python数据结构之链表
目录
(原来整理了部分,参考这篇博客http://blog.csdn.net/tinkle181129/article/details/79332331(博主知道啦),决定对这篇文章进行补充)
1. 链表的基础知识
2. 链表逆序 (LeetCode 206)
3. 链表中间段逆序(LeetCode 92)
4. 求两个链表的交点(LeetCode 160)
5. 排序链表的合并(LeetCode 21,23)
6. 链表求环(LeetCode 142)
7. 链表划分(LeetCode 86)
8. 复杂链表的深度拷贝(LeetCode 138)
9. 从链表中删除元素(LeetCode 83,82,237,203,19)
10. 链表求和(LeetCode2,445)
11. 交换链表节点(LeetCode24,25)
12. 旋转链表(LeetCode61)
13. 链表拆分(LeetCode725)
14. 改写链表(LeetCode109,328)
15. 链表重排序(LeetCode143)
16. 判断回文链表(LeetCode234)
17. 链表排序(LeetCode147,148)
1.链表的基础知识
链表的结构:
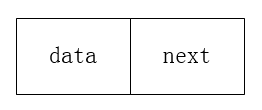
data为定义数据,next为下一个节点的位置。
python实现链表的方法为:
class Node:
'''
data: 节点保存的数据
_next: 保存下一个节点对象
'''
def __init__(self, data, pnext=None):
self.data = data
self._next = pnext2.链表逆序(LeetCode206 Reverse Linked List)
2.1题目
Reverse a singly linked list.
2.2思路
以0—>1—>2—>3为例
初始化,newhead=None
1. p=head:p=0—>1—>2—>3,head=head.next:head=1—>2—>3
2. p.next=newhead:p=0—>None
3. newhead=p:newhead=0—>None
循环直到head为空
2.3代码
class Solution(object):
def reverseList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
new_head = None
while head:
p = head
head = head.next
p.next = new_head
new_head = p
return new_head3.链表中间段逆序(LeetCode 92 Reverse Linked List II)
3.1题目
Reverse a linked list from position m to n. Do it in-place and in one-pass.
For example:
Given 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2 and n = 4,
return 1->4->3->2->5->NULL.
3.2思路
新建一个ListNode,先遍历前m-1个,m-n之间进行逆序,使用上面的方法
3.3代码
class Solution(object):
def reverseBetween(self, head, m, n):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type m: int
:type n: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if m == n:
return head
new_head = ListNode(-1)
new_head.next = head
q = new_head
for i in range(m-1):
head = head.next
new_head = new_head.next
t = None
for i in range(n - m+1):
p = head
head = head.next
p.next = t
t = p
new_head.next = t
for i in range(n - m+1):
new_head = new_head.next
new_head.next = head
return q.next4.求两个链表的交点(LeetCode 160 Intersection of Two Linked Lists)
4.1题目
Write a program to find the node at which the intersection of two singly linked lists begins.
For example, the following two linked lists:
A: a1 → a2
↘
c1 → c2 → c3
↗
B: b1 → b2 → b3begin to intersect at node c1.
4.2思路
遍历两个链表分别统计其长度,让长链先走|m-n|步,则公共节点必定存在于后面,依次遍历,则第一个相等的点则为公共点。
4.3代码
class Solution(object):
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA, headB):
"""
:type head1, head1: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
p1 = headA
p2 = headB
m = 0
n = 0
while p1:
p1 = p1.next
m += 1
while p2:
p2 = p2.next
n += 1
if m > n:
for i in range(m - n):
headA = headA.next
else:
for i in range(n - m):
headB = headB.next
while headA:
if headA.val == headB.val:
return headA
headA = headA.next
headB = headB.next
return None5.排序链表的合并(LeetCode 21 Merge Two Sorted Lists,LeetCode 23 )
5.1题目
- LeetCode 21 Merge Two Sorted Lists(合并两个有序链表)
Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
Example:
Input: 1->2->4, 1->3->4
Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4 - LeetCode 23 Merge k Sorted Lists(合并k个有序链表)
Merge k sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list. Analyze and describe its complexity.
