HotSpotVM 对象机制实现浅析
今天来看下,借助HotSpot SA这个工具,HotSpot VM所实现的对象机制。关于HotSpot SA前面已有几篇博文介绍过了,这里再说一点,SA提供的大多是HotSpot的镜像,所以非常有助于我们理解HotSpotVM,不管是运行时还是具体代码实现。
oop
那么HotSpot的对象机制应该从哪扯起呢?oop无疑。oop又是啥?
An “oop”, or “ordinary object pointer” in HotSpot parlance is a managed pointer to an object. It is normally the same size as a native machine pointer. A managed pointer is carefully tracked by the Java application and GC subsystem, so that storage for unused objects can be reclaimed.
也就是说,我们平时经常提及的对象实例,在HotSpot的内部表示,实际上是一个oop。具体地,oop的定义是oopDesc结构体,其中很重要的两个字段,
volatile markOop _mark;
union _metadata {
wideKlassOop _klass;
narrowOop _compressed_klass;
} _metadata;
_mark是用于GC,对象锁的字段,而_metadata,很明显,就是这个实例的Class元数据。
oop有一个层次结构,
// OBJECT hierarchy
// This hierarchy is a representation hierarchy, i.e. if A is a superclass
// of B, A's representation is a prefix of B's representation.
typedef class oopDesc* oop;
typedef class instanceOopDesc* instanceOop;
typedef class methodOopDesc* methodOop;
typedef class constMethodOopDesc* constMethodOop;
typedef class methodDataOopDesc* methodDataOop;
typedef class arrayOopDesc* arrayOop;
typedef class objArrayOopDesc* objArrayOop;
typedef class typeArrayOopDesc* typeArrayOop;
typedef class constantPoolOopDesc* constantPoolOop;
typedef class constantPoolCacheOopDesc* constantPoolCacheOop;
typedef class klassOopDesc* klassOop;
typedef class markOopDesc* markOop;
typedef class compiledICHolderOopDesc* compiledICHolderOop;
// The klass hierarchy is separate from the oop hierarchy.
class Klass;
class instanceKlass;
class instanceMirrorKlass;
class instanceRefKlass;
class methodKlass;
class constMethodKlass;
class methodDataKlass;
class klassKlass;
class instanceKlassKlass;
class arrayKlassKlass;
class objArrayKlassKlass;
class typeArrayKlassKlass;
class arrayKlass;
class objArrayKlass;
class typeArrayKlass;
class constantPoolKlass;
class constantPoolCacheKlass;
class compiledICHolderKlass;
这些类在SA里面会有镜像,所以我们很容易就可以通过SA来看看这些oop,klass到底是个啥。但是这里有一点要注意,在HotSpot中,oop与klass体系,注释中也说到了,是分开的,然后采用组合的方式,所以会有klassOop,而在SA中,则是采用了继承的方式,klass直接继承了oop。是SA的开发者偷懒了吗:)
下面直接上代码看下如何使用SA来帮助我们理解oop体系,
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
new Foo(8888);
System.in.read();
}
}
public class Foo {
public static int foo_static_i = 7777777;
private int foo_instance_i;
public Foo(int foo_instance_i) {
this.foo_instance_i = foo_instance_i;
}
public int getFoo_instance_i() {
return foo_instance_i;
}
}
import sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.*;
import sun.jvm.hotspot.runtime.VM;
import sun.jvm.hotspot.tools.Tool;
public class KlassKicker extends Tool {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
KlassKicker kk = new KlassKicker();
kk.start(args);
kk.stop();
}
@Override
public void run() {
VM vm = VM.getVM();
final ObjectHeap objectHeap = vm.getObjectHeap();
objectHeap.iterate(new HeapVisitor() {
@Override
public void prologue(long l) {
}
@Override
public boolean doObj(Oop oop) {
System.out.println("////////////////////////////////////////");
System.out.println("OOP#"+oop);
oop.iterate(new OopPrinter(System.out), true);
System.out.println("////////////////////////////////////////");
System.out.println("OOP.KLASS#"+oop.getKlass());
oop.getKlass().iterate(new OopPrinter(System.out), true);
System.out.println("////////////////////////////////////////");
System.out.println("OOP.KLASS.MIRROR#"+oop.getKlass().getJavaMirror());
oop.getKlass().getJavaMirror().iterate(new OopPrinter(System.out), true);
System.out.println("////////////////////////////////////////");
System.out.println("OOP.KLASS.KLASS#" + oop.getKlass().getKlass());
