OpenCV3特征提取与目标检测之HOG(三)——使用HOG加SVM训练自己的行人检测模型
前言
法国人Navneet Dalal 和Bill Triggs在2005年CVPR(IEEE国际计算机视觉与模式识别会议)上提出,有兴趣的可看那时候的论文,利用Hog进行特征提取和用SVM作为分类器,来实现行人检测。他们经过大量测试发现,Hog加SVM是速度和效果综合平衡性能较好的一种行人检测方法。后来,虽然许多研究人员也提出了很多改进的行人检测算法,但大部分都以该算法为基础框架。再那之后Hog加SVM也成为算法被写入到OpenCV中。在OpenCV2.0的版本,OpneCV开发人员封装了提取Hog特征描述算子的API,而SVM,OpenCV 1.0开始就已经集成进去了;虽然OpenCV提供了Hog和SVM的相关API和官方样例,但OpenCV并没有提供训练的训练的正负样本。我在前面的博文试了官方行人检测的样例,运行得到的结果并不见得都能适用个人项目的应用场合。因此,针对个人的特定应用场景,有时候很有必要进行重新训练得到适合自己使用的分类器。
一、资源环境
1.我工程的环境是Win7 64位,VS2015,Boost 1.60,OpenCV3.30加OpnCV_contrib。其中Boost是用来处理文件相关操作的库,这里关于什么配置VS2015下使用Boost,网上有很多教程可以参考;而VS2015下使用OpenCV3.30加OpenCV_Contrib,我前面有博文讲过如何配置,这里就不再多说。
2.工程所用到的行人数据库是INRIA数据库。
(1)正样本是来源于INRIA数据集中的96X160大小的内有人体图片,所有的图像大小一致,程序在做HOG特征提取时上下左右都去掉16个像素,只提取中间的64X128大小的包含人体特征描述子。
(2)负样本是从不包含人体的图片中随机裁取的,大小同样是64X128,这个可以自己写个程序从完全不包含人体的图片中随机剪裁出64X128大小的用于人体检测的负样本。
(3)我训练时的样本比例大概为1比4,就是正样本为1,负样本为4。
(4)负样本的剪切工具是用C++写了个对一张不包含人体的大图像随机的剪切出64X128的图像。下面是剪切负样本的代码部分。
声明文件
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
//boost 库(读取文件)
#include
//定义一个boost库的命名空间
namespace fs = boost::filesystem;
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
class Tool
{
public:
//构造函数
Tool(string _negative_src_dir, string _negative_dst_dir, int _image_width, int _image_height);
//剪切图像
void imageCut();
//保存剪切好的图像
int saveRoi(string _output_path, vector _vector_mat, int index);
//随机生成文件名
string generateLenString(int name_len);
//读取文件夹下的图像
vector readDirImage(string dir);
~Tool();
private:
vector all_negative;
vector dst_negative;
//源图像路径
string negative_src_dir;
//保存的图像路径
string negative_dst_dir;
//裁剪出来的负样本图片文件名
char saveName[256];
//剪切宽度
int image_width;
//剪切高度
int image_height;
Mat src, dst;
};
实现文件
#include "Tool.h"
Tool::Tool(string _negative_src_dir, string _negative_dst_dir, int _image_width, int _image_height)
{
negative_src_dir = _negative_src_dir;
negative_dst_dir = _negative_dst_dir;
image_width = _image_width;
image_height = _image_height;
}
void Tool::imageCut()
{
all_negative = readDirImage(negative_src_dir);
for (int i = 0; i < all_negative.size(); i++)
{
src = all_negative.at(i);
//图片大小应该能能至少包含一个64*128的窗口
if (src.cols >= 128 && src.rows >= 128)
{
srand(time(NULL));//设置随机数种子 time(NULL)表示当前系统时间
//从每张图片中随机采样10个64*128大小的不包含人的负样本
for (int i = 0; i<10; i++)
{
int x = (rand() % (src.cols - image_width)); //左上角x坐标
int y = (rand() % (src.rows - image_height)); //左上角y坐标
Mat imgROI = src(Rect(x, y, image_width, image_height));
dst_negative.push_back(imgROI);
}
}
}
saveRoi(negative_dst_dir, dst_negative, dst_negative.size());
}
int Tool::saveRoi(string _output_path, vector _vector_mat, int index)
{
string output_path = _output_path;
fs::path output_dir(output_path);
if (!fs::exists(output_dir))
{
cout << "请转入一个合法的路径!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
vector vector_mat = _vector_mat;
for (int i = 0; i < vector_mat.size(); i++)
{
string name = generateLenString(10);
string path_name = output_path + name + to_string(index) + to_string(i) + string(".jpg");
imwrite(path_name, vector_mat.at(i));
}
cout << "保存了" << vector_mat.size() << "张图像!" << endl;
