MySQL开发C版
MySQL开发C版
- MD DoCUMEnT: 3/4/2016 3:25:55 PM by Jimbowhy
- CSDN PuBliShEd: http://blog.csdn.net/WinsenJiansbomber/article/details/50806962
MySQL这个开源的数据系统曾经是PHP平台开发的热门软件,现在也挺好,很多项目都可以使用得上。当然数据库还有很多选择,而我最喜欢的一个就是 sqlite 可以说它就是一个不像数据库的数据库!
开发前准备
当前系统使用 MySQL Server 5.1,在安装过程中选上开发包,这样就会安装开发中需要的头文件和库文件 C Include Files / Lib Files。可以直接下载 mysql 连接器 mysql-connector-c-noinstall-6.0.2-win32.zip,需要用到头文件 mysql.h 和库文件 libmysql.lib,还有动态链接库 libmysql.dll。编译器使用的是 TDM-GCC 4.7.1,到官方网站下载安装即可以,通过命令行它,在环境变量PATH中添加BIN目录的路径即可以使用。官方收录的连接器,有下面这些,其中 C API 是安装包自带的:
[MySQL Connectors][3]
ADO.NET Driver for MySQL (Connector/NET)
ODBC Driver for MySQL (Connector/ODBC)
JDBC Driver for MySQL (Connector/J)
Python Driver for MySQL (Connector/Python)
C++ Driver for MySQL (Connector/C++)
C Driver for MySQL (Connector/C)
C API for MySQL (mysqlclient)
PHP Drivers for MySQL (mysqli, ext/mysqli, PDO_MYSQL, PHP_MYSQLND)
Perl Driver for MySQL (DBD::mysql)
Ruby Driver for MySQL (ruby-mysql)
C++ Wrapper for MySQL C API (MySQL++)
C API 文档见这里 21.8.6 C API Function Overview。
如果系统已经安装好 MySQL,请通过 services.msc 运行 mysql 服务。如果是手动安装包,还需要以下命令来安装服务,或手动运行服务程序 mysqld.exe。可以使用Windows系统的服务管理命令 SC 安装实例,又或者通过 mysqld.exe 进行实例安装:
mysqld-nt --install MySQL
mysqld-nt --remove MySQL
sc create MySQL binPath= "patch\to\bin\mysqld --defaults-file=path\to\my.ini" start= demand
安装完后,使用 mysql 命令进行登录测试,按提示输入密码,确保帐户正常:
mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p
登录后,可以通过以下命令来查询数据库,或对数据库进行管理,注意以下命令作为参考,不要一条条照着执行:
mysql> show databases;
mysql> SELECT VERSION(),CURRENT_DATE;
mysql> USE mysql;
mysql> SELECT DataBase();
mysql> SHOW TABLES;
mysql> SHOW TABLES LIKE '%post%';
mysql> SHOW TABLES FROM mydb;
mysql> DESCRIBE TABLE;
mysql> CREATE DATABASE pubs;
mysql> ALTER DATABASE pubs CHARACTER SET 'utf8';
mysql> CREATE DATABASE pubs CHARACTER SET 'utf8';
mysql> DROP DATABASE pubs;
mysql> USE pubs;
mysql> CREATE TABLE people (id int NOT NULL, name varchar(24));
mysql> INSERT people VALUE(0, 'Jimbo');
mysql> DROP TABLE people;
关于字符集与代码页
Windows系统通过管理代码页来实现对各种字符集的支持,在Windows 9x以前,操作系统本身只支持一个多字节类型的代码页,如果说,简体中文版只使用GBK,对于其它不兼容的中文字符集如BIG5是不能处理的,只能通过转码软件解决,因此那时就有个名词称之为系统内码。而从新一代的XP系统开始,系统内部使用Unicode编码,因此就可以同时支持多个字符集了,包括简体繁体,韩文日文等等。
我们的程序为什么能显示不同的字符,为什么同样一个程序在不同的字符集下会乱码?要解决这个问题就要从低层说起,咳…咳…其实这并不是什么难理解的事,难的是没有很好的资料在手才是个问题。计算机显示字符是从内存开始的,也就是显示缓冲区,当程序把要显示的字符编码值发送到显示缓冲区后,显示驱动程序主会把当前字符集映射到的符号定义,即字符编码是个数值,它会和字体定义的一个图像符号相映射,驱动程序读取到图形数据后最终以点阵的形式点亮显示器,这就是我们现在正在看到文字内容了。以“河源”两个简体字为例,它的GB18030编码值对应为0xD3BA、0xB4D4,而两个简体字的图形定义就和这个码值产生映射关系,用以下的点字图表示:
●○○○●●●●●●●● ●●○○●●●●●●●○
●●○○●●●●●●●● ●●●○●●●●●●●●
●●●○○○○○○○●● ○●●○●●○○●○○○
○●●○●●●●●○●● +----------+ ○○●○●○●●●●●○
