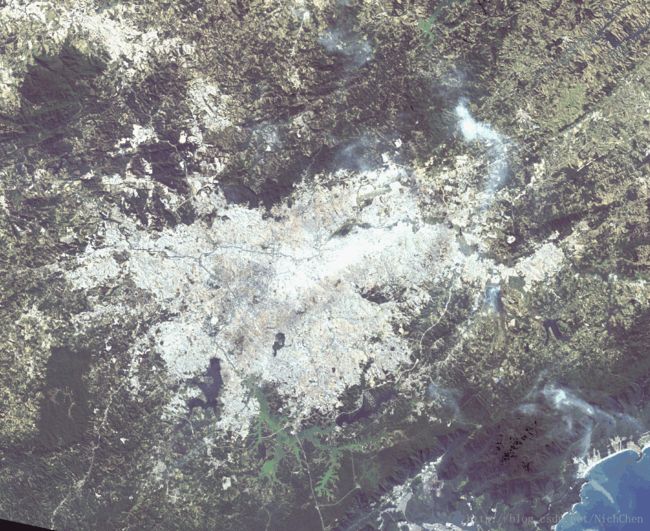
2017年IEE IGRASS多光谱影像分类比赛,选用两个卫星landsat_8和sentinel_2所拍摄的多光谱图像作为输入,输出像素级分类图像。其中landsat_8有4个时段的影像数据,sentinel_2只有一个时段的影像数据。拍摄城市有巴黎/柏林/罗马/香港/圣保罗 五个地区,模型选用前4个地区的数据作为训练样本,圣保罗地区数据作为测试样本。依次选取landsat_8的每个时段数据与sentinel_2的数据组合,作为输入数据,输出为所属种类。开始采用分割图的方法,将训练影像分割为若干个28*28*channel 的小图,每个小图的label对应为中心像素点坐标在groundtruth上划分的种类。训练模型选用双通道2层CNN架构,即(conv+relu+pool)*2,最后一层将双通道的稀疏特征进行级联,作为最终的特征向量,再通过2层全连接层,并送入softmax层输出最终分类结果。训练时采用dropout和全连接层权值正则化的方式防止过拟合,在训练样本的采集方面也先进行了边缘填充,并将各个种类的样本都选择1000个,不够1000的则全部选用,以保证样本的多样性和平衡性,并对数据进行归一化。在最后的测试时,将landsat_8的4个时段的预测结果进行投票打分,最后选择得分最高的类作为最终label。在对数据进行划分时,可以采用稀疏采样,用5*5像素块对原始图进行滑窗操作,若块内像素类全部相同且不是背景类,则间隔一个像素进行稀疏采样,只选取一半的像素点作为训练数据,以保证训练样本的多样性,最后测试结果显示,稀疏采样可提高模型预测的准确率。
2.代码:
# This Python file uses the following encoding: utf-8
import tensorflow as tf # 深度学习框架
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 画图包
import numpy as np # 矩阵运算包
import scipy.io # 保存图片
from PIL import Image # 图像处理
from tqdm import tqdm # 进度条
import os # 读取文件
import time # 获取时钟时间
import h5py # 读取文件
import sys # 系统输出格式
# 定义输入图像的大小 28*28
IMAGE_SIZE = 28
# 两个卫星的通道数,分别为9和10
NUM_CHANNELS_1 = 9
NUM_CHANNELS_2 = 10
# 像素值0~255
PIXEL_DEPTH = 255
# 分类个数为17
NUM_LABELS = 17
# 验证集共有1000个样本
VALIDATION_SIZE = 1000
# 设置随机种子大小
# SEED = np.random.randint(1, 10**5)
SEED = 52014
# 批量处理BATCH大小
BATCH_SIZE = 30
# 训练代数
NUM_EPOCHS = 50
# 验证集批量处理大小
EVAL_BATCH_SIZE = 256
# 验证时间间隔,每训练多少个批次做一次评估
EVAL_FREQUENCY = 5000
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_boolean("self_test", False, "True if running a self test.")