return vector_mat.size();
}
//读取文件夹下的所有图像
vector Tool::readDirImage(string dir)
{
vector vector_mat;
//boost库文件 遍历数据文件夹 directory_iterator(p)就是迭代器的起点,无参数的directory_iterator()就是迭代器的终点。
fs::directory_iterator begin_iter(dir);
fs::directory_iterator end_iter;
//获取该目录下的所有文件名
for (; begin_iter != end_iter; ++begin_iter)
{
//得到绝对路径
string filename = string(dir) + begin_iter->path().filename().string();
//读入模板图片
Mat image = imread(filename);
//判断是否为图片类型
if (image.empty())
{
cout << "当前模板不为图片类型!" << endl;
continue;
}
vector_mat.push_back(image);
}
return vector_mat;
}
string Tool::generateLenString(int name_len)
{
srand((int)time(NULL));
char ch;
string str;
for (int i = 1; i <= name_len; i++)
{
int x, s;
s = rand() % 2;
if (s == 1)
{
x = rand() % ('Z' - 'A' + 1) + 'A';
}
else
{
x = rand() % ('z' - 'a' + 1) + 'a';
}
ch = x;
str.push_back(ch);
}
return str;
}
Tool::~Tool()
{
}
主函数
#include "Tool.h"
int main(void)
{
string src_dir = "C:/Users/matt/Desktop/demo/";
string dst_dir = "C:/Users/matt/Desktop/01/";
Tool tool(src_dir, dst_dir, 64, 128);
tool.imageCut();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
代码不多,也是相对好理解。
3.也可以直接下载剪切好的正负样本,下载地址,正样本:https://download.csdn.net/download/matt45m/11044598
负样本:https://download.csdn.net/download/matt45m/11044603
测试的图像是随便找包含行人的图像。下载好的样本存放如下图,可以按自己的路径更改配置文件。
二、项目流程
1.程序主要思想
使用HOG + SVM进行行人检测时, 采集HOG特征的主要思想是通过对一幅图像进行分析, 局部目标的表象和形状可以被剃度或者边缘密度方向分布很好的好的描述. 我们对图像的各个像素点采集土堆或者边缘的方向直方图, 根据直方图的信息就可以描述图片的特征. 而OpenCV已经提供了计算HOG特征的方法, 根据采集到的HOG特征向量, 提供给SVM分类使用。如果想了HOG的提取特征描述子与计算方式,可以看我之前的博文。
SVM简单来说就是一个分类器, 在行人检测中就可以转化为行人与非行人的两类分类问题, 在OpenCV中运用到的是基于网格法的SVM.使用采集到的正样本和负样本的HOG特征, 然后使用SVM分类器进行训练, 得到行人检测模型, 进行行人检测。
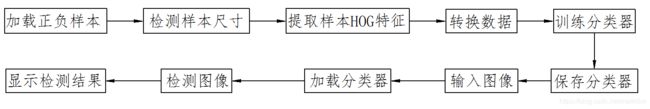
2.代码流程
三、具体代码
1.配置文件
配置文件有正样本、负样本、测试图像存放的路径,和各种关键设置的参数。代码有明确的标注,做训练时基本不用去改动别的代码模块,只要更改配置文件的相关参数就可以了。代码给出的路径是在我工程上的路径,按照着自己路径改就可以了。
2.声明文件
类里面有两个构造函数,一个是默认的构造函数,只传入正负样本路径,和测试图像存放路径就可以了,这个是做行人检测 用的。别一个构造函数要传入包含HOG检测窗口在内的几个参数 ,可以做行人,也可以做别的物体检测;比如我之前用来做马匹检测的数据,我传入的参数为128X128,那么正样本的尺寸我全部剪切成160X160,负样本还是128X128。
#pragma once
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
//boost 库(读取文件)
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
namespace fs = boost::filesystem;
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace cv::ml;
class TargetDetection
{
public:
//默认构造函数
TargetDetection(string _positive_samples_dir, string _negative_sampl_dir, string _test_dir);
//析构函数
~TargetDetection();
//重载构造函数
TargetDetection(string _positive_samples_dir, string _negative_sampl_dir, string _test_dir,
string _xml_filename, string _video_filename, bool _test_detector, bool _train_twice,
bool _visualization, int _detector_windows_width, int _detector_windows_height);
//训练样本
int sampleTraining();
//加载样本
vector loadSamples(string &dir_name,bool show_images);
//计算样本HOG的特征
void computeHogFeature(Size windows_size, const vector& image_list, vector& gradient_list);
//转换数据类型
void convertToMl(const vector& train_samples, Mat& train_data);
//得到训练好的模型
void getSvmDetector(const Ptr& svm, vector & hog_detector);
//测试图像
