Tensorflow学习——5 TextCnn的研究
TextCnn的学习
- 1、TextCnn的论文
- 2、TextCnn的理解
- 3、TextCnn的数据准备
- 4、TextCnn的网络结构
- 5、TextCnn的代码
1、TextCnn的论文
论文地址:
Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1408.5882.pdf
A Sensitivity Analysis of (and Practitioners’ Guide to) Convolutional Neural Networks for Sentence Classification
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1510.03820.pdf
源码地址:https://github.com/dennybritz/cnn-text-classification-tf
2、TextCnn的理解
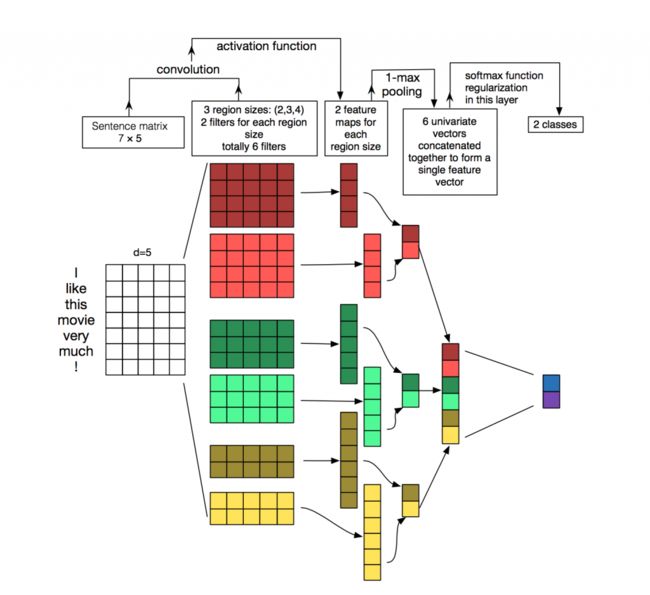 1、对于I like this movie very much ! 这句话进行词分割,word embedding的维度是5,也就是上图的空白矩阵7*5。
1、对于I like this movie very much ! 这句话进行词分割,word embedding的维度是5,也就是上图的空白矩阵7*5。
2、采用了6个卷积核,有三种尺寸,分别是2×5×2、3×5×2、4×5×2,也就是说,卷积的过程只是纵向的移动。
3、与卷积核进行valid卷积操作之后,使用激活函数激活。这样每个卷积核都得到了特征向量。
4、池化采用最大池化,3层池化,对应不同的卷积核,得到三种卷积核维度相同的矩阵,然后直接reshape,这儿采用最大池化的原因是,对于每一句话,采用定长输入,所以存在补0的情况,使用了最大池化,那么相当于补0的操作不会影响数据本身的特征。
5、将所有特征进行softmax操作,并且在全连接层进行类l2正则化操作。得到分类类别。
3、TextCnn的数据准备
对于数据处理。
1、打标签分类,对每句话进行分类
2、jieba分词,可以选取的操作,自己添加词库和停用词。
可以参考博客
3、得到想要的分词后,进行word2id操作,获取文本特征。
4、shuf 制作好训练、测试、验证数据集
4、TextCnn的网络结构
1、Embedding Layer
将稀疏的原始one-hot编码的词映射到低维向量表达,降低特征维数
2、Convolution Layer
源代码采用(3×128)(4×128)(5×128)三种卷积核,每种都有128个。采用valid的卷积方式。在纵轴进行卷积。
3、Pooling Layer
采用最大池化,对补0进行过滤,3层池化。
4、SoftMax
输出各类别的概率
5、TextCnn的代码
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
class TextCNN(object):
"""
A CNN for text classification.
Uses an embedding layer, followed by a convolutional, max-pooling and softmax layer.
sequence_length =
"""
def __init__(
self, sequence_length, num_classes, vocab_size,
embedding_size, filter_sizes, num_filters, l2_reg_lambda=0.0):
# 定义模型数据输出结构 定长的sequence_length
self.input_x = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, sequence_length], name="input_x")
self.input_y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, num_classes], name="input_y")
self.dropout_keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="dropout_keep_prob")
# Keeping track of l2 regularization loss (optional)
l2_loss = tf.constant(0.0)
# Embedding layer
with tf.device('/cpu:0'), tf.name_scope("embedding"):
self.W = tf.Variable(
# 每一个词都是embedding_size长度的特征向量 (18758,128)
tf.random_uniform([vocab_size, embedding_size], -1.0, 1.0),
name="W")
#根据词的下标,获取它们的word2vec。
#embedded_chars的shape[sequence_length, embedding_size]
# (none,56,128) sequence_length = 56
self.embedded_chars = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(self.W, self.input_x)
#扩充维度 相当于一个1维的通道数
# [None,56,128,1]
self.embedded_chars_expanded = tf.expand_dims(self.embedded_chars, -1)
# Create a convolution + maxpool layer for each filter size
pooled_outputs = []
for i, filter_size in enumerate(filter_sizes):
with tf.name_scope("conv-maxpool-%s" % filter_size):
# Convolution Layer
# filter_size 分别为3 4 5
filter_shape = [filter_size, embedding_size, 1, num_filters]
W = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal(filter_shape, stddev=0.1), name="W")
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[num_filters]), name="b")
conv = tf.nn.conv2d( # [None,56-3+1,1,128] [None,56-4+1,1,128] [None,56-5+1,1,128]
self.embedded_chars_expanded,
W,
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding="VALID",
name="conv")
# Apply nonlinearity
h = tf.nn.relu(tf.nn.bias_add(conv, b), name="relu")
# Maxpooling over the outputs
pooled = tf.nn.max_pool( #[None,1,1,128]
h,
ksize=[1, sequence_length - filter_size + 1, 1, 1], #[1,54,1,1] [1,53,1,1] [1,52,1,1]
strides=[1, 1, 1, 1],
padding='VALID',
name="pool")
print(pooled)
pooled_outputs.append(pooled)
# Combine all the pooled features
num_filters_total = num_filters * len(filter_sizes)
self.h_pool = tf.concat(pooled_outputs, 3)
self.h_pool_flat = tf.reshape(self.h_pool, [-1, num_filters_total])
# 全连接dropout
with tf.name_scope("dropout"):
self.h_drop = tf.nn.dropout(self.h_pool_flat, self.dropout_keep_prob)
# Final (unnormalized) scores and predictions
with tf.name_scope("output"):
W = tf.get_variable(
"W",
shape=[num_filters_total, num_classes],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
b = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1, shape=[num_classes]), name="b")
l2_loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(W)
l2_loss += tf.nn.l2_loss(b)
self.scores = tf.nn.xw_plus_b(self.h_drop, W, b, name="scores")
self.predictions = tf.argmax(self.scores, 1, name="predictions")
# Calculate mean cross-entropy loss
with tf.name_scope("loss"):
losses = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=self.scores, labels=self.input_y)
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(losses) + l2_reg_lambda * l2_loss
# Accuracy
with tf.name_scope("accuracy"):
correct_predictions = tf.equal(self.predictions, tf.argmax(self.input_y, 1))
self.accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_predictions, "float"), name="accuracy")