5.2思路
- LeetCode 21 Merge Two Sorted Lists
首先创建一个新的链表节点
依次遍历两个链表,比较两个链表的指针指向的节点的值的大小,将值较小的节点放入新的链表中,直到某个链表为空,则剩下的链表直接放进新的链表中。
注:两个链表都为空的情况 - LeetCode 23 Merge k Sorted Lists
使用python的优先队列,from Queue immport PriorityQueue,优先队列在插入元素的时候已经对元素做了排序,把最小的元素放在队尾。
首先新创建一个节点,然后将列表中各个链表的起始节点按(值,节点)放入优先队列中,从优先队列中弹出值最小的节点,将新创建的节点指向它,并判断弹出的节点是否已到达链尾,如果没有,则将弹出节点的下一节点按(值,节点)的方式放入优先队列,以此类推,指导优先队列为空。
5.3代码
- LeetCode 21 Merge Two Sorted Lists
class Solution(object):
def mergeTwoLists(self, l1, l2):
"""
:type l1: ListNode
:type l2: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
ans = ListNode(0)
p = ans
while l1 and l2:
if l1.val <= l2.val:
p.next = l1
l1 = l1.next
else:
p.next = l2
l2 = l2.next
p = p.next
if l1:
p.next = l1
elif l2:
p.next = l2
return ans.next- LeetCode 23 Merge k Sorted Lists
from Queue import PriorityQueue
class Solution(object):
def mergeKLists(self, lists):
"""
:type lists: List[ListNode]
:rtype: ListNode
"""
q = PriorityQueue()
ans = ListNode(None)
temp = ans
for list1 in lists:
if list1:
q.put((list1.val, list1))
while q.qsize() > 0:
temp.next = q.get()[1]
temp = temp.next
if temp.next:
q.put((temp.next.val, temp.next))
return ans.next6.链表求环(LeetCode 141Linked List Cycle,142Linked List Cycle II)
6.1题目
leetcode141. Linked List Cycle
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
leetcode142. Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
6.2思路
leetcode141. Linked List Cycle 判断链表中是否存在环
使用快慢指针方法,起始时,快慢指针都位于链表头部,快指针以慢指针两倍的速度向后遍历,若链表存在环,则快慢指针会相遇,否则不会相遇
注:当快指针指向None或者next为None,则说明不存在环
leetcode142. Linked List Cycle II 返回环的起始位置
还是使用快慢指针的方法,快指针以慢指针2倍的速度向后依次遍历
fast = 2slow,假设环的起始位置距离链表起始位置的距离为K,相遇点距离环的起始位置的距离为M,环的周长为L
则在相遇点:
lslow = K + M
lfast = K + M + nL
lfast = 2* lslow
整理上式可以得到:K=(n-1)L + L-M
即从相遇点开始,再走K步一定能回到环的起始点,故此时可以将lslow回到head,lfast在相遇点,二者以相同的速度(单倍速度)向后遍历,再次相遇的位置即为环起始的位置
6.3代码
leetcode141. Linked List Cycle 判断链表中是否存在环
class Solution(object):
def hasCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
fast = head
slow = head
while True:
if fast == None or fast.next == None:
return False
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if fast and slow and fast.val == slow.val:
return Trueleetcode142. Linked List Cycle II 返回环的起始位置
class Solution(object):
def detectCycle(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if head == None or head.next == None:
return None
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if fast == slow:
break
if slow == fast:
slow = head
while slow != fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
return slow
return None7.链表划分(LeetCode 86 Partition List)
7.1题目
Given a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before nodes greater than or equal to x.
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
For example,
Given 1->4->3->2->5->2 and x = 3,
return 1->2->2->4->3->5.
7.2思路
创建两个链表,一个用于存放小于x值的链表,另一个用于存放大于x值的链表,最后将两个链表合并
7.3代码
class Solution(object):
def partition(self, head, x):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type x: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
head1 = ListNode(0)
head2 = ListNode(0)
Tmp = head
phead1 = head1
phead2 = head2
while Tmp:
if Tmp.val < x:
phead1.next = Tmp
Tmp = Tmp.next
phead1 = phead1.next
phead1.next = None
else:
phead2.next = Tmp
Tmp = Tmp.next
phead2 = phead2.next
phead2.next = None
phead1.next = head2.next
return head1.next8.复杂链表的深度拷贝(LeetCode 138Copy List with Random Pointer)
8.1题目
A linked list is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer which could point to any node in the list or null.
