吴恩达作业11:残差网络实现手势数字的识别(基于 keras)+tensorbord显示loss值和acc值
一,残差网络实现手写数字识别
数据集地址:https://download.csdn.net/download/fanzonghao/10551018
首先来resnets_utils.py,里面有手势数字的数据集载入函数和随机产生mini-batch的函数,代码如下:
import os
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
import h5py
import math
def load_dataset():
train_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/train_signs.h5', "r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_x"][:]) # your train set features
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # your train set labels
# print(train_set_x_orig.shape)
# print(train_set_y_orig.shape)
test_dataset = h5py.File('datasets/test_signs.h5', "r")
test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) # your test set features
test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) # your test set labels
# print(test_set_x_orig.shape)
# print(test_set_y_orig.shape)
classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # the list of classes
train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape((1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes
#load_dataset()
def random_mini_batches(X, Y, mini_batch_size = 64, seed = 0):
"""
Creates a list of random minibatches from (X, Y)
Arguments:
X -- input data, of shape (input size, number of examples) (m, Hi, Wi, Ci)
Y -- true "label" vector (containing 0 if cat, 1 if non-cat), of shape (1, number of examples) (m, n_y)
mini_batch_size - size of the mini-batches, integer
seed -- this is only for the purpose of grading, so that you're "random minibatches are the same as ours.
Returns:
mini_batches -- list of synchronous (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
"""
m = X.shape[0] # number of training examples
mini_batches = []
np.random.seed(seed)
# Step 1: Shuffle (X, Y)
permutation = list(np.random.permutation(m))
shuffled_X = X[permutation,:,:,:]
shuffled_Y = Y[permutation,:]
# Step 2: Partition (shuffled_X, shuffled_Y). Minus the end case.
num_complete_minibatches = math.floor(m/mini_batch_size) # number of mini batches of size mini_batch_size in your partitionning
for k in range(0, num_complete_minibatches):
mini_batch_X = shuffled_X[k * mini_batch_size : k * mini_batch_size + mini_batch_size,:,:,:]
mini_batch_Y = shuffled_Y[k * mini_batch_size : k * mini_batch_size + mini_batch_size,:]
mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
mini_batches.append(mini_batch)
# Handling the end case (last mini-batch < mini_batch_size)
if m % mini_batch_size != 0:
mini_batch_X = shuffled_X[num_complete_minibatches * mini_batch_size : m,:,:,:]
mini_batch_Y = shuffled_Y[num_complete_minibatches * mini_batch_size : m,:]
mini_batch = (mini_batch_X, mini_batch_Y)
mini_batches.append(mini_batch)
return mini_batches
def convert_to_one_hot(Y, C):
Y = np.eye(C)[Y.reshape(-1)].T
return Y
def forward_propagation_for_predict(X, parameters):
"""
Implements the forward propagation for the model: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SOFTMAX
Arguments:
X -- input dataset placeholder, of shape (input size, number of examples)
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters "W1", "b1", "W2", "b2", "W3", "b3"
the shapes are given in initialize_parameters
Returns:
Z3 -- the output of the last LINEAR unit
"""
# Retrieve the parameters from the dictionary "parameters"
W1 = parameters['W1']
b1 = parameters['b1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
b2 = parameters['b2']
W3 = parameters['W3']
b3 = parameters['b3']
# Numpy Equivalents:
Z1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W1, X), b1) # Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
A1 = tf.nn.relu(Z1) # A1 = relu(Z1)
Z2 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W2, A1), b2) # Z2 = np.dot(W2, a1) + b2
A2 = tf.nn.relu(Z2) # A2 = relu(Z2)
Z3 = tf.add(tf.matmul(W3, A2), b3) # Z3 = np.dot(W3,Z2) + b3
return Z3
def predict(X, parameters):
W1 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["W1"])
b1 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["b1"])
W2 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["W2"])
b2 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["b2"])
W3 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["W3"])
b3 = tf.convert_to_tensor(parameters["b3"])
params = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2,
"W3": W3,
"b3": b3}
x = tf.placeholder("float", [12288, 1])
