Google TensorFlow课程 编程笔记(8)———神经网络简介
神经网络简介
学习目标:
- 使用 TensorFlow
DNNRegressor类定义神经网络 (NN) 及其隐藏层 - 训练神经网络学习数据集中的非线性规律,并实现比线性回归模型更好的效果
在之前的练习中,我们使用合成特征来帮助模型学习非线性规律。
一组重要的非线性关系是纬度和经度的关系,但也可能存在其他非线性关系。
现在我们从之前练习中的逻辑回归任务回到标准的(线性)回归任务。也就是说,我们将直接预测 median_house_value。
第1步:设置:加载必要的库+加载数据+数据预处理
from __future__ import print_function
import math
from IPython import display
from matplotlib import cm
from matplotlib import gridspec
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn import metrics
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.data import Dataset
tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.ERROR)
pd.options.display.max_rows = 10
pd.options.display.float_format = '{:.1f}'.format
california_housing_dataframe = pd.read_csv("https://dl.google.com/mlcc/mledu-datasets/california_housing_train.csv", sep=",")
california_housing_dataframe = california_housing_dataframe.reindex(
np.random.permutation(california_housing_dataframe.index))def preprocess_features(california_housing_dataframe):
"""Prepares input features from California housing data set.
Args:
california_housing_dataframe: A Pandas DataFrame expected to contain data
from the California housing data set.
Returns:
A DataFrame that contains the features to be used for the model, including
synthetic features.
"""
selected_features = california_housing_dataframe[
["latitude",
"longitude",
"housing_median_age",
"total_rooms",
"total_bedrooms",
"population",
"households",
"median_income"]]
processed_features = selected_features.copy()
# Create a synthetic feature.
processed_features["rooms_per_person"] = (
california_housing_dataframe["total_rooms"] /
california_housing_dataframe["population"])
return processed_features
def preprocess_targets(california_housing_dataframe):
"""Prepares target features (i.e., labels) from California housing data set.
Args:
california_housing_dataframe: A Pandas DataFrame expected to contain data
from the California housing data set.
Returns:
A DataFrame that contains the target feature.
"""
output_targets = pd.DataFrame()
# Scale the target to be in units of thousands of dollars.
output_targets["median_house_value"] = (
california_housing_dataframe["median_house_value"] / 1000.0)
return output_targets
第2步:预览检查数据
# Choose the first 12000 (out of 17000) examples for training.
training_examples = preprocess_features(california_housing_dataframe.head(12000))
training_targets = preprocess_targets(california_housing_dataframe.head(12000))
# Choose the last 5000 (out of 17000) examples for validation.
validation_examples = preprocess_features(california_housing_dataframe.tail(5000))
validation_targets = preprocess_targets(california_housing_dataframe.tail(5000))
# Double-check that we've done the right thing.
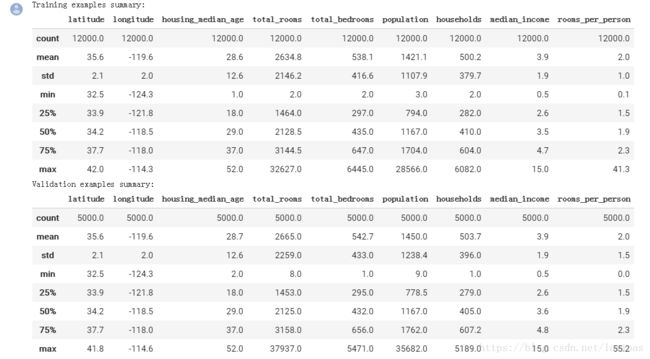
print("Training examples summary:")
display.display(training_examples.describe())
print("Validation examples summary:")
display.display(validation_examples.describe())
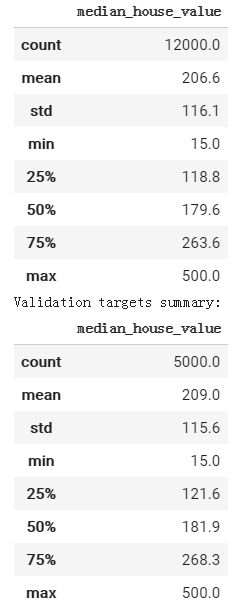
print("Training targets summary:")
display.display(training_targets.describe())
print("Validation targets summary:")
display.display(validation_targets.describe())构建神经网络
神经网络由 DNNRegressor 类定义。
使用 hidden_units 定义神经网络的结构。hidden_units 参数会创建一个整数列表,其中每个整数对应一个隐藏层,表示其中的节点数。以下面的赋值为例:
hidden_units=[3,10]
上述赋值为神经网络指定了两个隐藏层:
- 第一个隐藏层包含 3 个节点。
- 第二个隐藏层包含 10 个节点。
如果我们想要添加更多层,可以向该列表添加更多整数。例如,hidden_units=[10,20,30,40] 会创建 4 个分别包含 10、20、30 和 40 个单元的隐藏层。
默认情况下,所有隐藏层都会使用 ReLu 激活函数,且是全连接层。
第三步:样本特征列的选择
def construct_feature_columns(input_features):
"""Construct the TensorFlow Feature Columns.