○○○○●●●●●○●● <====| 0xD3BA | ●○○○●○●○○○●○
●●●○●●○●●○●● +----------+ ●●●○●○●●●●●○
○●●●●●●●●○●● +----------+ ○●●○●○●○○○●○
○○○●●●●●●○●● | 0xB4D4 |====> ○○●●●○●●●●●○
○○●●○○○○○○●● +----------+ ○●●○●○●○●○●○
○●●○○●●●○○●● ○●●○●○●●●○●○
●●●○○○○●●●●● ●●●●●○●●●○●○
●●●○○○○○●●●○ ●○○●○●○○●○○●
抱歉,我不能将点阵字的符号定义点得更形象一点,如果字符设置得对,这些小点会规矩得很有效果。事实上这就是内部的基本原理,这是12x12的点阵汉字,尽管精度不高,但也已经是200多个点了!当我们的程序通过 printf 这样函数把代表字符的编码值发送到缓冲区后,要怎样去显示就是系统的事了。如果系统支持,GB18030,那很好,“河源”就看得清清的,如果系统不支持这个字符编码方案,或都系统设置不对,那么这是很抱歉的事,让你看到不该看到的马赛克。这里还要注意的是,如果 printf 这样的函数不是把 0xD3BA 这样的值当字符编码值来处理,而是当数值来处理,那么这是真的极抱谦的啊!没有按原有的意图去处理,就只能得不到想要的汉字。另外还有一个比较隐蔽的问题,直接在代码文件中保存多字节字符时会受当前文件所使用的编码方案的影响,如“河源”两个字在UTF-8编码方案中,都变为三个字节 0xB3B2E6 0x90BAE6。所以UTF-8保存的代码编译后,如果用GB18030编码方案来显示,那么就会变成三个谁也不认得的字符“娌虫簮” ,这就是乱码的根源。而编译器使用的编码方案也会影响这些字符串,gcc就可以通过参数 -fexec-charset 来指定编码方案来编译程序。
像GB18030这样的字符集,每个字符的码值并不是占一个字节的,而是占两个字节,那么就叫做双字节字符集 DBCS(Double-byte charachter set),而像UTF-8这样的字符集,编码长度是可变的,ASCII字符编码为一个字符,汉字一般为3个字节,这种字符集就叫做多字节字符集 MBCS(Multi-byte character set)。在Win32命令控制台中,可以使用 chcp 来更改代码页,即Windows支持的字符集,1251 西里尔语,1250 中欧语言,950 繁体中文,65001为UTF-8,20936对应GB18030,然后在属性中选择中文字体就可以显示中文了:
chcp 65001
chcp 20936
在较新的C语言标准库还会有一个叫本地化的库,通过头文件 locale.h 引用,默认C语言程序开始时设置为 setlocale(LC_ALL,”C”),改变它会影响到一些类似如货币符号、日期格式等等的差异。可以使用 setlocale(LC_ALL,”“) 来读取当前系统的环境设置,内容类似这样:
Chinese (Simplified)_People's Republic of China.936
为了测试命令行运行程序时的字符集的支持情况,使用以下一小段测试代码:
#include
#include
char TIP_GBK[5] = {0xBA, 0xD3, 0xD4, 0xB4, 0x00}; //"河源";
char TIP_BIG[5] = {0xAA, 0x65, 0xB7, 0xBD, 0x00};
char TIP_UNILE[5] = {0xB3, 0x6C, 0x90, 0x6E, 0x00};
char TIP_UNIBE[5] = {0x6C, 0xB3, 0x6E, 0x90, 0x00};
char TIP_UTF[7] = {0xE6, 0xB2, 0xB3, 0xE6, 0xBA, 0x90, 0x00};
char *TIP_CHARSET =
"Test charset for 中文字符集:\nGBK: %s, BIG5: %s, UNI-LE: %s, UNI-BE: %s, UTF-8: %s\n";
int main()
{
printf(TIP_CHARSET, TIP_GBK, TIP_BIG, TIP_UNILE, TIP_UNIBE, TIP_UTF);
char *locale;
locale = setlocale(LC_ALL, "");
printf("locale %s\n", locale);
int c = getchar();
printf("bye 0x%x", c);
return 0;
}
编译运行,在控制台输出的内容类似如下第一行,就说明UTF-8环境是支持的,如果是第二行的样子就支持GBK中文字符集。要支持GBK,使用 chcp 将Windows的字符集设置为 20936 以支持中文编码方案,支持UTF-8则要设置代码页 65001:
Test charset for GBK: ��Դ ... UTF-8: 河源
Test charset for GBK: 河源 ... UTF-8: 娌虫?
而使用时mysql系统也要注意字符集的设置,涉及两处设置 character set 和 collation,前者是指定用来保存数据的编码方案,后者指定用来在运算比对时的编码方案。collation 的编码方案中可以看到有 ci/cs 这样的后缀,分别表示 case insensitive/case sensitive。客户端主要是通过 mysql_set_character_set 函数来修改传递过程使用的编码方案。可以查询字符集设置或,通过 outfile 导出数据以检查所属字符集:
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE 'character%';
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "collation%";
mysql> SHOW COLLATION;
