5.推荐系统之HBase
一.Hbase简介
1.1什么是Hbase
- Hbase是一个分布式的、面向列的开源数据库
- Hbase是Google BigTable的开源实现
- HBase不同于一般的关系数据库, 适合非结构化数据存储
1.2 BigTable
- BigTable是Google设计的分布式数据存储系统,用来处理海量的数据的一种非关系型的数据库。
- 适合大规模海量数据,PB级数据;
- 分布式、并发数据处理,效率极高;
- 易于扩展,支持动态伸缩
- 适用于廉价设备;
- 不适用于传统关系型数据的存储;
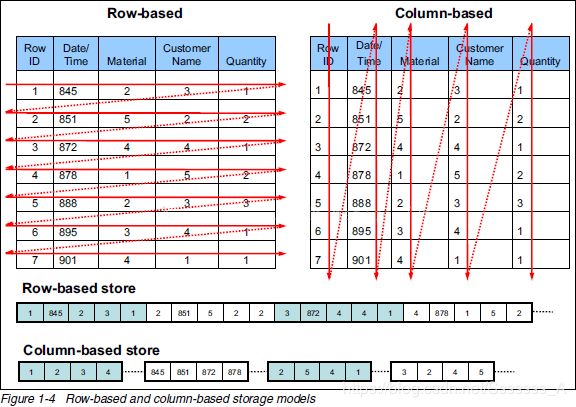
1.3面向列的数据库
Hbase和传统关系数据库的区别
| Hbase | 关系型数据库 | |
|---|---|---|
| 数据库大小 | PB级别 | GB TB |
| 数据类型 | Bytes | 丰富的数据类型 |
| 事务支持 | ACID只支持单个Row级别 | 全面的ACID支持,对Row和表 |
| 索引 | 只支持Row-key | 支持 |
| 吞吐量 | 百万写入/秒 | 数千写入/秒 |
-
关系型数据库中数据示例
ID FILE NAME FILE PATH FILE TYPE FILE SIZE CREATOR 1 File1.txt /home txt 1024 tom 2 File2.txt /home/pics Jpg 5032 jerry -
同样数据保存到列式数据库中
RowKey FILE INFO SAVE INFO 1 name:file1.txt type:txt size:1024 path:/home/pics creator:Jerry 2 name:file2.jpg type:jpg size:5032 path:/home creator:Tom -
行数据库和列数据库存储方式比较
1.4什么是非结构化数据存储
- 结构化数据
- 适合用二维表来展示的数据
- 非结构化数据
- 非结构化数据是数据结构不规则或不完整
- 没有预定义的数据模型
- 不方便用数据库二维逻辑表来表现
- 办公文档、文本、图片、XML, HTML、各类报表、图像和音频/视频信息等
1.5 Hbase在Hadoop生态中的地位
- HBase是Apache基金会顶级项目
- HBase基于HDFS进行数据存储
- HBase可以存储超大数据并适合用来进行大数据的实时查询
1.6 Hbase与HDFS
- HBase建立在Hadoop文件系统上, 利用了HDFS的容错能力
- HBase提供对数据的随机实时读/写访问功能
- HBase内部使用哈希表, 并存储索引, 可以快速查找HDFS中数据
1.7 Hbase使用场景
- 瞬间写入量很大
- 大量数据需要长期保存, 且数量会持续增长
- HBase不适合有join, 多级索引, 表关系复杂的数据模型
二.HBase的数据模型
- NameSpace: 关系型数据库的"数据库"(database)
- 表(table):用于存储管理数据,具有稀疏的、面向列的特点。HBase中的每一张表,就是所谓的大表(Bigtable),可以有上亿行,上百万列。对于为值为空的列,并不占用存储空间,因此表可以设计的非常稀疏。
- 行(Row):在表里面,每一行代表着一个数据对象,每一行都是以一个行键(Row Key)来进行唯一标识的, 行键并没有什么特定的数据类型, 以二进制的字节来存储
- 列(Column): HBase的列由 Column family 和 Column qualifier 组成, 由冒号: 进行行间隔, 如 family: qualifier
- 行键(RowKey):类似于MySQL中的主键,HBase根据行键来快速检索数据,一个行键对应一条记录。与MySQL主键不同的是,HBase的行键是天然固有的,每一行数据都存在行键。
- 列族(ColumnFamily):是列的集合。列族在表定义时需要指定,而列在插入数据时动态指定。列中的数据都是以二进制形式存在,没有数据类型。在物理存储结构上,每个表中的每个列族单独以一个文件存储。一个表可以有多个列簇。
- 列修饰符(Column Qualifier) : 列族中的数据通过列标识来进行映射, 可以理解为一个键值对(key-value), 列修饰符(Column Qualifier) 就是key 对应关系型数据库的列
- 时间戳(TimeStamp):是列的一个属性,是一个64位整数。由行键和列确定的单元格,可以存储多个数据,每个数据含有时间戳属性,数据具有版本特性。可根据版本(VERSIONS)或时间戳来指定查询历史版本数据,如果都不指定,则默认返回最新版本的数据。
- 区域(Region):HBase自动把表水平划分成的多个区域,划分的区域随着数据的增大而增多。
- HBase 支持特定场景下的 ACID,即对行级别的 操作保证完全的 ACID
Cap定理
-
分布式系统的最大难点,就是各个节点的状态如何同步。CAP 定理是这方面的基本定理,也是理解分布式系统的起点。
hbase是CAP中的CP系统,即hbase是强一致性的
三.Hbase Shell操作
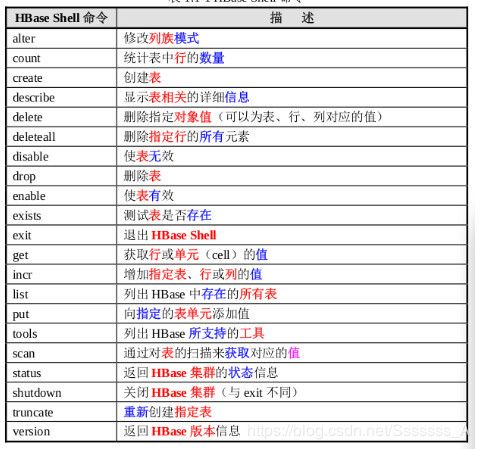
3.1Hbase DDL和DML命令
| 名称 | 命令表达式 |
|---|---|
| 创建表 | create ‘表名’, ‘列族名1’,‘列族名2’,‘列族名n’ |
| 添加记录 | put ‘表名’,‘行名’,‘列名:’,'值 |
| 查看记录 | get ‘表名’,‘行名’ |
| 查看表中的记录总数 | count ‘表名’ |
| 删除记录 | delete ‘表名’, ‘行名’,‘列名’ |
| 删除一张表 | 第一步 disable ‘表名’ 第二步 drop ‘表名’ |
| 查看所有记录 | scan “表名称” |
| 查看指定表指定列所有数据 | scan ‘表名’ ,{COLUMNS=>‘列族名:列名’} |
| 更新记录 | 重写覆盖 |
3.2基本操作
-
连接集群
hbase shell -
创建表
create 'user','base_info' -
删除表
disable 'user' drop 'user' -
创建名称空间
create_namespace 'test' -
展示现有名称空间
list_namespace -
创建表的时候添加namespace
create 'test:user','base_info' -
显示某个名称空间下有哪些表