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
# 假数据,用于功能检测
def fake_data(num_images):
data1 = np.ndarray(
shape=(num_images, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, NUM_CHANNELS_1),
dtype=np.int32)
data2 = np.ndarray(
shape=(num_images, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, NUM_CHANNELS_2),
dtype=np.int32)
labels = np.zeros(shape=(num_images,), dtype=np.int32)
data1 = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=data1.shape)
data2 = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=data2.shape)
labels = np.random.randint(0, NUM_LABELS-1, size=labels.shape)
return data1, data2, labels
# 计算匪类错误率
def error_rate(predictions, labels):
correction = np.sum(np.argmax(predictions, axis=1) == labels) / predictions.shape[0]
return (1 - correction) * 100
# def main(argv = None):
# matfn = './p_cf_ave_28_city_10928_sparse.mat'
matfn = './learnCNN9428.mat'
# matfn = './learnCNN_sparse9428.mat'
model_path = "./checkpoints-non/model_conMy.ckpt"
# model_path = "./checkpoints-sparse/model_conMy.ckpt"
data = h5py.File(matfn)
arrays = {}
# print(list(data.items()))
for k, v in data.items():
arrays[k] = np.array(v)
train_data1 = arrays['train_x1'] # 一号卫星输入图片,大小为(10928, 28, 28, 9) 注意:python读入时维度与matlab读入的维度顺序有所不同
# train_data1 = train_data1.transpose(3, 1, 2, 0) # 必要时,可将维度转换成python对应顺序
train_data2 = arrays['train_x2'] # 二号卫星输入图片,大小为(10928, 28, 28, 10)
train_labels = arrays['train_y'] # 图片分类标签,大小为(1, 10928)
train_labels = train_labels.reshape(train_labels.shape[1]).astype(np.int64) # 将label维度转换为(10928, )
train_labels -= 1 # 类别由从1计数变为从0计数
test_data1 = arrays['yanzheng_x1']
test_data2 = arrays['yanzheng_x2']
test_labels = arrays['yanzheng_y']
test_labels = test_labels.reshape(test_labels.shape[1]).astype(np.int64)
test_labels -= 1 # 类别由从1计数变为从0计数
train_data1 = train_data1.astype(np.float32)
train_data2 = train_data2.astype(np.float32)
test_data1 = test_data1.astype(np.float32)
test_data2 = test_data2.astype(np.float32)
# train_data1 = train_data1 / PIXEL_DEPTH - 0.5 # 将像素值归一化到[-0.5, 0.5]
# train_data2 = train_data2 / PIXEL_DEPTH - 0.5
# test_data1 = test_data1 / PIXEL_DEPTH - 0.5
# test_data2 = test_data2 / PIXEL_DEPTH - 0.5
# 打乱数据
# np.random.seed(SEED)
index = [i for i in range(len(train_data1))]
np.random.shuffle(index)
train_data1 = train_data1[index]
train_data2 = train_data2[index]
train_labels = train_labels[index]
index2 = [i for i in range(len(test_data1))] # len(array)取的是array数组第一维度的值
np.random.shuffle(index2)
test_data1 = test_data1[index2]
test_data2 = test_data2[index2]
test_labels = test_labels[index2]
# 产生评测集
validation_data1 = test_data1[:VALIDATION_SIZE, ...]
validation_data2 = test_data2[:VALIDATION_SIZE, ...]
validation_labels = test_labels[:VALIDATION_SIZE, ...]
train_size = train_labels.shape[0]
# 训练样本和标签从这里送入网络
train_data_node1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(BATCH_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, NUM_CHANNELS_1))
train_data_node2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(BATCH_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, NUM_CHANNELS_2))
train_labels_node = tf.placeholder(tf.int64, shape=(BATCH_SIZE, ))
# 评测数据节点
eval_data_node1 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(EVAL_BATCH_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, NUM_CHANNELS_1))
eval_data_node2 = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(EVAL_BATCH_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, NUM_CHANNELS_2))
# 下面的变量为网络的可训练权值,1号卫星
# conv1 权值维度为 5*5*channel1*32, 32为输出特征图数目
conv11_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, NUM_CHANNELS_1, 32], # 5*5 filter, depth=32
stddev=0.1,
seed=SEED),
name='conv11_weights'
)
# conv1 偏置
conv11_bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([32]), name='conv11_bias')
# conv2 权值维度为 5*5*32*64
conv12_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 32, 64],
stddev=0.1,
seed=SEED),
name='conv12_weights'
)
conv12_bias = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[64]), name='conv12_bias')
# 下面的变量为网络的可训练权值,2号卫星
# conv1 权值维度为 5*5*channel2*32, 32为输出特征图数目
conv21_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, NUM_CHANNELS_2, 32], # 5*5 filter, depth=32
stddev=0.1,
seed=SEED),
name='conv21_weights'
)
# conv1 偏置
conv21_bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([32]), name='conv21_bias')
# conv2 权值维度为 5*5*32*64
conv22_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 32, 64],
stddev=0.1,
seed=SEED),
name='conv22_weights'
)
conv22_bias = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[64]), name='conv22_bias')
# 全连接层 fc1 权值,神经元数目为5122
fc1_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([(IMAGE_SIZE // 4) ** 2 * 64 * 2, 512],
stddev=0.01,
seed=SEED),
name='fc1_weights'
)
fc1_biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[512]), name='fc1_biases')
fc2_weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal([512, NUM_LABELS],
stddev=0.1,
seed=SEED),
name='fc2_weights'
)
fc2_biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[NUM_LABELS]), name='fc2_biases')
# 两个网络并行,双通道CNN,误差共享
# 实现 LeNet-5 模型,该函数输入两组卫星图像数据,输出fc2响应
def model(data1, data2, train=False):
"""the model definition."""