Return a deep copy of the list.
# Definition for singly-linked list with a random pointer.
# class RandomListNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.label = x
# self.next = None
# self.random = None8.2思路
利用字典存储每个结点的具体信息,技巧是使用python的collection.defaultdict(lambda: RandomListNode(0))
8.3代码
class Solution(object):
def copyRandomList(self, head):
"""
:type head: RandomListNode
:rtype: RandomListNode
"""
dict1 = collections.defaultdict(lambda: RandomListNode(0))
t = head
dict1[None] = None
while t:
dict1[t].label = t.label
dict1[t].next = dict1[t.next]
dict1[t].random = dict1[t.random]
t = t.next
return dict1[head]9. 从链表中删除元素(LeetCode 83,82,237,203,19)
9.1题目
- LeetCode19 Remove Nth Node From End of List
Given a linked list, remove the nth node from the end of list and return its head.
For example,
Given linked list: 1->2->3->4->5, and n = 2.
After removing the second node from the end, the linked list becomes 1->2->3->5. - LeetCode83 Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
Given a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such that each element appear only once.
For example,
Given 1->1->2, return 1->2.
Given 1->1->2->3->3, return 1->2->3. - LeetCode82 Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
Given a sorted linked list, delete all nodes that have duplicate numbers, leaving only distinct numbers from the original list.
For example,
Given 1->2->3->3->4->4->5, return 1->2->5.
Given 1->1->1->2->3, return 2->3. - LeetCode237 Delete Node in a Linked List
Write a function to delete a node (except the tail) in a singly linked list, given only access to that node.
Supposed the linked list is 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 and you are given the third node with value 3, the linked list should become 1 -> 2 -> 4 after calling your function. - LeetCode203 Remove Linked List Elements
Remove all elements from a linked list of integers that have value val.
Example
Given: 1 –> 2 –> 6 –> 3 –> 4 –> 5 –> 6, val = 6
Return: 1 –> 2 –> 3 –> 4 –> 5
Credits:
Special thanks to @mithmatt for adding this problem and creating all test cases.
9.2思路
- LeetCode19 Remove Nth Node From End of List
使用快慢指针的思想,假设链表长度为L,先将temp1前进n步,则temp1剩下L-n步,此时temp2从头开始前进直到temp1到达链尾,此时temp2的位置恰好位于要跳过的节点的前一个。 - LeetCode83 Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
依次遍历,由于链表是有序的,只需将当前链表的节点与前一个节点的值相比,若相等,则直接跳过该结点。 - LeetCode82 Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
此题要求将由重复的节点全部删除,需新创建一个节点,指向目标链表。使用两个指针,pre和cur,初始时,cur指向当前节点,也就是head,pre指向当前节点的前一个节点。向后遍历,如果cur.next.val == pre.next.val,则cur指针后移,直到不满足cur.next.val == pre.next.val条件,此时如果pre.next == cur(cur指针即为pre指针的下一个节点,上一步骤中cur未进行移动,注意,此处比较的是链表节点而不是值),则pre指针后移,否则,pre.next = cur.next。最后,cur指针后移一个。直到cur指针到达链表结尾。 - LeetCode237 Delete Node in a Linked List
直接修改,将下一节点的值赋给当前节点,node.next = node.next.next - LeetCode203 Remove Linked List Elements
依次遍历判断,当前节点的值是否等于给定值,若相等则跳过。技巧是使用两个指针pre和cur,初始时,cur指向当前节点,也就是head,pre指向当前节点的前一个节点。
9.3代码
- LeetCode19 Remove Nth Node From End of List
class Solution(object):
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type n: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
ans = ListNode(0)
ans.next = head
temp1 = ans
temp2 = ans
i = 0
while i < n:
temp1 = temp1.next
i += 1
while temp1.next:
temp1 = temp1.next
temp2 = temp2.next
temp2.next = temp2.next.next
return ans.next- LeetCode83 Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
class Solution(object):
def deleteDuplicates(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if head == None or head.next == None:
return head
ans = ListNode(0)
ans.next = head
pre = ans.next
cur = ans.next
while cur != None:
if pre.val != cur.val:
pre.next = cur
pre = pre.next
else:
pre.next = cur.next
cur = cur.next
return ans.next- LeetCode82 Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II
class Solution(object):
def deleteDuplicates(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if head == None or head.next == None:
return head
ans = ListNode(0)
ans.next = head
pre = ans
cur = ans.next
while cur != None:
while cur.next and cur.next.val == pre.next.val:
cur = cur.next
if pre.next == cur:
pre = pre.next
else:
pre.next = cur.next
cur = cur.next
return ans.next- LeetCode237 Delete Node in a Linked List
class Solution(object):
def deleteNode(self, node):
"""
:type node: ListNode
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify node in-place instead.
