opengl es3.0游戏开发学习笔记2--绘制地月星系
下面是效果图,是旋转的的照片看不出旋转效果,可以运行源码点击打开链接
我的开发环境是Android studio 2.1.3 自带的模拟器不支持opengl es3.0 只能在真机上调试
各个类
Celestial 类实现的是绘制星星,原理是绘制一个大的球并且在一个打球随机产生亮点,这样在内部看起来就实现天空中星星的效果
Constantl类实现的一个是存放了一些常量
Earth类是绘制一个地球
Moon是绘制一个月亮,和地球的原理是一样的都是绘制球,不过是纹理不同
MatrixState类是个矩阵的帮助类,里面写的一些常用的矩阵变换
MyActive是建立一个活动,并且让屏幕显示MySurfaceView创建的视口
MySurfaceView是创建opengl的视窗口还有触摸事件的响应
ShaderUtil类是个纹理的帮助类,实现纹理的编译和着色器的创建
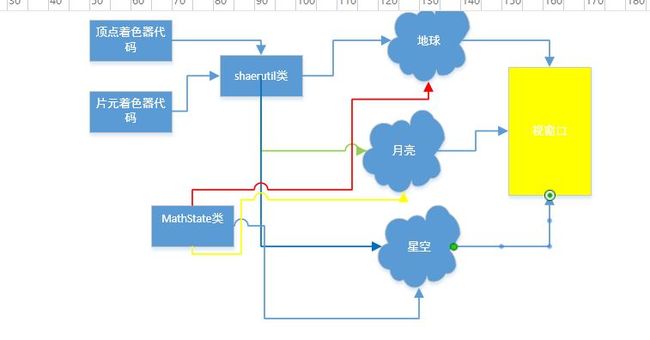
整体应该是这个样
MatrState来类 由于opengl 都是用矩阵去控制的有这个类比较方便,里面还有相机位置和太阳位置的控制
package com.opengl.a7_5_earthmoon;
import android.opengl.Matrix;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.nio.FloatBuffer;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* Created by admin on 2016/11/14.
*/
//存储系统存储矩阵的类
public class MatrixState {
private static float [] mProjMatrix=new float[16];//4*4矩阵投影用
private static float [] mVMatrix=new float[16];//摄像机位置朝向9参数矩阵
private static float [] currMatrix;//当前变换矩阵
public static float[] lightLocationSun=new float[]{0,0,0};//太阳定位光光源的位置
public static FloatBuffer cameraFB;//相机参数的缓冲区
public static FloatBuffer lightPositionFBSun;
public static StackmStack=new Stack();//保护变换矩阵的栈
public static void setInitStack()//获取不变初始矩阵
{
currMatrix=new float[16];
Matrix.setRotateM(currMatrix,0,0,1,0,0);//这里是把矩阵在x轴上旋转0度
}
public static void pushMatrix()//获取不变换初始矩阵
{
mStack.push(currMatrix.clone());//clone功能是复制 把这个矩阵复制后然后存进栈中
}
public static void popMatrix()//恢复变换矩阵
{
currMatrix=mStack.pop();
}
public static void translate(float x,float y,float z)//设置沿xyz轴移动
{
Matrix.translateM(currMatrix,0,x,y,z);
}
public static void rotate(float angle,float x,float y,float z)//设置绕xyz轴旋转
{
Matrix.rotateM(currMatrix,0,angle,x,y,z);
}
//设置摄像机
public static void setCamera
(
float cx, //摄像机位置x
float cy, //摄像机位置y
float cz, //摄像机位置z
float tx, //摄像机目标点x
float ty, //摄像机目标点y
float tz, //摄像机目标点z
float upx, //摄像机UP向量X分量
float upy, //摄像机UP向量Y分量
float upz //摄像机UP向量Z分量
)
{
Matrix.setLookAtM
(
mVMatrix,
0,
cx,
cy,
cz,
tx,
ty,
tz,
upx,
upy,
upz
);
float[] cameraLocation=new float[3];//摄像机位置
cameraLocation[0]=cx;
cameraLocation[1]=cy;
cameraLocation[2]=cz;
ByteBuffer llbb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(3*4);
llbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());//设置字节顺序
cameraFB=llbb.asFloatBuffer();
cameraFB.put(cameraLocation);
cameraFB.position(0);
}
//设置透视投影参数
public static void setProjectFrustum
(
float left, //near面的left
float right, //near面的right
float bottom, //near面的bottom
float top, //near面的top
float near, //near面距离
float far //far面距离
)
{
Matrix.frustumM(mProjMatrix, 0, left, right, bottom, top, near, far);
}
//设置正交投影参数
public static void setProjectOrtho
(
float left, //near面的left
float right, //near面的right
float bottom, //near面的bottom
float top, //near面的top
float near, //near面距离
float far //far面距离
)
{
Matrix.orthoM(mProjMatrix, 0, left, right, bottom, top, near, far);
}
//获取总的变换矩阵
public static float[] getFinalMatrix(){
float[] mMVPMatrix=new float[16];
Matrix.multiplyMM(mMVPMatrix,0,mVMatrix,0,currMatrix,0);
Matrix.multiplyMM(mMVPMatrix,0,mProjMatrix,0,mMVPMatrix,0);
return mMVPMatrix;
}
//获取具体物体的变换矩阵
public static float[] getMMatrix(){
return currMatrix;
}
//设置太阳光源的位置的方法
public static void setLightLocationSun(float x,float y,float z){
lightLocationSun[0]=x;
lightLocationSun[1]=y;
lightLocationSun[2]=z;
ByteBuffer llbb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(3*4);
llbb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());//设置字节顺序