oop.getKlass().getKlass().iterate(new OopPrinter(System.out), true);
System.out.println("////////////////////////////////////////");
System.out.println("OOP.KLASS.KLASS.KLASS#" + oop.getKlass().getKlass().getKlass());
oop.getKlass().getKlass().getKlass().iterate(new OopPrinter(System.out), true);
System.out.println("////////////////////////////////////////");
System.out.println("OOP.KLASS.KLASS.KLASS.KLASS#" + oop.getKlass().getKlass().getKlass().getKlass());
oop.getKlass().getKlass().getKlass().getKlass().iterate(new OopPrinter(System.out), true);
return false;
}
@Override
public void epilogue() {
}
}, new ObjectHeap.ObjectFilter() {
@Override
public boolean canInclude(Oop oop) {
Klass klass = oop.getKlass();
return klass.getName() != null &&
"me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo".equals(klass.getName().asString());
}
});
}
}
通过继承sun.jvm.hotspot.tools.Tool可以很方便地使用SA的API。栗子中我们直接遍历了虚拟机运行时的堆,并且通过Filter可以只处理我们new出来的Foo对象实例。
要运行SA Tool需要将目标进程pid传过去。输出结果如下,
Attaching to process ID 5508, please wait...
Debugger attached successfully.
Server compiler detected.
JVM version is 24.51-b03
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.Instance@d6157f10
Oop for me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo @ 0x00000007d6157f10 (object size = 16)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :InstanceKlass for me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo @ 0x000000077d0c3010
- foo_instance_i: {12} :8888
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP.KLASS#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.InstanceKlass@7d0c3010
InstanceKlass for me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo @ 0x000000077d0c3010 (object size = 560)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :InstanceKlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00270
- _java_mirror: {120} :Oop for java/lang/Class @ 0x00000007d6157e98
- _super: {128} :InstanceKlass for java/lang/Object @ 0x000000077ce02bb0
- _layout_helper: {24} :16
- _access_flags: {156} :2097185
- _subklass: {136} :null
- _next_sibling: {144} :InstanceKlass for java/lang/reflect/TypeVariable @ 0x000000077d0c0fa8
- _alloc_count: {160} :0
- _array_klasses: {200} :null
- _methods: {208} :ObjArray @ 0x000000077d0c2d38
- _method_ordering: {216} :[I @ 0x000000077d0c2ff0
- _local_interfaces: {224} :ObjArray @ 0x000000077ce01bf8
- _transitive_interfaces: {232} :ObjArray @ 0x000000077ce01bf8
- _fields: {240} :[S @ 0x000000077d0c2d10
- _constants: {248} :ConstantPool for me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo @ 0x000000077d0c2bc0
- _class_loader: {256} :Oop for sun/misc/Launcher$AppClassLoader @ 0x00000007d60a32f0
- _protection_domain: {264} :Oop for java/security/ProtectionDomain @ 0x00000007d6152fa8
- _signers: {272} :null
- _inner_classes: {280} :[S @ 0x000000077ce01bd8
- _nonstatic_field_size: {360} :1
- _static_field_size: {364} :1
- _static_oop_field_count: {368} :0
- _nonstatic_oop_map_size: {372} :0
- _is_marked_dependent: {376} :0
- _init_state: {490} :5
- _vtable_len: {392} :6
- _itable_len: {396} :2
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP.KLASS.MIRROR#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.Instance@d6157e98
Oop for java/lang/Class @ 0x00000007d6157e98 (object size = 120)
- _mark: {0} :501373421313
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :InstanceKlass for java/lang/Class @ 0x000000077ce15e48
- cachedConstructor: {12} :null
- newInstanceCallerCache: {16} :null
- name: {20} :null
- declaredFields: {24} :null
- publicFields: {28} :null