"""
if node.next:
node.val = node.next.val
node.next = node.next.next- LeetCode203 Remove Linked List Elements
class Solution(object):
def removeElements(self, head, val):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type val: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if head == None:
return None
pre = ListNode(0)
pre.next = head
ans = pre
cur = head
while cur:
if cur.val == val:
if cur.next == None:
pre.next = None
cur = cur.next
else:
pre.next = cur.next
cur = cur.next
else:
pre = pre.next
cur = cur.next
return ans.next10. 链表求和(LeetCode2,445)
10.1题目
- LeetCode2 Add Two Numbers
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807. - LeetCode445 Add Two Numbers II
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The most significant digit comes first and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example:
Input: (7 -> 2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 8 -> 0 -> 7
10.2思路
- LeetCode2 Add Two Numbers
新创建一个节点,使用一个标记符flag来记录进位情况,依次遍历链表,对应位置数值相加,对10取整,取余即可 - LeetCode445 Add Two Numbers II
此题与上一题的区别是按位求和的顺序相反。
可以考虑先将两个链表转成数字,求和后再转成链表。
10.3代码
- LeetCode2 Add Two Numbers
class Solution(object):
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1, l2):
"""
:type l1: ListNode
:type l2: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
nHead, flag = ListNode(0), 0
head = nHead
while flag or l1 or l2:
node = ListNode(flag)
if l1:
node.val += l1.val
l1 = l1.next
if l2:
node.val += l2.val
l2 = l2.next
flag = node.val // 10
node.val %= 10
head.next, head = node, node
return nHead.next
- LeetCode445 Add Two Numbers II
class Solution(object):
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1, l2):
"""
:type l1: ListNode
:type l2: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
c1, c2 = '', ''
while l1:
c1 += str(l1.val)
l1 = l1.next
while l2:
c2 += str(l2.val)
l2 = l2.next
num = str(int(c1) + int(c2))
dummy = ListNode(0)
c = dummy
for i in range(len(num)):
c.next = ListNode(num[i])
c = c.next
return dummy.next11. 交换链表节点(LeetCode24,25)
11.1题目
- LeetCode24 Swap Nodes in Pairs
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
For example,
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
Your algorithm should use only constant space. You may not modify the values in the list, only nodes itself can be changed. - LeetCode25 Reverse Nodes in k-Group
Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list k at a time and return its modified list.
k is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of k then left-out nodes in the end should remain as it is.
You may not alter the values in the nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
Only constant memory is allowed.