z3 = forward_propagation_for_predict(x, params)
p = tf.argmax(z3)
sess = tf.Session()
prediction = sess.run(p, feed_dict = {x: X})
return prediction测试数据集,代码如下:
import resnets_utils
import cv2
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y, classes=resnets_utils.load_dataset()
print('训练样本={}'.format(train_x.shape))
print('训练样本标签={}'.format(train_y.shape))
print('测试样本={}'.format(test_x.shape))
print('测试样本标签={}'.format(test_y.shape))
print('第五个样本={}'.format(train_y[0,5]))
cv2.imshow('1.jpg',train_x[5,:,:,:]/255)
cv2.waitKey()打印结果:可看出训练样本有1080个,size为(64,64,3),测试样本有120个,手势四是用4代替。
先测试第一个残差学习单元,模型如下:
代码如下:
from keras.layers import Dense,Flatten,Input,Activation,ZeroPadding2D,AveragePooling2D,BatchNormalization,Conv2D,Add,MaxPooling2D
from keras.models import Model
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
import resnets_utils
import keras.backend as K
import numpy as np
from keras.initializers import glorot_uniform
import tensorflow as tf
def identity_block(X,f,filters,stage,block):
conv_name_base='res'+str(stage)+block+'_branch'
bn_name_base='bn'+str(stage)+block+'_branch'
F1,F2,F3=filters
X_shortcut=X
print('输入尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#first conv
X=Conv2D(filters=F1,kernel_size=(1,1),strides=(1,1),padding='valid',name=conv_name_base+'2a',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X=BatchNormalization(axis=3,name=bn_name_base+'2a')(X)
X=Activation('relu')(X)
#second conv
X = Conv2D(filters=F2, kernel_size=(f, f), strides=(1, 1), padding='same', name=conv_name_base + '2b',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '2b')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
#third conv
X = Conv2D(filters=F3, kernel_size=(1, 1), strides=(1, 1), padding='valid', name=conv_name_base + '2c',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '2c')(X)
print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#ResNet
X=Add()([X,X_shortcut])
X = Activation('relu')(X)
print('最终输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
return X
def test_identity_block():
with tf.Session() as sess:
np.random.seed(1)
A_prev=tf.placeholder('float',[3,4,4,6])
X=np.random.randn(3,4,4,6)
A=identity_block(A_prev,f=2,filters=[2,4,6],stage=1,block='a')
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
out=sess.run([A],feed_dict={A_prev:X,K.learning_phase():0})
if __name__=='__main__':
test_identity_block()打印结果:由此可见经过三层卷积,该残差单元的输出size和维度不变,因为原始输入未进行卷积,故只能这样才能进行特征融合。
下面是输出维度会发生变化的,对原始输入X做了卷积变换再融合输出得到最终的输出,模型如下
代码如下:
from keras.layers import Dense,Flatten,Input,Activation,ZeroPadding2D,AveragePooling2D,BatchNormalization,Conv2D,Add,MaxPooling2D
from keras.models import Model
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
import resnets_utils
import keras.backend as K
import numpy as np
from keras.initializers import glorot_uniform
import tensorflow as tf
def convolutional_block(X,f,filters,stage,block,s=2):
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
F1, F2, F3 = filters
X_shortcut = X
print('输入尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
# first conv
X = Conv2D(filters=F1, kernel_size=(1, 1), strides=(s, s), padding='valid', name=conv_name_base + '2a',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '2a')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
# second conv
X = Conv2D(filters=F2, kernel_size=(f, f), strides=(1, 1), padding='same', name=conv_name_base + '2b',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '2b')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#third conv
X = Conv2D(filters=8, kernel_size=(1, 1), strides=(1, 1), padding='valid', name=conv_name_base + '2c',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '2c')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#ResNet
X_shortcut=Conv2D(filters=8, kernel_size=(1, 1), strides=(s, s), padding='valid', name=conv_name_base + '1',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X_shortcut)
X_shortcut = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '1')(X_shortcut)
print('原始输入X经过变化的输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X = Add()([X, X_shortcut])
X = Activation('relu')(X)
print('最终输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
return X
def test_convolutional_block():
#tf.reset_default_graph()
with tf.Session() as sess:
np.random.seed(1)
A_prev=tf.placeholder('float',[3,4,4,6])
X=np.random.randn(3,4,4,6)
