Android RelativeLayout(7.1) 源码解析
这节看一下RelativeLayout是如何实现的,它继承ViewGroup,下面主要分析它的
1、onMeasure
2、onLayout
Note:
1、onMeasure时,有三种测量模式:UNSPECIFIED、EXACTLY、AT_MOST
2、UNSPECIFIED 发生在创建的View没有明确layout_width和layout_height
3、EXACTLY发生在明确layout_width和layout_height具体大小,或者设置value为match_parent
4、AT_MOST发生在 layout_width和layout_height的value为wrap_content
5、下面定义 水平方向例外规则为:(LEFT_OF, RIGHT_OF, ALIGN_LEFT, ALIGN_RIGHT, START_OF, END_OF, ALIGN_START, ALIGN_END)
6、下面定义垂直方向的依赖关系为:(ABOVE,BELOW, ALIGN_BASELINE, ALIGN_TOP, ALIGN_BOTTOM)
下面是onMeasure的全部code
RelativeLayout.java
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
if (mDirtyHierarchy) {
mDirtyHierarchy = false;
sortChildren();
}
int myWidth = -1;
int myHeight = -1;
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
final int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// Record our dimensions if they are known;
if (widthMode != MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
myWidth = widthSize;
}
if (heightMode != MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
myHeight = heightSize;
}
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
width = myWidth;
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
height = myHeight;
}
View ignore = null;
int gravity = mGravity & Gravity.RELATIVE_HORIZONTAL_GRAVITY_MASK;
final boolean horizontalGravity = gravity != Gravity.START && gravity != 0;
gravity = mGravity & Gravity.VERTICAL_GRAVITY_MASK;
final boolean verticalGravity = gravity != Gravity.TOP && gravity != 0;
int left = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int top = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int right = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int bottom = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
boolean offsetHorizontalAxis = false;
boolean offsetVerticalAxis = false;
if ((horizontalGravity || verticalGravity) && mIgnoreGravity != View.NO_ID) {
ignore = findViewById(mIgnoreGravity);
}
final boolean isWrapContentWidth = widthMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
final boolean isWrapContentHeight = heightMode != MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
// We need to know our size for doing the correct computation of children positioning in RTL
// mode but there is no practical way to get it instead of running the code below.
// So, instead of running the code twice, we just set the width to a "default display width"
// before the computation and then, as a last pass, we will update their real position with
// an offset equals to "DEFAULT_WIDTH - width".
final int layoutDirection = getLayoutDirection();
if (isLayoutRtl() && myWidth == -1) {
myWidth = DEFAULT_WIDTH;
}
View[] views = mSortedHorizontalChildren;
int count = views.length;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int[] rules = params.getRules(layoutDirection);
applyHorizontalSizeRules(params, myWidth, rules);
measureChildHorizontal(child, params, myWidth, myHeight);
if (positionChildHorizontal(child, params, myWidth, isWrapContentWidth)) {
offsetHorizontalAxis = true;
}
}
}
views = mSortedVerticalChildren;
count = views.length;
final int targetSdkVersion = getContext().getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
applyVerticalSizeRules(params, myHeight, child.getBaseline());
measureChild(child, params, myWidth, myHeight);
if (positionChildVertical(child, params, myHeight, isWrapContentHeight)) {
offsetVerticalAxis = true;
}
if (isWrapContentWidth) {
if (isLayoutRtl()) {
if (targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
width = Math.max(width, myWidth - params.mLeft);
} else {
width = Math.max(width, myWidth - params.mLeft - params.leftMargin);
}
} else {
if (targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
width = Math.max(width, params.mRight);
} else {
width = Math.max(width, params.mRight + params.rightMargin);
}
}
}
if (isWrapContentHeight) {
if (targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
height = Math.max(height, params.mBottom);
} else {
height = Math.max(height, params.mBottom + params.bottomMargin);
}
}
if (child != ignore || verticalGravity) {
left = Math.min(left, params.mLeft - params.leftMargin);
top = Math.min(top, params.mTop - params.topMargin);
}
if (child != ignore || horizontalGravity) {
right = Math.max(right, params.mRight + params.rightMargin);
bottom = Math.max(bottom, params.mBottom + params.bottomMargin);
}
}
}
// Use the top-start-most laid out view as the baseline. RTL offsets are
// applied later, so we can use the left-most edge as the starting edge.