- declaredMethods: {32} :null
- publicMethods: {36} :null
- declaredConstructors: {40} :null
- publicConstructors: {44} :null
- declaredPublicFields: {48} :null
- declaredPublicMethods: {52} :null
- classRedefinedCount: {96} :0
- lastRedefinedCount: {100} :0
- genericInfo: {56} :null
- enumConstants: {60} :null
- enumConstantDirectory: {64} :null
- annotations: {68} :null
- declaredAnnotations: {72} :null
- annotationType: {76} :null
- classValueMap: {80} :null
Oop for java/lang/Class @ 0x00000007d6157e98 (object size = 120)
- foo_static_i: {112} :7777777
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP.KLASS.KLASS#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.InstanceKlassKlass@7ce00270
InstanceKlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00270 (object size = 208)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :KlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00000
- _java_mirror: {120} :null
- _super: {128} :null
- _layout_helper: {24} :0
- _access_flags: {156} :0
- _subklass: {136} :null
- _next_sibling: {144} :null
- _alloc_count: {160} :0
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP.KLASS.KLASS.KLASS#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.KlassKlass@7ce00000
KlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00000 (object size = 208)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :KlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00000
- _java_mirror: {120} :null
- _super: {128} :null
- _layout_helper: {24} :0
- _access_flags: {156} :0
- _subklass: {136} :null
- _next_sibling: {144} :null
- _alloc_count: {160} :0
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP.KLASS.KLASS.KLASS.KLASS#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.KlassKlass@7ce00000
KlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00000 (object size = 208)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :KlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00000
- _java_mirror: {120} :null
- _super: {128} :null
- _layout_helper: {24} :0
- _access_flags: {156} :0
- _subklass: {136} :null
- _next_sibling: {144} :null
- _alloc_count: {160} :0
下面就来说说这些输出结果。
instanceOop
从上面的结果可以看到,对象实例,具体一点,是一个instanceOop,它的layout也很清晰,
+-----------+
| _mark |
+-----------+
| _metadata |
+-----------+
| instance |
| fields |
+-----------+
instanceKlass
instanceOop的metadata是一个instanceKlass,也就是用来描述类的数据结构,它的layout是这样的,
// An instanceKlass is the VM level representation of a Java class.
// It contains all information needed for a class at execution runtime.
// instanceKlass layout:
// [header ] klassOop
// [klass pointer ] klassOop
// [C++ vtbl pointer ] Klass
// [subtype cache ] Klass
// [instance size ] Klass
// [java mirror ] Klass
// [super ] Klass
// [access_flags ] Klass
// [name ] Klass
// [first subklass ] Klass
// [next sibling ] Klass
// [array klasses ]
// [methods ]
// [local interfaces ]
// [transitive interfaces ]
// [fields ]
// [constants ]
// [class loader ]
// [protection domain ]
// [signers ]
// [source file name ]
// [inner classes ]
// [static field size ]
// [nonstatic field size ]
// [static oop fields size ]
// [nonstatic oop maps size ]
// [has finalize method ]
// [deoptimization mark bit ]
// [initialization state ]
// [initializing thread ]
// [Java vtable length ]
// [oop map cache (stack maps) ]
// [EMBEDDED Java vtable ] size in words = vtable_len
// [EMBEDDED nonstatic oop-map blocks] size in words = nonstatic_oop_map_size
// The embedded nonstatic oop-map blocks are short pairs (offset, length)
// indicating where oops are located in instances of this klass.
