第4门课程-卷积神经网络-第四周作业(图像风格转换)
0- 背景
所谓的风格转换是基于一张Content图像和一张Style图像,将两者融合,生成一张新的图像,分别兼具两者的内容和风格。
所需要的依赖如下:
import os
import sys
import scipy.io
import scipy.misc
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.pyplot import imshow
from PIL import Image
from nst_utils import *
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
%matplotlib inline1- Transfer Learning
迁移学习是将其他任务的学习结果应用于一个新的任务。Neural Style Transfer (NST) 就是基于已经训练过用于其他任务的convolutional network模型。
我们采用的是VGG network,该模型是基于大量的ImageNet database训练出的,学习到很多高级和低级层次的特征。
模型加载:
model = load_vgg_model("pretrained-model/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat")
print(model)
#注:该模型可以从http://www.vlfeat.org/matconvnet/models/beta16/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat下载到,有些大,500MB左右输出信息:
{'conv5_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_12:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_8:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool1': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool:0' shape=(1, 150, 200, 64) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_3': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_10:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv2_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_2:0' shape=(1, 150, 200, 128) dtype=float32>, 'conv5_3': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_14:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'input': <tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(1, 300, 400, 3) dtype=float32_ref>, 'avgpool2': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_1:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 128) dtype=float32>, 'conv3_4': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_7:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv5_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_13:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv3_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_4:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv3_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_5:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool3': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_2:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv3_3': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_6:0' shape=(1, 75, 100, 256) dtype=float32>, 'conv5_4': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_15:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv1_1': <tf.Tensor 'Relu:0' shape=(1, 300, 400, 64) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_9:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool5': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_4:0' shape=(1, 10, 13, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv4_4': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_11:0' shape=(1, 38, 50, 512) dtype=float32>, 'conv2_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_3:0' shape=(1, 150, 200, 128) dtype=float32>, 'conv1_2': <tf.Tensor 'Relu_1:0' shape=(1, 300, 400, 64) dtype=float32>, 'avgpool4': <tf.Tensor 'AvgPool_3:0' shape=(1, 19, 25, 512) dtype=float32>}该model以字典方式存储,其中的key是变量名,对应的值则是其作为一个tensor所对应的变量值。我们可以通过以下方式将图像输入到模型中:
model["input"].assign(image)当我们想要查看特定网络层的激活值,可以如下操作:
sess.run(model["conv4_2"])conv4_2是对应的Tensor。
2- Neural Style Transfer
构建风格转换算法的流程如下:
- 创建content cost function Jcontent(C,G) J c o n t e n t ( C , G )
- 创建the style cost function Jstyle(S,G) J s t y l e ( S , G )
- 联合创建整体代价函数 J(G)=αJcontent(C,G)+βJstyle(S,G) J ( G ) = α J c o n t e n t ( C , G ) + β J s t y l e ( S , G ) .
2-1 - Computing the content cost
对于content image C,可以采用以下方式show查看:
content_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/louvre.jpg")
imshow(content_image)对于层数的选择,我们一般不取太大也不取太小。层数太多,提取了更高级特征,在内容上的相似度,在视觉效果上就不好,层数太少,提取的特征又太低级,也不行。这点,可以设置不同的网络层数,然后观察对比具体结果。
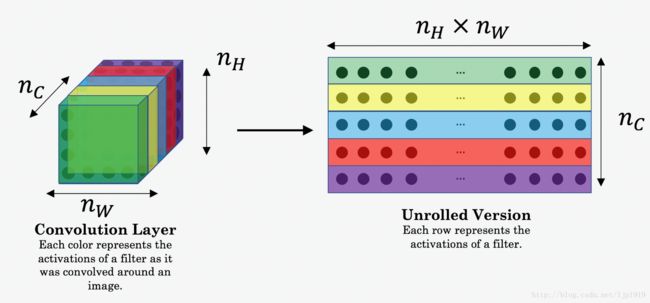
假设我们选取第 l l 层的网络进行分析,image C输入到预训练的VGG network,并进行前向传播。 a(C) a ( C ) 是该层的激活值,其tensor的尺寸= nH×nW×nC n H × n W × n C 。对于image G做相同的处理:图像 G输入到网络,前向传播。同样记 a(G) a ( G ) 为对应的激活值。定义content cost function如下:
这里的 a(C) a ( C ) and a(G) a ( G ) 都是体数据(volumes ),即三维堆叠起来的。 在计算 cost Jcontent(C,G) J c o n t e n t ( C , G ) 时候,可以展开为2D。其实在计算 Jcontent J c o n t e n t , 可以不用,而在计算style 代价函数 Jstyle J s t y l e 时需要。展开方法如下:
content的代价函数实现如下:
# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_content_cost
def compute_content_cost(a_C, a_G):
"""
Computes the content cost
Arguments:
a_C -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing content of the image C
a_G -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing content of the image G
Returns:
J_content -- scalar that you compute using equation 1 above.
