Python-opencv之目标定位
最近团队准备参加一个无人机比赛,大致的规则是这样的:固定翼飞机从跑道起飞,然后在空中转体360°,通过GPS粗定位飞行至一个高13米左右,宽6米左右八字形框前(距离约50米左右),这时依靠计算机视觉的方法,让飞机准确的穿过去。(之后还有其他的动作,但是第一步大体就是这样)。
初步的方案:①通过机载摄像机获取图像序列
②选取关键帧进行处理,获得框的中心点图像坐标
③将框的中心点图像坐标与图像中心坐标进行比较,将偏差信息反馈给控制系统,使其自动调节
关键点:如何准确地定位目标框,并提取出框中心点图像坐标。
——————————————————————————————————————————————
以下是一个比较简单的实现方案:
通过颜色提取出大致区域->形态学处理->轮廓提取->利用轮廓大小关系找到目标框->获得中心点信息并比较反馈
代码部分:
# coding:UTF-8
import cv2
import numpy as np
class Detect:
def __init__(self, path):
# 原始图像信息
self.ori_img = cv2.imread(path)
self.gray = cv2.cvtColor(self.ori_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
self.hsv = cv2.cvtColor(self.ori_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# 获得原始图像行列
rows, cols = self.ori_img.shape[:2]
# 工作图像
self.work_img = cv2.resize(self.ori_img, (cols / 4, rows / 4))
self.work_gray = cv2.resize(self.gray, (cols / 4, rows / 4))
self.work_hsv = cv2.resize(self.hsv, (cols / 4, rows / 4))
# 颜色区域提取
def color_area(self):
# 提取红色区域(暂定框的颜色为红色)
low_red = np.array([156, 43, 46])
high_red = np.array([180, 255, 255])
mask = cv2.inRange(self.work_hsv, low_red, high_red)
red = cv2.bitwise_and(self.work_hsv, self.work_hsv, mask=mask)
return red
# 形态学处理
def good_thresh_img(self, img):
# hsv空间变换到gray空间
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 阈值处理
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(img, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
# 做一些形态学操作,去一些小物体干扰
img_morph = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, (3, 3))
cv2.erode(img_morph, (3, 3), img_morph, iterations=2)
cv2.dilate(img_morph, (3, 3), img_morph, iterations=2)
return img_morph
# 矩形四角点提取
def key_points_tap(self, img):
img_cp = img.copy()
# 按结构树模式找所有轮廓
cnts, _ = cv2.findContours(img_cp, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
# 按区域大小排序,找到第二大轮廓
cnt_second = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)[1]
# 找轮廓的最小外接矩形((point), (w, h))
box = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt_second)
# ->(points)->(l_ints)
return np.int0(cv2.cv.BoxPoints(box))
# 画出关键轮廓的最校外接矩形
def key_cnt_draw(self, points):
mask = np.zeros(self.work_gray.shape, np.uint8)
cv2.drawContours(mask, [points], -1, 255, 2)
return mask
# 目标框图像中心点提取
def center_point_cal(self, points):
pt1_x, pt1_y = points[0, 0], points[0, 1]
pt3_x, pt3_y = points[2, 0], points[2, 1]
center_x, center_y = (pt1_x + pt3_x) / 2, (pt1_y + pt3_y) / 2
return center_x, center_y
# 中心点比较,进行反馈
def feedback(self, rect_center_point):
# 获取矩形框中心
rect_center_point_x, rect_center_point_y = rect_center_point[0], rect_center_point[1]
# 得到图像中心
rows, cols = self.work_img.shape[:2]
img_center_x, img_center_y = cols / 2, rows / 2
# 相对x、y
delta_x = rect_center_point_x - img_center_x
delta_y = rect_center_point_y - img_center_y
# 条件判断
print '-------------------'
if delta_x > 0:
print '->right'
elif delta_x < 0:
print 'left <-'
else:
print 'v_hold'
if delta_y < 0:
print '+up'
elif delta_y > 0:
print '-down'
else:
print 'h_hold'
# 运行主函数
def img_process_main(self):
# 找到红色区域
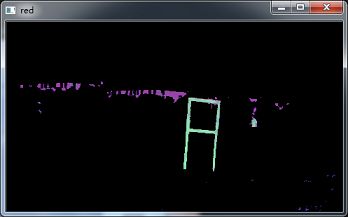
red = self.color_area()
# 处理得到一个比较好的二值图
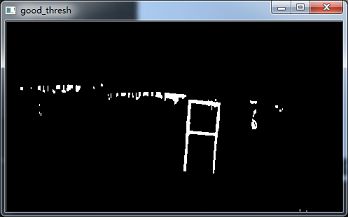
img_morph = self.good_thresh_img(red)
# 获取矩形框的四个关键点
points = self.key_points_tap(img_morph)
# 找到矩形中心点
rect_center_point = self.center_point_cal(points)
# 画出关键轮廓(调试用,并没有什么卯月)
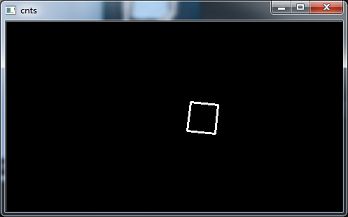
cnt_img = self.key_cnt_draw(points)
# 反馈信息
self.feedback(rect_center_point)
# 显示图像
cv2.imshow('ori', self.work_img)
cv2.imshow('red', red)
cv2.imshow('good_thresh', img_morph)
cv2.imshow('cnts', cnt_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
if __name__ == '__main__':
root_path = './201655'
img_index = 0
while True:
img_index += 1
img_path = root_path + '/' + str(img_index) + '.bmp'
d = Detect(img_path)
d.img_process_main()
实际效果:
实验用的是等比例缩小做的模型。