数据结构 JAVA描述(八) 最短路径+拓扑排序+关键路径
最短路径
迪杰斯特拉算法
原文分析思路(理解不了这里就pass掉):在有向网中,从某一源点到其余各点都有一条最短路径。首先在这些最短路径中,长度最短的必定只有一条弧,且它的权值是从源点出发的所有弧上权的最小值;其次,第二条长度次短的最短路径只可能有两种情况:
从源点出发的一条弧,权值大于已求的最短路径的那条弧,但小于其他的从源点出发的弧的权值
是一条经过已求得最短路径的路径
该算法需要引入辅助数组D,每个分量D[i]存放当前所找到的从源点到各个终点vi的最短路径的长度。过程是:
(1)令S = {v},其中v为源点,并设定D[i] 的初始值为:D[i] = |v,vi|
(2)选择顶点vj使得:D[j] = min{D[i]}(i∈V-S),并将vj并入到S中
(3)对集合V-S的所有顶点vk,若D[j] + |vj,vk| < D[k],则修改D[k]的值
(4)重复(2)、(3)的操作共n-1次,由此求得的所有最短路径是按路径长度递增的序列
ShortestPath_DIJ
package Graph;
/**
* @description 求最短路径的问题 迪杰斯特拉 算法
* (1)令S = {v},其中v为源点,并设定D[i] 的初始值为:D[i] = |v,vi|
* (2)选择顶点vj使得:D[j] = min{D[i]}(i∈V-S),并将vj并入到S中
* (3)对集合V-S的所有顶点vk,若D[j] + |vj,vk| < D[k],则修改D[k]的值
* (4)重复(2)、(3)的操作共n-1次,由此求得的所有最短路径是按路径长度递增的序列
* @date 2015年12月31日
*/
public class ShortestPath_DIJ {
// v0到其余顶点的最短路径,若p[v][w]为true,则w是从v0到v当前求得最短路径上的顶点
private boolean[][] P;
// v0到其余顶点的最小带权长度 (是变化的,一旦发现更小的,就重新赋值,到最后就是最短路径长度了)
private int[] D;
private final static int INFINITY = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public boolean[][] getP() {
return P;
}
public int[] getD() {
return D;
}
/**
* @description 用迪杰斯特拉算法求有向网的v0到其余顶点的最短路径p[v]及其权值D[v]
* @date 2015年12月31日
*/
public void DIJ(MGraph G, int v0){
int vexNum = G.getVexNum(); // 顶点数
this.P = new boolean[vexNum][vexNum];
this.D = new int[vexNum];
//finish[v]为true当且仅当v属于S,即已经求得从v0到v的最短路径
boolean[] finish = new boolean[vexNum];
//初始化所有数据
for(int v = 0; v < vexNum; v++){
finish[v] = false;
D[v] = G.getArcs()[v0][v];
for(int w = 0; w < vexNum; w++){
P[v][w] = false;
}
if(D[v] < INFINITY){
P[v][v0] = true;
P[v][v] = true;
}
}
D[v0] = 0; //从v0开始,并入S集
finish[v0] = true;
int v = -1 ; // 这里的赋值没有什么实际意义,只是为了保证编译正确
//开始主循环,每次求得v0到某个v顶点的最短路径,并将v加入到S集.循环n-1次
for(int i = 1; i < vexNum; i++){
int min = INFINITY; //当前所知离v0最近的距离
for(int w = 0; w < vexNum; w++){
if( !finish[w]){
if(D[w] < min){
v = w;
min = D[w];
}
}
}
finish[v] = true; //离v0最近的v并入S
//更新当前最短路径和距离
for(int w = 0; w < vexNum; w++){
if( !finish[w] && G.getArcs()[v][w] < INFINITY && (min + G.getArcs()[v][w] < D[w])){
