Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks
ICML 2017
Paper:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.03400.pdf
Code for the regression and supervised experiments:https://github.com/cbfinn/maml
Code for the RL experiments:https://github.com/cbfinn/maml_rl
Abstract:
我们提出一种 meta-learning 算法,该算法是模型无关的,适用于任何利用梯度下降的方法来训练的模型,并且适用于任何任务,包括:classification,regression,and reinforcement learning. meta-learning 的目标是在不同的任务上训练一个模型,使得该模型可以仅仅利用少量的数据,就可以解决新的任务。在我们的方法中,该模型的参数,是显示的进行训练的,这样的话,a small number of gradient steps with a small amount of training data from a new task will produce good generalization performance on that task. 效果上来说,我们的方法得到的模型更加容易进行微调。我们表明这种方法可以在两个 few-shot image classification benchmarks 得到顶尖的效果,并且加速了策略梯度强化学习算法。
Introduction:
如何快速的进行学习是最近机器学习领域的一个研究热点问题。我们人类可以根据已有的先验知识,就可以根据少量新的信息,快速的掌握一项新的技能。如,会写普通钢笔字的人,可能很快就会写毛笔字。但是这种快速且灵活的学习任务对于机器来说,确是非常困难的。因为:智能体必须将少量新的信息与其先验知识结合起来,与此同时,避免对于新的数据过拟合。此外,这种先验经历以及新的数据的格式将会依赖于 task。
本文提出一种 general 的并且与模型无关的 meta-learning algorithm,可以直接应用于任何基于策略梯度的方法中。我们集中于 deep neural network models, 但是我们的模型也可以通过微小的改变就很容易处理不同的结构,以及不同的问题设定,如分类,回归,策略梯度强化学习。在 meta-learning 中,所训练的模型的目标是:快速的从少量新的数据上学习一个新的任务,然后该模型通过 meta-learner 来训练,使得能够在大量不同的任务上进行学习。
本文方法的 key idea 是:train the model's initial parameters such that the model has maximal performance on a new task after the parameters have been updated through one or more gradient steps computed with a small amount of data from that new task. 与前人的工作不同,他们通常基于 learn an update function or learning rule, 我们的方法不会增加所需要学习参数的数量,也不会限制模型的框架,可以很容易与各种全连接,全卷积,或者循环神经网络。也可以与各种损失函数结合,如:可微分的监督损失函数,或者不可导的强化学习目标函数。
训练一个模型参数的过程,使得一些梯度步骤,甚至是单步梯度步骤,可以在一个新的任务上,产生较好的效果,可以看做是构建中间表达,广泛的适用于许多任务。如果该中间表达适应于许多任务,简单的微调该参数,可以产生较好的结果。实际上,我们的参数优化是非常简单,并且快速进行微调的,使得 adaptation 可以在合适的空间进行快速学习。从一个动态系统的角度,我们的学习过程可以看做是:maximizing the sensitivity of the loss functions of new tasks with respect to the parameters: 当敏感度高的时候,对参数进行较小的局部改变可以带来任务损失上大的改善。
该任务较大的贡献在于:a simple model-and task-agnostic algorithmm for meta-learning that trains a model's parameters such that a small number of gradient updates will lead to fast learning on a new task.
Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning:
1. Meta-Learning Problem Setup
Few-shot meta-learning 的目标是:学习一个模型,仅仅通过少量数据以及训练迭代次数,就使其能够快速适应于新的任务。
我们考虑一个模型,表示为 f,将观测数据 x 映射为 a。在 meta-learning 的过程中,该模型被训练使得能够适应于大量或者有限的任务。因为我们将会应用于不同的学习任务,从分类到强化学习,我们引入一个 generic 的学习任务。正式的说,每一个任务:
包含损失函数 L,基于初始观测的分布 q(x1),转移分布 q(xt+1|xt, at),以及 episode 长度 H。
在独立同分布的监督学习问题中,长度 H = 1.