list_namespace_tables 'test'
3.3增删改查
-
插入数据
- put ‘表名’,‘rowkey的值’,’列族:列标识符‘,’值‘
put 'user','rowkey_10','base_info:username','Tom' put 'user','rowkey_10','base_info:birthday','2014-07-10' put 'user','rowkey_10','base_info:sex','1' put 'user','rowkey_10','base_info:address','Tokyo' put 'user','rowkey_16','base_info:username','Mike' put 'user','rowkey_16','base_info:birthday','2014-07-10' put 'user','rowkey_16','base_info:sex','1' put 'user','rowkey_16','base_info:address','beijing' put 'user','rowkey_22','base_info:username','Jerry' put 'user','rowkey_22','base_info:birthday','2014-07-10' put 'user','rowkey_22','base_info:sex','1' put 'user','rowkey_22','base_info:address','Newyork' put 'user','rowkey_24','base_info:username','Nico' put 'user','rowkey_24','base_info:birthday','2014-07-10' put 'user','rowkey_24','base_info:sex','1' put 'user','rowkey_24','base_info:address','shanghai' put 'user','rowkey_25','base_info:username','Rose' put 'user','rowkey_25','base_info:birthday','2014-07-10' put 'user','rowkey_25','base_info:sex','1' put 'user','rowkey_25','base_info:address','Soul' -
查询表中所有数据
scan 'user' # HBase中一般存储数据量都很大 很少使用全表查询 scan会加上一些条件限制 -
Scan查询中添加限制条件
scan '名称空间:表名', {COLUMNS => ['列族名1', '列族名2'], LIMIT => 10, STARTROW => '起始的rowkey'} # 通过COLUMNS LIMIT STARTROW 等条件缩小查询范围 #LIMIT=>2 限制输出两行 scan 'user' ,{COLUMNS =>['base_info'],LIMIT=>2} ## 返回结果 ROW COLUMN+CELL rowkey_10 column=base_info:address, timestamp=1558323139732, value=Tokyo rowkey_10 column=base_info:birthday, timestamp=1558323139636, value=2014-07-10 rowkey_10 column=base_info:sex, timestamp=1558323139678, value=1 rowkey_10 column=base_info:username, timestamp=1558323918953, value=Tom4 rowkey_16 column=base_info:address, timestamp=1558323139963, value=beijing rowkey_16 column=base_info:birthday, timestamp=1558323139866, value=2014-07-10 rowkey_16 column=base_info:sex, timestamp=1558323139907, value=1 #STARTROW 限制起始的Rowkey scan 'user' ,{COLUMNS =>['base_info'],LIMIT=>2,STARTROW=>'rowkey_16'} #返回结果: ROW COLUMN+CELL rowkey_16 column=base_info:address, timestamp=1558323139963, value=beijing rowkey_16 column=base_info:birthday, timestamp=1558323139866, value=2014-07-10 rowkey_16 column=base_info:sex, timestamp=1558323139907, value=1 rowkey_22 column=base_info:address, timestamp=1558323140188, value=Newyork rowkey_22 column=base_info:birthday, timestamp=1558323140107, value=2014-07-10 rowkey_22 column=base_info:sex, timestamp=1558323140143, value=1 rowkey_22 column=base_info:username, timestamp=1558323140036, value=Jerry -
scan查询添加过滤器
-
ROWPREFIXFILTER rowkey 前缀过滤器
scan 'user', {ROWPREFIXFILTER=>'rowkey_22'} #显示结果 ROW COLUMN+CELL rowkey_22 column=base_info:address, timestamp=1558323140188, value=Newyork rowkey_22 column=base_info:birthday, timestamp=1558323140107, value=2014-07-10 rowkey_22 column=base_info:sex, timestamp=1558323140143, value=1 rowkey_22 column=base_info:username, timestamp=1558323140036, value=Jerry 1 row(s) Took 0.0120 seconds