lightPositionFBSun=llbb.asFloatBuffer();
lightPositionFBSun.put(lightLocationSun);
lightPositionFBSun.position(0);
}
}
Eearth类 主要是绘制一个球,然后在在纹理时采用的两个纹理,根据收到的太阳光,太阳光强的地方用白天的纹理,太阳光弱的用晚上的纹理。这种绘制球的方式和网上大部分绘制球的教程是一样的就是把球分割然后绘制,但是这个有个缺陷是两个极点点会非常密集,比较好的方式是几何球的绘制方法,用正十二面体,但是还没看懂这种绘制的代码,看懂在写几何绘制球
public class Earth {
Context context;
int mProgram;//自定义渲染管线程序id
int muMVPMatrixHandle;//总变换矩阵引用
int muMMatrixHandle;//位置,旋转变换矩阵
int maCameraHandle;//摄像机位置属性引用
int maPositionHandle;//顶点位置属性引用
int maNormalHandle;//顶点法向量属性引用
int maTexCoorHandle;//顶点纹理坐标属性引用
int maSunLightLocationHandle;//光源位置属性引用
int uDayTexHandle;//白天纹理属性引用
int uNightTexHandle;//黑夜纹理属性引用
String mVertexShader;//顶点着色器代码脚本
String mFragmentShader;//片元着色器代码脚本
FloatBuffer mVertexBuffer;//顶点坐标数据缓冲
FloatBuffer mTexCoorBuffer;//顶点纹理坐标数据缓冲
int vCount=0;
public Earth(MySurfaceView mv , float r, Context context){
this.context=context;
//调用初始化顶点数据的initVertexData
initVertexData(r);
//调用初始化着色器的intiShader方法
initShaderGLSL(mv);
}
//初始化顶点数据的方法
public void initVertexData(float r)
{
//顶点坐标数据的初始化
final float UNIT_SIZE=0.5f;
ArrayListalVertix=new ArrayList();//存放顶点坐标数据ArrayList
final float angleSpan=10f;//将球单位切分的角度
for(float vAngle=90;vAngle>-90;vAngle=vAngle-angleSpan) //垂直方向angleSpan度一份
{
for (float hAngle=360;hAngle>0;hAngle=hAngle-angleSpan) //水平方向angleSpan度一份
{
//纵向横向各到一个角度后计算对应的此点在球面上的坐标
double xozLength=r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(vAngle));
float x1=(float)(xozLength*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(hAngle)));
float z1=(float)(xozLength*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(hAngle)));
float y1=(float)(r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(vAngle)));
xozLength=r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(vAngle-angleSpan));
float x2=(float)(xozLength*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(hAngle)));
float z2=(float)(xozLength*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(hAngle)));
float y2=(float)(r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(vAngle-angleSpan)));
xozLength=r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(vAngle-angleSpan));
float x3=(float)(xozLength*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(hAngle-angleSpan)));
float z3=(float)(xozLength*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(hAngle-angleSpan)));
float y3=(float)(r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(vAngle-angleSpan)));
xozLength=r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(vAngle));
float x4=(float)(xozLength*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(hAngle-angleSpan)));
float z4=(float)(xozLength*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(hAngle-angleSpan)));
float y4=(float)(r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(vAngle)));
//构建第一三角形
alVertix.add(x1);alVertix.add(y1);alVertix.add(z1);
alVertix.add(x2);alVertix.add(y2);alVertix.add(z2);
alVertix.add(x4);alVertix.add(y4);alVertix.add(z4);
//构建第二三角形
alVertix.add(x4);alVertix.add(y4);alVertix.add(z4);
alVertix.add(x2);alVertix.add(y2);alVertix.add(z2);
alVertix.add(x3);alVertix.add(y3);alVertix.add(z3);
}
}
vCount=alVertix.size()/3;//顶点的数量为坐标值数量的1/3,因为一个顶点有3个坐标
//将alVertix中的坐标值转存到一个float数组中
float vertices[]=new float[vCount*3];
for(int i=0;i Moon和地球是一样的,就是纹理不同
package com.opengl.a7_5_earthmoon;
import android.content.Context;
import android.opengl.GLES30;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.nio.FloatBuffer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