// [EMBEDDED implementor of the interface] only exist for interface
// [EMBEDDED host klass ] only exist for an anonymous class (JSR 292 enabled)
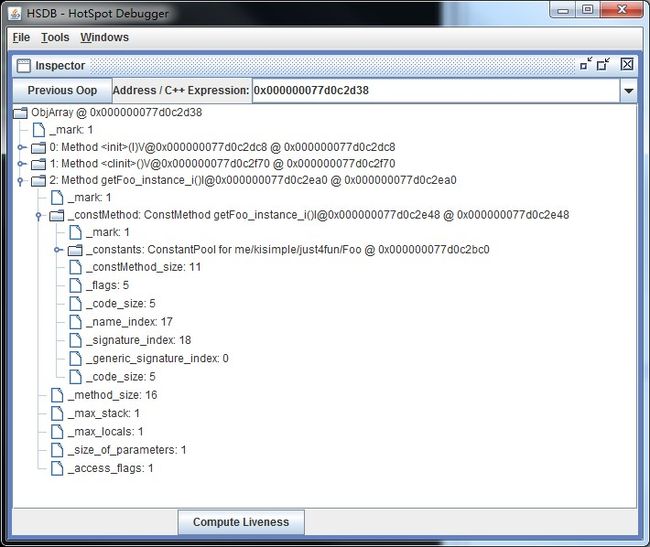
在我们的输出结果中,可以看到methods这个字段的值,_methods: {208} :ObjArray @ 0x000000077d0c2d38,这个ObjArray也是个oop,是数组对象,它的地址是0x000000077d0c2d38。下面我们使用SA自带的一个小神器,HSDB(HotSpotDeBugger),来看看这个地址上面是个啥。
很简单,直接java sun.jvm.hotspot.HSDB启动HSDB。启动之后需要先attach到目标进程,然后既可以使用图形界面(Tools->inspect),也可以使用命令行(Windows->console,这其实是命令行版本的HSDB,也就是sun.jvm.hotspot.CLHSDB)来inspect这些地址(还有其他很多功能,可以自己把玩一下),结果如下,
可以看到,是一个methodOop的数组对象。
Java镜像
接下来输出的实际是instanceKlass的_java_mirror字段,也是个oop。那么这个_java_mirror又是个啥?看下这篇官网文档中的描述,
The instanceKlass refers to a java mirror, which is the instance of java.lang.Class mirroring this class.
看下面的栗子会更容易理解这个镜像,
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(Main.class);
System.out.println(Main.class.getClass());
System.out.println(Main.class instanceof Class);
}
class me.kisimple.just4fun.Main
class java.lang.Class
true
这里的Main.class实际上就是上面所说的Java镜像,它是一个java.lang.Class的实例,因此Main.class instanceof Class才会是true。可以看到HotSpot将那些类变量(上面的foo_static_i)都放到这个镜像上面了。至于输出的很多字段都是null,感觉应该是SA有问题,暂不深究。
klassKlass
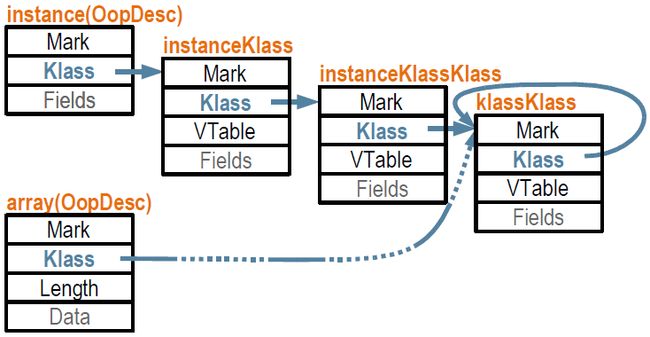
从后面的输出可以看出来,oop的klass链是下图这样的,
那么instanceKlassKlass和klassKlass这俩货又是干啥用的?