D[w] = min + G.getArcs()[v][w];
//下面两句这么理解,现在路径是v0-v-w,所以经过了v点,那么v0到v的最小路径自然要给w,同时再加上w点(P[W][W] = true)
System.arraycopy(P[v], 0, P[w], 0, P[v].length);
P[w][w] = true;
}
}
}
}
// 测试
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
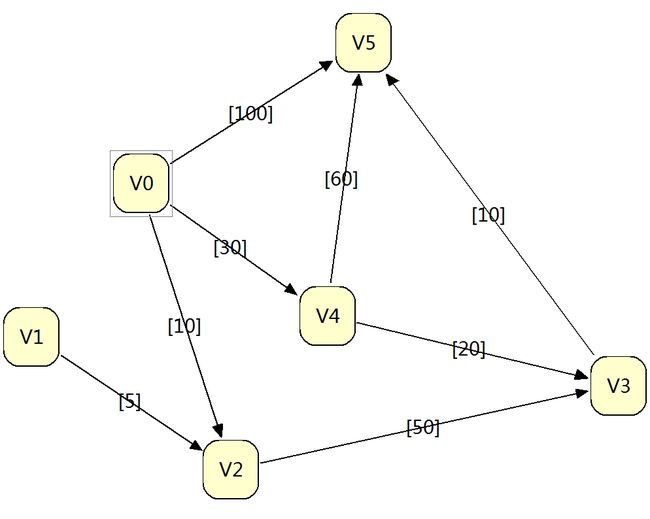
Object[] vexs = { "v0", "v1", "v2", "v3", "v4", "v5" };
int[][] arcs = { { INFINITY, INFINITY, 10, INFINITY, 30, 100 },
{ INFINITY, INFINITY, 5, INFINITY, INFINITY, INFINITY },
{ INFINITY, INFINITY, INFINITY, 50, INFINITY, INFINITY },
{ INFINITY, INFINITY, INFINITY, INFINITY, INFINITY, 10 },
{ INFINITY, INFINITY, INFINITY, 20, INFINITY, 60 },
{ INFINITY, INFINITY, INFINITY, INFINITY, INFINITY, INFINITY } };
MGraph G = new MGraph(GraphKind.DG, 6, 8, vexs, arcs);
ShortestPath_DIJ dij = new ShortestPath_DIJ();
dij.DIJ(G, 0);
for(int i = 0; i < vexs.length; i++){
System.out.println("从v0出发,到" + G.getVex(i) + "的最短路径长度是:" + (dij.getD()[i] == INFINITY ? "∞" : dij.getD()[i]) );
System.out.print("经过结点有:");
for(int j = 0; j < vexs.length; j++){
if(dij.getP()[i][j]) //即从v0到i位置的顶点经过了j位置的顶点
System.out.print(G.getVex(j) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}测试分析图
从源点v0到各个终点的D值和最短路径的求解过程:
| 终点 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| v1 | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞ | ∞无 |
| v2 | 10(v0,v2) | ||||
| v3 | ∞ | 60(v0,v2,v3) | 50(v0,v4,v3) | ||
| v4 | 30(v0,v4) | 30(v0,v4) | |||
| v5 | 100(v0,v5) | 100(v0,v5) | 90(v0,v4,v5) | 60(v0,v4,v3,v5) | |
| vj | v2 | v4 | v3 | v5 | |
| S | {v0,v2} | {v0,v2,v4} | {v0,v2,v3,v4} | {v0,v2,v3,v4,v5} |
弗洛伊德算法
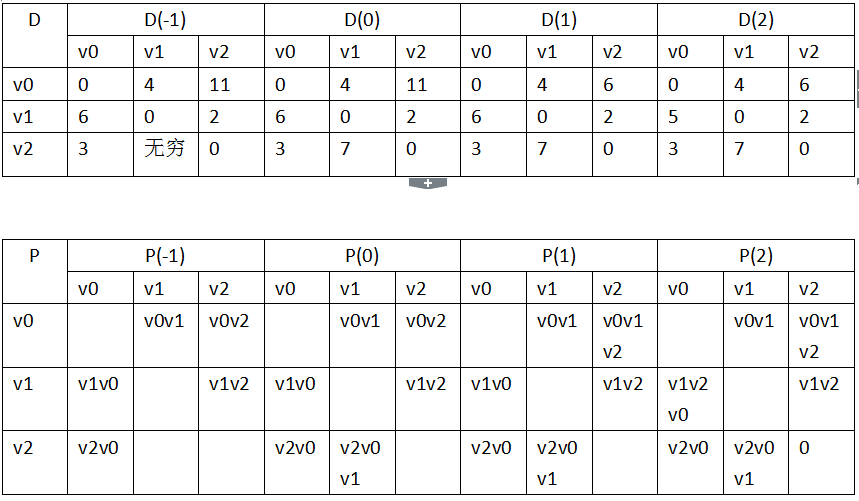
基本思想是:求得一个n阶方阵序列:{D(-¹),D(º),D(¹) …… D(n-1)},其中D(-¹)[i][j]表示从vi出发,不经过其他顶点直接到达vj的路径长度,D(k)则表示从vi到vj的中间只可能经过v0,v1……,vk,而不可能经过v k+1,v k+2等顶点的最短路径长度。
ShortestPath_FLOYD
package Graph;
/**
* @description 求最短路径的问题 弗洛伊德 算法 注意其成员变量的含义和迪杰斯特拉算法的完全不一样
* @date 2015年12月31日
*/
public class ShortestPath_FLOYD {
//顶点v和w之间的最短路径P[v][w],若P[v][w][u]为true,则u是从v到w当前求得最短路径上的顶点
private boolean[][][] P;
//顶点v和w之间的最短路径的带权长度D[v][w]
