Opencv Mat 类详解以及像素点基本读取方法
上一节已经介绍了Opnecv的基本构成,下面正式介绍如何使用opencv。
1.Mat类
class CV_EXPORTS Mat
{
public:
//! default constructor
Mat();
//! constructs 2D matrix of the specified size and type
// (_type is CV_8UC1, CV_64FC3, CV_32SC(12) etc.)
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type);
Mat(Size size, int type);
//! constucts 2D matrix and fills it with the specified value _s.
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, const Scalar& s);
Mat(Size size, int type, const Scalar& s);
//! constructs n-dimensional matrix
Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type);
Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, const Scalar& s);
//! copy constructor
Mat(const Mat& m);
//! constructor for matrix headers pointing to user-allocated data
Mat(int rows, int cols, int type, void* data, size_t step=AUTO_STEP);
Mat(Size size, int type, void* data, size_t step=AUTO_STEP);
Mat(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type, void* data, const size_t* steps=0);
//! creates a matrix header for a part of the bigger matrix
Mat(const Mat& m, const Range& rowRange, const Range& colRange=Range::all());
Mat(const Mat& m, const Rect& roi);
Mat(const Mat& m, const Range* ranges);
//! converts old-style CvMat to the new matrix; the data is not copied by default
Mat(const CvMat* m, bool copyData=false);
//! converts old-style CvMatND to the new matrix; the data is not copied by default
Mat(const CvMatND* m, bool copyData=false);
//! converts old-style IplImage to the new matrix; the data is not copied by default
Mat(const IplImage* img, bool copyData=false);
//! builds matrix from std::vector with or without copying the data
template explicit Mat(const vector<_Tp>& vec, bool copyData=false);
//! builds matrix from cv::Vec; the data is copied by default
template explicit Mat(const Vec<_Tp, n>& vec, bool copyData=true);
//! builds matrix from cv::Matx; the data is copied by default
template explicit Mat(const Matx<_Tp, m, n>& mtx, bool copyData=true);
//! builds matrix from a 2D point
template explicit Mat(const Point_<_Tp>& pt, bool copyData=true);
//! builds matrix from a 3D point
template explicit Mat(const Point3_<_Tp>& pt, bool copyData=true);
//! builds matrix from comma initializer
template explicit Mat(const MatCommaInitializer_<_Tp>& commaInitializer);
//! download data from GpuMat
explicit Mat(const gpu::GpuMat& m);
//! destructor - calls release()
~Mat();
//! assignment operators
Mat& operator = (const Mat& m);
Mat& operator = (const MatExpr& expr);
//! returns a new matrix header for the specified row
Mat row(int y) const;
//! returns a new matrix header for the specified column
Mat col(int x) const;
//! ... for the specified row span
Mat rowRange(int startrow, int endrow) const;
Mat rowRange(const Range& r) const;
//! ... for the specified column span
Mat colRange(int startcol, int endcol) const;
Mat colRange(const Range& r) const;
//! ... for the specified diagonal
// (d=0 - the main diagonal,
// >0 - a diagonal from the lower half,
// <0 - a diagonal from the upper half)
Mat diag(int d=0) const;
//! constructs a square diagonal matrix which main diagonal is vector "d"
static Mat diag(const Mat& d);
//! returns deep copy of the matrix, i.e. the data is copied
Mat clone() const;
//! copies the matrix content to "m".
// It calls m.create(this->size(), this->type()).
void copyTo( OutputArray m ) const;
//! copies those matrix elements to "m" that are marked with non-zero mask elements.
void copyTo( OutputArray m, InputArray mask ) const;
//! converts matrix to another datatype with optional scalng. See cvConvertScale.
void convertTo( OutputArray m, int rtype, double alpha=1, double beta=0 ) const;
void assignTo( Mat& m, int type=-1 ) const;
//! sets every matrix element to s
Mat& operator = (const Scalar& s);
//! sets some of the matrix elements to s, according to the mask
Mat& setTo(InputArray value, InputArray mask=noArray());
//! creates alternative matrix header for the same data, with different
// number of channels and/or different number of rows. see cvReshape.
Mat reshape(int cn, int rows=0) const;
Mat reshape(int cn, int newndims, const int* newsz) const;
//! matrix transposition by means of matrix expressions
MatExpr t() const;
//! matrix inversion by means of matrix expressions
MatExpr inv(int method=DECOMP_LU) const;
//! per-element matrix multiplication by means of matrix expressions
MatExpr mul(InputArray m, double scale=1) const;
//! computes cross-product of 2 3D vectors
Mat cross(InputArray m) const;
//! computes dot-product
double dot(InputArray m) const;
//! Matlab-style matrix initialization
static MatExpr zeros(int rows, int cols, int type);
static MatExpr zeros(Size size, int type);
static MatExpr zeros(int ndims, const int* sz, int type);
static MatExpr ones(int rows, int cols, int type);
static MatExpr ones(Size size, int type);
static MatExpr ones(int ndims, const int* sz, int type);
static MatExpr eye(int rows, int cols, int type);
static MatExpr eye(Size size, int type);
//! allocates new matrix data unless the matrix already has specified size and type.
