django入门到实战
文章目录
- 1. 初识web框架
- 1.1 http协议
- 1.2 socket简介
- 1.3 socket服务端概述
- 1.4 自己写web框架
- 1.5 web框架的分类
- 2. 初识django
- 3. django程序目录
- 4. 第一个django请求
- 5. 静态文件以及模板的配置
- 5.1 静态文件路径的配置
- 5.2 HttpResponse与render函数
- 5.3 模板路径的配置
- 6. 创建程序步骤
- 6.1 创建project
- 6.2 配置模板路径
- 6.3 配置静态文件目录
- 6.4 额外配置
- 7. 用户登录示例
- 8. request.GET与 request.POST
- 8.1 request.GET
- 8.2 request.POST
- 9. django模板语言特殊标记(重点)
- 9.1 取字符串的值
- 9.2 取列表的值
- 9.3 取字典的值
- 9.4 取嵌套于列表中字典的值
- 10. 学生信息管理系统(一)
- 10.1 数据库表的结构设计
- 11. 学生信息管理系统(二)
- 11.1 向班级表中添加数据
- 11.2 查询班级信息
- 11.3 添加班级信息
- 12. 学生信息管理系统(三)
- 12.1 删除班级信息
- 13. 学生信息管理系统(四)
- 13.1 编辑班级信息
1. 初识web框架
1.1 http协议
http协议是无状态,短连接的。客户端连接服务器,发送请求,服务器响应请求后断开连接。
1.2 socket简介
所有的网络请求都是基于socket,浏览器是socket客户端,网站是socket服务端。
1.3 socket服务端概述
根据url的不同返回给用户不同的内容,使用路由系统,路由系统是url与函数的对应关系。返回给用户的内容本质是字符串,基本上返回的内容是动态的,所以需要使用到模板渲染。模板渲染实际上是把html充当模板,自己创造任意数据替换模板中的特殊字符,比如替换特殊字符为数据库中的数据。
1.4 自己写web框架
- 静态应用
# coding:utf-8
import socket
def f1(request):
'''
处理用户请求,并返回相应的内容
:param request:用户请求的所有信息
:return:返回相应的内容
'''
return b'f1'
def f2(request):
'''
处理用户请求,并返回相应的内容
:param request:
:return:
'''
f = open('index.html', 'rb')
data = f.read()
f.close()
return data
def f3(request):
'''
处理用户请求,并返回相应的内容
:param request:
:return:
'''
f = open('news.html', 'rb')
data = f.read()
f.close()
return data
routers = [
('/user', f1),
('/', f2)
]
def run():
sock = socket.socket()
sock.bind(('127.0.0.1', 8080))
sock.listen(5)
while True:
conn, addr = sock.accept()
'''
有用户来连接,
获取用户发送的数据
'''
data = conn.recv(8096)
print(data)
'''请求头:
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:8080
Connection: keep-alive
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1\
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/75.0.3770.100 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3
Purpose: prefetch
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate,
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
'''
# 解析请求头,目标:获取请求头中的url,并根据url向服务端发送请求
data = str(data, encoding='utf-8')
headers, bodys = data.split('\r\n\r\n')
headers_list = headers.split('\r\n')
methods, url, protocal = headers_list[0].split(' ')
func_name = None
for item in routers:
if item[0] == url:
func_name = item[1]
break
if func_name:
response = func_name(data)
else:
response = '404'
# if url == '/user':
# conn.send(b'user page')
# else:
# conn.send(b'404 is not found!')
# conn.send(b"HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n\r\n") # 响应头
# conn.send(b"hello thanlon!") # 相应体
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
- 动态应用示例一
# coding:utf-8
import socket
def f1(request):
'''
处理用户请求,并动态返回相应的内容
:param request:
:return:
'''
f = open('news.html', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
data = f.read()
f.close()
import time
ctime = time.time()
data = data.replace('%', str(ctime))
return bytes(data, encoding='utf-8')
routers = [
('/user', f1),
]
def run():
sock = socket.socket()
sock.bind(('127.0.0.1', 8080))
sock.listen(5)
while True:
conn, addr = sock.accept()
'''
有用户来连接,
获取用户发送的数据
'''
data = conn.recv(8096)
print(data)
'''请求头:
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:8080
Connection: keep-alive
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1\
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/75.0.3770.100 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3
Purpose: prefetch
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate,
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
'''
# 解析请求头,目标:获取请求头中的url,并根据url向服务端发送请求
data = str(data, encoding='utf-8')
headers, bodys = data.split('\r\n\r\n')
headers_list = headers.split('\r\n')
methods, url, protocal = headers_list[0].split(' ')
func_name = None
for item in routers:
if item[0] == url:
func_name = item[1]
break
if func_name:
response = func_name(data)
else:
response = '404'