private int[][] D;
public final static int INFINITY = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
public boolean[][][] getP() {
return P;
}
public int[][] getD() {
return D;
}
public void FLOYD(MGraph G){
int vexNum = G.getVexNum();
this.P = new boolean[vexNum][vexNum][vexNum];
this.D = new int[vexNum][vexNum];
//初始化所有数据
for(int v = 0; v < vexNum; v++){
for(int w = 0; w < vexNum; w++){
D[v][w] = G.getArcs()[v][w];
for(int u = 0; u < vexNum; u++)
P[v][w][u] = false;
if(D[v][w] < INFINITY) { //从v到w有直接路径
P[v][w][v] = true;
P[v][w][w] = true;
}
}
}
for(int u = 0; u < vexNum; u++)
for(int v = 0; v < vexNum; v++)
for(int w = 1; w < vexNum; w++)
if(D[v][u] < INFINITY && D[u][w] < INFINITY && D[v][u] + D[u][w] < D[v][w]){
D[v][w] = D[v][u] + D[u][w];
for(int i = 0; i< vexNum; i++)
P[v][w][i] = P[v][u][i] || P[u][w][i];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
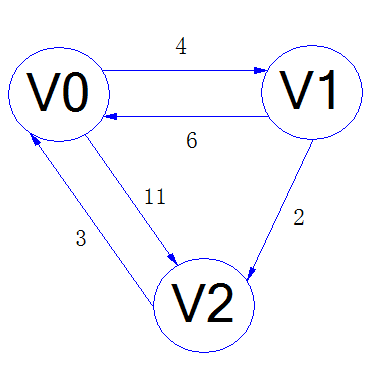
Object[] vexs = { "A", "B", "C", "D"};
int[][] arcs = { { 0, 15, 3, INFINITY},
{ 10, 0, 2, INFINITY},
{ INFINITY, INFINITY, 0, 2},
{ INFINITY, 8, 4, 0} };
MGraph G = new MGraph(GraphKind.DG, 4, 7, vexs, arcs);
ShortestPath_FLOYD floyd = new ShortestPath_FLOYD();
floyd.FLOYD(G);
for(int i = 0; i < vexs.length; i++){
System.out.println("从" + G.getVex(i) + "出发:");
for(int j = 0; j < vexs.length; j++){
System.out.println("到" + G.getVex(j) + "的最短路径长度是:" + (floyd.getD()[i][j] == INFINITY ? "∞" : floyd.getD()[i][j]) );
System.out.print("经过结点有:");
for(int k = 0; k < vexs.length; k++){
if(floyd.getP()[i][j][k]) //即从vi到vj经过了k位置的顶点
System.out.print(G.getVex(k) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
}测试分析图
拓扑排序
判断有向网中是否存在有向环的一个办法是:针对AOV(活动顶点图,Activity On Vertex Network)网进行拓扑排序
在AOV网中选择一个没有前驱的结点并输出
从AOV网中删除该结点以及从它出发的弧
重复以上过程,直至AOV网为空,或者剩余子图中不存在没有前驱的顶点(说明该AOV网中存在有向环)
Topological
package Graph;
import Stack.LinkStack;
/**
* @Description 拓扑排序算法
* @author liuquan
* @time 2016年1月1日 下午3:58:13
*/
public class Topological {
/**
* @description 求各个顶点入度的算法
* @param G
* @return
* @throws Exception