/**
* Created by admin on 2016/11/15.
*/
//表示月球的类,为普通纹理球,未采用多重纹理
public class Moon
{
Context context;
int mProgram;//自定义渲染管线程序id
int muMVPMatrixHandle;//总变换矩阵引用
int muMMatrixHandle;//位置、旋转变换矩阵
int maCameraHandle; //摄像机位置属性引用
int maPositionHandle; //顶点位置属性引用
int maNormalHandle; //顶点法向量属性引用
int maTexCoorHandle; //顶点纹理坐标属性引用
int maSunLightLocationHandle;//光源位置属性引用
String mVertexShader;//顶点着色器 代码脚本
String mFragmentShader;//片元着色器代码脚本
FloatBuffer mVertexBuffer;//顶点坐标数据缓冲
FloatBuffer mTexCoorBuffer;//顶点纹理坐标数据缓冲
int vCount=0;
public Moon(MySurfaceView mv,float r,Context context)
{
this.context=context;
//调用初始化顶点数据的方法
initVertexData(r);
//调用初始化着色器的方法
initShader(mv);
}
//初始化顶点数据的方法
public void initVertexData(float r)
{
//顶点坐标数据的初始化================begin============================
final float UNIT_SIZE=0.5f;
ArrayList alVertix=new ArrayList();//存放顶点坐标的ArrayList
final float angleSpan=10f;//将球进行单位切分的角度
for(float vAngle=90;vAngle>-90;vAngle=vAngle-angleSpan)//垂直方向angleSpan度一份
{
for(float hAngle=360;hAngle>0;hAngle=hAngle-angleSpan)//水平方向angleSpan度一份
{//纵向横向各到一个角度后计算对应的此点在球面上的坐标
double xozLength=r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(vAngle));
float x1=(float)(xozLength*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(hAngle)));
float z1=(float)(xozLength*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(hAngle)));
float y1=(float)(r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(vAngle)));
xozLength=r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(vAngle-angleSpan));
float x2=(float)(xozLength*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(hAngle)));
float z2=(float)(xozLength*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(hAngle)));
float y2=(float)(r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(vAngle-angleSpan)));
xozLength=r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(vAngle-angleSpan));
float x3=(float)(xozLength*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(hAngle-angleSpan)));
float z3=(float)(xozLength*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(hAngle-angleSpan)));
float y3=(float)(r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(vAngle-angleSpan)));
xozLength=r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(vAngle));
float x4=(float)(xozLength*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(hAngle-angleSpan)));
float z4=(float)(xozLength*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(hAngle-angleSpan)));
float y4=(float)(r*UNIT_SIZE*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(vAngle)));
//构建第一三角形
alVertix.add(x1);alVertix.add(y1);alVertix.add(z1);
alVertix.add(x2);alVertix.add(y2);alVertix.add(z2);
alVertix.add(x4);alVertix.add(y4);alVertix.add(z4);
//构建第二三角形
alVertix.add(x4);alVertix.add(y4);alVertix.add(z4);
alVertix.add(x2);alVertix.add(y2);alVertix.add(z2);
alVertix.add(x3);alVertix.add(y3);alVertix.add(z3);
}
}
vCount=alVertix.size()/3;//顶点的数量为坐标值数量的1/3,因为一个顶点有3个坐标
//将alVertix中的坐标值转存到一个float数组中
float vertices[]=new float[vCount*3];
for(int i=0;i 把原来的坐标保存起来,然后移动旋转坐标绘制物体。在恢复后又回来没绘制之前的地方,方便绘制别的物体
package com.opengl.a7_5_earthmoon;
import android.annotation.SuppressLint;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.opengl.GLES30;
import android.opengl.GLSurfaceView;
import android.opengl.GLUtils;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import javax.microedition.khronos.egl.EGLConfig;
import javax.microedition.khronos.opengles.GL10;
/**
* Created by admin on 2016/11/14.