# 二维卷积,使用“不变形”补零(即输入特征图与输出特征图尺寸一致)
# 通道一内的卷积运算
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(data1, conv11_weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
# 加偏置,过激活函数一块完成
relu1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv1, conv11_bias))
# 最大值下采样
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# 第二个卷基层
conv1 = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1, conv12_weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
relu1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv1, conv12_bias))
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu1, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
# 特征图变形为2维矩阵,便于送入全连接层
pool_shape1 = pool1.get_shape().as_list()
reshape1 = tf.reshape(pool1, [pool_shape1[0], pool_shape1[1] * pool_shape1[2] * pool_shape1[3]])
# 通道二内的卷积运算
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(data2, conv21_weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
relu2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv2, conv21_bias))
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
conv2 = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2, conv22_weights, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
relu2 = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv2, conv22_bias))
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(relu2, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
pool_shape2 = pool2.get_shape().as_list()
reshape2 = tf.reshape(pool2, [pool_shape2[0], pool_shape2[1] * pool_shape2[2] * pool_shape2[3]])
# 特征融合
rs = tf.concat((reshape1, reshape2), 1)
# 全连接层,注意‘+’运算自动广播偏置
hidden = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(rs, fc1_weights) + fc1_biases)
# 训练阶段,增加 50% dropout;而测评阶段无需该操作
if train:
hidden = tf.nn.dropout(hidden, 0.5, seed=SEED)
return tf.matmul(hidden, fc2_weights) + fc2_biases # 最后一步连接softmax层, 因此不需要再进行relu
# 训练阶段计算:对数+交叉熵 损失函数
# 定义网络流图
logits = model(train_data_node1, train_data_node2, True)
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits, labels=train_labels_node)) # labels是一个数,会自动转成one-hot编码
# 全连接层参数进行L2正则化
regularizers = (tf.nn.l2_loss(fc1_weights) + tf.nn.l2_loss(fc1_biases) +
tf.nn.l2_loss(fc2_weights) + tf.nn.l2_loss(fc2_biases))
loss += 5e-4 * regularizers
# 优化器,设置一个变量,每个批处理递增,控制学习速率衰减
batch_steps = tf.Variable(0)
# 指数衰减
learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(
0.001, # 基本学习速率
batch_steps * BATCH_SIZE, # 当前批处理在数据全集中的位置
train_size, # Decay step / 每过多少步衰减一次
0.95, # Decay rate / 衰减率
staircase=True # 使用阶梯式衰减
)
# 使用 momentum 优化器
optimizer = tf.train.MomentumOptimizer(learning_rate, 0.9).minimize(loss, global_step=batch_steps)
# 使用softmax 计算测评批处理的预测概率
train_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
eval_prediction = tf.nn.softmax(model(eval_data_node1, eval_data_node2))
def eval_in_batches(data1, data2, sess):
size = data1.shape[0]
if size < EVAL_BATCH_SIZE:
raise ValueError("batch size for evals larger than dataset: %d" % size)
predictions = np.ndarray(shape=(size, NUM_LABELS), dtype=np.float32)
for begin in range(0, size, EVAL_BATCH_SIZE):
end = begin + EVAL_BATCH_SIZE
if end <= size:
predictions[begin:end, :] = sess.run(eval_prediction,
feed_dict={eval_data_node1: data1[begin:end, ...],
eval_data_node2: data2[begin:end, ...]})
else:
batch_predictions = sess.run(eval_prediction,
feed_dict={eval_data_node1: data1[-EVAL_BATCH_SIZE:, ...], # 倒数凑一个BATCH
eval_data_node2: data2[-EVAL_BATCH_SIZE:, ...]})
predictions[begin:, :] = batch_predictions[begin - size:, :] # 刚好凑齐整个begin:end
return predictions
lst = []
saver = tf.train.Saver()
start_time = time.time()
# train = True
# yanzheng = False
# test = False
train = False
yanzheng = True
test = True
# test_error = True
# Create a local session to run the training
# 限制GPU使用率:
# gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=1)
# with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)) as sess:
with tf.Session() as sess:
# Run all the initializers to prepare the trainable parameters
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
print("Initialized!")