A=convolutional_block(A_prev,f=2,filters=[2,4,6],stage=1,block='a',s=2)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
out=sess.run(A,feed_dict={A_prev:X})
if __name__=='__main__':
#test_identity_block()
test_convolutional_block()打印结果:可看出原始输入改变size为(3,2,2,8)最终融合的输出也是(3,2,2,8),故此种残差单元能够解决输出尺寸和维度的问题。
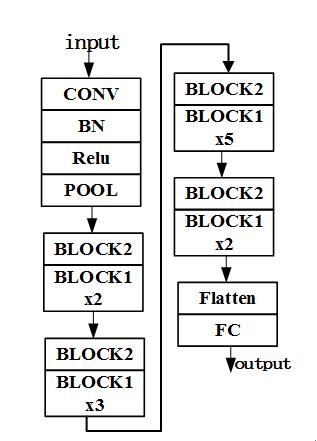
总体模型:其中BLOCK2值得是输出尺度和维度会变化的,BLOCK1指的是不会变化的。
下面用开始调用数据集:其中convolutional_block表示输出尺寸和维度会变化,identity_block表示输出与输入一样,模型如下,
代码如下:
from keras.layers import Dense,Flatten,Input,Activation,ZeroPadding2D,AveragePooling2D,BatchNormalization,Conv2D,Add,MaxPooling2D
from keras.models import Model
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
import resnets_utils
import keras.backend as K
import numpy as np
from keras.initializers import glorot_uniform
import tensorflow as tf
import time
"""
获取数据 并将标签转换成one-hot
"""
def convert_data():
train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes=resnets_utils.load_dataset()
train_x=train_set_x_orig/255
test_x = test_set_x_orig / 255
train_y=resnets_utils.convert_to_one_hot(train_set_y_orig,6).T
test_y = resnets_utils.convert_to_one_hot(test_set_y_orig, 6).T
#print(train_y.shape)
return train_x,train_y,test_x,test_y
"""
三层卷积的 残差单元 输出尺寸和维度不会变化
"""
def identity_block(X,f,filters,stage,block):
conv_name_base='res'+str(stage)+block+'_branch'
bn_name_base='bn'+str(stage)+block+'_branch'
F1,F2,F3=filters
X_shortcut=X
# print('输入尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#first conv
X=Conv2D(filters=F1,kernel_size=(1,1),strides=(1,1),padding='valid',name=conv_name_base+'2a',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
# print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X=BatchNormalization(axis=3,name=bn_name_base+'2a')(X)
X=Activation('relu')(X)
#second conv
X = Conv2D(filters=F2, kernel_size=(f, f), strides=(1, 1), padding='same', name=conv_name_base + '2b',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
# print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '2b')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
#third conv
X = Conv2D(filters=F3, kernel_size=(1, 1), strides=(1, 1), padding='valid', name=conv_name_base + '2c',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '2c')(X)
# print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#ResNet
X=Add()([X,X_shortcut])
X = Activation('relu')(X)
# print('最终输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
return X
"""
三层卷积的 残差单元 输出尺寸和维度会变化
"""
def convolutional_block(X,f,filters,stage,block,s=2):
conv_name_base = 'res' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
bn_name_base = 'bn' + str(stage) + block + '_branch'
F1, F2, F3 = filters
X_shortcut = X
# print('输入尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
# first conv
X = Conv2D(filters=F1, kernel_size=(1, 1), strides=(s, s), padding='valid', name=conv_name_base + '2a',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '2a')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
# print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
# second conv
X = Conv2D(filters=F2, kernel_size=(f, f), strides=(1, 1), padding='same', name=conv_name_base + '2b',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '2b')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
# print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#third conv
X = Conv2D(filters=F3, kernel_size=(1, 1), strides=(1, 1), padding='valid', name=conv_name_base + '2c',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
X = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '2c')(X)
X = Activation('relu')(X)
# print('输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#ResNet
X_shortcut=Conv2D(filters=F3, kernel_size=(1, 1), strides=(s, s), padding='valid', name=conv_name_base + '1',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X_shortcut)
X_shortcut = BatchNormalization(axis=3, name=bn_name_base + '1')(X_shortcut)
# print('原始输入X经过变化的输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X = Add()([X, X_shortcut])
X = Activation('relu')(X)
# print('最终输出尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
return X
"""
50层残差网络
"""
def ResNet50(input_shape=(64,64,3),classes=6):
X_input=Input(input_shape)
print('输入尺寸={}'.format(X_input.shape))
X=ZeroPadding2D((3,3))(X_input)
print('补完零尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#Stage 1