Args:
input_features: The names of the numerical input features to use.
Returns:
A set of feature columns
"""
return set([tf.feature_column.numeric_column(my_feature)
for my_feature in input_features])第四步:输入函数
def my_input_fn(features, targets, batch_size=1, shuffle=True, num_epochs=None):
"""Trains a linear regression model of one feature.
Args:
features: pandas DataFrame of features
targets: pandas DataFrame of targets
batch_size: Size of batches to be passed to the model
shuffle: True or False. Whether to shuffle the data.
num_epochs: Number of epochs for which data should be repeated. None = repeat indefinitely
Returns:
Tuple of (features, labels) for next data batch
"""
# Convert pandas data into a dict of np arrays.
features = {key:np.array(value) for key,value in dict(features).items()}
# Construct a dataset, and configure batching/repeating
ds = Dataset.from_tensor_slices((features,targets)) # warning: 2GB limit
ds = ds.batch(batch_size).repeat(num_epochs)
# Shuffle the data, if specified
if shuffle:
ds = ds.shuffle(10000)
# Return the next batch of data
features, labels = ds.make_one_shot_iterator().get_next()
return features, labels第五步:训练模型:神经网络回归模型
def train_nn_regression_model(
learning_rate,
steps,
batch_size,
hidden_units,
training_examples,
training_targets,
validation_examples,
validation_targets):
"""Trains a neural network regression model.
In addition to training, this function also prints training progress information,
as well as a plot of the training and validation loss over time.
Args:
learning_rate: A `float`, the learning rate.
steps: A non-zero `int`, the total number of training steps. A training step
consists of a forward and backward pass using a single batch.
batch_size: A non-zero `int`, the batch size.
hidden_units: A `list` of int values, specifying the number of neurons in each layer.
training_examples: A `DataFrame` containing one or more columns from
`california_housing_dataframe` to use as input features for training.
training_targets: A `DataFrame` containing exactly one column from
`california_housing_dataframe` to use as target for training.
validation_examples: A `DataFrame` containing one or more columns from
`california_housing_dataframe` to use as input features for validation.
validation_targets: A `DataFrame` containing exactly one column from
`california_housing_dataframe` to use as target for validation.
Returns:
A `LinearRegressor` object trained on the training data.
"""
periods = 10
steps_per_period = steps / periods
# Create a linear regressor object.
my_optimizer = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate)
my_optimizer = tf.contrib.estimator.clip_gradients_by_norm(my_optimizer, 5.0)
"""这里使用 TensorFlow DNNRegressor 类定义神经网络 (NN) 及其隐藏层"""
dnn_regressor = tf.estimator.DNNRegressor(
feature_columns=construct_feature_columns(training_examples),
hidden_units=hidden_units
)
# Create input functions
training_input_fn = lambda: my_input_fn(training_examples,
training_targets["median_house_value"],
batch_size=batch_size)
predict_training_input_fn = lambda: my_input_fn(training_examples,
training_targets["median_house_value"],
num_epochs=1,
shuffle=False)
predict_validation_input_fn = lambda: my_input_fn(validation_examples,
validation_targets["median_house_value"],
num_epochs=1,
shuffle=False)
# Train the model, but do so inside a loop so that we can periodically assess
# loss metrics.
print("Training model...")