# Loop through training steps
if train:
for step in range(int(NUM_EPOCHS * train_size) // BATCH_SIZE):
offset = (step * BATCH_SIZE) % (train_size - BATCH_SIZE) # 确保数组下标不出现越界
batch_data1 = train_data1[offset:(offset + BATCH_SIZE), ...]
batch_data2 = train_data2[offset:(offset + BATCH_SIZE), ...]
batch_labels = train_labels[offset:(offset + BATCH_SIZE)]
feed_dict = {train_data_node1: batch_data1,
train_data_node2: batch_data2,
train_labels_node: batch_labels}
# run the graph and fetch some of the nodes
_, l, lr, predictions = sess.run([optimizer, loss, learning_rate, train_prediction],
feed_dict=feed_dict)
lst.append(l)
if step % EVAL_FREQUENCY == 0:
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
start_time = time.time()
print("Step %d (epoch %.2f), %.1f ms" % (step, float(step) * BATCH_SIZE / train_size, 1000 * elapsed_time / EVAL_FREQUENCY))
print("Batch loss: %.3f, learning rate: %.6f" % (l, lr))
print("Batch error: %.1f%%" % error_rate(predictions, batch_labels))
print("Validation error: %.1f%%" % error_rate(eval_in_batches(validation_data1, validation_data2, sess), validation_labels))
sys.stdout.flush() # 一次输出4行
# Save model weights to disk
save_path = saver.save(sess, model_path, global_step=step)
print("Model saved in file: %s" % save_path)
# finally print the result
plt.plot(lst)
plt.show()
if yanzheng:
saver = tf.train.Saver()
saver.restore(sess, model_path + '-15000')
test_error = error_rate(eval_in_batches(test_data1, test_data2, sess), test_labels)
print('Test error: %.2f%%' % test_error)
if FLAGS.self_test:
print('Test_error', test_error)
# assert test_error == 0, 'expected 0 test_error, got %.2f' % (test_error, )
if test:
# 定义变量值
w = IMAGE_SIZE
d = w//2
mn = np.array([8000, 7300, 6800, 6100, 5500, 5100, 5050, 20000, 18000])
mx = np.array([15000, 15000, 15000, 16000, 28000, 24000, 21500, 36000, 31000])
mn1 = np.array([670, 470, 255, 245, 200, 190, 150, 130, 30, 10])
mx1 = np.array([4000, 4000, 4000, 4000, 4300, 5200, 5200, 5500, 5000, 4000])
# 定义子函数
def neg2zero(img):
for i in range(img.shape[0]):
for j in range(img.shape[1]):
if img[i, j] < 0:
img[i, j] = np.array([0])
return img
def mat2mat(img, c):
m = img.shape[0]
n = img.shape[1]
b = np.zeros([m + 2 * c, n + 2 * c])
b[c: m + c, c: n + c] = img
return b
def fun(path, list):
for filename in os.listdir(path):
# print(filename)
list.append(os.path.join(path, filename))
return list
def normal(img, mn, mx):
img = neg2zero(img)
img = (img - mn) / (mx - mn)
for i in range(img.shape[0]):
for j in range(img.shape[1]):
if img[i, j] < 0:
img[i, j] = 0
elif img[i, j] > 1:
img[i, j] = 1
return img
def relist(list):
list2 = [i for i in range(9)]
list2[0] = list[0]
list2[1] = list[3]
list2[2] = list[4]
list2[3] = list[5]
list2[4] = list[6]
list2[5] = list[7]