X=Conv2D(filters=64,kernel_size=(7,7),strides=(2,2),name='conv1',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
print('第一次卷积尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X=BatchNormalization(axis=3,name='bn_conv1')(X)
X=Activation('relu')(X)
X=MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(3,3),strides=(2,2))(X)
print('第一次池化尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#Stage 2
X=convolutional_block(X,f=3,filters=[64,64,256],stage=2,block='a',s=1)
print('第一次convolutional_block尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='b')
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[64, 64, 256], stage=2, block='c')
print('两次identity_block尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#Stage 3
X = convolutional_block(X, f=3, filters=[128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='a', s=2)
print('第二次convolutional_block尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='b')
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='c')
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[128, 128, 512], stage=3, block='d')
print('三次identity_block尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#Stage 4
X = convolutional_block(X, f=3, filters=[256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='a', s=2)
print('第三次convolutional_block尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='b')
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='c')
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='d')
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='e')
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[256, 256, 1024], stage=4, block='f')
print('五次identity_block尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#Stage 5
X = convolutional_block(X, f=3, filters=[512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='a', s=2)
print('第四次convolutional_block尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='b')
X = identity_block(X, f=3, filters=[512, 512, 2048], stage=5, block='c')
print('两次identity_block尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#Pool
X=AveragePooling2D(pool_size=(2,2))(X)
print('最后一次平均池化尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
#OutPut Flatten+FULLYCONNECTED
X=Flatten()(X)
X=Dense(units=classes,activation='softmax',name='fc'+str(classes),kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X)
#create model
model=Model(inputs=X_input,outputs=X,name='ResNet50')
return model
def test_identity_block():
with tf.Session() as sess:
np.random.seed(1)
A_prev=tf.placeholder('float',[3,4,4,6])
X=np.random.randn(3,4,4,6)
A=identity_block(A_prev,f=2,filters=[2,4,6],stage=1,block='a')
init=tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
out=sess.run([A],feed_dict={A_prev:X,K.learning_phase():0})
# print('out=',out[0][1][1][0])
def test_convolutional_block():
#tf.reset_default_graph()
with tf.Session() as sess:
np.random.seed(1)
A_prev=tf.placeholder('float',[3,4,4,6])
X=np.random.randn(3,4,4,6)
A=convolutional_block(A_prev,f=2,filters=[2,4,6],stage=1,block='a',s=2)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
out=sess.run(A,feed_dict={A_prev:X})
print('out=',out[0][0][0])
def test_ResNet50():
#定义好模型结构
Resnet50_model=ResNet50(input_shape=(64,64,3),classes=6)
#选定训练参数
Resnet50_model.compile(optimizer='adam',loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['accuracy'])
#获取训练集和测试集
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y=convert_data()
#训练集上训练
start_time=time.time()
print('============开始训练===============')
Resnet50_model.fit(x=train_x,y=train_y,batch_size=32,epochs=2)
end_time=time.time()
print('train_time={}'.format(end_time-start_time))
#测试集上测试
preds=Resnet50_model.evaluate(x=test_x,y=test_y,batch_size=32,)
print('loss={}'.format(preds[0]))
print('Test Accuracy={}'.format(preds[1]))
if __name__=='__main__':
#test_identity_block()
#test_convolutional_block()
#convert_data()
test_ResNet50()
其中问号代表的是样本数,可看出最终卷积输出是1×1×2048
训练样本为1080个,第一个Epoch每个样本时间为175ms,所以共189s.第一次epoch训练精度为0.27。
第二个Epoch每个样本时间为165ms,所以共178s.训练两次epoch时间为376S,不等于两次epoch时间之和,应该是有别的开支。第二次epoch训练精度为0.40提高了。
经过两次epoch的模型来测试120个样本,测试精度为0.19,恩很低,所以还要多训练嘛。
二,tensorboard显示
首先安装graphviz用于可视化网络
apt-get install graphviz
pip install graphviz
pip install pydot
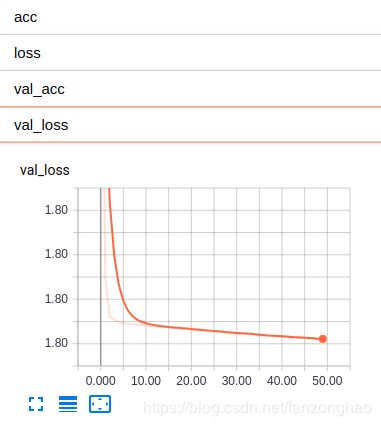
可视化网络如下:
调节学习率的clr_callback.py文件:
from keras.callbacks import *
class CyclicLR(Callback):
"""This callback implements a cyclical learning rate policy (CLR).