-
-
查询某个rowkey的数据
get 'user','rowkey_16' -
查询某个列族的数据
get 'user','rowkey_16','base_info' get 'user','rowkey_16','base_info:username' get 'user', 'rowkey_16', {COLUMN => ['base_info:username','base_info:sex']} -
删除表中的数据
delete 'user', 'rowkey_16', 'base_info:username' -
清空数据
truncate 'user' -
操作列簇
alter 'user', NAME => 'f2' alter 'user', 'delete' => 'f2' -
HBase追加型数据库,会保留多个版本数据
desc 'user' Table user is ENABLED user COLUMN FAMILIES DESCRIPTION {NAME => 'base_info', VERSIONS => '1', EVICT_BLOCKS_ON_CLOSE => 'false', NEW_VERSION_B HE_DATA_ON_WRITE => 'false', DATA_BLOCK_ENCODING => 'NONE', TTL => 'FOREVER', MI ER => 'NONE', CACHE_INDEX_ON_WRITE => 'false', IN_MEMORY => 'false', CACHE_BLOOM se', COMPRESSION => 'NONE', BLOCKCACHE => 'false', BLOCKSIZE => '65536'}-
VERSIONS=>'1’说明最多可以显示一个版本 修改数据
put 'user','rowkey_10','base_info:username','Tom' -
指定显示多个版本
get 'user','rowkey_10',{COLUMN=>'base_info:username',VERSIONS=>2} -
修改可以显示的版本数量
alter 'user',NAME=>'base_info',VERSIONS=>10
-
-
通过时间戳查询
-
通过TIMERANGE 指定时间范围
scan 'user',{COLUMNS => 'base_info', TIMERANGE => [1558323139732, 1558323139866]} get 'user','rowkey_10',{COLUMN=>'base_info:username',VERSIONS=>2,TIMERANGE => [1558323904130, 1558323918954]} -
通过时间戳过滤器 指定具体时间戳的值
scan 'user',{FILTER => 'TimestampsFilter (1558323139732, 1558323139866)'} get 'user','rowkey_10',{COLUMN=>'base_info:username',VERSIONS=>2,FILTER => 'TimestampsFilter (1558323904130, 1558323918954)'} -
获取最近多个版本的数据
get 'user','rowkey_10',{COLUMN=>'base_info:username',VERSIONS=>10} COLUMN CELL base_info:username timestamp=1558323918953, value=Tom4 base_info:username timestamp=1558323904133, value=Tom3 base_info:username timestamp=1558323758696, value=Tom2 base_info:username timestamp=1558323139575, value=Tom -
通过指定时间戳获取不同版本的数据
get 'user','rowkey_10',{COLUMN=>'base_info:username',TIMESTAMP=>1558323904133} #返回结果如下 COLUMN CELL base_info:username timestamp=1558323904133, value=Tom3 get 'user','rowkey_10',{COLUMN=>'base_info:username',TIMESTAMP=>1558323918953} #返回结果如下 COLUMN CELL base_info:username timestamp=1558323918953, value=Tom4
-
四. HappyBase操作HBase
-
什么是HappyBase
- HappyBase is a developer-friendly Python library to interact with Apache HBase. HappyBase is designed for use in standard HBase setups, and offers application developers a Pythonic API to interact with HBase. Below the surface, HappyBase uses the Python Thrift library to connect to HBase using its Thrift gateway, which is included in the standard HBase 0.9x releases.
-
HappyBase 是FaceBook员工开发的操作HBase的python库, 其基于Python Thrift, 但使用方式比Thrift简单, 已被广泛应用
-
启动hbase thrift server : hbase-daemon.sh start thrift
-
安装happy base
- pip install happybase
-
如何使用HappyBase
-
建立连接
import happybase connection = happybase.Connection('somehost') -