int testTrainedDetector(string obj_det_filename, string test_dir, string videofilename);
private:
//正样本目录
string positive_samples_dir;
//负样本目录
string negative_sampl_dir;
//测试样本目录
string test_image_dir;
//训练好的SVM检测文件名
string xml_filename;
//要测试的视频路径名
string video_filename;
//检测器宽度
int detector_windows_width;
//检测器高度
int detector_windows_height;
//测试训练好的检测器
bool test_detector;
//训练两次
bool train_twice;
//训练过程可视化
bool visualization;
//保存正样本图片容器向量
vector positive_list;
//负样本图片向量
vector negative_image_list;
//采样后的负样本图片向量
vector negative_list;
//HOG描述符存入到该梯度信息里面
vector gradient_list;
//标签向量
vector labels;
//统计时间
clock_t start, end;
};
3.实现文件
#include "TargetDetection.h"
TargetDetection::TargetDetection(string _positive_samples_dir, string _negative_sampl_dir, string _test_image_dir)
{
positive_samples_dir = _positive_samples_dir;
negative_sampl_dir = _negative_sampl_dir;
test_image_dir = _test_image_dir;
xml_filename = "hog.xml";
//video_filename = "0";
detector_windows_width = 64;
detector_windows_height = 128;
//测试训练好的检测器
test_detector = false;
//训练两次
train_twice = false;
//训练过程可视化
visualization = false;
}
TargetDetection::TargetDetection(string _positive_samples_dir, string _negative_sampl_dir, string _test_image_dir,
string _xml_filename, string _video_filename, bool _test_detector, bool _train_twice, bool _visualization,int _detector_windows_width,int _detector_windows_height)
{
positive_samples_dir = _positive_samples_dir;
negative_sampl_dir = _negative_sampl_dir;
test_image_dir = _test_image_dir;
xml_filename = _xml_filename;
video_filename = _video_filename;
detector_windows_width = _detector_windows_width;
detector_windows_height = _detector_windows_height;
//测试训练好的检测器
test_detector = _test_detector;
//训练两次
train_twice = _train_twice;
//训练过程可视化
visualization = _visualization;
}
//训练样本
int TargetDetection::sampleTraining()
{
//若为true,测对测试集进行测试
if (test_detector)
{
//调用测试函数
testTrainedDetector(xml_filename, test_image_dir, video_filename);
exit(1);
}
//检测正负样本的目录
if (positive_samples_dir.empty() || negative_sampl_dir.empty())
{
cout << "请转入路径!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
//判断是否为路径
fs::path positive(positive_samples_dir);
fs::path negative(negative_sampl_dir);
if (!fs::exists(positive))
{
cout << "请转入一个合法的正样本路径!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
if (!fs::exists(negative))
{
cout << "请转入一个合法的负样本路径!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
//加载正样本
cout << "开始加载正样本......";
positive_list = loadSamples(positive_samples_dir,visualization);
if (positive_list.size() > 0)
{
cout << "[加载完成]" << endl;
cout << "总共有" << positive_list.size() << "个正样本。" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "当前目录:" << positive_samples_dir << "没有要训练的图像" << endl;
return -1;
}
//让检测尺寸等于正样本尺寸第一张的尺寸
Size positive_image_size = positive_list[0].size();
cout << "正样本的尺寸是:" << positive_image_size << endl;
//遍历所有样品,检测尺寸是否相同
for (size_t i = 0; i < positive_list.size(); i++)
{
if (positive_image_size != positive_list[i].size())
{
cout << "所有的样本的尺寸大小不一,请重新调整好样本大小!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