# if url == '/user':
# conn.send(b'user page')
# else:
# conn.send(b'404 is not found!')
# conn.send(b"HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n\r\n") # 响应头
# conn.send(b"hello thanlon!") # 相应体
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
- 动态应用示例二
# coding:utf-8
import socket
def f1(request):
import pymysql
# 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='wwwnxl', db='test')
# 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 执行sql语句,并返回受影响的行数
cursor.execute("select id,name,passwd from userinfo")
user_list = cursor.fetchall()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
# print(user_list)
content_list = []
for row in user_list:
tp = '%s %s %s ' % (row['id'], row['name'], row['passwd'],)
content_list.append(tp)
content = ''.join(content_list)
f = open('userlist.html', 'r', encoding='utf-8')
template = f.read()
f.close()
data = template.replace('{{content}}', content)
print(data)
return bytes(data, encoding='utf-8')
routers = [
('/user', f1),
]
def run():
sock = socket.socket()
sock.bind(('127.0.0.1', 8080))
sock.listen(5)
while True:
conn, addr = sock.accept()
'''
有用户来连接,
获取用户发送的数据
'''
data = conn.recv(8096)
# print(data)
'''请求头:
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:8080
Connection: keep-alive
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1\
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/75.0.3770.100 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3
Purpose: prefetch
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate,
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
'''
# 解析请求头,目标:获取请求头中的url,并根据url向服务端发送请求
data = str(data, encoding='utf-8')
headers, bodys = data.split('\r\n\r\n')
headers_list = headers.split('\r\n')
methods, url, protocal = headers_list[0].split(' ')
func_name = None
for item in routers:
if item[0] == url:
func_name = item[1]
break
if func_name:
response = func_name(data)
else:
response = b'404'
conn.send(response)
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
1.5 web框架的分类
为了方便开发者开发web应用,web框架应用而生。有的web框架帮助开发者构建好了socket服务端,有的web框架帮助开发者写好了模板渲染。总之,借助web框架可以减轻了开发者的工作量。flask框架只有路由系统,没有socket服务端和模板引擎,socket服务端使用是python第三方模块,如wsgiref。模板引擎使用的也是第三方模块jinjia2。django框架有路由系统、模板引擎,但是没有socket服务端,socket服务端使用的是python的第三方内置模块wsgiref,wsgiref把请求交给django做处理。另外,还有一种叫Tornado的框架,Tornado框架包含socket服务端、路由系统、模板引擎。可以将web框架这样分类,django框架和其它框架。因为django框架提供了很多特殊的功能,如缓存、分布式。其它框架是轻量级的web框架。
2. 初识django
安装django:pip3 install django
创建django程序:django-admin startproject 项目名称
运行django程序:python manager.py runserver 127.0.0.1:8080(如果不指定,默认运行在8000端口)
3. django程序目录
manager.py:对当前django程序所有操作可以基于python manager.py runserver
settings.py:django配置文件
url.py:路由系统,url->函数
wsgi.py:用于定义django使用什么socket服务端,如wsgiref,uwsgi(wsgiref性能比较低)
4. 第一个django请求
usr.py:
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse
# 处理请求的函数
def login(request): #
'''
处理用户请求,返回相响应结果
:param request:用户请求的相关信息(不是字节,是对象)
:return:
'''
pass
return HttpResponse('login!')