list2[6] = list[8]
list2[7] = list[1]
list2[8] = list[2]
return list2
def getimage(list, d, mn, mx):
# 根据路径读出图像,将图像进行扩充,归一化,并且将九个波段拼到一起
img0 = Image.open(list[0])
width, hight = img0.size
lad8 = np.zeros((hight + w, width + w, len(list)))
i = 0
for imgpath in list:
# print(imgpath)
img = Image.open(imgpath)
im_array = np.asarray(img)
im_array.flags.writeable = True
im_array = normal(im_array, mn[i], mx[i])
im_array = mat2mat(im_array, d)
lad8[..., i] = im_array
i += 1
return lad8
def colorshow(gt):
x = gt.shape[0]
y = gt.shape[1]
c = np.ones((x, y, 3))*255
for i in range(x):
for j in range(y):
if gt[i, j] == 1:
c[i, j, :] = [140, 0, 30]
elif gt[i, j] == 2:
c[i, j, :] = [209, 0, 0]
elif gt[i, j] == 3:
c[i, j, :] = [255, 0, 0]
elif gt[i, j] == 4:
c[i, j, :] = [191, 77, 0]
elif gt[i, j] == 5:
c[i, j, :] = [255, 102, 0]
elif gt[i, j] == 6:
c[i, j, :] = [255, 153, 85]
elif gt[i, j] == 8:
c[i, j, :] = [188, 188, 188]
elif gt[i, j] == 9:
c[i, j, :] = [255, 204, 170]
elif gt[i, j] == 10:
c[i, j, :] = [85, 85, 85]
elif gt[i, j] == 11:
c[i, j, :] = [0, 106, 0]
elif gt[i, j] == 12:
c[i, j, :] = [0, 170, 0]
elif gt[i, j] == 13:
c[i, j, :] = [100, 133, 37]
elif gt[i, j] == 14:
c[i, j, :] = [185, 219, 121]
elif gt[i, j] == 15:
c[i, j, :] = [0, 0, 0]
elif gt[i, j] == 16:
c[i, j, :] = [251, 247, 174]
elif gt[i, j] == 17:
c[i, j, :] = [106, 106, 255]
c = np.array(c, dtype=np.uint8)
return c
def getgt(path1, path2, d):
# start = time.clock()
ladlist = []
ladlist = fun(path1, ladlist)
ladlist.sort()
ladlist = relist(ladlist)
lad = getimage(ladlist, d, mn, mx)
sentlist = []
sentlist = fun(path2, sentlist)
sentlist.sort()
sent = getimage(sentlist, d, mn1, mx1)
print('image finished! test now!')
img0 = Image.open(ladlist[0])
width, hight = img0.size
gt = np.zeros((hight, width, NUM_LABELS)) # np.zeros初始化参数分别为 ‘行’和‘列’ , 即 hight 和 width, 这与img.size 相反
for i in tqdm(range(d, d + hight)):
eval1 = np.zeros((width, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, NUM_CHANNELS_1))
eval2 = np.zeros((width, IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE, NUM_CHANNELS_2))
for j in range(d, d + width):
batch1 = lad[i - d + 1: i + d + 1, j - d + 1: j + d + 1, :] # 滑块方式应该与训练集中滑块方式保持一致
# tf.expand_dims(batch1, axis=0) # 中心点位于块中心的左上角
batch2 = sent[i - d + 1: i + d + 1, j - d + 1: j + d + 1, :]
# tf.expand_dims(batch2, axis=0)
eval1[j - d, :] = batch1
eval2[j - d, :] = batch2
prediction = eval_in_batches(eval1, eval2, sess)
# label = np.argmax(prediction, 1)
# gt[i - d, :] = label + 1
gt[i - d] = prediction
GT = np.array(gt, dtype=np.float32)
return GT
# color = colorshow(GT)
# scipy.misc.imsave(spath1, GT)
# scipy.misc.imsave(spath2, color)
# end = time.clock()
# print("time: %f s" % (end - start))
path = '/home/nick/weishubo2/IGRASS/train/'