// previous data is unreferenced if needed.
void create(int rows, int cols, int type);
void create(Size size, int type);
void create(int ndims, const int* sizes, int type);
//! increases the reference counter; use with care to avoid memleaks
void addref();
//! decreases reference counter;
// deallocates the data when reference counter reaches 0.
void release();
//! deallocates the matrix data
void deallocate();
//! internal use function; properly re-allocates _size, _step arrays
void copySize(const Mat& m);
//! reserves enough space to fit sz hyper-planes
void reserve(size_t sz);
//! resizes matrix to the specified number of hyper-planes
void resize(size_t sz);
//! resizes matrix to the specified number of hyper-planes; initializes the newly added elements
void resize(size_t sz, const Scalar& s);
//! internal function
void push_back_(const void* elem);
//! adds element to the end of 1d matrix (or possibly multiple elements when _Tp=Mat)
template void push_back(const _Tp& elem);
template void push_back(const Mat_<_Tp>& elem);
void push_back(const Mat& m);
//! removes several hyper-planes from bottom of the matrix
void pop_back(size_t nelems=1);
//! locates matrix header within a parent matrix. See below
void locateROI( Size& wholeSize, Point& ofs ) const;
//! moves/resizes the current matrix ROI inside the parent matrix.
Mat& adjustROI( int dtop, int dbottom, int dleft, int dright );
//! extracts a rectangular sub-matrix
// (this is a generalized form of row, rowRange etc.)
Mat operator()( Range rowRange, Range colRange ) const;
Mat operator()( const Rect& roi ) const;
Mat operator()( const Range* ranges ) const;
//! converts header to CvMat; no data is copied
operator CvMat() const;
//! converts header to CvMatND; no data is copied
operator CvMatND() const;
//! converts header to IplImage; no data is copied
operator IplImage() const;
template operator vector<_Tp>() const;
template operator Vec<_Tp, n>() const;
template operator Matx<_Tp, m, n>() const;
//! returns true iff the matrix data is continuous
// (i.e. when there are no gaps between successive rows).
// similar to CV_IS_MAT_CONT(cvmat->type)
bool isContinuous() const;
//! returns true if the matrix is a submatrix of another matrix
bool isSubmatrix() const;
//! returns element size in bytes,
// similar to CV_ELEM_SIZE(cvmat->type)
size_t elemSize() const;
//! returns the size of element channel in bytes.
size_t elemSize1() const;
//! returns element type, similar to CV_MAT_TYPE(cvmat->type)
int type() const;
//! returns element type, similar to CV_MAT_DEPTH(cvmat->type)
int depth() const;
//! returns element type, similar to CV_MAT_CN(cvmat->type)
int channels() const;
//! returns step/elemSize1()
size_t step1(int i=0) const;
//! returns true if matrix data is NULL
bool empty() const;
//! returns the total number of matrix elements
size_t total() const;
//! returns N if the matrix is 1-channel (N x ptdim) or ptdim-channel (1 x N) or (N x 1); negative number otherwise
int checkVector(int elemChannels, int depth=-1, bool requireContinuous=true) const;
//! returns pointer to i0-th submatrix along the dimension #0
uchar* ptr(int i0=0);
const uchar* ptr(int i0=0) const;
//! returns pointer to (i0,i1) submatrix along the dimensions #0 and #1
uchar* ptr(int i0, int i1);
const uchar* ptr(int i0, int i1) const;
//! returns pointer to (i0,i1,i3) submatrix along the dimensions #0, #1, #2
uchar* ptr(int i0, int i1, int i2);
const uchar* ptr(int i0, int i1, int i2) const;
//! returns pointer to the matrix element
uchar* ptr(const int* idx);
//! returns read-only pointer to the matrix element
const uchar* ptr(const int* idx) const;
template uchar* ptr(const Vec& idx);
template const uchar* ptr(const Vec& idx) const;
//! template version of the above method
template _Tp* ptr(int i0=0);
template const _Tp* ptr(int i0=0) const;
template _Tp* ptr(int i0, int i1);
template const _Tp* ptr(int i0, int i1) const;
template _Tp* ptr(int i0, int i1, int i2);
template const _Tp* ptr(int i0, int i1, int i2) const;
template _Tp* ptr(const int* idx);
template const _Tp* ptr(const int* idx) const;
template _Tp* ptr(const Vec& idx);
template const _Tp* ptr(const Vec& idx) const;
//! the same as above, with the pointer dereferencing
template _Tp& at(int i0=0);
template const _Tp& at(int i0=0) const;
template _Tp& at(int i0, int i1);
template const _Tp& at(int i0, int i1) const;
template _Tp& at(int i0, int i1, int i2);
template const _Tp& at(int i0, int i1, int i2) const;
template _Tp& at(const int* idx);
template const _Tp& at(const int* idx) const;
template _Tp& at(const Vec& idx);
template const _Tp& at(const Vec& idx) const;
//! special versions for 2D arrays (especially convenient for referencing image pixels)
template _Tp& at(Point pt);
template const _Tp& at(Point pt) const;
//! template methods for iteration over matrix elements.