# url
urlpatterns = [
# path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('login/', login),
]
5. 静态文件以及模板的配置
5.1 静态文件路径的配置
# Static files (CSS, JavaScript, Images)
# https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.2/howto/static-files/
'''
只要是使用/static/的前缀,就在这个目录(static目录)下找静态文件
'''
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS = (
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'static'),
)
5.2 HttpResponse与render函数
- 返回字符串
return HttpResponse(‘login!’)
return HttpResponse(’< input type=“text”>’) - 返回模板
render函数默认是在“templates”中自动找文件,读取文件内容后返回给用户。
return render(request, ‘xxx.html’)
render函数本质上是调用HttpResponse。
5.3 模板路径的配置
6. 创建程序步骤
6.1 创建project
django-admin startproject project名,也可以在pycharm中选择Django,创建project
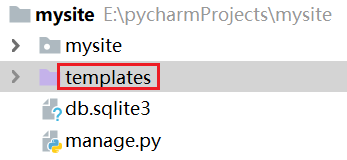
6.2 配置模板路径
创建templates目录,然后修改配置文件:
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'templates')]#BASE_DIR指当前路径
,
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]
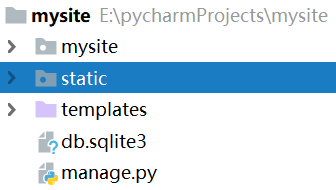
6.3 配置静态文件目录
创建static目录,然后修改配置文件:
'''
只要是使用/static/的前缀,就在这个目录下找静态文件
'''
STATIC_URL = '/static/'
STATICFILES_DIRS = (
os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'static'),
)
6.4 额外配置
将 django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware注释掉:
MIDDLEWARE = [
'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware',
'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware',
'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
# 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware',
'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware',
'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware',
'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware',
]
7. 用户登录示例
urls.py:
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from django.shortcuts import HttpResponse, render, redirect
def login(request): #
'''
处理用户请求,返回相响应结果
:param request:用户请求的相关信息(不是字节,是对象)
:return:
'''
if request.method == 'GET':
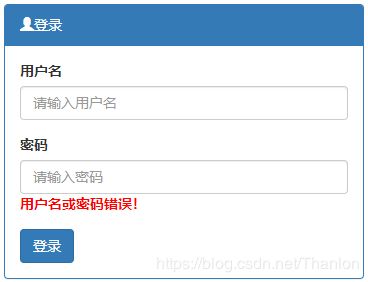
return render(request, 'login.html') # 本质上是调用HttpResponse,自动找到login.html文件,读取内容并返回给用户
else:
# print(request.POST) # 用户POST提交的数据(请求体)login.html:
<form action="/login/" method="POST" name="loginForm">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="name">用户名</label> <input type="text" class="form-control" name="username" placeholder="请输入用户名">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="">密码</label> <input type="password" class="form-control" name="pwd" placeholder="请输入密码">
<div style="color: red;font-weight: bold">{{ msg }}</div>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary" onclick="return checkForm()">登录</button>
</form>
8. request.GET与 request.POST
8.1 request.GET
request.GET是从请求头的url中获取值
8.2 request.POST
request.POST是从请求体中获取值。GET请求时,只有request.GET可以获取值。但POST请求时,request.POST和request.GET都可能获取值。
<form action="/login/?page=1" method="POST" name="loginForm">……
可以通过request.GET获取url中的page
9. django模板语言特殊标记(重点)
9.1 取字符串的值
def index(request):
return render(request, 'index/index.html', {'username': '一问奈何'})
<p>{{ username }}p> # 一问奈何
9.2 取列表的值
def index(request):
# return render(request, 'index/index.html', {'username': '一问奈何'})
return render(request, 'index/index.html', {'username': ['thanlon','Kiku']})
- 直接通过索引
{#<p>{{ username }}p>#}
{{ username }}
{{ username.0 }}
{{ username.1 }}
- 通过循环遍历
{% for item in username %}
{{ item }}
{% endfor %}
![]()
9.3 取字典的值
def index(request):
return render(request, 'index/index.html', {
'user_dict': {'name': '一问奈何', 'age': 23}
})
<body>
{{ user_dict.name }}
{{ user_dict.age }}
<body>
9.4 取嵌套于列表中字典的值
def index(request):
return render(request, 'index/index.html', {
'user_list_dict': [
{'id': 1, 'name': 'thanlon'},
{'id': 2, 'name': 'kuku'},
]
})
- 通过索引取值
{{ user_list_dict.0.id}}--{{ user_list_dict.0.name}}
{{ user_list_dict.1.id}}--{{ user_list_dict.0.name}}
- 通过循环取值
{% for row in user_list_dict %}
{{ row.id }}--{{ row.name }}
{% endfor %}
![]()
10. 学生信息管理系统(一)
10.1 数据库表的结构设计
# 创建test数据库
create database test default character set utf8;
# 创建班级表
create table class(id int auto_increment primary key, title varchar(20) not null);