引用R大的一段说明,
HotSpot VM在JDK8之前的版本都是把Java对象和元数据对象以统一的方式由GC管理的。为了让GC能统一的处理这些对象,每个由GC管理的对象都继承自oopDesc,而每个oopDesc都有一个_klass字段指向描述它的Klass对象。GC在找到一个对象之后,要知道对象大小、对象里什么位置有GC需要知道的指针之类的信息,就会通过从_klass字段找到Klass对象,从Klass对象获取。更准确说Klass对象是嵌在klassOopDesc对象,以便Klass对象也同样得到GC的统一管理。
所以其实是由于将instanceKlass这样的元数据也使用oop由GC来管理才会引入了instanceKlassKlass,到JDK8已经没有xxxKlassKlass了,因为instanceKlass这些元数据已经被移出GC堆,也不再需要klassOopDesc来指向instanceKlass了,oopDesc的_metadata字段定义已经改成下面这样了,
union _metadata {
/////// 之前都是oop,现在直接指向Klass了
Klass* _klass;
narrowKlass _compressed_klass;
} _metadata;
这应该也是移除PermGen的好处之一吧:)
这里有一个问题需要考虑下,为什么要多出xxxKlassKlass这一层呢?直接使用klassKlass来描述instanceKlass不OK吗(python就是这样的设计,见下文)?很明显,因为各种xxxKlassKlass要描述的xxxKlass并不同(xxxKlass的创建也都是由xxxKlassKlass来完成,例如instanceKlassKlass::allocate_instance_klass),具体的看代码吧:)
还有一点说明,instanceKlassKlass是个单例,
// An InstanceKlassKlass is the klass of an InstanceKlass.
// There only exist one instance Universe::instanceKlassKlassObj()
在虚拟机启动的时候,会调用instanceKlassKlass::create_klass来创建这个universe::instanceKlassKlassObj。
当然,klassKlass也会是单例。
数组对象
下面依葫芦画瓢,看下数组对象在HotSpotVM中是怎么表示的。new了这么一个数组对象,Foo[] fooArray = new Foo[]{new Foo(1234), new Foo(5678)},修改下Filter,
@Override
public boolean canInclude(Oop oop) {
if(oop.isObjArray()) {
Klass klass = ((ObjArrayKlass)oop.getKlass()).getElementKlass();
return klass.getName() != null &&
"me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo".equals(klass.getName().asString());
}
return false;
}
输出如下,
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.ObjArray@d6157fc8
ObjArray @ 0x00000007d6157fc8 (object size = 24)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :ObjArrayKlass for InstanceKlass for me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo @ 0x000000077d0c3278
- 0: {16} :Oop for me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo @ 0x00000007d6157fe0
- 1: {20} :Oop for me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo @ 0x00000007d6157ff0
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP.KLASS#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.ObjArrayKlass@7d0c3278
ObjArrayKlass for InstanceKlass for me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo @ 0x000000077d0c3278 (object size = 536)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :ObjArrayKlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce001a0
- _java_mirror: {120} :Oop for java/lang/Class @ 0x00000007d6157f58
- _super: {128} :ObjArrayKlass for InstanceKlass for java/lang/Object @ 0x000000077cea4810
- _layout_helper: {24} :-2146431998
- _access_flags: {156} :-2147483648
- _subklass: {136} :null
- _next_sibling: {144} :null
- _alloc_count: {160} :0
- _dimension: {200} :1
- _higher_dimension: {208} :null
- _lower_dimension: {216} :null
- _vtable_len: {224} :5
- _alloc_size: {228} :0
- _component_mirror: {232} :Oop for java/lang/Class @ 0x00000007d6157ee0
- _element_klass: {240} :InstanceKlass for me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo @ 0x000000077d0c3048
- _bottom_klass: {248} :InstanceKlass for me/kisimple/just4fun/Foo @ 0x000000077d0c3048
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP.KLASS.KLASS#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.ObjArrayKlassKlass@7ce001a0
ObjArrayKlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce001a0 (object size = 208)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :KlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00000
- _java_mirror: {120} :null
- _super: {128} :null
- _layout_helper: {24} :0
- _access_flags: {156} :0
- _subklass: {136} :null
- _next_sibling: {144} :null
- _alloc_count: {160} :0
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP.KLASS.KLASS.KLASS#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.KlassKlass@7ce00000
KlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00000 (object size = 208)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :KlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00000
- _java_mirror: {120} :null
- _super: {128} :null
- _layout_helper: {24} :0
- _access_flags: {156} :0
- _subklass: {136} :null
- _next_sibling: {144} :null
- _alloc_count: {160} :0
上面的输出有个问题,本来arrayOop的layout应该是这样的,
// The layout of array Oops is:
//
// markOop
// klassOop // 32 bits if compressed but declared 64 in LP64.
