cartographer_ros_传感器数据篇
这篇主要介绍cartographer_ros中传感器数据是如何传递到cartographer中,特别是激光laserscan数据
文章目录
- cartographer_ros
- node_main.cc
- Node
- LoadState
- StartTrajectoryWithDefaultTopics
- AddTrajectory
- LaunchSubscribers
- HandleLaserScanMessage
- MapBuilderBridge
- SensorBridge
- ToPointCloudWithIntensities
- HandleLaserScan
- HandleRangefinder
- 总结
cartographer_ros
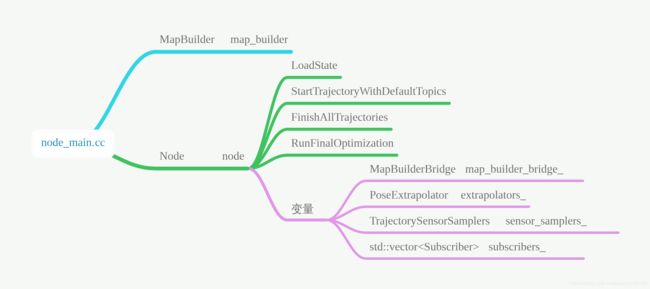
node_main.cc
node_main.cc的Run函数作为ros工程的主入口,主要定义了两个变量MapBuilder map_builder_和Node node;如下图所示, 其中map_builder_以参数的形式传递给node
Node node(node_options, std::move(map_builder), &tf_buffer);
Node

node_main中MapBuilder map_builder_被作为参数传递给了MapBuilderBridge map_builder_bridge_中用于调用其AddTrajectory. node主要的工作就是进行初始化和启动见图和最后收尾优化的工作
LoadState
void Node::LoadState(const std::string& state_filename, const bool load_frozen_state)
{
carto::common::MutexLocker lock(&mutex_);
map_builder_bridge_.LoadState(state_filename, load_frozen_state);
}
StartTrajectoryWithDefaultTopics
启动核心的AddTrajectory模块
void Node::StartTrajectoryWithDefaultTopics(const TrajectoryOptions& options)
{
carto::common::MutexLocker lock(&mutex_);
CHECK(ValidateTrajectoryOptions(options));
AddTrajectory(options, DefaultSensorTopics());
}
AddTrajectory
int Node::AddTrajectory(const TrajectoryOptions& options,
const cartographer_ros_msgs::SensorTopics& topics)
{
const std::set
expected_sensor_ids = ComputeExpectedSensorIds(options, topics);
const int trajectory_id = map_builder_bridge_.AddTrajectory(expected_sensor_ids, options);
AddExtrapolator(trajectory_id, options);
AddSensorSamplers(trajectory_id, options);
LaunchSubscribers(options, topics, trajectory_id);
is_active_trajectory_[trajectory_id] = true;
for (const auto& sensor_id : expected_sensor_ids)
{
subscribed_topics_.insert(sensor_id.id);
}
return trajectory_id;
}
其中 cartographer_ros_msgs::SensroTipics 有
string laser_scan_topic
string multi_echo_laser_scan_topic
string point_cloud2_topic
string imu_topic
string odometry_topic
string nav_sat_fix_topic
string landmark_topic
cartographer::mapping::TrajectoryBuilderInterface::SensorId主要由两个组成:
SensorType type 表示传感器数据类型:激光数据; IMU数据; 里程计数据; LandMark数据等
string id 表示topic
struct SensorId
{
enum class SensorType
{
RANGE = 0,
IMU,
ODOMETRY,
FIXED_FRAME_POSE,
LANDMARK,
LOCAL_SLAM_RESULT
};
SensorType type;
std::string id;
bool operator==(const SensorId& other) const
{
return std::forward_as_tuple(type, id) == std::forward_as_tuple(other.type, other.id);
}
bool operator<(const SensorId& other) const
{
return std::forward_as_tuple(type, id) < std::forward_as_tuple(other.type, other.id);
}
};
LaunchSubscribers

在ros端订阅相关的传感器数据, SubscribeWithHandler
// Subscribes to the 'topic' for 'trajectory_id' using the 'node_handle' and
// calls 'handler' on the 'node' to handle messages. Returns the subscriber.
template
::ros::Subscriber SubscribeWithHandler(void (Node::*handler)(int, const std::string&,const typename MessageType::ConstPtr&),/* handle function*/
const int trajectory_id, const std::string& topic,
::ros::NodeHandle* const node_handle,
Node* const node)
{
return node_handle->subscribe(topic, kInfiniteSubscriberQueueSize,
boost::function(
[node, handler, trajectory_id,
topic](const typename MessageType::ConstPtr& msg) {
(node->*handler)(trajectory_id, topic, msg);
}));
}
订阅话题并启动对应话题的回调处理函数
node_handle->subscribe(topic, kInfiniteSubscriberQueueSize, boost::function)
boost::function回调函数
boost::function
(
[node, handler, trajectory_id, topic]
(const typename MessageType::ConstPtr& msg) { (node->*handler)(trajectory_id, topic, msg)})
)
这里主要void (Node::*handler)(in t, const std::string& , const typename MessageType::ConstPtr& ) 主要就是对应
1 2 3
// The following functions handle adding sensor data to a trajectory.