The method cycles the learning rate between two boundaries with
some constant frequency, as detailed in this paper (https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.01186).
The amplitude of the cycle can be scaled on a per-iteration or
per-cycle basis.
This class has three built-in policies, as put forth in the paper.
"triangular":
A basic triangular cycle w/ no amplitude scaling.
"triangular2":
A basic triangular cycle that scales initial amplitude by half each cycle.
"exp_range":
A cycle that scales initial amplitude by gamma**(cycle iterations) at each
cycle iteration.
For more detail, please see paper.
# Example
```python
clr = CyclicLR(base_lr=0.001, max_lr=0.006,
step_size=2000., mode='triangular')
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, callbacks=[clr])
```
Class also supports custom scaling functions:
```python
clr_fn = lambda x: 0.5*(1+np.sin(x*np.pi/2.))
clr = CyclicLR(base_lr=0.001, max_lr=0.006,
step_size=2000., scale_fn=clr_fn,
scale_mode='cycle')
model.fit(X_train, Y_train, callbacks=[clr])
```
# Arguments
base_lr: initial learning rate which is the
lower boundary in the cycle.
max_lr: upper boundary in the cycle. Functionally,
it defines the cycle amplitude (max_lr - base_lr).
The lr at any cycle is the sum of base_lr
and some scaling of the amplitude; therefore
max_lr may not actually be reached depending on
scaling function.
step_size: number of training iterations per
half cycle. Authors suggest setting step_size
2-8 x training iterations in epoch.
mode: one of {triangular, triangular2, exp_range}.
Default 'triangular'.
Values correspond to policies detailed above.
If scale_fn is not None, this argument is ignored.
gamma: constant in 'exp_range' scaling function:
gamma**(cycle iterations)
scale_fn: Custom scaling policy defined by a single
argument lambda function, where
0 <= scale_fn(x) <= 1 for all x >= 0.
mode paramater is ignored
scale_mode: {'cycle', 'iterations'}.
Defines whether scale_fn is evaluated on
cycle number or cycle iterations (training
iterations since start of cycle). Default is 'cycle'.
"""
def __init__(self, base_lr=0.001, max_lr=0.006, step_size=2000., mode='triangular',
gamma=1., scale_fn=None, scale_mode='cycle'):
super(CyclicLR, self).__init__()
self.base_lr = base_lr
self.max_lr = max_lr
self.step_size = step_size
self.mode = mode
self.gamma = gamma
if scale_fn == None:
if self.mode == 'triangular':
self.scale_fn = lambda x: 1.
self.scale_mode = 'cycle'
elif self.mode == 'triangular2':
self.scale_fn = lambda x: 1 / (2. ** (x - 1))
self.scale_mode = 'cycle'
elif self.mode == 'exp_range':
self.scale_fn = lambda x: gamma ** (x)
self.scale_mode = 'iterations'
else:
self.scale_fn = scale_fn
self.scale_mode = scale_mode
self.clr_iterations = 0.
self.trn_iterations = 0.
self.history = {}
self._reset()
def _reset(self, new_base_lr=None, new_max_lr=None,
new_step_size=None):
"""Resets cycle iterations.