// length // shares klass memory or allocated after declared fields.
但是输出中并没有看到_length字段,不知道是SA的问题,还是下面这个原因?
// The _length field is not declared in C++. It is allocated after the
// declared nonstatic fields in arrayOopDesc if not compressed, otherwise
// it occupies the second half of the _klass field in oopDesc.
vs. python
python(准确点说是CPython)的对象机制实现其实跟HotSpotVM类似,下面将HotSpot的实现对应到python中来(使用python2.7版本)。
python中用于实现对象的基础数据结构定义在object.h中。HotSpot的instanceOop对应了PyObject,arrayOop对应了PyVarObject,
#ifdef Py_TRACE_REFS
/* Define pointers to support a doubly-linked list of all live heap objects. */
#define _PyObject_HEAD_EXTRA \
struct _object *_ob_next; \
struct _object *_ob_prev;
#define _PyObject_EXTRA_INIT 0, 0,
#else
#define _PyObject_HEAD_EXTRA
#define _PyObject_EXTRA_INIT
#endif
/* PyObject_HEAD defines the initial segment of every PyObject. */
#define PyObject_HEAD \
_PyObject_HEAD_EXTRA \
Py_ssize_t ob_refcnt; \
struct _typeobject *ob_type;
#define PyObject_HEAD_INIT(type) \
_PyObject_EXTRA_INIT \
1, type,
#define PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(type, size) \
PyObject_HEAD_INIT(type) size,
/* PyObject_VAR_HEAD defines the initial segment of all variable-size
* container objects. These end with a declaration of an array with 1
* element, but enough space is malloc'ed so that the array actually
* has room for ob_size elements. Note that ob_size is an element count,
* not necessarily a byte count.
*/
#define PyObject_VAR_HEAD \
PyObject_HEAD \
Py_ssize_t ob_size; /* Number of items in variable part */
#define Py_INVALID_SIZE (Py_ssize_t)-1
/* Nothing is actually declared to be a PyObject, but every pointer to
* a Python object can be cast to a PyObject*. This is inheritance built
* by hand. Similarly every pointer to a variable-size Python object can,
* in addition, be cast to PyVarObject*.
