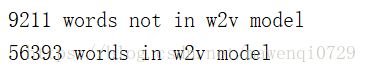新闻分类器的模型训练与单篇分类(cnn+word2vec)
新闻分类器的模型训练与单篇分类(cnn+word2vec)
在cnn之上引入word2vec的好处:(1)间接引入外部训练数据,防止过拟合;(2)减少需要训练的参数个数,提高训练效率
数据预处理
将下载的原始数据进行转码,然后给文本标类别的标签,然后制作训练与测试数据,然后控制文本长度,分词,去标点符号
哎,坑多,费事,比较麻烦
首先,搜狗实验室提供的数据下载下来是 xml 格式,并且是 GBK (万恶之源)编码,需要转成 UTF8,并整理成 json 方便处理。原始数据长这个样:
利用 python 先读入数据然后转码再保存
挑选出的11个类分别为:
- 政治
- 社会
- 军事
- 财经
- 教育
- 体育
- 娱乐
- 反腐
- 科技
- 健康
用序号1~11表示
对这些新闻的长度进行统计结果如下:
由于发现短文本居多所以选择截取每段文字的前100字进行短文本的训练。去掉停用词并用jieba进行分词后的新闻如下图:
1 CNN
深度学习用的 keras 工具,操作简单易懂,模型上手飞快,居家旅行必备。keras 后端用的 Tensorflow,虽然用什么都一样
不使用预训练 word2vec 模型的 CNN:
首先一些先设定一些会用到的参数
MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH = 100 # 每条新闻最大长度
EMBEDDING_DIM = 200 # 词向量空间维度
VALIDATION_SPLIT = 0.16 # 验证集比例
TEST_SPLIT = 0.2 # 测试集比例第一步先把训练与测试数据放在一起提取特征,使用 keras 的 Tokenizer 来实现,将新闻文档处理成单词索引序列,单词与序号之间的对应关系靠单词的索引表 word_index 来记录,这里从所有新闻中提取到 65604 个单词,比如 [苟,国家,生死] 就变成了 [1024, 666, 233] ;然后将长度不足 100 的新闻用 0 填充(在前端填充),用 keras 的 pad_sequences 实现;最后将标签处理成 one-hot 向量,比如 6 变成了 [0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0],用 keras 的 to_categorical 实现
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
from keras.utils import to_categorical
import numpy as np
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(all_texts)
sequences = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(all_texts)
word_index = tokenizer.word_index
print('Found %s unique tokens.' % len(word_index))
data = pad_sequences(sequences, maxlen=MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH)
labels = to_categorical(np.asarray(all_labels))
print('Shape of data tensor:', data.shape)
print('Shape of label tensor:', labels.shape)再将处理后的新闻数据按 6.4:1.6:2 分为训练集,验证集,测试集
p1 = int(len(data)*(1-VALIDATION_SPLIT-TEST_SPLIT))
p2 = int(len(data)*(1-TEST_SPLIT))
x_train = data[:p1]
y_train = labels[:p1]
x_val = data[p1:p2]
y_val = labels[p1:p2]
x_test = data[p2:]
y_test = labels[p2:]
print 'train docs: '+str(len(x_train))
print 'val docs: '+str(len(x_val))
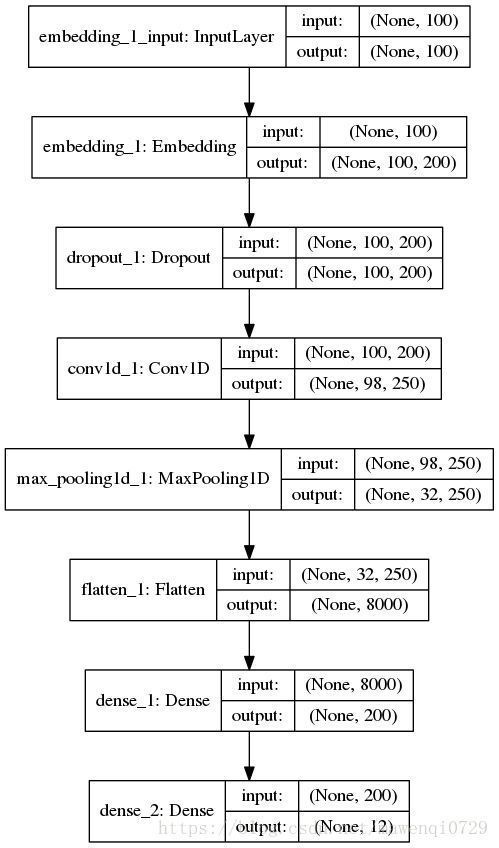
print 'test docs: '+str(len(x_test))然后就是搭建模型,首先是一个将文本处理成向量的 embedding 层,这样每个新闻文档被处理成一个 100 x 200 的二维向量,100 是每条新闻的固定长度,每一行的长度为 200 的行向量代表这个单词在空间中的词向量。下面通过 1 层卷积层与池化层来缩小向量长度,再加一层 Flatten 层将 2 维向量压缩到 1 维,最后通过两层 Dense(全连接层)将向量长度收缩到 12 上,对应新闻分类的 12 个类(其实只有 11 个类,标签 0 没有用到)。搭完收工,最后,训练模型,测试模型,一鼓作气,攻下高地。
from keras.layers import Dense, Input, Flatten, Dropout
from keras.layers import Conv1D, MaxPooling1D, Embedding
from keras.models import Sequential
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(len(word_index) + 1, EMBEDDING_DIM, input_length=MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH))
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Conv1D(250, 3, padding='valid', activation='relu', strides=1))
model.add(MaxPooling1D(3))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(EMBEDDING_DIM, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(labels.shape[1], activation='softmax'))
model.summary()模型长这个样子
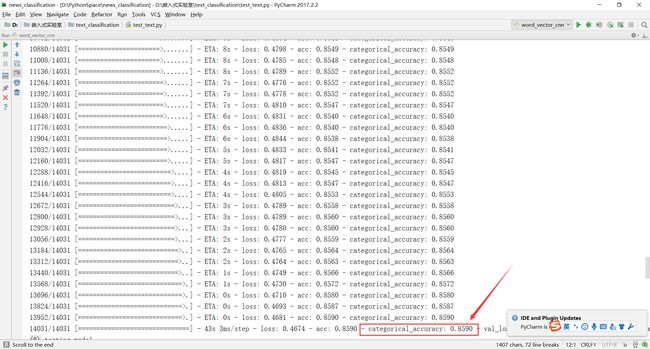
训练结果如图所示:
准确率81.5279%
正常的深度学习训练,比如上面的 CNN 模型,第一层(除去 Input 层)是一个将文本处理成向量的 embedding 层。这里为了使用预训练的 word2vec 来代替这个 embedding 层,就需要将 embedding 层的 1312 万个参数用 word2vec 模型中的词向量替换。替换后的 embedding 矩阵形状为 65604 x 200,65604 行代表 65604 个单词,每一行的这长度 200 的行向量对应这个词在 word2vec 空间中的 200 维向量。最后,设定 embedding 层的参数固定,不参加训练,这样就把预训练的 word2vec 嵌入到了深度学习的模型之中