city = 'sao_paulo'
pathlist1 = []
pathlist2 = []
# spath1 = city + '_gts3.tif'
# spath2 = city + '_color3.tif'
spath1 = city + '_gts3_non.tif'
spath2 = city + '_color3_non.tif'
for filename in os.listdir(os.path.join(path, city, "landsat_8")):
pathlist1.append(os.path.join(path, city, "landsat_8", filename))
pathlist2.append(os.path.join(path, city, "sentinel_2"))
pathlist1.sort()
pathlist2.sort()
gtmix = []
for i in range(len(pathlist1)):
gtmix.append(getgt(pathlist1[i], pathlist2[i], d))
gtmix = np.array(gtmix)
gtfinal = np.sum(gtmix, axis=0)
label = np.argmax(gtfinal, 2).astype(np.uint8) + 1
scipy.misc.imsave(spath1, label)
color = colorshow(label)
scipy.misc.imsave(spath2, color)
# if test_error:
# path = '/home/nick/weishubo2/IGRASS/train/'
# city = 'sao_paulo'
# spath1 = 'sao_paulo_gts3.tif'
# spath2 = 'train/sao_paulo/lcz/sao_paulo_lcz_GT.tif'
#
# img = Image.open(spath1)
# groundtruth = Image.open(spath2)
#
# correction = np.sum(np.argmax(predictions, axis=1) == labels) / predictions.shape[0]
# return (1 - correction) * 100
# if __name__ == '__main__': #在直接运行脚本时可以调用,使用import模块时不调用
# main()
测试代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image # 图像处理
import numpy as np
path_gt = 'train/sao_paulo/lcz/sao_paulo_lcz_GT.tif'
path_test_non = 'sao_paulo_gts3_non.tif'
path_test = 'sao_paulo_gts3.tif'
# img = Image.open(test)
gt = np.array(Image.open(path_gt))
test_non = np.array(Image.open(path_test_non))
test = np.array(Image.open(path_test))
high, width = gt.shape
num = 0
num_non = 0
total = 0
for i in range(high):
for j in range(width):
if gt[i][j] != 0:
total += 1
if test_non[i][j] == gt[i][j]:
num_non += 1
if test[i][j] == gt[i][j]:
num += 1
correct_non = num_non / total
correct = num / total
print('correct: ' + str(correct))
print('correct_non:' + str(correct_non))
matlab提取数据代码:
generate_data.m
clear all;
disp(['time:']);
tic;
path = 'D:\IGRSS2017\46_dataset\';
str{1}{1}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\berlin\landsat_8\LC81930232015084LGN00\'));
str{1}{2}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\berlin\landsat_8\LC81930232015100LGN00\'));
str{2}{1}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\hong_kong\landsat_8\LC81220442013333LGN00\'));
str{2}{2}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\hong_kong\landsat_8\LC81220442014288LGN00\'));
str{2}{3}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\hong_kong\landsat_8\LC81220442014320LGN00\'));
str{3}{1}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\paris\landsat_8\LC81990262014139LGN00\'));
str{3}{2}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\paris\landsat_8\LC81990262015270LGN00\'));
str{4}{1}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\rome\landsat_8\LC81910312013208LGN00\'));