*/
typedef struct _object {
PyObject_HEAD
} PyObject;
typedef struct {
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
} PyVarObject;
两者的头部信息中,只有一个ob_refcnt来实现引用计数,不像HotSpot用了一个比较重的_mark对象指针(所以python没有办法像Java那样使用对象锁)。
Klass则对应了PyTypeObject,
typedef struct _typeobject {
PyObject_VAR_HEAD
const char *tp_name; /* For printing, in format "." */
Py_ssize_t tp_basicsize, tp_itemsize; /* For allocation */
/* Methods to implement standard operations */
destructor tp_dealloc;
printfunc tp_print;
getattrfunc tp_getattr;
setattrfunc tp_setattr;
cmpfunc tp_compare;
reprfunc tp_repr;
/* Method suites for standard classes */
PyNumberMethods *tp_as_number;
PySequenceMethods *tp_as_sequence;
PyMappingMethods *tp_as_mapping;
/* More standard operations (here for binary compatibility) */
hashfunc tp_hash;
ternaryfunc tp_call;
reprfunc tp_str;
getattrofunc tp_getattro;
setattrofunc tp_setattro;
/* Functions to access object as input/output buffer */
PyBufferProcs *tp_as_buffer;
/* Flags to define presence of optional/expanded features */
long tp_flags;
const char *tp_doc; /* Documentation string */
/* Assigned meaning in release 2.0 */
/* call function for all accessible objects */
traverseproc tp_traverse;
/* delete references to contained objects */
inquiry tp_clear;
/* Assigned meaning in release 2.1 */
/* rich comparisons */
richcmpfunc tp_richcompare;
/* weak reference enabler */
Py_ssize_t tp_weaklistoffset;
/* Added in release 2.2 */
/* Iterators */
getiterfunc tp_iter;
iternextfunc tp_iternext;
/* Attribute descriptor and subclassing stuff */
struct PyMethodDef *tp_methods;
struct PyMemberDef *tp_members;
struct PyGetSetDef *tp_getset;
struct _typeobject *tp_base;
PyObject *tp_dict;
descrgetfunc tp_descr_get;
descrsetfunc tp_descr_set;
Py_ssize_t tp_dictoffset;
initproc tp_init;
allocfunc tp_alloc;
newfunc tp_new;
freefunc tp_free; /* Low-level free-memory routine */
inquiry tp_is_gc; /* For PyObject_IS_GC */
PyObject *tp_bases;
PyObject *tp_mro; /* method resolution order */
PyObject *tp_cache;
PyObject *tp_subclasses;
PyObject *tp_weaklist;
destructor tp_del;
/* Type attribute cache version tag. Added in version 2.6 */
unsigned int tp_version_tag;
#ifdef COUNT_ALLOCS
/* these must be last and never explicitly initialized */
Py_ssize_t tp_allocs;
Py_ssize_t tp_frees;
Py_ssize_t tp_maxalloc;
struct _typeobject *tp_prev;
struct _typeobject *tp_next;
#endif
} PyTypeObject;
上面的tp_methods应该就相当于是我们看到的instanceKlass的methods字段了。
还有那俩胃疼的instanceKlassKlass和klassKlass对应的是啥?python的对象机制没有这么复杂,和这俩货对应的只有一个,PyType_Type,而它并不是又一个struct,它是一个PyTypeObject,在typeobject.c中定义,
PyTypeObject PyType_Type = {
PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(&PyType_Type, 0)
"type", /* tp_name */
sizeof(PyHeapTypeObject), /* tp_basicsize */
sizeof(PyMemberDef), /* tp_itemsize */
(destructor)type_dealloc, /* tp_dealloc */
0, /* tp_print */
0, /* tp_getattr */
0, /* tp_setattr */
0, /* tp_compare */
(reprfunc)type_repr, /* tp_repr */
0, /* tp_as_number */
0, /* tp_as_sequence */
0, /* tp_as_mapping */
(hashfunc)_Py_HashPointer, /* tp_hash */
(ternaryfunc)type_call, /* tp_call */
0, /* tp_str */
(getattrofunc)type_getattro, /* tp_getattro */
(setattrofunc)type_setattro, /* tp_setattro */
0, /* tp_as_buffer */
Py_TPFLAGS_DEFAULT | Py_TPFLAGS_HAVE_GC |
Py_TPFLAGS_BASETYPE | Py_TPFLAGS_TYPE_SUBCLASS, /* tp_flags */
type_doc, /* tp_doc */
(traverseproc)type_traverse, /* tp_traverse */
(inquiry)type_clear, /* tp_clear */
type_richcompare, /* tp_richcompare */
offsetof(PyTypeObject, tp_weaklist), /* tp_weaklistoffset */
0, /* tp_iter */
0, /* tp_iternext */
type_methods, /* tp_methods */
type_members, /* tp_members */
type_getsets, /* tp_getset */
0, /* tp_base */
0, /* tp_dict */
0, /* tp_descr_get */
0, /* tp_descr_set */
offsetof(PyTypeObject, tp_dict), /* tp_dictoffset */
type_init, /* tp_init */
0, /* tp_alloc */
type_new, /* tp_new */
PyObject_GC_Del, /* tp_free */
(inquiry)type_is_gc, /* tp_is_gc */
};
看上去要比HotSpot的实现清晰简洁一点。
下面我们再来对比下二者具体的整数对象的实现。python的整数对象定义在intobject.h(python3中已经统一到PyLongObject了),
typedef struct {
PyObject_HEAD
long ob_ival;
} PyIntObject;
而描述它的PyTypeObject则是PyInt_Type
PyTypeObject PyInt_Type = {
PyVarObject_HEAD_INIT(&PyType_Type, 0)
"int",
...