print("RMSE (on training data):")
training_rmse = []
validation_rmse = []
for period in range (0, periods):
# Train the model, starting from the prior state.
dnn_regressor.train(
input_fn=training_input_fn,
steps=steps_per_period
)
# Take a break and compute predictions.
training_predictions = dnn_regressor.predict(input_fn=predict_training_input_fn)
training_predictions = np.array([item['predictions'][0] for item in training_predictions])
validation_predictions = dnn_regressor.predict(input_fn=predict_validation_input_fn)
validation_predictions = np.array([item['predictions'][0] for item in validation_predictions])
# Compute training and validation loss.
training_root_mean_squared_error = math.sqrt(
metrics.mean_squared_error(training_predictions, training_targets))
validation_root_mean_squared_error = math.sqrt(
metrics.mean_squared_error(validation_predictions, validation_targets))
# Occasionally print the current loss.
print(" period %02d : %0.2f" % (period, training_root_mean_squared_error))
# Add the loss metrics from this period to our list.
training_rmse.append(training_root_mean_squared_error)
validation_rmse.append(validation_root_mean_squared_error)
print("Model training finished.")
# Output a graph of loss metrics over periods.
plt.ylabel("RMSE")
plt.xlabel("Periods")
plt.title("Root Mean Squared Error vs. Periods")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.plot(training_rmse, label="training")
plt.plot(validation_rmse, label="validation")
plt.legend()
print("Final RMSE (on training data): %0.2f" % training_root_mean_squared_error)
print("Final RMSE (on validation data): %0.2f" % validation_root_mean_squared_error)
return dnn_regressor任务 1:训练神经网络模型
调整超参数,目标是将 RMSE 降到 110 以下。
运行以下代码块来训练神经网络模型。
我们已经知道,在使用了很多特征的线性回归练习中,110 左右的 RMSE 已经是相当不错的结果。我们将得到比它更好的结果。
在此练习中,您的任务是修改各种学习设置,以提高在验证数据上的准确率。
对于神经网络而言,过拟合是一种真正的潜在危险。您可以查看训练数据损失与验证数据损失之间的差值,以帮助判断模型是否有过拟合的趋势。如果差值开始变大,则通常可以肯定存在过拟合。