View baselineView = null;
LayoutParams baselineParams = null;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams childParams = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (baselineView == null || baselineParams == null
|| compareLayoutPosition(childParams, baselineParams) < 0) {
baselineView = child;
baselineParams = childParams;
}
}
}
mBaselineView = baselineView;
if (isWrapContentWidth) {
// Width already has left padding in it since it was calculated by looking at
// the right of each child view
width += mPaddingRight;
if (mLayoutParams != null && mLayoutParams.width >= 0) {
width = Math.max(width, mLayoutParams.width);
}
width = Math.max(width, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
width = resolveSize(width, widthMeasureSpec);
if (offsetHorizontalAxis) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int[] rules = params.getRules(layoutDirection);
if (rules[CENTER_IN_PARENT] != 0 || rules[CENTER_HORIZONTAL] != 0) {
centerHorizontal(child, params, width);
} else if (rules[ALIGN_PARENT_RIGHT] != 0) {
final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
params.mLeft = width - mPaddingRight - childWidth;
params.mRight = params.mLeft + childWidth;
}
}
}
}
}
if (isWrapContentHeight) {
// Height already has top padding in it since it was calculated by looking at
// the bottom of each child view
height += mPaddingBottom;
if (mLayoutParams != null && mLayoutParams.height >= 0) {
height = Math.max(height, mLayoutParams.height);
}
height = Math.max(height, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
height = resolveSize(height, heightMeasureSpec);
if (offsetVerticalAxis) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int[] rules = params.getRules(layoutDirection);
if (rules[CENTER_IN_PARENT] != 0 || rules[CENTER_VERTICAL] != 0) {
centerVertical(child, params, height);
} else if (rules[ALIGN_PARENT_BOTTOM] != 0) {
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
params.mTop = height - mPaddingBottom - childHeight;
params.mBottom = params.mTop + childHeight;
}
}
}
}
}
if (horizontalGravity || verticalGravity) {
final Rect selfBounds = mSelfBounds;
selfBounds.set(mPaddingLeft, mPaddingTop, width - mPaddingRight,
height - mPaddingBottom);
final Rect contentBounds = mContentBounds;
Gravity.apply(mGravity, right - left, bottom - top, selfBounds, contentBounds,
layoutDirection);
final int horizontalOffset = contentBounds.left - left;
final int verticalOffset = contentBounds.top - top;
if (horizontalOffset != 0 || verticalOffset != 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE && child != ignore) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (horizontalGravity) {
params.mLeft += horizontalOffset;
params.mRight += horizontalOffset;
}
if (verticalGravity) {
params.mTop += verticalOffset;
params.mBottom += verticalOffset;
}
}
}
}
}
if (isLayoutRtl()) {
final int offsetWidth = myWidth - width;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
params.mLeft -= offsetWidth;
params.mRight -= offsetWidth;
}
}
}
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);
}接下来,我们一点一点的分析上面的code
onMeasure
if (mDirtyHierarchy) {
mDirtyHierarchy = false;
sortChildren();
}
int myWidth = -1;
int myHeight = -1;
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
final int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
final int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
final int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// Record our dimensions if they are known;
if (widthMode != MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
myWidth = widthSize;
}
if (heightMode != MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) {
myHeight = heightSize;
}
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
width = myWidth;
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
height = myHeight;
}1、当view执行requestLayout时,mDirtyHierarchy会变为true,此时就会执行sortChildren()方法,该方法 主要是将RelativeLayout的sub child进行两种规则的排序,一种是按照水平依赖关系(LEFT_OF、RIGHT_OF,etc)进行排序用数组mSortedHorizontalChildren保存结果,另一种是按照垂直依赖关系(ABOVE、BELOW,etc)进行排序用数组mSortedVerticalChildren保存结果
2、MeasureSpec.getMode获得开始时的measure mode
3、MeasureSpec.getSize或则开始时的width 和height
final int layoutDirection = getLayoutDirection();这里我们默认的layoutDirection是LTR:水平方向从左往右排版,
而RTL正好相反,是从右向左排版,如下图
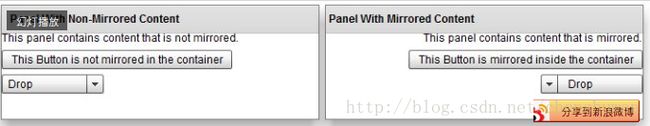
onMeasure
View[] views = mSortedHorizontalChildren;
int count = views.length;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int[] rules = params.getRules(layoutDirection);
applyHorizontalSizeRules(params, myWidth, rules);