};
然后我们再来看下HotSpot的整数对象,还是使用上面SA的栗子,Integer integer = new Integer(7777777),输出如下,
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.Instance@d6158058
Oop for java/lang/Integer @ 0x00000007d6158058 (object size = 16)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :InstanceKlass for java/lang/Integer @ 0x000000077cea0e78
- value: {12} :7777777
////////////////////////////////////////
OOP.KLASS#sun.jvm.hotspot.oops.InstanceKlass@7cea0e78
InstanceKlass for java/lang/Integer @ 0x000000077cea0e78 (object size = 624)
- _mark: {0} :1
- _metadata._compressed_klass: {8} :InstanceKlassKlass @ 0x000000077ce00270
- _java_mirror: {120} :Oop for java/lang/Class @ 0x00000007d6003200
- _super: {128} :InstanceKlass for java/lang/Number @ 0x000000077ce97230
- _layout_helper: {24} :16
- _access_flags: {156} :49
- _subklass: {136} :null
- _next_sibling: {144} :InstanceKlass for java/lang/Short @ 0x000000077ce9d238
- _alloc_count: {160} :0
- _array_klasses: {200} :ObjArrayKlass for InstanceKlass for java/lang/Integer @ 0x000000077d0bc920
- _methods: {208} :ObjArray @ 0x000000077ce9dee0
- _method_ordering: {216} :[I @ 0x000000077cea0dc0
- _local_interfaces: {224} :ObjArray @ 0x000000077ce9de30
- _transitive_interfaces: {232} :ObjArray @ 0x000000077cea0da8
- _fields: {240} :[S @ 0x000000077ce9de48
- _constants: {248} :ConstantPool for java/lang/Integer @ 0x000000077ce9d4a8
- _class_loader: {256} :null
- _protection_domain: {264} :null
- _signers: {272} :null
- _inner_classes: {280} :[S @ 0x000000077cea0d88
- _nonstatic_field_size: {360} :1
- _static_field_size: {364} :6
- _static_oop_field_count: {368} :5
- _nonstatic_oop_map_size: {372} :0
- _is_marked_dependent: {376} :0
- _init_state: {490} :5
- _vtable_len: {392} :11
- _itable_len: {396} :5
所以其实PyIntObject对应的还是一个instanceOop(oop使用offset的方式来填充实例数据,所以不需要重新再定义一个数据结构),而PyInt_Type应该说对应的是一个instanceKlass的实例,其实也可以说是java.lang.Integer了:)
参考资料
- https://wiki.openjdk.java.net/display/HotSpot/CompressedOops
- http://openjdk.java.net/groups/hotspot/docs/FOSDEM-2007-HotSpot.pdf
- http://rednaxelafx.iteye.com/blog/730461
- http://rednaxelafx.iteye.com/blog/1847971
- http://hllvm.group.iteye.com/group/topic/37605
- http://blog.csdn.net/balabalamerobert/article/category/168910