void HandleOdometryMessage(int trajectory_id, const std::string& sensor_id, const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr& msg);
void HandleNavSatFixMessage(int trajectory_id, const std::string& sensor_id,const sensor_msgs::NavSatFix::ConstPtr& msg);
void HandleLandmarkMessage(int trajectory_id, const std::string& sensor_id,const cartographer_ros_msgs::LandmarkList::ConstPtr& msg);
void HandleImuMessage(int trajectory_id, const std::string& sensor_id, const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr& msg);
void HandleLaserScanMessage(int trajectory_id, const std::string& sensor_id, const sensor_msgs::LaserScan::ConstPtr& msg);
void HandleMultiEchoLaserScanMessage(int trajectory_id, const std::string& sensor_id,const sensor_msgs::MultiEchoLaserScan::ConstPtr& msg);
void HandlePointCloud2Message(int trajectory_id, const std::string& sensor_id, const sensor_msgs::PointCloud2::ConstPtr& msg);
HandleLaserScanMessage
处理LaserScan数据的方法,其他数据类似, 将数据通过map_builder_bridge_从ros端传递到cartographer中
void Node::HandleLaserScanMessage(const int trajectory_id,
const std::string& sensor_id,
const sensor_msgs::LaserScan::ConstPtr& msg)
{
carto::common::MutexLocker lock(&mutex_);
if (!sensor_samplers_.at(trajectory_id).rangefinder_sampler.Pulse())
{
return;
}
LOG(INFO)<<"Handle Laser Scan Message";
map_builder_bridge_.sensor_bridge(trajectory_id)->HandleLaserScanMessage(sensor_id, msg);
}
MapBuilderBridge
SensorBridge
传感器桥接模块,处理消息生成点云数据
void SensorBridge::HandleLaserScanMessage(const std::string& sensor_id, const sensor_msgs::LaserScan::ConstPtr& msg)
{
carto::sensor::PointCloudWithIntensities point_cloud;
carto::common::Time time;
std::tie(point_cloud, time) = ToPointCloudWithIntensities(*msg);
HandleLaserScan(sensor_id, time, msg->header.frame_id, point_cloud);
}
ToPointCloudWithIntensities
typedef std::vector PointCloud;
// Stores 3D positions of points with their relative measurement time in the
// fourth entry. Time is in seconds, increasing and relative to the moment when
// the last point was acquired. So, the fourth entry for the last point is 0.f.
// If timing is not available, all fourth entries are 0.f. For 2D points, the
// third entry is 0.f (and the fourth entry is time).
typedef std::vector TimedPointCloud;
struct PointCloudWithIntensities
{
TimedPointCloud points;
std::vector intensities;
};
HandleLaserScan
void SensorBridge::HandleLaserScan(const std::string& sensor_id,
const carto::common::Time time,
const std::string& frame_id,
const carto::sensor::PointCloudWithIntensities& points)
{
if (points.points.empty())
{
return;
}
CHECK_LE(points.points.back()[3], 0);
// TODO(gaschler): Use per-point time instead of subdivisions.
//divid into 10
for (int i = 0; i != num_subdivisions_per_laser_scan_; ++i)
{
const size_t start_index = points.points.size() * i / num_subdivisions_per_laser_scan_;
const size_t end_index = points.points.size() * (i + 1) / num_subdivisions_per_laser_scan_;
carto::sensor::TimedPointCloud subdivision(
points.points.begin() + start_index, points.points.begin() + end_index);
if (start_index == end_index)
{
continue;
}
const double time_to_subdivision_end = subdivision.back()[3];
// `subdivision_time` is the end of the measurement so sensor::Collator will
// send all other sensor data first.
const carto::common::Time subdivision_time = time + carto::common::FromSeconds(time_to_subdivision_end);
auto it = sensor_to_previous_subdivision_time_.find(sensor_id);
if (it != sensor_to_previous_subdivision_time_.end() && it->second >= subdivision_time)
{
LOG(WARNING) << "Ignored subdivision of a LaserScan message from sensor "
<< sensor_id << " because previous subdivision time "
<< it->second << " is not before current subdivision time "
<< subdivision_time;
continue;
}
sensor_to_previous_subdivision_time_[sensor_id] = subdivision_time;
for (Eigen::Vector4f& point : subdivision)
{
point[3] -= time_to_subdivision_end;
}
CHECK_EQ(subdivision.back()[3], 0);
HandleRangefinder(sensor_id, subdivision_time, frame_id, subdivision);
}
}
HandleRangefinder
void SensorBridge::HandleRangefinder(const std::string& sensor_id,
const carto::common::Time time,
const std::string& frame_id,
const carto::sensor::TimedPointCloud& ranges)
{
const auto sensor_to_tracking = tf_bridge_.LookupToTracking(time, CheckNoLeadingSlash(frame_id));
if (sensor_to_tracking != nullptr)
{
trajectory_builder_->AddSensorData(sensor_id,
carto::sensor::TimedPointCloudData{time,sensor_to_tracking->translation().cast(),
carto::sensor::TransformTimedPointCloud(ranges, sensor_to_tracking->cast())});
}
}
trajectory_builder 的定义为::cartographer::mapping::TrajectoryBuilderInterface从
map_builder_->GetTrajectoryBuilder(trajectory_id))中获得,
map_builder.cc中AddTrajectoryBuilder
trajectory_builders_.push_back(
common::make_unique(sensor_collator_.get(),
trajectory_id,
expected_sensor_ids,
CreateGlobalTrajectoryBuilder2D(std::move(local_trajectory_builder),
trajectory_id,
static_cast(pose_graph_.get()),
local_slam_result_callback)));
总结
Node中通过map_builder_bridge_进行操作主要功能AddTrajectory和 HandleLaserScanMessage