# 创建学生表
create table student(id int auto_increment primary key,name varchar(10) not null,class_id int not null);
# 创建教师表
create table teacher(id int auto_increment primary key,name varchar(10) not null);
# 创建教师课程表
create table teacher2class(id int primary key,teacher_id int not null,class_id int not null);
11. 学生信息管理系统(二)
11.1 向班级表中添加数据
insert class values(null,'软件工程'),(null,'计算机科学与技术');
11.2 查询班级信息
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('classes/', views.classes),
]
- 在views.py的classes函数(路径对应此函数)中写查询班级信息的逻辑代码
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
import pymysql
def classes(request):
'''
查询班级id、班级名称
:param request:对象相关的数据
:return:渲染后的模板
'''
# 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='wwwnxl', db='test')
# 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# 执行sql语句
cursor.execute("select id,title from class")
classes_list = cursor.fetchall()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
return render(request, 'classes.html', {'classes_list': classes_list})
- 在templates文件夹下新建classes.html
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>班级信息title>
head>
<body>
<p><a href="/add-class/">添加a>p>
{% for row in classes_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ row.id }}td>
<td>{{ row.title }}td>
tr>
<br>
{% endfor %}
body>
html>
运行程序后,访问http://127.0.0.1:8000/classes/可以查看到页面效果:

11.3 添加班级信息
- 配置路径,修改urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('classes/', views.classes),
path('add-class/', views.add_class),
]
- 在templates文件夹下新建add_class.html
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>添加班级信息title>
head>
<body>
<h1>添加班级h1>
<form action="/add-class/" method="post">
<label>班级名称:label>
<input type="text" name="class_title">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
form>
body>
html>
- 在views.py的add_class函数中写添加学生班级信息的逻辑代码
def add_class(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
return render(request, 'add_class.html')
else:
class_title = request.POST.get('class_title')
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='wwwnxl', db='test')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# cursor.execute("insert into class(title) values(%s)", [class_title, ])
cursor.execute('insert into class(title) values(%s)', class_title)
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
return redirect('/classes/')
程序正常运行后,在班级信息页面(http://127.0.0.1:8000/classes/)中点击添加按钮,进入添加班级信息界面(http://127.0.0.1:8000/add-class/)。提交添加的班级信息后,自动跳转到班级信息页面。
12. 学生信息管理系统(三)
12.1 删除班级信息
view.py
def del_class(request):
nid = request.GET.get('nid')
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='wwwnxl', db='test')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# cursor.execute("insert into class(title) values(%s)", [class_title, ])
cursor.execute('delete from class where id=%s', nid)
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
return redirect('/classes/')
浏览器向服务端发送删除数据的请求,服务端接收请求删除数据后向浏览器发送响应,告诉浏览器重定向到/classes/。服务端向浏览器发送响应的响应头中有location:http://127.0.0.1:8000/classes/,即是:告诉浏览器向此链接发送一次请求。
13. 学生信息管理系统(四)
13.1 编辑班级信息
view.py:
def edit_class(request):
if request.method == 'GET':
nid = request.GET.get('nid')
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='wwwnxl', db='test')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
cursor.execute('select id,title from class where id=%s', nid)
result = cursor.fetchone()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
return render(request, 'edit_class.html', {'result': result})
else:
# nid = request.POST.get('nid') # 放到请求体
nid = request.GET.get('nid') # 放到请求头
title = request.POST.get('title')
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='wwwnxl', db='test')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
cursor.execute('update class set title=%s where id = %s', [title, nid])
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
return redirect('/classes/')
edit_class.html:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>修改班级信息title>
head>
<body>
<h3>编辑班级信息h3>
<form action="/edit-class/?nid={{ result.id }}" method="post">
<label>班级名称:label>
{# #}
<input type="text" name="title" value="{{ result.title }}">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
form>
body>
html>