【LeetCode】64. Minimum Path Sum
64. Minimum Path Sum
Description:
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example:
Input: [ [1,3,1], [1,5,1], [4,2,1] ] Output: 7 Explanation: Because the path 1→3→1→1→1 minimizes the sum.
解题思路:
(1) 递归法
问题分析:
1)假如我们就在最右下角的格子(也可以想象成网格只有一个格子),那么最短路径和就是格子中的值;
2)假如我们在最后一行的格子中,假如是grid[grid.length - 1][col],那么从这个点出发到最右下角的最小路径和就是它本身加上它右边的格子到最右下角的最小路径和。
3)最后一列和最后一行是同理的。
4)一个普通的位置,它到最右下角的最小路径和是多少呢,是它左边一个位置和它下面一个位置的最小路径和中最小的那个加上它自己格子的值。
递归实现代码:
public class gridMinPathSum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int[][] arr = {
{1, 3, 1},
{1, 5, 1},
{4, 2, 1},
};
System.out.println(minPathSum(arr));
}
public static int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
return pathSum(grid, 0, 0);
}
public static int pathSum(int[][] grid, int row, int col) {
if(row == grid.length-1 && col == grid[0].length-1)
return grid[row][col];
if(row == grid.length -1)
return grid[row][col] + pathSum(grid, row, col + 1);
if(col == grid[0].length - 1)
return grid[row][col] + pathSum(grid, row + 1, col);
return grid[row][col] + Math.min(pathSum(grid, row + 1, col),
pathSum(grid, row, col + 1));
}
}
(2)记忆化搜索
既然上面的过程有很多重复计算的子问题,那我们可以在递归的过程中记录子问题的解,如果之前已经求解过,使用一个二位数组记录一下,那么我们下次再需要这个子问题的解的时候不需要递归,直接拿出来用即可。
已经AC的代码:
public class gridMinPathSum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int[][] arr = {
{1, 3, 1},
{1, 5, 1},
{4, 2, 1},
};
System.out.println(minPathSum(arr));
}
public static int[][] memo;
public static int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
memo = new int[grid.length][grid[0].length];
for(int i=0; i(3)动态规划法
动态规划的过程可以看做是递归的逆过程,既然递归是从上往下求解,每个大的问题都要先去求解子问题。所以,动态规划是先求解小的子问题,依次往上,所以大问题需要的子问题已经提前求好了。
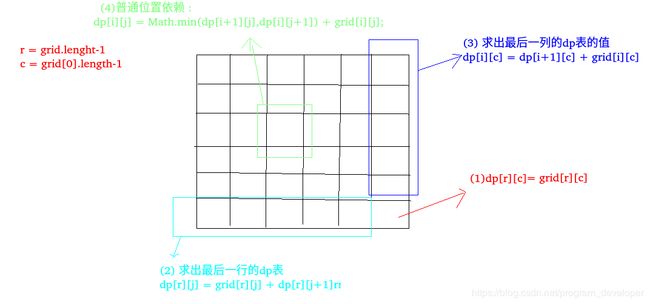
对于这个题目:
- 先生成一张二维dp表,然后按照递归相反的方向求解;
- 先把dp表的最右下角,最后一行,和最后一列的位置填好;
- 然后一个其它的位置依赖它下面的位置和右边的位置,所以我们依次从下到上,做右往左,填整张dp表,最后dp[0][0]就是答案。
已经AC的代码:
public class gridMinPathSum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int[][] arr = {
{1, 3, 1},
{1, 5, 1},
{4, 2, 1},
};
System.out.println(minPathSum(arr));
}
public static int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
int row = grid.length ;
int col = grid[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[row][col];
dp[row - 1][col - 1] = grid[row - 1][col - 1];
//填充最后一行
for(int i = col - 2; i>=0; i-- ) {
dp[row - 1][i] = dp[row - 1][i + 1] + grid[row - 1][i];
}
//填充最后一列
for(int i = row - 2; i>=0; i-- ) {
dp[i][col - 1] = dp[i + 1][col - 1] + grid[i][col - 1];
}
//填充其他
for(int i = row - 2; i>=0; i--) {
for(int j = col - 2; j>=0; j--) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i + 1][j], dp[i][j + 1]) + grid[i][j];
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
}Reference:
【1】https://blog.csdn.net/zxzxzx0119/article/details/81227300