// the iterators take care of skipping gaps in the end of rows (if any)
template MatIterator_<_Tp> begin();
template MatIterator_<_Tp> end();
template MatConstIterator_<_Tp> begin() const;
template MatConstIterator_<_Tp> end() const;
enum { MAGIC_VAL=0x42FF0000, AUTO_STEP=0, CONTINUOUS_FLAG=CV_MAT_CONT_FLAG, SUBMATRIX_FLAG=CV_SUBMAT_FLAG };
/*! includes several bit-fields:
- the magic signature
- continuity flag
- depth
- number of channels
*/
int flags;
//! the matrix dimensionality, >= 2
int dims;
//! the number of rows and columns or (-1, -1) when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
int rows, cols;
//! pointer to the data
uchar* data;
//! pointer to the reference counter;
// when matrix points to user-allocated data, the pointer is NULL
int* refcount;
//! helper fields used in locateROI and adjustROI
uchar* datastart;
uchar* dataend;
uchar* datalimit;
//! custom allocator
MatAllocator* allocator;
struct CV_EXPORTS MSize
{
MSize(int* _p);
Size operator()() const;
const int& operator[](int i) const;
int& operator[](int i);
operator const int*() const;
bool operator == (const MSize& sz) const;
bool operator != (const MSize& sz) const;
int* p;
};
struct CV_EXPORTS MStep
{
MStep();
MStep(size_t s);
const size_t& operator[](int i) const;
size_t& operator[](int i);
operator size_t() const;
MStep& operator = (size_t s);
size_t* p;
size_t buf[2];
protected:
MStep& operator = (const MStep&);
};
MSize size;
MStep step;
protected:
void initEmpty();
}; /*! includes several bit-fields:
- the magic signature
- continuity flag
- depth
- number of channels
*/
int flags;
//! the matrix dimensionality, >= 2
int dims;
//! the number of rows and columns or (-1, -1) when the matrix has more than 2 dimensions
int rows, cols;
//! pointer to the data
uchar* data;
//! pointer to the reference counter;
// when matrix points to user-allocated data, the pointer is NULL
int* refcount;
//! helper fields used in locateROI and adjustROI
uchar* datastart;
uchar* dataend;
uchar* datalimit;2像素值的读写
2.1第一种方法灰度和rgb at(存储时候按照BRG)
2.2第二种方法灰度和rgb 迭代器(存储时候按照BRG)
2.3第三种方法灰度和rgb 指针(存储时候按照BRG)
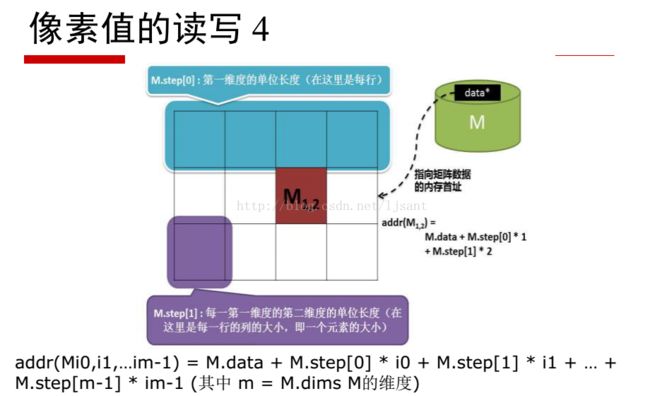
2.4第四种方法灰度和rgb 三维(存储时候按照BRG)
2.5第五种方法灰度和rgb Mat类 (存储时候按照BRG)
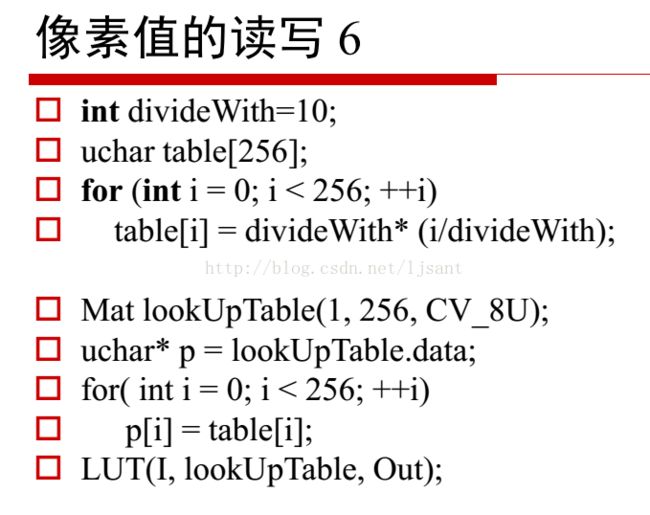
2.6第六种方法灰度和rgb(存储时候按照BRG)