mysql> SHOW CHARACTER SET;
mysql> SET character_set_client = utf8;
mysql> SET character_set_results = utf8;
mysql> SET character_set_connection = utf8;
mysql> select post_title from wp_posts into outfile "c:/mysql.txt";
数据库的配置都是按UTF-8设置的,而客户端使用的是gb2312来测试的,Windows系统代码页设置为20936,即GB18030字符集:
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE "character%";
+--------------------------+-----------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+--------------------------+-----------------------+
| character_set_client | utf8 |
| character_set_connection | utf8 |
| character_set_database | utf8 |
| character_set_filesystem | binary |
| character_set_results | utf8 |
| character_set_server | utf8 |
| character_set_system | utf8 |
+--------------------------+-----------------------+
以下是设置客户端编码方案的前后差别,以及设置使用的函数参数:
Charset=latin1_swedish_ci; collation=latin1; dir=(null)
Charset=gb2312_chinese_ci; collation=gb2312; dir=(null)
Charset=utf8_general_ci; collation=utf8; dir=(null)
mysql_set_character_set(&db, "utf8");
mysql_set_character_set(&db, "gb2312")
关于字符集编码问题可以参考《编程与编码》,准备好数据库后,就可以开始编程开发方面的工作了。
C版MySQL开发
首先,来了解一下MySQL的C语言API的工作流程。C语言是过程式编程,因此MySQL这套API也是由独立的函数构成的一个集合,定义了MYSQL、MYSQL_RES 和 MYSQL_ROW 等数据库对像,分别对应数据库链接、数据为库记录集,数据行。一个典型的客户端需要收集登录信息,含有目标主机地址、端口,登录名和密码。或一个目标数据库,这个可选项,链接后可以通过 SQL 语句来建立和管理数据库。
收集足够的登信息后,就可以通过 mysql_init 初始化一个 MYSQL 对象,即数据的链接对象,然后将登录信息传入链接建立函数 mysql_real_connect(),以连接数据库服务器。连接后可以先探测服务器的版本信息,还包括编码方案设置等等。在连接建立后,数据开始传输前,需要确定并设置好一个在传输数据过程中使用的编码方案,如本列中使用的gbk或utf8都可以。
初步建立与服务器的连接后就可以开始进行数据的查询了,可以用 mysql_query 函数来执行SQL语句,服务器收到命令后就会生成查询结果。客户端则要指定一个接收数据的方法,有两种,一种是一行行数据进行传输,即客户端需要一行数据就请求传输一行。第二种是一次性从服务器中传送全部查询到的数据到客户端,这样可以在充足的内存条件下优化客户端的运行速度。这两种方式分别通过 mysql_use_result 和 mysql_store_result 来实现,在读取数据行之前必须执行二者其中之一。这期间还可以通过其它函数来查询数据的总行数、查询数据的段数。
在使用数据的过程中通过 mysql_fetch_row 函数来获取数据记录,数据记录对象就是一个字符串数据,数组各个元素对应了记录的数据段,段数可以通过 mysql_field_count 函数查询得到。如果使用 store result 方式,则可以通过 mysql_num_rows 先行查询数据记录的总数,使用 use result 方式则要等到所有记录都读取后才有效。
最后,就贴代码的时间了,还有最重要的一点,不要释放记录集所占的内存,NEVER foget this free: mysql_free_result!
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define TIP_ERROR "ERROR(%s:%d) #%d %s\n"
#define TIP_ERROR_CONNECT "Connection error #%d!\n"
#define TIP_CONNECT_OK "Demo by Jimbowhy. Mysql %s has connected!\n"
#define TIP_TEST "MySQL database testing...\n"
#define TIP_DBINFO "Charset=%s; collation=%s; dir=%s\n"
#define TIP_RSINFO "%d data rows, %d field count\n"
#define SQL_TEST "SELECT ID,post_title FROM wp_posts;\n"
#define USER "root"
#define PASSWORD "password"
#define HOST "localhost"
#define PORT 3306
#define DATABASE "hyc_hr"