VECTOR_DIR = 'wiki.zh.vector.bin' # 词向量模型文件
from keras.utils import plot_model
from keras.layers import Embedding
import gensim
w2v_model = gensim.models.KeyedVectors.load_word2vec_format(VECTOR_DIR, binary=True)
embedding_matrix = np.zeros((len(word_index) + 1, EMBEDDING_DIM))
for word, i in word_index.items():
if unicode(word) in w2v_model:
embedding_matrix[i] = np.asarray(w2v_model[unicode(word)],
dtype='float32')
embedding_layer = Embedding(len(word_index) + 1,
EMBEDDING_DIM,
weights=[embedding_matrix],
input_length=MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH,
trainable=False)模型搭建与刚才类似,就是用嵌入了 word2vec 的 embedding_layer 替换原来的 embedding 层
from keras.layers import Dense, Input, Flatten, Dropout
from keras.layers import Conv1D, MaxPooling1D, Embedding
from keras.models import Sequential
model = Sequential()
model.add(embedding_layer)
model.add(Dropout(0.2))
model.add(Conv1D(250, 3, padding='valid', activation='relu', strides=1))
model.add(MaxPooling1D(3))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(EMBEDDING_DIM, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(labels.shape[1], activation='softmax'))
model.summary()
#plot_model(model, to_file='model.png',show_shapes=True)
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer='rmsprop',
metrics=['acc'])
model.fit(x_train, y_train, validation_data=(x_val, y_val), epochs=2, batch_size=128)
model.save('word_vector_cnn.h5')
print model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)模型长相跟之前一致,实验输出与测试结果如下:
准确率为:85.90%!!!
不仅准确率有显著地提高,而且时间也剪短了不少。
缺憾*
在训练过程中我输出了在w2v模型中找到及没找到的词的总数,发现虽然有56393个词找到了,却仍有9211个词未在模型中找到而在训练过程中遭到了抛弃,这是因为我用的是word2vec自带的embedding层,而如果我根据训练的新闻数据自己构造一个层,则可以加入那些新闻里特别的词汇,比如凯尔特人之类的,这点有待改善。
单篇新闻进行分类
直接调用之前训练好的模型,将另一篇新的新闻打开读入,然后放入模型中得到预测结果。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.models import load_model
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
import jieba
MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH = 100
model = load_model('word_vector_cnn.h5')
'''text = open('test.txt', 'r', encoding = 'utf-8').read()
result = jieba.cut(text)
rtext=""
for i in result:
rtext += i
rtext += ' '
print (rtext)'''
stopwords=[]
for word in open('stopword.txt','r',encoding='utf-8', errors='ignore').read():
stopwords.append(word.strip())
# print(word)
article=open('test.txt','r',encoding='utf-8', errors='ignore').read()
print(stopwords)
words=jieba.cut(article,cut_all=False)
rtext=""
for word in words:
print(word)
if word not in stopwords:
rtext+=word+" "
print (rtext)
tokenizer = Tokenizer()
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(rtext)
print(tokenizer.fit_on_texts(rtext))
sequences = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(rtext)
print(len(sequences))
print(sequences)
sequence=[]
for i in range(len(sequences)):
#print(sequences[i])
if sequences[i]:
sequence.append(sequences[i][0])
print(sequence)
seq = []
seq.append(sequence)
word_index = tokenizer.word_index
print(word_index)
data = pad_sequences(seq, maxlen=MAX_SEQUENCE_LENGTH)
print(data)
output = model.predict(data)
print (output)