*/
@SuppressLint("ClickableViewAccessibility")
public class MySurfaceView extends GLSurfaceView{
private final float TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR=180.0f/320;//角度缩放比例
private SceneRenderer mRenderer;//场景渲染器
private float mPreviousX;//上次的触控位置x坐标
private float mPreviousY;//上次的触控位置的y坐标
int textureIdEarth;//系统分配的地球纹理ID
int textureIdEarthNight;//系统分配的夜晚的纹理ID
int textureIdMoon;//系统分配的月球纹理ID
float yAngle=0;//太阳灯光绕y轴旋转的角度
float xAngle=0;//摄像机绕x轴旋转的角度
float eAngle=0;//地球自传的角度
float cAngle=0;//天球自传的角度
public MySurfaceView(Context context){
super(context);
this.setEGLContextClientVersion(3);//设置使用OPENGL ES3.0
mRenderer=new SceneRenderer(context);//创建场景渲染器
setRenderer(mRenderer);//设置渲染器
setRenderMode(GLSurfaceView.RENDERMODE_CONTINUOUSLY);//设置渲染模式为持续渲染
}
//触摸事件回调方法
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
float x = e.getX();
float y = e.getY();
switch (e.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
//触控横向位移太阳绕y轴旋转
float dx = x - mPreviousX;//计算触控笔X位移
yAngle += dx * TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR;//将X位移折算成角度
float sunx = (float) (Math.cos(Math.toRadians(yAngle)) * 100);
float sunz = -(float) (Math.sin(Math.toRadians(yAngle)) * 100);
MatrixState.setLightLocationSun(sunx, 5, sunz); //太阳位置
//触控纵向位移摄像机绕x轴旋转 -90~+90
float dy = y - mPreviousY;//计算触控笔Y位移
xAngle += dy * TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR;//将Y位移折算成绕X轴旋转的角度
if(xAngle>90)
{
xAngle=90;
}
else if(xAngle<-90)
{
xAngle=-90;
}
float cy=(float) (7.2*Math.sin(Math.toRadians(xAngle)));
float cz=(float) (7.2*Math.cos(Math.toRadians(xAngle)));
float upy=(float) Math.cos(Math.toRadians(xAngle));
float upz=-(float) Math.sin(Math.toRadians(xAngle));
MatrixState.setCamera(0, cy, cz, 0, 0, 0, 0, upy, upz);
}
mPreviousX = x;//记录触控笔位置
mPreviousY = y;
return true;
}
private class SceneRenderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer
{
Context context;
Earth earth;//地球
Moon moon;//月亮
Celestial cSmall;//小星星天球
Celestial cBig;//大星星天球
public SceneRenderer(Context context){
this.context=context;
}
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl)
{
//清楚屏幕深度缓冲与颜色缓冲
GLES30.glClear(GLES30.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT | GLES30.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
//保护现场
MatrixState.pushMatrix();
//地球自转
MatrixState.rotate(eAngle,0,1,0);
//绘制地球
earth.drawSelf(textureIdEarth,textureIdEarthNight);
//推坐标系统月球的位置
MatrixState.translate(2f,0,0);
//月球自传
MatrixState.rotate(eAngle,0,1,0);
//绘制月球
moon.drawSelf(textureIdMoon);
//恢复现场
MatrixState.popMatrix();
//保护现场
MatrixState.pushMatrix();
//星空天球旋转
MatrixState.rotate(cAngle,0,1,0);
//绘制小尺寸星星的天球
cSmall.drawSelf();
//恢复现场
MatrixState.popMatrix();
}
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl,int width,int height){
//设置视窗大小及位置
GLES30.glViewport(0,0,width,height);
//计算GLSurfaeVIew的宽高比
Constant.ratio=(float)width/height;
//调用此方法计算产生透视投影矩阵