measureChildHorizontal(child, params, myWidth, myHeight);
if (positionChildHorizontal(child, params, myWidth, isWrapContentWidth)) {
offsetHorizontalAxis = true;
}
}
}1、applyHorizontalSizeRules方法通过水平方向的依赖规则对params的right和left进行计算赋值
2、measureChildHorizontal 方法里面主要是调用child.mesuare方法
3、positionChildHorizontal 这个方法判断改child view是否设置在 parent view里面为水平居中
onMeasure
views = mSortedVerticalChildren;
count = views.length;
final int targetSdkVersion = getContext().getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
applyVerticalSizeRules(params, myHeight, child.getBaseline());
measureChild(child, params, myWidth, myHeight);
if (positionChildVertical(child, params, myHeight, isWrapContentHeight)) {
offsetVerticalAxis = true;
}
if (isWrapContentWidth) {
if (isLayoutRtl()) {
if (targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
width = Math.max(width, myWidth - params.mLeft);
} else {
width = Math.max(width, myWidth - params.mLeft - params.leftMargin);
}
} else {
if (targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
width = Math.max(width, params.mRight);
} else {
width = Math.max(width, params.mRight + params.rightMargin);
}
}
}
if (isWrapContentHeight) {
if (targetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT) {
height = Math.max(height, params.mBottom);
} else {
height = Math.max(height, params.mBottom + params.bottomMargin);
}
}
if (child != ignore || verticalGravity) {
left = Math.min(left, params.mLeft - params.leftMargin);
top = Math.min(top, params.mTop - params.topMargin);
}
if (child != ignore || horizontalGravity) {
right = Math.max(right, params.mRight + params.rightMargin);
bottom = Math.max(bottom, params.mBottom + params.bottomMargin);
}
}
}这里的code logic不做多少讲解
onMeasure
View baselineView = null;
LayoutParams baselineParams = null;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams childParams = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (baselineView == null || baselineParams == null
|| compareLayoutPosition(childParams, baselineParams) < 0) {
baselineView = child;
baselineParams = childParams;
}
}
}
mBaselineView = baselineView;这几行code是为了找出在最left和最top的 View,用mBaselineView保存符合条件的view
onMeasure
if (isWrapContentWidth) {
// Width already has left padding in it since it was calculated by looking at
// the right of each child view
width += mPaddingRight;
if (mLayoutParams != null && mLayoutParams.width >= 0) {
width = Math.max(width, mLayoutParams.width);
}
width = Math.max(width, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
width = resolveSize(width, widthMeasureSpec);
if (offsetHorizontalAxis) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int[] rules = params.getRules(layoutDirection);
if (rules[CENTER_IN_PARENT] != 0 || rules[CENTER_HORIZONTAL] != 0) {
centerHorizontal(child, params, width);
} else if (rules[ALIGN_PARENT_RIGHT] != 0) {
final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
params.mLeft = width - mPaddingRight - childWidth;
params.mRight = params.mLeft + childWidth;
}
}
}
}
}这里code很简单,centerHorizontal 这个方法是设置params的left和right的值
onMeasure
if (isWrapContentHeight) {
// Height already has top padding in it since it was calculated by looking at
// the bottom of each child view
height += mPaddingBottom;
if (mLayoutParams != null && mLayoutParams.height >= 0) {
height = Math.max(height, mLayoutParams.height);
}
height = Math.max(height, getSuggestedMinimumHeight());
height = resolveSize(height, heightMeasureSpec);
if (offsetVerticalAxis) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int[] rules = params.getRules(layoutDirection);
if (rules[CENTER_IN_PARENT] != 0 || rules[CENTER_VERTICAL] != 0) {
centerVertical(child, params, height);
} else if (rules[ALIGN_PARENT_BOTTOM] != 0) {
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
params.mTop = height - mPaddingBottom - childHeight;
params.mBottom = params.mTop + childHeight;
}
}
}
}
}这里的code不做多少解析,继续往下看
onMeasure
if (horizontalGravity || verticalGravity) {
final Rect selfBounds = mSelfBounds;
selfBounds.set(mPaddingLeft, mPaddingTop, width - mPaddingRight,
height - mPaddingBottom);
final Rect contentBounds = mContentBounds;
Gravity.apply(mGravity, right - left, bottom - top, selfBounds, contentBounds,
layoutDirection);
final int horizontalOffset = contentBounds.left - left;
final int verticalOffset = contentBounds.top - top;
if (horizontalOffset != 0 || verticalOffset != 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = views[i];
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE && child != ignore) {