当连接建立时, 会自动创建一个与 HBase Thrift server的socket链接. 可以通过参数禁止自动链接, 然后再需要连接是调用
Connection.open():connection = happybase.Connection('somehost', autoconnect=False) # before first use: connection.open() -
Connection这个类提供了一个与HBase交互的入口, 比如获取HBase中所有的表:Connection.tables():print(connection.tables()) -
操作表
- Table类提供了大量API, 这些API用于检索和操作HBase中的数据。 在上面的示例中,我们已经使用Connection.tables()方法查询HBase中的表。 如果还没有任何表,可使用Connection.create_table()创建一个新表:
connection.create_table('users',{'cf1': dict()}) -
创建表之后可以传入表名获取到Table类的实例
table = connection.table('mytable') -
查询操作
-
# api table.scan() #全表查询 table.row('row_key') # 查询一行 table.rows([row_keys]) # 查询多行 #封装函数 def scanQuery(): # 创建和hbase的连接 connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') #通过connection找到user表 获得table对象 table = connection.table('user') filter = "ColumnPrefixFilter('username')" #row_start 指定起始rowkey 缩小查询范围 #filter 添加过滤器 for key,value in table.scan(row_start='rowkey_10',filter=filter): print(key,value) # 关闭连接 connection.close() def getQuery(): connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') # 通过connection找到user表 获得table对象 table = connection.table('user') result = table.row('rowkey_22',columns=['base_info:username']) #result = table.row('rowkey_22',columns=['base_info:username']) result = table.rows(['rowkey_22','rowkey_16'],columns=['base_info:username']) print(result) # 关闭连接 connection.close() -
插入数据
#api table.put(row_key, {'cf:cq':'value'}) def insertData(): connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') # 通过connection找到user表 获得table对象 table = connection.table('users') table.put('rk_01',{'cf1:address':'beijing'}) # 关闭连接 for key,value in table.scan(): print(key,value) connection.close() -
删除数据
#api table.delete(row_key, cf_list) def deleteData(): connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') # 通过connection找到user表 获得table对象 table = connection.table('users') table.delete('rk_01',['cf1:username']) # 关闭连接 for key,value in table.scan(): print(key,value) connection.close() -
删除表
#api conn.delete_table(table_name, True) #函数封装 def delete_table(table_name): pretty_print('delete table %s now.' % table_name) conn.delete_table(table_name, True)
-
-
完整代码
import happybase def connectHBase(): #创建和hbase的连接 connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') #获取hbase中的所有表 print(connection.tables()) #关闭连接 connection.close() def createTable(): connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') connection.create_table('users',{'cf1': dict()}) print(connection.tables()) connection.close() def scanQuery(): # 创建和hbase的连接 connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') #通过connection找到user表 获得table对象 table = connection.table('user') filter = "ColumnPrefixFilter('username')" #row_start 指定起始rowkey 缩小查询范围 #filter 添加过滤器 for key,value in table.scan(row_start='rowkey_10',filter=filter): print(key,value) # 关闭连接 