MatrixState.setProjectFrustum(-Constant.ratio,Constant.ratio,-1,1,4f,100);
//设置相机9参数
MatrixState.setCamera(0f,0f,7.2f,0f,0f,0f,0f,1.0f,0f);
//打开背面剪切
GLES30.glEnable(GLES30.GL_CULL_FACE);
//初始化纹理
textureIdEarth=initTexture(R.drawable.earth);
textureIdEarthNight=initTexture(R.drawable.earthn);
textureIdMoon=initTexture(R.drawable.moon);
//设置太阳灯光的初始位置
MatrixState.setLightLocationSun(100,5,0);
//启动一个线程定时旋转地球、月球
new Thread()
{
public void run()
{
while(Constant.threadFlag)
{
//地球自转角度
eAngle=(eAngle+2)%360;
//天球自转角度
cAngle=(cAngle+0.2f)%360;
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
}
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl,EGLConfig config){
//设置屏幕背景颜色RGBA
GLES30.glClearColor(0.0f,0.0f,0.0f,1.0f);
//创建地球对象
earth=new Earth(MySurfaceView.this,2.0f,context);
//创建月球对象
moon=new Moon(MySurfaceView.this,1.0f,context);
//创建小星星天球对象
cSmall=new Celestial(1,0,1000,MySurfaceView.this,context);
//创建大星天球对象
cBig=new Celestial(2,0,500,MySurfaceView.this,context);
GLES30.glEnable(GLES30.GL_DEPTH_TEST);
//初始化变换矩阵
MatrixState.setInitStack();
}
}
public int initTexture(int drawableId)//textureId
{
//生成纹理ID
int[] textures = new int[1];
GLES30.glGenTextures
(
1, //产生的纹理id的数量
textures, //纹理id的数组
0 //偏移量
);
int textureId=textures[0];
GLES30.glBindTexture(GLES30.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureId);
GLES30.glTexParameterf(GLES30.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES30.GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER,GLES30.GL_NEAREST);
GLES30.glTexParameterf(GLES30.GL_TEXTURE_2D,GLES30.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER,GLES30.GL_LINEAR);
GLES30.glTexParameterf(GLES30.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES30.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S,GLES30.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
GLES30.glTexParameterf(GLES30.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES30.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T,GLES30.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
//通过输入流加载图片===============begin===================
InputStream is = this.getResources().openRawResource(drawableId);
Bitmap bitmapTmp;
try
{
bitmapTmp = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(is);
}
finally
{
try
{
is.close();
}
catch(IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//通过输入流加载图片===============end=====================
//实际加载纹理
GLUtils.texImage2D
(
GLES30.GL_TEXTURE_2D, //纹理类型
0, //纹理的层次,0表示基本图像层,可以理解为直接贴图
bitmapTmp, //纹理图像
0 //纹理边框尺寸
);
bitmapTmp.recycle(); //纹理加载成功后释放图片
return textureId;
}
}
下边是着色器
地球和月球的着色器加入了对光照的处理,要处理环境光,散射光和镜面光,通过算法模拟出光照的效果
vertex_earth.glsl
#version 300 es
uniform mat4 uMVPMatrix;//总的变换矩阵
uniform mat4 uMMatrix; //变换矩阵
uniform vec3 uCamera;//摄像机的位置
uniform vec3 uLightLocationSun;//太阳光源的位置
in vec3 aPosition;//顶点位置
in vec2 aTexCoor;//顶点纹理坐标
in vec3 aNormal;//法向量
out vec2 vTextureCood; //用于传递给片元着色器的变量