char TIP_GBK[5] = {0xBA, 0xD3, 0xD4, 0xB4, 0x00}; //"河源";
char TIP_UTF[7] = {0xE6, 0xB2, 0xB3, 0xE6, 0xBA, 0x90, 0x00};
char *TIP_CHARSET = "Test charset for GBK: %s, UTF-8: %s\n";
void query(MYSQL db, char *sql){
printf(TIP_TEST);
printf("SQL: %s", sql);
MYSQL_RES *rs;
MYSQL_ROW row;
unsigned long *len;
unsigned long fc, rc;
if(0!=mysql_query(&db,sql)){
printf("ERR %s\n", mysql_error(&db));
return;
}
//rs = mysql_use_result(&db);
rs = mysql_store_result(&db);
if(NULL==rs){
printf(TIP_ERROR,__FILE__, __LINE__, mysql_errno(&db),mysql_error(&db));
}
fc = mysql_field_count(&db);
rc = mysql_num_rows(rs);
printf(TIP_RSINFO, rc, fc);
int c = 1;
while ((row = mysql_fetch_row(rs)) != NULL && c>-1){
len = mysql_fetch_lengths(rs);
if(NULL==len){
printf(TIP_ERROR,__FILE__, __LINE__, mysql_errno(&db),mysql_error(&db));
}
printf("%s\t%s\n", row[0],row[1]);
c % 16 == 0 && getch() == 'x'? c=-1 : c++;
}
mysql_free_result(rs); /* NEVER forget this free */
}
int main()
{
printf(TIP_CHARSET, TIP_GBK, TIP_UTF);
MYSQL db;
mysql_init(&db);
MY_CHARSET_INFO dbi;
if(mysql_real_connect(&db,HOST,USER,PASSWORD,DATABASE,PORT,NULL,0)){
printf(TIP_CONNECT_OK, mysql_get_server_info(&db));
mysql_get_character_set_info(&db, &dbi);
printf(TIP_DBINFO, dbi.name, dbi.csname, dbi.dir);
mysql_set_character_set(&db, "utf8");
mysql_get_character_set_info(&db, &dbi);
printf(TIP_DBINFO, dbi.name, dbi.csname, dbi.dir);
query(db,SQL_TEST);
}else{
printf(TIP_ERROR_CONNECT, mysql_errno(&db));
printf(TIP_ERROR,__FILE__, __LINE__, mysql_errno(&db),mysql_error(&db));
//fprintf(stderr, "ERROR: %s\n", mysql_error(&db));
}
mysql_close(&db);
return 0;
}
GNU make 自动编译脚本文件 makefile:
#
# Demo MySQL with C++ by Jimbowy 2016/3/4 15:42:27
# GNU makefile demo
#
CC=g++
CFLAGS=-g
LFLAGS=-Wl,--enable-stdcall-fixup
ifdef REBUILD
endif
ifeq "$(BUILD)" "RELEASE"
LFLAGS:=-s $(LFLAGS)
CFLAGS:=
endif
#$(info $(LFLAGS))
INC:=-I"C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.1\include"
LIB:=-L"C:\Program Files (x86)\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.1\lib\opt"
LIBS:=-lmysql
all: main.exe codepage.exe
@echo off
main.exe: main.o
$(CC) $(LFLAGS) $(INC) $(LIB) -o main.exe $(LIBS) main.o
main.o:
$(CC) -c $(CFLAGS) -o main.o $(INC) main.cpp
codepage.exe:codepage.cpp
clear:
@del main.exe main.o codepage.exe codepage.o
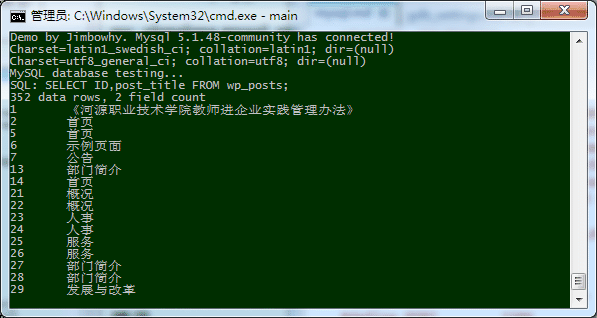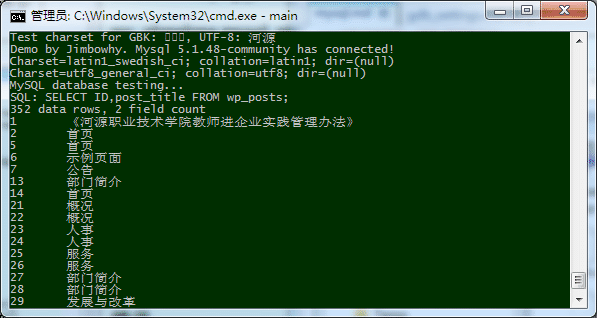
编译运行效果:
MySQL 5.1 支持编码方案
此表打印命令:mysql> SHOW CHARACTER SET;
+----------+-----------------------------+---------------------+--------+
| Charset | Description | Default collation | Maxlen |
+----------+-----------------------------+---------------------+--------+