由于存在很多不同的可能设置,强烈建议您记录每次试验,以在开发流程中进行参考。
此外,获得效果出色的设置后,尝试多次运行该设置,看看结果的重复程度。由于神经网络权重通常会初始化为较小的随机值,因此每次运行结果应该存在差异。
第六步:调整训练模型参数开始训练
初次输入参数
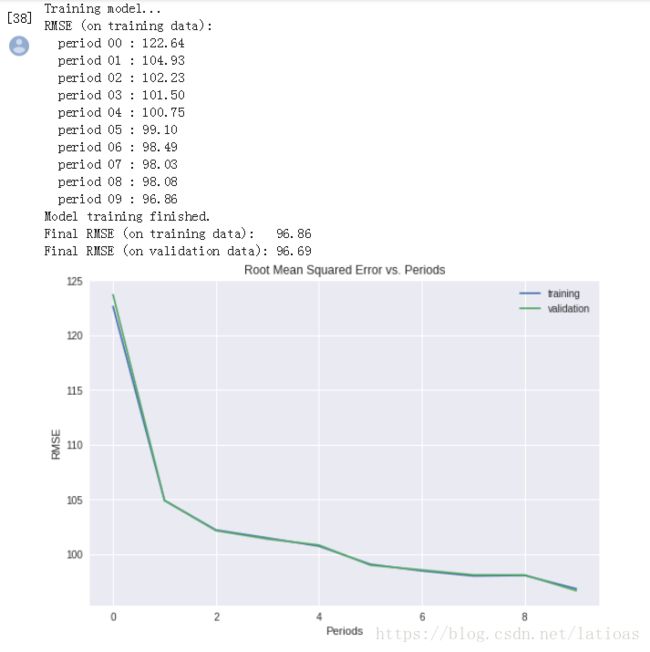
dnn_regressor = train_nn_regression_model(
learning_rate=0.01,
steps=500,
batch_size=10,
hidden_units=[10, 2],
training_examples=training_examples,
training_targets=training_targets,
validation_examples=validation_examples,
validation_targets=validation_targets)第二次调整参数,希望训练损失可以更少一点,减小学习速率,增加节点个数等
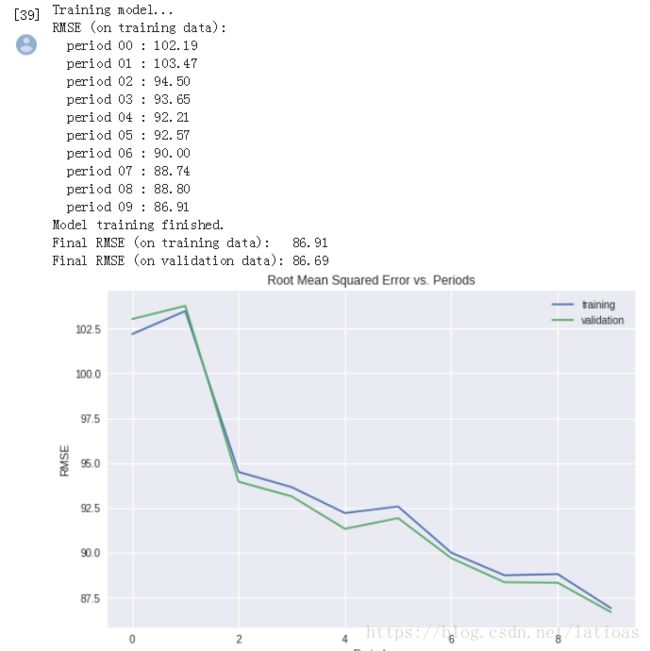
dnn_regressor = train_nn_regression_model(
learning_rate=0.001,
steps=2000,
batch_size=100,
hidden_units=[10, 10],
training_examples=training_examples,
training_targets=training_targets,
validation_examples=validation_examples,
validation_targets=validation_targets)
训练损失从96降至86,效果好了很多。
第七步:用测试数据进行评估
确认您的验证效果结果经受得住测试数据的检验。
获得满意的模型后,用测试数据评估该模型,以与验证效果进行比较。
california_housing_test_data = pd.read_csv("https://dl.google.com/mlcc/mledu-datasets/california_housing_test.csv", sep=",")
test_examples = preprocess_features(california_housing_test_data)
test_targets = preprocess_targets(california_housing_test_data)
predict_testing_input_fn = lambda: my_input_fn(test_examples,
test_targets["median_house_value"],
num_epochs=1,
shuffle=False)
test_predictions = dnn_regressor.predict(input_fn=predict_testing_input_fn)
test_predictions = np.array([item['predictions'][0] for item in test_predictions])
root_mean_squared_error = math.sqrt(
metrics.mean_squared_error(test_predictions, test_targets))
print("Final RMSE (on test data): %0.2f" % root_mean_squared_error)
测试损失为87.18,和我们的训练效果接近,说明泛化效果良好。
在调节参数的时候我进行了多次尝试,发现神经网络的层数不是越多越好,所以调参的时候并不能一味地增加神经网络的层数。
而增加每层神经网络的节点数,不会有明显的恶化效果,但也没有明显的效果提升,而且数据量大的时候运行速度很受影响。
本文仅为个人学习笔记记录,请结合Google 机器学习,编程练习:神经网络简介
编程练习地址:https://colab.research.google.com/notebooks/mlcc/intro_to_neural_nets.ipynb?hl=zh-cn#scrollTo=vhb0CtdvrWZx