For example,
Given this linked list: 1->2->3->4->5
For k = 2, you should return: 2->1->4->3->5
For k = 3, you should return: 3->2->1->4->5
11.2思路
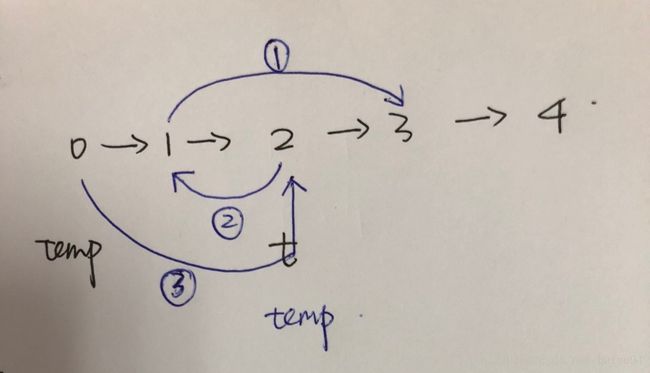
- LeetCode24 Swap Nodes in Pairs
将每相邻两个节点进行翻转,翻转顺序如图所示,temp其实位于0节点。翻转过程借助临时链表t
- LeetCode25 Reverse Nodes in k-Group
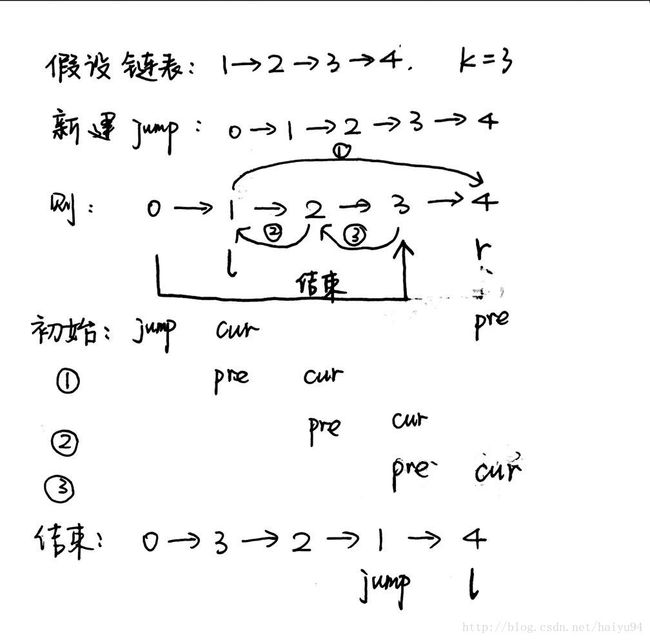
使用l,r指针指向翻转部分链表的左端和右端,jump为新建链表节点ListNode(0),下一节点指向head。
首先找到翻转的左右端,然后使用循环进行翻转,翻转顺序如下图所示
11.3代码
- LeetCode24 Swap Nodes in Pairs
class Solution(object):
def swapPairs(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
ans = ListNode(0)
ans.next = head
temp = ans
i = 0
if head == None:
return None
while temp.next and temp.next.next:
t = temp.next.next
temp.next.next = t.next
t.next = temp.next
temp.next = t
temp = temp.next.next
return ans.next- LeetCode25 Reverse Nodes in k-Group
class Solution(object):
def reverseKGroup(self, head, k):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type k: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
dummy = jump = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = l = r = head
while True:
i = 0
while r and i < k:
r = r.next
i += 1
if i == k:
pre = r
cur = l
for j in range(k):
cur.next, cur, pre = pre, cur.next, cur
jump.next, jump, l = pre, l, r
else:
return dummy.next12. 旋转链表(LeetCode61 Rotate List)
12.1题目
Given a list, rotate the list to the right by k places, where k is non-negative.
Example:
Given 1->2->3->4->5->NULL and k = 2,
return 4->5->1->2->3->NULL.
12.2思路
相当于链表依次右移k次,首先定位到旋转后链尾节点的位置,size-k%size,原来链尾指向原来的链表的起始节点
12.3代码
class Solution(object):
def rotateRight(self, head, k):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:type k: int
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if k == 0 or head ==None:
return head
temp = ListNode(0)
temp.next = head
t = temp
size = 0
while t.next:
size += 1
t = t.next
t.next = temp.next
for i in range(size - k % size):
t = t.next
head = t.next
t.next = None
return head13. 链表拆分(LeetCode725 Split Linked List in Parts)
13.1题目
Given a (singly) linked list with head node root, write a function to split the linked list into k consecutive linked list “parts”.
The length of each part should be as equal as possible: no two parts should have a size differing by more than 1. This may lead to some parts being null.
The parts should be in order of occurrence in the input list, and parts occurring earlier should always have a size greater than or equal parts occurring later.
Return a List of ListNode’s representing the linked list parts that are formed.
Examples 1->2->3->4, k = 5 // 5 equal parts [ [1], [2], [3], [4], null ]
Example 1:
Input:
root = [1, 2, 3], k = 5
Output: [[1],[2],[3],[],[]]
Explanation:
The input and each element of the output are ListNodes, not arrays.