| big5 | Big5 Traditional Chinese | big5_chinese_ci | 2 |
| dec8 | DEC West European | dec8_swedish_ci | 1 |
| cp850 | DOS West European | cp850_general_ci | 1 |
| hp8 | HP West European | hp8_english_ci | 1 |
| koi8r | KOI8-R Relcom Russian | koi8r_general_ci | 1 |
| latin1 | cp1252 West European | latin1_swedish_ci | 1 |
| latin2 | ISO 8859-2 Central European | latin2_general_ci | 1 |
| swe7 | 7bit Swedish | swe7_swedish_ci | 1 |
| ascii | US ASCII | ascii_general_ci | 1 |
| ujis | EUC-JP Japanese | ujis_japanese_ci | 3 |
| sjis | Shift-JIS Japanese | sjis_japanese_ci | 2 |
| hebrew | ISO 8859-8 Hebrew | hebrew_general_ci | 1 |
| tis620 | TIS620 Thai | tis620_thai_ci | 1 |
| euckr | EUC-KR Korean | euckr_korean_ci | 2 |
| koi8u | KOI8-U Ukrainian | koi8u_general_ci | 1 |
| gb2312 | GB2312 Simplified Chinese | gb2312_chinese_ci | 2 |
| greek | ISO 8859-7 Greek | greek_general_ci | 1 |
| cp1250 | Windows Central European | cp1250_general_ci | 1 |
| gbk | GBK Simplified Chinese | gbk_chinese_ci | 2 |
| latin5 | ISO 8859-9 Turkish | latin5_turkish_ci | 1 |
| armscii8 | ARMSCII-8 Armenian | armscii8_general_ci | 1 |
| utf8 | UTF-8 Unicode | utf8_general_ci | 3 |
| ucs2 | UCS-2 Unicode | ucs2_general_ci | 2 |
| cp866 | DOS Russian | cp866_general_ci | 1 |
| keybcs2 | DOS Kamenicky Czech-Slovak | keybcs2_general_ci | 1 |
| macce | Mac Central European | macce_general_ci | 1 |
| macroman | Mac West European | macroman_general_ci | 1 |
| cp852 | DOS Central European | cp852_general_ci | 1 |
| latin7 | ISO 8859-13 Baltic | latin7_general_ci | 1 |
| cp1251 | Windows Cyrillic | cp1251_general_ci | 1 |
| cp1256 | Windows Arabic | cp1256_general_ci | 1 |
| cp1257 | Windows Baltic | cp1257_general_ci | 1 |
| binary | Binary pseudo charset | binary | 1 |
| geostd8 | GEOSTD8 Georgian | geostd8_general_ci | 1 |
| cp932 | SJIS for Windows Japanese | cp932_japanese_ci | 2 |
| eucjpms | UJIS for Windows Japanese | eucjpms_japanese_ci | 3 |
+----------+-----------------------------+---------------------+--------+
C API 参考
Table 21.4 C API Function Names and Descriptions
Function Description
my_init() Initialize global variables, and thread handler in thread-safe programs
mysql_affected_rows() Returns the number of rows changed/deleted/inserted
mysql_autocommit() Toggles autocommit mode on/off
mysql_change_user() Changes user and database on an open connection
mysql_character_set_name() Return default character set name for current connection
mysql_close() Closes a server connection
mysql_commit() Commits the transaction