str{4}{2}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\rome\landsat_8\LC81910312015182LGN00\'));
str{4}{3}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\rome\landsat_8\LC81910312015198LGN00\'));
str{5}{1}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\sao_paulo\landsat_8\LC82190762013244LGN00\'));
str{5}{2}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\sao_paulo\landsat_8\LC82190762014039LGN00\'));
str{5}{3}=lujing(strcat(path,'train\sao_paulo\landsat_8\LC82190762015266LGN00\'));
str2{1}=lujings(strcat(path,'train\berlin\sentinel_2\'));
str2{2}=lujings(strcat(path,'train\hong_kong\sentinel_2\'));
str2{3}=lujings(strcat(path,'train\paris\sentinel_2\'));
str2{4}=lujings(strcat(path,'train\rome\sentinel_2\'));
str2{5}=lujings(strcat(path,'train\sao_paulo\sentinel_2\'));
% 稀疏采样后的groundtruth
gt{1}=strcat('new_berlin_learnCNN_gt.tif');
gt{2}=strcat('new_hong_kong_learnCNN_gt.tif');
gt{3}=strcat('new_paris_learnCNN_gt.tif');
gt{4}=strcat('new_rome_learnCNN_gt.tif');
gt{5}=strcat(path,'train\sao_paulo\lcz\sao_paulo_lcz_GT.tif'); %测试,直接选原先的groundtruth
% 原始groundtruth
% gt{1}=strcat(path,'train\berlin\lcz\berlin_lcz_GT.tif');
% gt{2}=strcat(path,'train\hong_kong\lcz\hong_kong_lcz_GT.tif');
% gt{3}=strcat(path,'train\paris\lcz\paris_lcz_GT.tif');
% gt{4}=strcat(path,'train\rome\lcz\rome_lcz_GT.tif');
% gt{5}=strcat(path,'train\sao_paulo\lcz\sao_paulo_lcz_GT.tif');
w=28;
d=floor(w/2);
sam=xlsread('num_sparse_eachclass600.xlsx');
%sam=xlsread('num_eachclass1000.xlsx');
train_x1=[];
train_x2=[];
train_y=[];
yanzheng_x1=[];
yanzheng_x2=[];
yanzheng_y=[];
traincity = [1 2 3 4]; % 选取前4个城市作为训练数据,共有10张图片可进行切割
zt=1;
for i=1:length(traincity)
cc = traincity(i);
for j=1:length(str{cc})
Tu(zt) = data_13t(str{cc}{j},str2{cc},gt{cc},w,zt);
%sam1(:,zt)= sam(:,cc);
zt = zt+1;
end
end
% num=3000;
% sam1=getsam(sam1,num);
% sam1 = ceil(sam1*0.2);
sam1=sam';
X1=cell(17,1);
TX1=cell(17,1);
for j=1:17
X1t=[];
TX1t=[];
for k=1:size(Tu,2)
if ~isempty(Tu(k).index{j})
[x1,tx1]=selectsample(Tu(k).index{j},ceil(sam1(k,j)));
X1t=cat(1,X1t,x1);
TX1t=cat(1,TX1t,tx1);
end
end
X1{j}=X1t;
TX1{j}=TX1t;
end
for i=1:17
if ~isempty(X1{i})
aa = size(X1{i},1);
train_lei_x1 = zeros(w,w,9,aa);
train_lei_x2 = zeros(w,w,10,aa);
for p=1:aa
m=X1{i}(p,1);
n=X1{i}(p,2);
o=X1{i}(p,3);
train_lei_x1(:,:,:,p) = Tu(o).P1(m-d+1:m+d,n-d+1:n+d,:);
train_lei_x2(:,:,:,p) = Tu(o).P2(m-d+1:m+d,n-d+1:n+d,:);
end
train_x1=cat(4,train_x1,train_lei_x1);
train_x2=cat(4, train_x2,train_lei_x2);
Y1=zeros(size( X1{i},1),1);
Y1(:,1)=i;
train_y=cat(1,train_y, Y1);
end
if ~isempty(TX1{i})
bb = size( TX1{i},1);
yz_lei_x1 = zeros(w,w,9,bb);
yz_lei_x2 = zeros(w,w,10,bb);
for p=1:bb
m=TX1{i}(p,1);
n=TX1{i}(p,2);
o=TX1{i}(p,3);
yz_lei_x1(:,:,:,p) = Tu(o).P1(m-(d-1):m+d,n-(d-1):n+d,:);