For example, the input root has root.val = 1, root.next.val = 2, \root.next.next.val = 3, and root.next.next.next = null.
The first element output[0] has output[0].val = 1, output[0].next = null.
The last element output[4] is null, but it’s string representation as a ListNode is [].
Example 2:
Input:
root = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], k = 3
Output: [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7], [8, 9, 10]]
Explanation:
The input has been split into consecutive parts with size difference at most 1, and earlier parts are a larger size than the late
13.2思路
首先求解链表的长度L,L/k即为每段链表的基本长度,L%k为除去k段基本长度之后剩余部分的长度,由于每段之间相差的长度不超多1,故将剩余部分添加到前面几段上,每段在基本长度的节点上添加一个节点,直到剩余部分的长度为0,后面每段的长度为基本长度。
13.3代码
class Solution(object):
def splitListToParts(self, root, k):
"""
:type root: ListNode
:type k: int
:rtype: List[ListNode]
"""
L = 0
head = root
temp2 = root
while head:
L += 1
head = head.next
n = L / k
left = L % k
ans = []
for i in range(k):
nhead = ListNode(0)
nhead.next = temp2
if nhead:
temp1 = nhead.next
else:
temp1 = None
temp2 = nhead
for j in range(n):
nhead = nhead.next
temp2 = temp2.next
if left > 0:
nhead = nhead.next
temp2 = temp2.next
left -= 1
if nhead:
nhead = nhead.next
temp2.next = None
ans.append(temp1)
temp2 = nhead
return ans14. 改写链表(LeetCode109,328)
14.1题目
- LeetCode109 Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
Given a singly linked list where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of every node never differ by more than 1.
Example:
Given the sorted linked list: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST:
0
/ \
-3 9
/ /
-10 5- LeetCode 328 Odd Even Linked List
Given a singly linked list, group all odd nodes together followed by the even nodes. Please note here we are talking about the node number and not the value in the nodes.
You should try to do it in place. The program should run in O(1) space complexity and O(nodes) time complexity.
Example:
Given 1->2->3->4->5->NULL,
return 1->3->5->2->4->NULL.
14.2思路
- LeetCode109 Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
将有序链表转换成平衡二叉树,平衡二叉树的特点:空树或左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一颗平衡二叉树。采用递归的方法生成二叉树,首先找到链表的中间位置,该位置上的数为根节点,使用快慢指针的方法进行寻找,起始时,慢指针位于链首,快指针位于第三个位置,快指针是慢指针速度的两倍,当快指针到达链尾时,慢指针恰好位于中间位置的前一个(1234的root为3,12345的root为3),则中间位置左边的链表生成左子树,右边的链表生成右子树,返回root节点 - LeetCode 328 Odd Even Linked List
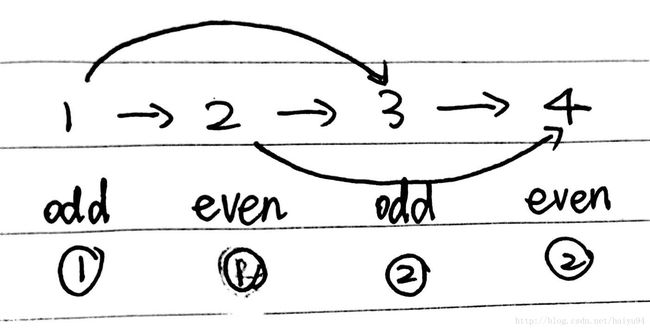
奇节点在前,偶节点在后,用一个链表存放奇节点,一个链表存放偶数节点,其实时,奇数节点指向链表的起始位,偶数节点指向链表的第二位,则奇数节点的下一个奇数节点为偶数链表的下一个节点,偶数节点的下一个偶数节点是奇数链表的下一个节点,以此类推,直到链表尾部。最后将两个链表拼接。
14.3代码
- LeetCode109 Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree
class Solution(object):
def sortedListToBST(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if not head:
return None
if not head.next:
return TreeNode(head.val)
slow = head
fast = head.next.next
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
temp = slow.next
slow.next = None
root = TreeNode(temp.val)
root.left = self.sortedListToBST(head)
root.right = self.sortedListToBST(temp.next)
return root- LeetCode 328 Odd Even Linked List
class Solution(object):
def oddEvenList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head:
return head
odd_list = head
# temp1 = odd_list
even_list = head.next
temp2 = even_list
while odd_list.next and even_list.next:
odd_list.next = even_list.next
odd_list = odd_list.next
if odd_list:
even_list.next = odd_list.next
even_list = even_list.next
odd_list.next = temp2
return head15. 链表重排序(LeetCode143 Reorder List)
15.1题目
Given a singly linked list L: L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln,
reorder it to: L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
You must do this in-place without altering the nodes’ values.