mysql_connect() Connects to a MySQL server (deprecated; use mysql_real_connect() instead)
mysql_create_db() Creates a database (deprecated; use the SQL statement CREATE DATABASE)
mysql_data_seek() Seeks to an arbitrary row number in a query result set
mysql_debug() Does a DBUG_PUSH with the given string
mysql_drop_db() Drops a database (deprecated; use the SQL statement DROP DATABASE)
mysql_dump_debug_info() Makes the server write debug information to the log
mysql_eof() Determines whether the last row of a result set has been read
(deprecated; mysql_errno() or mysql_error() may be used instead)
mysql_errno() Returns the error number for the most recently invoked MySQL function
mysql_error() Returns the error message for the most recently invoked MySQL function
mysql_escape_string() Escapes special characters in a string for use in an SQL statement
mysql_fetch_field() Returns the type of the next table field
mysql_fetch_field_direct() Returns the type of a table field, given a field number
mysql_fetch_fields() Returns an array of all field structures
mysql_fetch_lengths() Returns the lengths of all columns in the current row
mysql_fetch_row() Fetches the next row from the result set
mysql_field_count() Returns the number of result columns for the most recent statement
mysql_field_seek() Puts the column cursor on a specified column
mysql_field_tell() Returns the position of the field cursor used for the last mysql_fetch_field()
mysql_free_result() Frees memory used by a result set
mysql_get_character_set_info() Return information about default character set
mysql_get_client_info() Returns client version information as a string
mysql_get_client_version() Returns client version information as an integer
mysql_get_host_info() Returns a string describing the connection
mysql_get_proto_info() Returns the protocol version used by the connection
mysql_get_server_info() Returns the server version number
mysql_get_server_version() Returns version number of server as an integer
mysql_get_ssl_cipher() Return current SSL cipher
mysql_hex_string() Encode string in hexadecimal format
mysql_info() Returns information about the most recently executed query
mysql_init() Gets or initializes a MYSQL structure
mysql_insert_id() Returns the ID generated for an AUTO_INCREMENT column by the previous query
mysql_kill() Kills a given thread
mysql_library_end() Finalize the MySQL C API library
mysql_library_init() Initialize the MySQL C API library
mysql_list_dbs() Returns database names matching a simple regular expression
mysql_list_fields() Returns field names matching a simple regular expression