yz_lei_x2(:,:,:,p) = Tu(o).P2(m-(d-1):m+d,n-(d-1):n+d,:);
end
yanzheng_x1=cat(4,yanzheng_x1,yz_lei_x1);
yanzheng_x2=cat(4,yanzheng_x2,yz_lei_x2);
TY1=zeros(size( TX1{i},1),1);
TY1(:,1)=i;
yanzheng_y=cat(1,yanzheng_y, TY1);
end
end
train_x1=permute(train_x1,[3,1,2,4]); % 维度转换,保证与tensorflow的维度结构保持一致
train_x2=permute(train_x2,[3,1,2,4]);
yanzheng_x1=permute(yanzheng_x1,[3,1,2,4]);
yanzheng_x2=permute(yanzheng_x2,[3,1,2,4]);
save -v7.3 learnCNN_sparse.mat train_x1 train_x2 train_y yanzheng_x1 yanzheng_x2 yanzheng_y ;
toc;selectsample.m
function [X,TX]=selectsample(T1,s)
l=size(T1,1);
T2(1:l,:)=T1(randperm(l),:);
T = T2;
X=[];
TX=[];
if l>2*s-1
X=[X;T(1:s,:)];
TX=[TX;T(s+1:2*s,:)];
elseif l>s-1 && l<2*s
X=[X;T(1:s,:)];
TX=[TX;T(s+1:l,:)];
TX=[TX;T(1:2*s-l,:)];
elseif ls/2-1
X=[X;T(1:l,:)];%ldata_13t.m
function Tu=data_13t(stri1,stri2,gt,w,order)
%w为取块大小
d=floor(w/2);
GT=imread(gt);
GT=mat2mat(GT,d);%在图像边缘扩充0
mn=[8000 7300 6800 6100 5500 5100 5050 20000 18000];
mx=[15000 15000 15000 16000 28000 24000 21500 36000 31000];
mn2=[670 470 255 245 200 190 150 130 30 10];
mx2=[4000 4000 4000 4000 4300 5200 5200 5500 5000 4000];
A1=imread(stri1{1});
A1=mat2mat(A1,d);
a=size(A1,1);
b=size(A1,2);
B = zeros(a,b,length(stri1));
for i=1:9
A=imread(stri1{i});
A=normal(A,mn(i),mx(i));%归一化,
A=mat2mat(A,d);
B(:,:,i)=A;
end
Tu.P1=B;
D = zeros(a,b,length(stri2));
for i=1:10
C=imread(stri2{i});
C=normal(C,mn2(i),mx2(i));%归一化,
C=mat2mat(C , d);
D(:,:,i)=C;
end
Tu.P2=D;
for t=1:17
Tu.y{t}=[];
Tu.index{t}=[];
end
% Tp.w=w;
% Tp.o=order;
% [Tp.x,Tp.y]=size(GT);%扩展后图像的宽度和高度
S=tabulate(GT(:));%统计各类别的像素点数
l=size(S,1);
for i=2:l%对每一类的像素点进行循环
j=S(i,1);
[m,n]=find(GT==j);
Tu.index{j}(:,1)=m;
Tu.index{j}(:,2)=n;
Tu.index{j}(:,3)=order;
end
endfunction str=lujing(file)
filename=dir(strcat(file,'*.tif'));
str{1}=strcat(file,filename(1).name);
str{2}=strcat(file,filename(4).name);
str{3}=strcat(file,filename(5).name);
str{4}=strcat(file,filename(6).name);
str{5}=strcat(file,filename(7).name);
str{6}=strcat(file,filename(8).name);
str{7}=strcat(file,filename(9).name);
str{8}=strcat(file,filename(2).name);
str{9}=strcat(file,filename(3).name);
end
lujings.m
function str=lujing(file)
filename=dir(strcat(file,'*.tif'));
num=length(filename);
for i=1:num
str{i}=strcat(file,filename(i).name);
end
3.结果
圣保罗的groundtruth图为
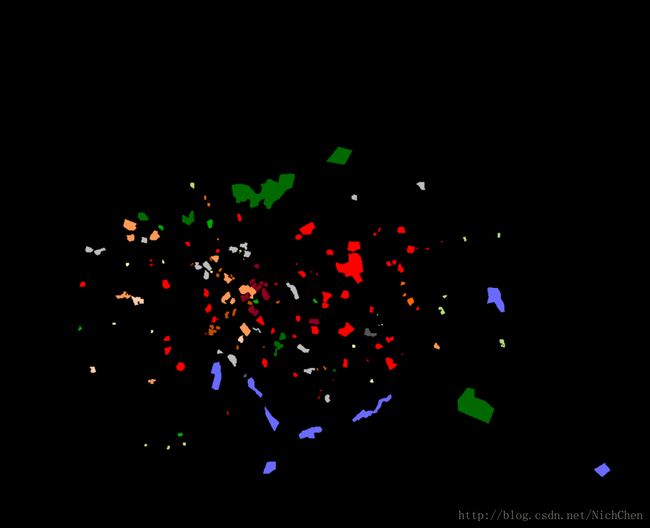
说明:图像显示黑色是因为该groundtruth图为4通道图,多一个alpha通道,实际黑色部分应显示为白色。图中黑色部分并不影响模型的训练,因为在选取训练数据时,是以图中彩色像素(即类别)为中心,划取的28*28*channel的小块,因此黑色部分的数据虽然在groundtruth图中被抹去,但它们不会作为训练数据中的样本。
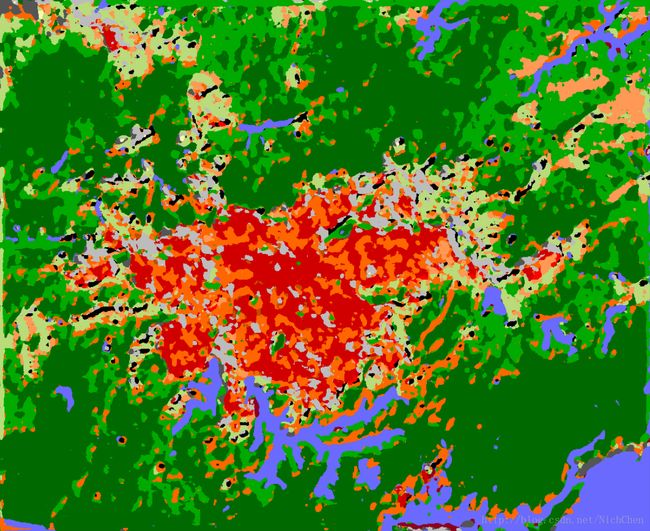
模型预测结果图转彩色图后:
说明:由于测试时是逐个像素点进行预测的,因此预测图片中不存在大面积的黑色像素(groundtruth中的抹黑像素),而实际的预测效果,应该通过对比预测图和实际RGB图进行判断。
实际RGB图:
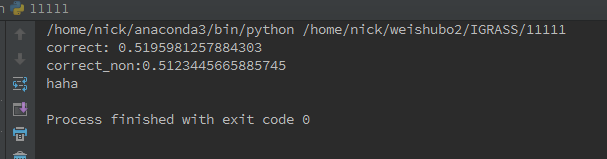
4.准确率
结果表明,稀疏采样后的准确率为51.958%,高于原先的准确率51.234%