//指定样本尺寸必须被8除开
positive_image_size = positive_image_size / 8 * 8;
//令pos_image_size的尺寸为检测器的尺寸
if (detector_windows_width && detector_windows_height)
{
positive_image_size = Size(detector_windows_width, detector_windows_height);
//cout << positive_image_size << endl;
}
//assign()为labels分配positive_list.size()大小的容器,用+1填充 表示为正样本
labels.assign(positive_list.size(), +1);
//旧标签大小
const unsigned int old = (unsigned int)labels.size();
cout << "开始加载负样本......";
negative_list = loadSamples(negative_sampl_dir, visualization);
if (negative_list.size() > 0)
{
cout << "[加载完成]" << endl;
cout << "总共有" << negative_list.size() << "个负样本。" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "当前目录:" << negative_sampl_dir << "没有要训练的图像" << endl;
return -1;
}
//在labels向量的尾部添加neg_lst.size()大小的容器,用-1填充表示为负样本
labels.insert(labels.end(), negative_list.size(), -1);
//CV_Assert()若括号中的表达式值为false,则返回一个错误信息。
CV_Assert(old < labels.size());
cout << "正在计算正样本HOG特征......";
//计算正样本图片的HOG特征
computeHogFeature(positive_image_size, positive_list, gradient_list);
cout << "[计算完成]" << endl;
cout << "正在计算负样本HOG特征......";
//计算负样本图片的HOG特征
computeHogFeature(positive_image_size, negative_list, gradient_list);
cout << "[计算完成]" << endl;
Mat train_data;
//转化为ml所需的训练数据形式
convertToMl(gradient_list, train_data);
//开始训练SVM
cout << "训练SVM.......";
Ptr svm = SVM::create();
//设置SVM的参数值
svm->setCoef0(0.0);
svm->setDegree(3);
svm->setTermCriteria(TermCriteria(CV_TERMCRIT_ITER + CV_TERMCRIT_EPS, 1000, 1e-3));
svm->setGamma(0);
//采用线性核函,其他的sigmoid 和RBF可自行设置,其值由0-5。
svm->setKernel(SVM::LINEAR);
svm->setNu(0.5);
svm->setP(0.1);
svm->setC(0.01);
svm->setType(SVM::EPS_SVR);
//训练SVM
svm->train(train_data, ROW_SAMPLE, Mat(labels));
cout << "[训练完成]" << endl;
//对样本进行两次训练
if (train_twice)
{
cout << "对样本进行第二次训练.......";
HOGDescriptor twice_hog;
twice_hog.winSize = positive_image_size;
// 将训练好的数据加入svm
vector hog_detector;
getSvmDetector(svm, hog_detector);
twice_hog.setSVMDetector(hog_detector);
vector< Rect > detections;
vector< double > foundWeights;
for (size_t i = 0; i < negative_image_list.size(); i++)
{
twice_hog.detectMultiScale(negative_image_list[i], detections, foundWeights);
for (size_t j = 0; j < detections.size(); j++)
{
Mat detection = negative_image_list[i](detections[j]).clone();
resize(detection, detection, positive_image_size);
negative_list.push_back(detection);
}
//可视化
if (visualization)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < detections.size(); j++)
{
rectangle(negative_image_list[i], detections[j], Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2);
}
imshow("testing trained detector on negative images", negative_image_list[i]);
waitKey(5);
}
}
cout << "[训练完成]" << endl;
//清空容器
labels.clear();
//赋size个值为1的元素到vector容器中,这个容器会清除掉vector容器中以前的内容
labels.assign(positive_list.size(), +1);
//将-1分别插入到向量元素结尾位置的negative_list.size处(共size个元素)
labels.insert(labels.end(), negative_list.size(), -1);
//清空容器
gradient_list.clear();
cout << "正在计算正样本的梯度直方图.......";
//计算正样本HOG特性
computeHogFeature(positive_image_size, positive_list, gradient_list);
cout << "[计算完成]" << endl;