mysql_list_processes() Returns a list of the current server threads
mysql_list_tables() Returns table names matching a simple regular expression
mysql_more_results() Checks whether any more results exist
mysql_next_result() Returns/initiates the next result in multiple-result executions
mysql_num_fields() Returns the number of columns in a result set
mysql_num_rows() Returns the number of rows in a result set
mysql_options() Sets connect options for mysql_real_connect()
mysql_ping() Checks whether the connection to the server is working, reconnecting as necessary
mysql_query() Executes an SQL query specified as a null-terminated string
mysql_real_connect() Connects to a MySQL server
mysql_real_escape_string() Escapes special characters in a string for use in an SQL statement
mysql_real_query() Executes an SQL query specified as a counted string
mysql_refresh() Flush or reset tables and caches
mysql_reload() Tells the server to reload the grant tables
mysql_rollback() Rolls back the transaction
mysql_row_seek() Seeks to a row offset in a result set, using value returned from mysql_row_tell()
mysql_row_tell() Returns the row cursor position
mysql_select_db() Selects a database
mysql_server_end() Finalize the MySQL C API library
mysql_server_init() Initialize the MySQL C API library
mysql_set_character_set() Set default character set for current connection
mysql_set_local_infile_default() Set the LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE handler callbacks to their default values
mysql_set_local_infile_handler() Install application-specific LOAD DATA LOCAL INFILE handler callbacks
mysql_set_server_option() Sets an option for the connection (like multi-statements)
mysql_sqlstate() Returns the SQLSTATE error code for the last error
mysql_shutdown() Shuts down the database server
mysql_ssl_set() Prepare to establish SSL connection to server
mysql_stat() Returns the server status as a string
mysql_store_result() Retrieves a complete result set to the client
mysql_thread_end() Finalize thread handler
mysql_thread_id() Returns the current thread ID
mysql_thread_init() Initialize thread handler
mysql_thread_safe() Returns 1 if the clients are compiled as thread-safe
mysql_use_result() Initiates a row-by-row result set retrieval
mysql_warning_count() Returns the warning count for the previous SQL statement
资源参考
- 《编程与编码》 by Jimbowhy
- MySQL Connectors Download
- MySQL C API Function Overview
- Unicode in C and C++ - Cp.com
- Samuel P. Harbison, Guy L. Steele - C,A Reference Manual,5th Edition
- The Standard C library - P.J. Plauger
- MySQL 5.1 Reference Manual - SHOW Syntax