* @time 2016年1月1日 下午4:02:49
*/
public static int[] findInDegree(ALGraph G) throws Exception{
int[] indegree = new int[G.getVexNum()];
for(int i = 0; i < G.getVexNum(); i++)
for(ArcNode arc = G.getVexs()[i].getFirstArc(); arc != null; arc = arc.getNextArc())
++ indegree[arc.getAdjVex()]; //入度增1
return indegree;
}
/**
* @description 若G无回路,则输出G的顶点的一个拓扑排序序列并返回true
* @param G
* @return
* @throws Exception
* @time 2016年1月1日 下午4:13:04
*/
public static boolean topologicalSort(ALGraph G) throws Exception{
int count = 0; //输出顶点计数
int[] indegree = findInDegree(G); //求各个顶点的入度
LinkStack S = new LinkStack(); //零入度的 顶点栈
for(int i = 0; i < G.getVexNum(); i++)
if(indegree[i] == 0)
S.push(i); //入度为0的进栈
while( !S.isEmpty()){
int i = (Integer) S.pop();
System.out.print(G.getVex(i) + " "); //输出v号顶点并计数
++count;
for(ArcNode arc = G.getVexs()[i].getFirstArc(); arc != null; arc = arc.getNextArc()){
int k = arc.getAdjVex();
if(--indegree[k] == 0) // 对k号顶点的每个邻接点的入度减1
S.push(k);
}
}
if(count < G.getVexNum())
return false; //该有向图有回路
else
return true;
}
// 测试
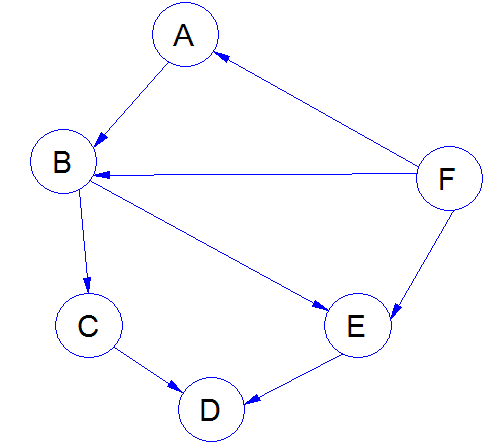
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ArcNode ab = new ArcNode(1);
VNode A = new VNode("A", ab);
ArcNode bc = new ArcNode(2);
ArcNode be = new ArcNode(4, 0, bc);
VNode B = new VNode("B", be);
ArcNode cd = new ArcNode(3);
VNode C = new VNode("C", cd);
VNode D = new VNode("D");
ArcNode ed = new ArcNode(3);
VNode E = new VNode("E", ed);
ArcNode fa = new ArcNode(0);
ArcNode fb = new ArcNode(1, 0, fa);
ArcNode fe = new ArcNode(4, 0, fb);
VNode F = new VNode("F", fb);
VNode[] vexs = {A, B, C, D, E, F};
ALGraph G = new ALGraph(GraphKind.DG, 6, 8, vexs);
System.out.println(topologicalSort(G));
}
}测试分析图:
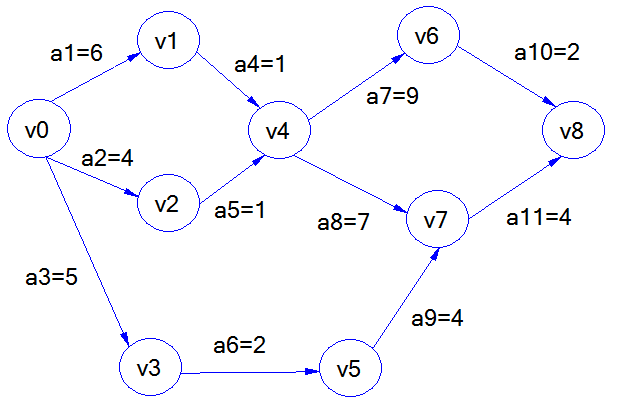
关键路径:
以弧表示活动,弧上的权值表示进行该项活动所需的时间,以顶点表示“事件”,称这种有向图为活动网,简称AOE(Activity On Edge)。
从源点v0出发,令ve0=0,按拓扑排序序列,求其余各顶点的ve(j)=max{ve(i) + |i,j|},i,j∈T,T是所有以第j个顶点为头的弧的集合
从汇点vn-1出发,令vl(n-1) = ve(n-1),按逆拓扑排序求其余顶点允许的最迟开始时间为:vl(i)= min{vl(j)-|i,j|},i,j∈S,S是所有以第j个顶点为尾的弧的集合