"""
### START CODE HERE ###
# Retrieve dimensions from a_G (≈1 line)
m, n_H, n_W, n_C = a_G.get_shape().as_list()
# Reshape a_C and a_G (≈2 lines)
a_C_unrolled = tf.transpose(tf.reshape(a_C, [n_H * n_W, n_C]))
a_G_unrolled = tf.transpose(tf.reshape(a_G, [n_H * n_W, n_C]))
# compute the cost with tensorflow (≈1 line)
J_content = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(a_C_unrolled,a_G_unrolled)))/(4*n_H*n_W*n_C)
### END CODE HERE ###
return J_content测试:
tf.reset_default_graph()
with tf.Session() as test:
tf.set_random_seed(1)
a_C = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4)
a_G = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4)
J_content = compute_content_cost(a_C, a_G)
print("J_content = " + str(J_content.eval()))测试结果:
J_content 6.76559 2-2 Computing the style cost
先看下style图像:
style_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/monet_800600.jpg")
imshow(style_image)2-2-1 Style matrix
style matrix也称为”Gram matrix.”(格拉姆矩阵) 。在线性代数中,vectors (v1,…,vn) ( v 1 , … , v n ) 的 Gram matrix G 中各个位置的元素是vector中dot product结果,即 Gij=vTivj=np.dot(vi,vj) G i j = v i T v j = n p . d o t ( v i , v j ) 。 Gij G i j 记录的是 vi v i 到 vj v j 之间的相似度,如果二者相似度高,则dot product的结果会很大, 即for Gij G i j 值很大。
这里Style matrix (or Gram matrix) 会和generated image G G 可能会在表示上有所冲突,所以具使用的时候,要注意区分。
计算Style matrix,是将unroll结果与unroll的转置相乘:
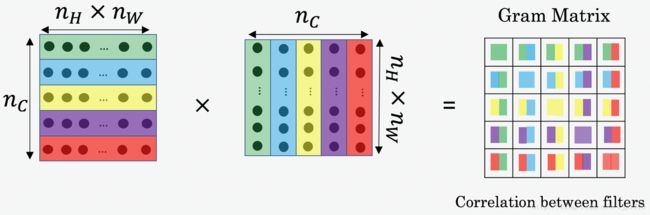
其结果矩阵尺寸= (nC,nC) ( n C , n C ) ,其中 nC n C 是number of filters。此时的 Gij G i j 度量了activations of filter i i 和 activations of filter j j 之间的相似性。Gram的对角线元素,还体现了每个特征在图像中出现的量,例如 Gii G i i 值大,则说明该filter探测到特征在图像中出现频繁。所以,Style matrix G G 可以用来度量 image的风格。
代码实现:
# GRADED FUNCTION: gram_matrix
def gram_matrix(A):
"""
Argument:
A -- matrix of shape (n_C, n_H*n_W)
Returns:
GA -- Gram matrix of A, of shape (n_C, n_C)
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈1 line)
GA = tf.matmul(A,tf.transpose(A))
#tf.matmul是矩阵乘法
#tf.multiply是点乘,即像素之间的乘法
### END CODE HERE ###
return GA测试如下:
tf.reset_default_graph()
with tf.Session() as test:
tf.set_random_seed(1)
A = tf.random_normal([3, 2*1], mean=1, stddev=4)
GA = gram_matrix(A)
print("GA = " + str(GA.eval()))测试结果:
GA =[[ 6.42230511 -4.42912197 -2.09668207]
[ -4.42912197 19.46583748 19.56387138]
[ -2.09668207 19.56387138 20.6864624 ]] 2-2-2 Style cost
在计算Style matrix (Gram matrix)后,我们要最小化 “style” image S的Gram matrix和”generated” image G之间的distance。我们先以第 l l 层为例,其对应的 style cost定义如下:
G(S) G ( S ) 和 G(G) G ( G ) 分别表示style image和generated image的Gram matrice。
具体的代码实现如下:
# GRADED FUNCTION: compute_layer_style_cost
def compute_layer_style_cost(a_S, a_G):
"""
Arguments:
a_S -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing style of the image S
a_G -- tensor of dimension (1, n_H, n_W, n_C), hidden layer activations representing style of the image G
Returns:
J_style_layer -- tensor representing a scalar value, style cost defined above by equation (2)
"""
### START CODE HERE ###
# Retrieve dimensions from a_G (≈1 line)
m, n_H, n_W, n_C = a_G.get_shape().as_list()
# Reshape the images to have them of shape (n_H*n_W, n_C) (≈2 lines)
a_S = tf.reshape(a_S, [n_H * n_W, n_C])
a_G = tf.reshape(a_G, [n_H * n_W, n_C])
# Computing gram_matrices for both images S and G (≈2 lines)
GS = gram_matrix(a_S)
GG = gram_matrix(a_G)