out vec4 vAmbient;//环境光
out vec4 vDiffuse;//发射光
out vec4 vSpecular;//镜面光
//定位光光照计算的方法
void pointLight( //定位光光照计算的方法
in vec3 normal, //法向量
inout vec4 ambient,//环境光的最终强度
inout vec4 diffuse,//散射光最终强度
inout vec4 specular,//镜面光的最终强度
in vec3 lightLocation,//光源位置
in vec4 lightAmbient,//环境光强度
in vec4 lightDiffuse,//散射光强度
in vec4 lightSpecular//镜面光强度
){
ambient=lightAmbient;//直接得出环境光的最终强度
vec3 normalTarget=aPosition+normal;//计算变化后的法向量
vec3 newNormal=(uMMatrix*vec4(normalTarget,1)).xyz-(uMMatrix*vec4(aPosition,1)).xyz;
newNormal=normalize(newNormal);//对法向量规格化
//计算从表面点到摄像机的向量
vec3 eye=normalize(uCamera-(uMMatrix*vec4(aPosition,1)).xyz);
//计算从表面点到光源位置的向量vp
vec3 vp=normalize(lightLocation-(uMMatrix*vec4(aPosition,1)).xyz);
vp=normalize(vp);//格式化
vec3 halfVector=normalize(vp+eye);//求视线与光线的半向量
float shiniess=50.0;//粗糙度,越小越光滑
float nDotViewPosition=max(0.0,dot(newNormal,vp));//求法向量与vp的点积与0的最大值
diffuse=lightDiffuse*nDotViewPosition;//计算散射光的最终的强度
float nDotViewHalfVector=dot(newNormal,halfVector);//法线和半向量 的点积
float powerFacetor=max(0.0,pow(nDotViewHalfVector,shiniess));//镜面反射光强度因子
specular=lightSpecular*powerFacetor;//计算镜面光的最终强度
}
void main() {
//地球着色器的main方法
gl_Position=uMVPMatrix*vec4(aPosition,1);//根据总的变换矩阵计算此次绘制顶点位置
vec4 ambientTemp=vec4(0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0);
vec4 diffuseTemp=vec4(0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0);
vec4 specularTemp=vec4(0.0,0.0,0.0,0.0);
//pointLight(normalize(aNormal),ambientTemp,diffuseTemp,specularTemp,uLightLocation,vec4(005,0.05,0.05,1.0)),vec4(1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0),vec4(0.3,0.3,0.3,1.0);
pointLight(normalize(aNormal),ambientTemp,diffuseTemp,specularTemp,uLightLocationSun,
vec4(0.05,0.05,0.05,1.0),vec4(1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0),vec4(0.3,0.3,0.3,1.0));
vAmbient=ambientTemp;
vDiffuse=diffuseTemp;
vSpecular=specularTemp;
//将顶点的纹理坐标传给片元着色器
vTextureCood=aTexCoor;
}frag_earth.glsl
#version 300 es
precision mediump float;//给出浮点数的精度
in vec2 vTextureCood;//接受从顶点着色器传过来的参数
in vec4 vAmbeient;//接受从顶点着色器过来环境光最终强度
in vec4 vDiffuse;//接受从顶点着色器过来的环境光最终的强度
in vec4 vSpecular;//接受从顶点着色器过来镜面反射光最终的强度
out vec4 fragColor;//传递到渲染管线的片元的颜色
uniform sampler2D sTextureDay;//白天纹理的内容数据
uniform sampler2D sTextureNight;//黑夜纹理的内容数据
void main() {
vec4 finalColorDay;//从白天纹理的采样值
vec4 finalColorNight;//从夜晚纹理只不过的采样的颜色值
finalColorDay=texture(sTextureDay,vTextureCood);//采样出白天纹理的颜色值
finalColorDay=finalColorDay*vAmbeient+finalColorDay*vSpecular+finalColorDay*vDiffuse;
finalColorNight=texture(sTextureNight,vTextureCood);//采样出夜晚纹理的颜色值
finalColorNight=finalColorNight*vec4(0.5,0.5,0.5,1);//计算出的该片元夜晚的颜色值
if(vDiffuse.x>0.21)
{
//当散射光分量大于0.21时
fragColor=finalColorDay;//采用白天的纹理
}
else if(vDiffuse.x<0.05)
{
fragColor=finalColorNight;//采样夜间的纹理
}
else{
float t=(vDiffuse.x-0.05)/0.6;//计算白天的纹理的过渡阶段的百分比
fragColor=t*finalColorDay+(1.0-t)*finalColorNight;//计算白天黑夜的过渡阶段的颜色值
}
}