求每一项活动ai的最早开始时间e(i)=ve(j)和最迟开始时间l(i)=vl(j)-|i,j|。若满足e(i)=l(i),则它是关键路径。
测试分析图:
| 事件 | ve | vl |
|---|---|---|
| v0 | 0 | 0 |
| v1 | 6 | 6 |
| v2 | 4 | 6 |
| v3 | 5 | 8 |
| v4 | 7 | 7 |
| v5 | 7 | 10 |
| v6 | 16 | 16 |
| v7 | 14 | 14 |
| v8 | 18 | 18 |
| 活动 | e | l | l-e |
|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | 0(ve0) | 0(vl1-/v0v1/) | 0 |
| a2 | 0(ve0) | 2(vl2-/v0v2/) | 2 |
| a3 | 0(ve0) | 3(vl3-/v0v3/) | 3 |
| a4 | 6(ve1) | 6(vl4-/v1v4/) | 0 |
| a5 | 4(ve2) | 6(vl4-/v2v4/) | 2 |
| a6 | 5(ve3) | 8(vl5-/v3v5/) | 3 |
| a7 | 7(ve4) | 7(vl6-/v4v6/) | 0 |
| a8 | 7(ve4) | 7(vl7-/v4v7/) | 0 |
| a9 | 7(ve5) | 10(vl7-/v5v7/) | 3 |
| a10 | 16(ve10) | 16(vl8-/v6v8/) | 0 |
| a11 | 14(ve11) | 14(vl8-/v7v8/) | 0 |
CriticalPath :
package Graph;
import Stack.LinkStack;
/**
* @Description AOE网的关键路径
* @time 2016年1月2日 下午10:24:51
*/
public class CriticalPath {
private LinkStack T = new LinkStack(); //拓扑排序的顶点栈
private int[] ve, vl; //各顶点的最早发生时间和最迟发生时间
/**
* @description 求各个顶点入度的算法
* @param G
* @return
* @throws Exception
* @time 2016年1月1日 下午4:02:49
*/
public int[] findInDegree(ALGraph G) throws Exception{
int[] indegree = new int[G.getVexNum()];
for(int i = 0; i < G.getVexNum(); i++)
for(ArcNode arc = G.getVexs()[i].getFirstArc(); arc != null; arc = arc.getNextArc())
++ indegree[arc.getAdjVex()]; //入度增1
return indegree;
}
/**
* @description 求各个顶点的最早发生时间ve,若G无回路,用栈T存放一个拓扑排序,且函数返回true
* @param G
* @return
* @throws Exception
* @time 2016年1月1日 下午4:13:04
*/
public boolean topologicalOrder(ALGraph G) throws Exception{
int count = 0; //输出顶点计数
int[] indegree = findInDegree(G); //求各个顶点的入度
LinkStack S = new LinkStack(); //零入度的 顶点栈
for(int i = 0; i < G.getVexNum(); i++)
if(indegree[i] == 0)
S.push(i); //入度为0的进栈
this.ve = new int[G.getVexNum()]; //初始化
while( !S.isEmpty()){
int i = (Integer) S.pop();
this.T.push(i); //i号顶点入T栈并计数
++count;
for(ArcNode arc = G.getVexs()[i].getFirstArc(); arc != null; arc = arc.getNextArc()){
int k = arc.getAdjVex();
if(--indegree[k] == 0) // 对k号顶点的每个邻接点的入度减1
S.push(k);
if(ve[i] + arc.getValue() > ve[k])