cout << "正在计算负样本的梯度直方图.......";
//计算负样本HOG特性
computeHogFeature(positive_image_size, negative_list, gradient_list);
cout << "[计算完成]" << endl;
cout << "第二次训练SVM...";
//转换数据
convertToMl(gradient_list, train_data);
//训练数据
svm->train(train_data, ROW_SAMPLE, Mat(labels));
cout << "[训练完成]" << endl;
}
//定义hog检测器
vector< float > hog_detector;
//得到训练好的检测器
getSvmDetector(svm, hog_detector);
HOGDescriptor hog;
//窗口大小
hog.winSize = positive_image_size;
hog.setSVMDetector(hog_detector);
//保存分类器
fstream file;
file.open(xml_filename, ios::in);
//保存训练好的分类器(其中包含了SVM的参数,支持向量,α和rho)
if (file)
{
file.close();
cout << xml_filename << "已存在!" << endl;
string new_xml_name = xml_filename + ".old";
rename(xml_filename.c_str(), new_xml_name.c_str());
cout << "保存的旧文件名为" << new_xml_name << endl;
hog.save(xml_filename);
cout << "保存训练文件完成。" << endl;
}
else
{
hog.save(xml_filename);
cout << "保存训练文件完成。" << endl;
}
//检测训练集
testTrainedDetector(xml_filename, test_image_dir, video_filename);
return 0;
}
//加载样本
vector TargetDetection::loadSamples(string &dir_name,bool show_images)
{
vector image_list;
//boost库文件 遍历数据文件夹 directory_iterator(p)就是迭代器的起点,无参数的directory_iterator()就是迭代器的终点。
fs::directory_iterator begin_iter(dir_name);
fs::directory_iterator end_iter;
//获取该目录下的所有文件名
for (; begin_iter != end_iter; ++begin_iter)
{
//得到绝对路径
string filename = string(dir_name) + begin_iter->path().filename().string();
Mat image = imread(filename);
//判断是否为图片类型
if (image.empty())
{
cout << filename << "图像无效!" << endl;
continue;
}
if (show_images)
{
imshow("image", image);
waitKey(1);
}
image_list.push_back(image);
}
return image_list;
}
//计算样本HOG的特征
void TargetDetection::computeHogFeature(Size windows_size, const vector& image_list, vector& gradient_list)
{
HOGDescriptor hog;
//窗口大小
hog.winSize = windows_size;
Rect r = Rect(0, 0, windows_size.width, windows_size.height);
//正样本图片的尺寸减去检测器的尺寸,再除以2
r.x += (image_list[0].cols - r.width) / 2;
r.y += (image_list[0].rows - r.height) / 2;
Mat gray;
vector descriptors;
//计算hog特征
for (size_t i = 0; i< image_list.size(); i++)
{
cvtColor(image_list[i](r), gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//Size(8,8)为窗口移动步长,置检测窗口步长,如果图片大小超过64×128,可以设置winStride
hog.compute(gray, descriptors, Size(8, 8), Size(0, 0));
//保存到特征向量矩阵中
gradient_list.push_back(Mat(descriptors).clone());
//cout << "描述子维数:" << descriptors.size() << endl;
}
}
//转换数据类型
void TargetDetection::convertToMl(const vector& train_samples, Mat& train_data)
{
//行数等于训练样本个数
const int rows = (int)train_samples.size();
//列数取样本图片中宽度与高度中较大的那一个
const int cols = (int)max(train_samples[0].cols, train_samples[0].rows);
//新建一个1行的Mat 矩阵
Mat temp_mat(1, cols, CV_32FC1);
//行与列为训练样本的参数
train_data = Mat(rows, cols, CV_32FC1);
for (size_t i = 0; i < train_samples.size(); ++i)
{
//若括号中的表达式值为false,则返回一个错误信息。
CV_Assert(train_samples[i].cols == 1 || train_samples[i].rows == 1);
if (train_samples[i].cols == 1)
{
//矩阵转置
transpose(train_samples[i], temp_mat);
temp_mat.copyTo(train_data.row((int)i));
}
else if (train_samples[i].rows == 1)
{
//深拷贝,目标矩阵头中的大小信息与源矩阵深拷贝并不申请新的空间,否则先申请空间后再进行拷贝.