# Computing the loss (≈1 line)
J_style_layer = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(GS,GG)))/(4*tf.square(tf.to_float(n_C))*tf.square(tf.to_float(n_H*n_W)))
#J_style_layer = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(GS,GG)))/(4 * n_C**2 * (n_W * n_H)**2)
### END CODE HERE ###
return J_style_layer代码测试如下:
tf.reset_default_graph()
with tf.Session() as test:
tf.set_random_seed(1)
a_S = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4)
a_G = tf.random_normal([1, 4, 4, 3], mean=1, stddev=4)
J_style_layer = compute_layer_style_cost(a_S, a_G)
print("J_style_layer = " + str(J_style_layer.eval()))测试结果输出:
J_style_layer=9.190282-2-3 Style Weights
上面,我们仅仅是计算了一层的style cost,我们需要根据不同层的取一定的权重,再将所有层的style cost按照权重进行求和。注:content部分,采用一层是足够的。
实现如下:
def compute_style_cost(model, STYLE_LAYERS):
"""
Computes the overall style cost from several chosen layers
Arguments:
model -- our tensorflow model
STYLE_LAYERS -- A python list containing:
- the names of the layers we would like to extract style from
- a coefficient for each of them
Returns:
J_style -- tensor representing a scalar value, style cost defined above by equation (2)
"""
# initialize the overall style cost
J_style = 0
for layer_name, coeff in STYLE_LAYERS:
# Select the output tensor of the currently selected layer
out = model[layer_name]
# Set a_S to be the hidden layer activation from the layer we have selected, by running the session on out
a_S = sess.run(out)
# Set a_G to be the hidden layer activation from same layer. Here, a_G references model[layer_name]
# and isn't evaluated yet. Later in the code, we'll assign the image G as the model input, so that
# when we run the session, this will be the activations drawn from the appropriate layer, with G as input.
a_G = out
# Compute style_cost for the current layer
J_style_layer = compute_layer_style_cost(a_S, a_G)
# Add coeff * J_style_layer of this layer to overall style cost
J_style += coeff * J_style_layer
return J_style2-3 total cost to optimize
总的代价函数定义如下:
函数实现:
# GRADED FUNCTION: total_cost
def total_cost(J_content, J_style, alpha = 10, beta = 40):
"""
Computes the total cost function
Arguments:
J_content -- content cost coded above
J_style -- style cost coded above
alpha -- hyperparameter weighting the importance of the content cost
beta -- hyperparameter weighting the importance of the style cost
Returns:
J -- total cost as defined by the formula above.
"""
### START CODE HERE ### (≈1 line)
J = alpha*J_content+beta*J_style
### END CODE HERE ###
return J函数测试:
tf.reset_default_graph()
with tf.Session() as test:
np.random.seed(3)
J_content = np.random.randn()
J_style = np.random.randn()
J = total_cost(J_content, J_style)
print("J = " + str(J))测试结果:
J=35.34667875478276 3- 优化
Neural Style Transfer的实现步骤如下:
- Create an Interactive Session
- Load the content image
- Load the style image
- Randomly initialize the image to be generated
- Load the VGG16 model
- Build the TensorFlow graph:
- Run the content image through the VGG16 model and compute the content cost
- Run the style image through the VGG16 model and compute the style cost
- Compute the total cost
- Define the optimizer and the learning rate
- Initialize the TensorFlow graph and run it for a large number of iterations, updating the generated image at every step.