connection.close() def getQuery(): connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') # 通过connection找到user表 获得table对象 table = connection.table('user') result = table.row('rowkey_22',columns=['base_info:username']) #result = table.row('rowkey_22',columns=['base_info:username']) result = table.rows(['rowkey_22','rowkey_16'],columns=['base_info:username']) print(result) # 关闭连接 connection.close() def insertData(): connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') # 通过connection找到user表 获得table对象 table = connection.table('users') table.put('rk_01',{'cf1:address':'beijing'}) # 关闭连接 for key,value in table.scan(): print(key,value) connection.close() def deleteData(): connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') # 通过connection找到user表 获得table对象 table = connection.table('users') table.delete('rk_01',['cf1:username']) # 关闭连接 for key,value in table.scan(): print(key,value) connection.close() def deletetable(): #创建和hbase的连接 connection = happybase.Connection('192.168.19.137') #获取hbase中的所有表 connection.delete_table('users',disable=True) print(connection.tables()) #关闭连接 connection.close() def main(): #connectHBase() #createTable() scanQuery() #getQuery() #insertData() #deleteData() #deletetable() if __name__ == "__main__": main()
五.HBase组件
5.1 Hbase基础架构
Client
- ①与zookeeper通信, 找到数据入口地址
- ②使用HBase RPC机制与HMaster和HRegionServer进行通信;
- ③Client与HMaster进行通信进行管理类操作;
- ④Client与HRegionServer进行数据读写类操作。
Zookeeper
- ①保证任何时候,集群中只有一个running master,避免单点问题;
- ②存贮所有Region的寻址入口,包括-ROOT-表地址、HMaster地址;
- ③实时监控Region Server的状态,将Region server的上线和下线信息,实时通知给Master;
- ④存储Hbase的schema,包括有哪些table,每个table有哪些column family。
HMaster
可以启动多个HMaster,通过Zookeeper的Master Election机制保证总有一个Master运行。
角色功能:
- ①为Region server分配region;
- ②负责region server的负载均衡;
- ③发现失效的region serve并重新分配其上的region;
- ④HDFS上的垃圾文件回收;
- ⑤处理用户对表的增删改查操作。
HRegionServer
HBase中最核心的模块,主要负责响应用户I/O请求,向HDFS文件系统中读写数据。
作用:
- ①维护Master分配给它的region,处理对这些region的IO请求;
- ②负责切分在运行过程中变得过大的region。
- 此外,HRegionServer管理一系列HRegion对象,每个HRegion对应Table中一个Region,HRegion由多个HStore组成,每个HStore对应Table中一个Column Family的存储,Column Family就是一个集中的存储单元,故将具有相同IO特性的Column放在一个Column Family会更高效。
HStore
-
HBase存储的核心,由MemStore和StoreFile组成
-
用户写入数据的流程为:client访问ZK, ZK返回RegionServer地址-> client访问RegionServer写入数据 -> 数据存入MemStore,一直到MemStore满 -> Flush成StoreFile
HRegion
- 一个表最开始存储的时候,是一个region。
- 一个Region中会有个多个store,每个store用来存储一个列簇。如果只有一个column family,就只有一个store。
- region会随着插入的数据越来越多,会进行拆分。默认大小是10G一个。
HLog
- 在分布式系统环境中,无法避免系统出错或者宕机,一旦HRegionServer意外退出,MemStore中的内存数据就会丢失,引入HLog就是防止这种情况。
5.2 HBase模块协作
- HBase启动
- HMaster启动, 注册到Zookeeper, 等待RegionServer汇报
- RegionServer注册到Zookeeper, 并向HMaster汇报
- 对各个RegionServer(包括失效的)的数据进行整理, 分配Region和meta信息
- RegionServer失效
- HMaster将失效RegionServer上的Region分配到其他节点
- HMaster更新hbase: meta 表以保证数据正常访问
- HMaster失效
- 处于Backup状态的其他HMaster节点推选出一个转为Active状态
- 数据能正常读写, 但是不能创建删除表, 也不能更改表结构