在我们 meta-learning 场景下,我们考虑一个基于任务的分布。
2. A Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning Algorithm:
与前人的方法不同,我们提出一种方法,可以学习任何标准模型的参数,通过 meta-learning,使该模型可以准备好进行 fast adaptation。这个方法的直观原因是:some internal representations are more transferrable than others. 例如,一个神经网络可能学习到 internal features,广泛的应用于所有的任务,而不是 single individual task。那么,我们如何鼓励这种 general-purpose representations?我们采用了一种直观的方法来解决这一问题:由于这个model 将会用基于梯度的方法在一个 new task 上进行微调,所以,我们将会瞄准使得学习到 model 具有下面的性质,this gradient-based learning rule can make rapid progress on new tasks drawn from p(T),whithout overfitting. 在实际操作中,我们的目标是知道一组模型参数,在当前任务中对 changes 是敏感的,使得较小的参数改变,任何任务的损失函数都会得到大幅度的改善,当改变 loss 的梯度方向时,如图1 所示(we will aim to find model parameters that are sensitive to changes in the task, such that small changes iin the parameters will produce large improvements on the loss function of any task drawn from p(T), when altered in the direction of the gradient of that loss). 我们不对该模型的形式做任何假设。
正式的,我们考虑一个模型,$f_{\theta}$,其参数为 $\theta$。当适应一个新的任务时 Ti, 模型的参数变为 $\theta'$。在我们的方法中,更新后的参数 $\theta'$ 是用一次或者多次在任务 Ti 上进行梯度更新得到的。例如,当进行一次梯度更新时:
此处,step size $\alpha$ 可以被固定为超参数,或者 meta-learned。为了符号的简化,我们将会考虑 one gradient update,但是也可以很直接的进行多次梯度更新。
The model parameters are trained by optimizing for the performance of $f_\theta'$ with respect to $\theta$ across tasks sampled from p(T). 具体来说,the meta-objective 被定义为:
注意到,the meta-optimization 是通过 model parameters $\theta$ 来实现的,其中,模型被用新的模型参数 $\theta'$ 进行计算。实际上,我们提出的模型,目标是优化模型的参数,使得 one or a small number of gradient steps on a new task will produce maximally effective behavior on that task.
The meta-optimization 在不同任务之间被执行,是通过 SGD 进行的,使得模型的参数 $\theta$ 被通过如下的方式进行更新:
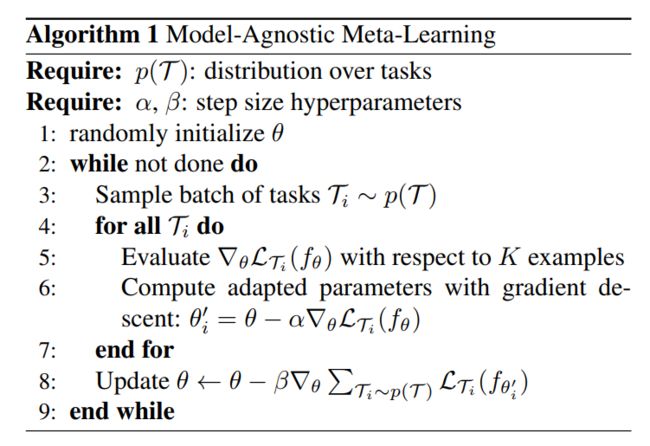
其中,$\beta$ 是 meta step size。整个算法,可以在 Algorithm 1 中找到。
The MAML meta-gradient update 涉及到 a gradient through a gradient. 计算上来说,这需要一个额外的反向传播,通过 f 来计算 Hessian-vector product, 这个很多深度学习框架都支持自动梯度计算,以及反向传播。
Species of MAML:
1. Supervised Regression and Classification:
Few-shot learning 是监督任务中被很好的研究了的课题,学习的目标就是从少量输入/输出对来学习一个新的函数,从相似的任务中利用先验知识进行 meta-learning。在 few-shot regression 中,学习的目标是: predict the outputs of a continuous-valued function from only a few datapoints sampled from that function, after training on many functions with similar statistical properties。
==