final LayoutParams params = (LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
if (horizontalGravity) {
params.mLeft += horizontalOffset;
params.mRight += horizontalOffset;
}
if (verticalGravity) {
params.mTop += verticalOffset;
params.mBottom += verticalOffset;
}
}
}
}
}
这里code主要功能还是对设置在parent view中水平居中或者垂直居中的处理
onMeasure
setMeasuredDimension(width, height);最后一行 设置RelativeLayout本身测量的width和height
以上是onMeasure的大概执行过程,下面我们看一下onMeasure里面调用的几个method
onMeasure -> sortChildren
private void sortChildren() {
final int count = getChildCount();
if (mSortedVerticalChildren == null || mSortedVerticalChildren.length != count) {
mSortedVerticalChildren = new View[count];
}
if (mSortedHorizontalChildren == null || mSortedHorizontalChildren.length != count) {
mSortedHorizontalChildren = new View[count];
}
final DependencyGraph graph = mGraph;
graph.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
graph.add(getChildAt(i));
}
graph.getSortedViews(mSortedVerticalChildren, RULES_VERTICAL);
graph.getSortedViews(mSortedHorizontalChildren, RULES_HORIZONTAL);
}code很简单,我们看一下graph.getSortedViews方法
void getSortedViews(View[] sorted, int... rules) {
final ArrayDeque roots = findRoots(rules);
int index = 0;
Node node;
while ((node = roots.pollLast()) != null) {
final View view = node.view;
final int key = view.getId();
sorted[index++] = view;
final ArrayMap dependents = node.dependents;
final int count = dependents.size();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final Node dependent = dependents.keyAt(i);
final SparseArray dependencies = dependent.dependencies;
dependencies.remove(key);
if (dependencies.size() == 0) {
roots.add(dependent);
}
}
}
if (index < sorted.length) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Circular dependencies cannot exist"
+ " in RelativeLayout");
}
} 1、这里面一开始调用了findRoots方法,该方法是找出所有完全不依赖其它view的RelativeLayout的child view
2、这里用到一个类Note,其中Node.dependents保存的是布局上其它所有依赖此Node的view信息,Node.dependencies保存的是此Node布局上所依赖的所有的View信息
onMeasure -> applyHorizontalSizeRules
private void applyHorizontalSizeRules(LayoutParams childParams, int myWidth, int[] rules) {
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams anchorParams;
childParams.mLeft = VALUE_NOT_SET;
childParams.mRight = VALUE_NOT_SET;
anchorParams = getRelatedViewParams(rules, LEFT_OF);
if (anchorParams != null) {
childParams.mRight = anchorParams.mLeft - (anchorParams.leftMargin +
childParams.rightMargin);
} else if (childParams.alignWithParent && rules[LEFT_OF] != 0) {
if (myWidth >= 0) {
childParams.mRight = myWidth - mPaddingRight - childParams.rightMargin;
}
}
anchorParams = getRelatedViewParams(rules, RIGHT_OF);
if (anchorParams != null) {
childParams.mLeft = anchorParams.mRight + (anchorParams.rightMargin +
childParams.leftMargin);
} else if (childParams.alignWithParent && rules[RIGHT_OF] != 0) {
childParams.mLeft = mPaddingLeft + childParams.leftMargin;
}
anchorParams = getRelatedViewParams(rules, ALIGN_LEFT);
if (anchorParams != null) {
childParams.mLeft = anchorParams.mLeft + childParams.leftMargin;
} else if (childParams.alignWithParent && rules[ALIGN_LEFT] != 0) {
childParams.mLeft = mPaddingLeft + childParams.leftMargin;
}
anchorParams = getRelatedViewParams(rules, ALIGN_RIGHT);
if (anchorParams != null) {
childParams.mRight = anchorParams.mRight - childParams.rightMargin;
} else if (childParams.alignWithParent && rules[ALIGN_RIGHT] != 0) {
if (myWidth >= 0) {
childParams.mRight = myWidth - mPaddingRight - childParams.rightMargin;
}
}
if (0 != rules[ALIGN_PARENT_LEFT]) {
childParams.mLeft = mPaddingLeft + childParams.leftMargin;
}
if (0 != rules[ALIGN_PARENT_RIGHT]) {
if (myWidth >= 0) {
childParams.mRight = myWidth - mPaddingRight - childParams.rightMargin;
}
}
}该方法根据水平方向的依赖规则去计算view params的right和left的值
在onMeasure其它的一些方法例如measureChildHorizontal、positionChildHorizontal等这样的Method都是一些logic的处理,感兴趣的可以自己查看一下source code
下面我们看一下onLayout的具体实现:
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// The layout has actually already been performed and the positions
// cached. Apply the cached values to the children.
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
RelativeLayout.LayoutParams st =
(RelativeLayout.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
child.layout(st.mLeft, st.mTop, st.mRight, st.mBottom);
}
}
}从code上来看,onLayout的实现很简单,原因是onMeasure里面已经处理好了每一个view的left 、top、right、bottom的值,所以这里只需要简单遍历所有的view并执行child.layout就ok了
summary:
RelativeLayout利用位置上相对依赖的关系,计算出每一个view的上下左右的值,我们可以从读code中来学习 编写自定义控件的ideal