ve[k] = ve[i] + arc.getValue();
}
}
if(count < G.getVexNum())
return false; //该有向图有回路
else
return true;
}
/**
* @description 输出G的各项关键活动
* @param G
* @return
* @throws Exception
* @time 2016年1月2日 下午10:53:20
*/
public boolean criticalPath(ALGraph G) throws Exception{
if( !topologicalOrder(G))
return false;
vl = new int[G.getVexNum()];
// 初始化各顶点事件的最迟发生时间
for(int i = 0; i < G.getVexNum(); i++){
vl[i] = ve[G.getVexNum() - 1];
}
while( !T.isEmpty()){ // 按拓扑序列 逆序 求各顶点的vl值
int i = (int) T.pop();
for(ArcNode arc = G.getVexs()[i].getFirstArc(); arc != null; arc = arc.getNextArc()){
int k = arc.getAdjVex();
int value = arc.getValue();
if(vl[k] - value < vl[i])
vl[i] = vl[k] - value;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < G.getVexNum(); i++){
//求ee,el和关键路径
for(ArcNode arc = G.getVexs()[i].getFirstArc(); arc != null; arc = arc.getNextArc()){
int k = arc.getAdjVex();
int value = arc.getValue();
int ee = ve[i];
int el = vl[k] - value;
System.out.println(G.getVex(i) + "->" + G.getVex(k) + "\t最早开始时间:" + ee + ",最迟开始时间:"+ el +"。" + (ee == el ? "YES" : "NO"));
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ArcNode v01 = new ArcNode(1, 6);
ArcNode v02 = new ArcNode(2, 4, v01);
ArcNode v03 = new ArcNode(3, 5, v02);
VNode v0 = new VNode("v0", v03);
ArcNode v14 = new ArcNode(4, 1);
VNode v1 = new VNode("v1", v14);
ArcNode v24 = new ArcNode(4, 1);
VNode v2 = new VNode("v2", v24);
ArcNode v35 = new ArcNode(5, 2);
VNode v3 = new VNode("v3", v35);
ArcNode v46 = new ArcNode(6, 9);
ArcNode v47 = new ArcNode(7, 7, v46);
VNode v4 = new VNode("v4", v47);
ArcNode v57 = new ArcNode(7, 4);
VNode v5 = new VNode("v5", v57);
ArcNode v68 = new ArcNode(8, 2);
VNode v6 = new VNode("v6", v68);
ArcNode v78 = new ArcNode(8, 4);
VNode v7 = new VNode("v7", v78);
VNode v8 = new VNode("v8");
VNode[] vexs = {v0, v1, v2, v3, v4, v5, v6, v7, v8};
ALGraph G = new ALGraph(GraphKind.DG, 9, 11, vexs);
new CriticalPath().criticalPath(G);
}
}需要注意的是:并不是加快任何一个关键路径活动都可以缩短整个工程完成的时间,只有在不改变AOE网的关键路径的前提下,加快包含在关键路径上的活动才可以缩短整个工程的完成时间。