train_samples[i].copyTo(train_data.row((int)i));
}
}
}
//得到svm检测器
//SVM训练完成后得到的XML文件里面,有一个数组,叫做support vector,还有一个数组,叫做alpha, 有一个浮点数,叫做rho;
//将alpha矩阵同support vector相乘,注意,alpha*supportVector, 将得到一个行向量,将该向量前面乘以 - 1。之后,再该行向量的最后添加一个元素rho。
//如此,变得到了一个分类器,利用该分类器,直接替换opencv中行人检测默认的那个分类器(cv::HOGDescriptor::setSVMDetector())
void TargetDetection::getSvmDetector(const Ptr& svm, vector & hog_detector)
{
//获取支持向量,但当内核不能设为 SVM::LINEAR,因为函数并不能得到支持向量,这是3以上版本的缺陷
Mat svm_mat = svm->getSupportVectors();
const int sv_total = svm_mat.rows;
//获取alpha和rho
Mat alpha;
//支持向量所在的索引
Mat svm_index;
//获得SVM的决策函数
double rho = svm->getDecisionFunction(0, alpha, svm_index);
//括号中的条件不满足时,返回错误
CV_Assert(alpha.total() == 1 && svm_index.total() == 1 && sv_total == 1);
CV_Assert((alpha.type() == CV_64F && alpha.at(0) == 1.) ||
(alpha.type() == CV_32F && alpha.at(0) == 1.f));
CV_Assert(svm_mat.type() == CV_32F);
hog_detector.clear();
hog_detector.resize(svm_mat.cols + 1);
//内存拷贝
memcpy(&hog_detector[0], svm_mat.ptr(), svm_mat.cols * sizeof(hog_detector[0]));
hog_detector[svm_mat.cols] = (float)-rho;
}
//测试图像
int TargetDetection::testTrainedDetector(string obj_det_filename, string test_dir, string videofilename)
{
cout << "开始测试图像..." << endl;
HOGDescriptor hog;
//加载训练好的文件
hog.load(obj_det_filename);
vector files;
glob(test_dir, files);
int delay = 0;
VideoCapture cap;
if (videofilename != "")
{
if (videofilename.size() < 3)
{
char* end;
int i = static_cast(strtol(videofilename.c_str(), &end, 10));
cap.open(i);
}
else
{
cap.open(videofilename);
}
}
obj_det_filename = "testing " + obj_det_filename;
//namedWindow(obj_det_filename, WINDOW_NORMAL);
for (size_t i = 0;; i++)
{
Mat img;
if (cap.isOpened())
{
cap >> img;
delay = 1;
}
else if (i < files.size())
{
img = imread(files[i]);
}
if (img.empty())
{
return 0;
}
vector foundWeights;
//矩形框数组
vector found, found_filtered;
//多尺度检测
hog.detectMultiScale(img, found, foundWeights);
//找出所有没有嵌套的矩形框r,并放入found_filtered中,如果有嵌套的话,则取外面最大的那个矩形框放入found_filtered中
for (int i = 0; i < found.size(); i++)
{
//清除权值较小的检测窗口
if (foundWeights[i] < 0.5)
{
continue;
}
Rect r = found[i];
int j = 0;
for (; j < found.size(); j++)
{
if (j != i && (r & found[j]) == r)
{
break;
}
}
if (j == found.size())
{
found_filtered.push_back(r);
}
}
//画矩形框,因为hog检测出的矩形框比实际人体框要稍微大些,所以这里需要做一些调整
for (int i = 0; i 训练总结
1.我自己测试用的正样本是2000多张,负样本为12000,达到的效果跟OpenCV官方样例差不多,会有漏检的现象,如果把负样本减少到6000张,会有误检的现象,之前我做过别的物体检测时,试过几种正样本和负样本的比例,最好的状态是1:4,但精准高一些的话,还要加大正负样本的数量。
2.代码只是一个框架,如果要用到项目上,还要优化好多细节的地方,代码并不只是用来做行人检测而已,我之前拿这个代码做过马匹、车辆的测试。
3.如果项目要求要很高的精准度,样本的数量又没有那么多,那么建议还是用caffe做相关的训练,OpenCV3之后的DNN模块可以使用caffe训练出来的模型。
4.有兴趣讨论学习可以加群:487350510。