各步骤的具体细节如下:
# Reset the graph
tf.reset_default_graph()
# Start interactive session
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()加载 “content” image并进行 reshape, and normalize:
content_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/louvre_small.jpg")
content_image = reshape_and_normalize_image(content_image)加载 “style” image并进行 reshape, and normalize:
style_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/monet.jpg")
style_image = reshape_and_normalize_image(style_image)“generated” image初始化: 通过对content_image添加噪声完成。添加的噪声较大,但是依然能够使其与content_image有一些些的相关性。这有助于”generated” image 能够更快速地与”content” image相匹配。
generated_image = generate_noise_image(content_image)
imshow(generated_image[0])加载VGG-16模型:
model = load_vgg_model("pretrained-model/imagenet-vgg-verydeep-19.mat")为了计算 content cost,我们需要将a_C and a_G 输入到合适的隐藏层,这里我们采用是 conv4_2层:
- 将content image输入到VGG model.
- Set a_C to be the tensor giving the hidden layer activation for layer “conv4_2”.
- Set a_G to be the tensor giving the hidden layer activation for the same layer.
- Compute the content cost using a_C and a_G.
实现如下:
# Assign the content image to be the input of the VGG model.
sess.run(model['input'].assign(content_image))
# Select the output tensor of layer conv4_2
out = model['conv4_2']
# Set a_C to be the hidden layer activation from the layer we have selected
a_C = sess.run(out)
# Set a_G to be the hidden layer activation from same layer. Here, a_G references model['conv4_2']
# and isn't evaluated yet. Later in the code, we'll assign the image G as the model input, so that
# when we run the session, this will be the activations drawn from the appropriate layer, with G as input.
a_G = out#a_G is a tensor and hasn't been evaluated
# Compute the content cost
J_content = compute_content_cost(a_C, a_G)注意:上面的a_G 还未被估计,其更新是在每轮迭代之后。
对于 “style” image :
# Assign the input of the model to be the "style" image
sess.run(model['input'].assign(style_image))
# Compute the style cost
J_style = compute_style_cost(model, STYLE_LAYERS)计算整体代价:
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
J = total_cost(J_content, J_style, alpha = 10, beta = 40)
### END CODE HERE ###优化:
# define optimizer (1 line)
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(2.0)
# define train_step (1 line)
train_step = optimizer.minimize(J)完整的模型实现:
def model_nn(sess, input_image, num_iterations = 200):
# Initialize global variables (you need to run the session on the initializer)
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
### END CODE HERE ###
# Run the noisy input image (initial generated image) through the model. Use assign().
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
generated_image = sess.run(model['input'].assign(input_image))
### END CODE HERE ###
for i in range(num_iterations):
# Run the session on the train_step to minimize the total cost
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
sess.run(train_step)
### END CODE HERE ###
# Compute the generated image by running the session on the current model['input']
### START CODE HERE ### (1 line)
generated_image = sess.run(model['input'])
### END CODE HERE ###
# Print every 20 iteration.
if i%20 == 0:
Jt, Jc, Js = sess.run([J, J_content, J_style])
print("Iteration " + str(i) + " :")
print("total cost = " + str(Jt))
print("content cost = " + str(Jc))
print("style cost = " + str(Js))
# save current generated image in the "/output" directory
save_image("output/" + str(i) + ".png", generated_image)
# save last generated image
save_image('output/generated_image.jpg', generated_image)
return generated_image模型测试:
model_nn(sess, generated_image)结果展示如下:
content图:

style图:

生成的图:

4- 其他图像的测试:
重新输入content image和style image:
content_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/my_content.jpg")
style_image = scipy.misc.imread("images/my_style.jpg")我们需要调整的超参数:
- Which layers are responsible for representing the style? STYLE_LAYERS
- 迭代次数, num_iterations
- What is the relative weighting between content and style? alpha/beta