For example,
Given {1,2,3,4}, reorder it to {1,4,2,3}.
15.2思路
首先将链表拆分为长度相等的左右两部分,拆分技巧,使用快慢指针的方法,快指针的速度是慢指针速度的两倍。然后将右边的链表进行翻转,最后将两个链表归并,生成结果。
15.3代码
class Solution(object):
def reorderList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: void Do not return anything, modify head in-place instead.
"""
if not head or not head.next or not head.next.next:
return
slow = head
fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
head2 = slow.next
slow.next = None
dummy = None
while head2:
p = head2
head2 = head2.next
p.next = dummy
dummy = p
head2 = dummy
head1 = head
while head2:
temp1 = head1.next
temp2 = head2.next
head1.next = head2
head2.next = temp1
head1 = temp1
head2 = temp2
16. 判断回文链表(LeetCode234 Palindrome Linked List)
16.1题目
Given a singly linked list, determine if it is a palindrome.
Follow up:
Could you do it in O(n) time and O(1) space?
16.2思路
利用快慢指针的思想,将链表分为左右等长链表,再将右部分链表逆序,与左部分逐一比较,判断是否是回文串
16.3代码
class Solution(object):
def isPalindrome(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: bool
"""
if not head or not head.next:
return True
slow = fast = head
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
head2 = slow
head1 = head
nhead = None
while head2:
p = head2
head2 = head2.next
p.next = nhead
nhead = p
head2 = nhead
while head2:
if head2.val != head1.val:
return False
head1 = head1.next
head2 = head2.next
return True17. 链表排序(LeetCode147,148)
17.1题目
LeetCode 147 Insertion Sort List
Sort a linked list using insertion sort.LeetCode148 Sort List
Sort a linked list in O(n log n) time using constant space complexity.
17.2思路
LeetCode 147 Insertion Sort List
插入排序的基本操作就是将一个数据插入到已经排好序的有序数据中,从而得到一个新的、个数加一的有序数据,算法适用于少量数据的排序,时间复杂度为O(n^2)。是稳定的排序方法。思路是对原链中的每个节点进行判断,找到合适的插入位置进行插入。LeetCode148 Sort List
时间复杂度O(n log n) time ,空间复杂度是常数,使用归并排序,链表的中点可以通过快慢指针法求得。
17.3代码
- LeetCode 147 Insertion Sort List
class Solution(object):
def insertionSortList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
p = dummy = ListNode(0)
cur = dummy.next = head
while cur and cur.next:
val = cur.next.val
if cur.val < val:
cur = cur.next
continue
if p.next.val > val:
p = dummy
while p.next.val < val:
p = p.next
new = cur.next
cur.next = new.next
new.next = p.next
p.next = new
return dummy.next- LeetCode148 Sort List
class Solution(object):
def sortList(self, head):
"""
:type head: ListNode
:rtype: ListNode
"""
if not head or not head.next:
return head
mid = self.getmiddle(head)
rhead = mid.next
mid.next = None
return self.merge(self.sortList(head), self.sortList(rhead))
def merge(self, lhead, rhead):
temp = dummy = ListNode(0)
while lhead and rhead:
if lhead.val < rhead.val:
temp.next = lhead
lhead = lhead.next
else:
temp.next = rhead
rhead = rhead.next
temp = temp.next
if lhead:
temp.next = lhead
if rhead:
temp.next = rhead
return dummy.next
def getmiddle(self, head):
if not head:
return head
slow = fast = head
while fast.next and fast.next.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
return slow