Optional boundary/step size adjustment.
"""
if new_base_lr != None:
self.base_lr = new_base_lr
if new_max_lr != None:
self.max_lr = new_max_lr
if new_step_size != None:
self.step_size = new_step_size
self.clr_iterations = 0.
def clr(self):
cycle = np.floor(1 + self.clr_iterations / (2 * self.step_size))
x = np.abs(self.clr_iterations / self.step_size - 2 * cycle + 1)
if self.scale_mode == 'cycle':
return self.base_lr + (self.max_lr - self.base_lr) * np.maximum(0, (1 - x)) * self.scale_fn(cycle)
else:
return self.base_lr + (self.max_lr - self.base_lr) * np.maximum(0, (1 - x)) * self.scale_fn(
self.clr_iterations)
def on_train_begin(self, logs={}):
logs = logs or {}
if self.clr_iterations == 0:
K.set_value(self.model.optimizer.lr, self.base_lr)
else:
K.set_value(self.model.optimizer.lr, self.clr())
def on_batch_end(self, epoch, logs=None):
logs = logs or {}
self.trn_iterations += 1
self.clr_iterations += 1
self.history.setdefault('lr', []).append(K.get_value(self.model.optimizer.lr))
self.history.setdefault('iterations', []).append(self.trn_iterations)
for k, v in logs.items():
self.history.setdefault(k, []).append(v)
K.set_value(self.model.optimizer.lr, self.clr())main.py文件
import keras
from keras.models import Model
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.applications.imagenet_utils import preprocess_input
import resnets_utils
import keras.backend as K
import numpy as np
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from keras.initializers import glorot_uniform
from clr_callback import CyclicLR
"""
获取数据 并将标签转换成one-hot
"""
def convert_data():
train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes=resnets_utils.load_dataset()
train_x=train_set_x_orig/255
test_x = test_set_x_orig / 255
train_y=resnets_utils.convert_to_one_hot(train_set_y_orig,6).T
test_y = resnets_utils.convert_to_one_hot(test_set_y_orig, 6).T
#print(train_y.shape)
return train_x[:320,...],train_y[:320,...],test_x,test_y
if __name__=='__main__':
train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y=convert_data()
print(train_x.shape)
print(train_y.shape)
print(test_x.shape)
print(test_y.shape)
best_score=0
classes=6
Epcoh=50
Batch=32
input_shape=(64,64,3)
X_input = keras.layers.Input(input_shape)
X = keras.layers.Conv2D(filters=6, kernel_size=(3, 3), strides=(2, 2), name='conv1',
kernel_initializer=glorot_uniform(seed=0))(X_input)
print('第一次卷积尺寸={}'.format(X.shape))
X=keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling2D()(X)
print(X.shape)
Y=keras.layers.Dense(classes, activation='softmax', name='fc_class')(X)
model = Model(inputs=X_input, outputs=Y)
model.summary()
keras.utils.plot_model(model,to_file='./model.jpg')
lr = 1e-2
clr = CyclicLR(base_lr=1e-5, max_lr=lr, step_size= Epcoh/ Batch * 2, mode='triangular2')
adam = Adam(lr=lr, beta_1=0.9, beta_2=0.999, epsilon=1e-08, amsgrad=True, )
model.compile(optimizer=adam, loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['acc']) #metrics=['mae', 'acc'])
tb_callback=keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir='./logs/keras',
histogram_freq=1,
write_graph=True,
write_images=1,
write_grads=True
)
history = model.fit(x=train_x, y=train_y,
batch_size=Batch,
validation_data=(test_x, test_y),
epochs=Epcoh,callbacks=[tb_callback,clr])
acc=history.history['acc']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
print('acc=', acc)
print('loss=', loss)
print('val_acc=',val_acc)
print('val_loss=',val_loss)
score = model.evaluate(x=test_x, y=test_y,batch_size=Batch)
print('loss=',score[0])
print('test_acc',score[1])
if score[1] > best_score:
best_score = score[1]
model.save('./model.h5', overwrite=True)