KMP入门必看
(转自队友Rain的整合:http://blog.csdn.net/Rain722/article/details/52673770)
首先声明:这篇博客来自于我初学KMP算法时对于大多数博客的筛选和整合。文章最下面给出了原文的出处。
KMP算法是拿来处理字符串匹配的。换句话说,给你两个字符串,你需要回答,B串是否是A串的子串(A串是否包含B串)。比如,字符串A="I'm Rain",字符串B="Rain",我们就说B是A的子串。你可以委婉地问你的MM:“假如你要向你喜欢的人表白的话,我的名字是你的告白语中的子串吗?”
首先给出阮一峰博客的图文详解(阮老师还是一如既往的强大)
原文链接http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2013/05/Knuth%E2%80%93Morris%E2%80%93Pratt_algorithm.html
1.
id="iframe_0.49126932986732585" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050103.png?_=0.9512412033042685%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.49126932986732585',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 590px; height: 146px;">
首先,字符串"BBC ABCDAB ABCDABCDABDE"的第一个字符与搜索词"ABCDABD"的第一个字符,进行比较。因为B与A不匹配,所以搜索词后移一位。
2.
id="iframe_0.7910685522381864" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050104.png?_=0.30098373002322676%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.7910685522381864',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 604px; height: 137px;">
因为B与A不匹配,搜索词再往后移。
3.
id="iframe_0.5032963465231861" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050105.png?_=0.6919482203780043%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.5032963465231861',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 577px; height: 137px;">
就这样,直到字符串有一个字符,与搜索词的第一个字符相同为止。
4.
id="iframe_0.44748964709236905" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050106.png?_=0.10721845961379417%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.44748964709236905',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 584px; height: 122px;">
接着比较字符串和搜索词的下一个字符,还是相同。
5.
id="iframe_0.4368114789623896" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050107.png?_=0.6945900020284765%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.4368114789623896',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 577px; height: 130px;">
直到字符串有一个字符,与搜索词对应的字符不相同为止。
6.
id="iframe_0.4976502798791931" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050108.png?_=0.549986092527551%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.4976502798791931',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 588px; height: 158px;">
这时,最自然的反应是,将搜索词整个后移一位,再从头逐个比较。这样做虽然可行,但是效率很差,因为你要把"搜索位置"移到已经比较过的位置,重比一遍。
7.
id="iframe_0.929158994855344" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050107.png?_=0.028987758655416807%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.929158994855344',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 577px; height: 130px;">
一个基本事实是,当空格与D不匹配时,你其实知道前面六个字符是"ABCDAB"。KMP算法的想法是,设法利用这个已知信息,不要把"搜索位置"移回已经比较过的位置,继续把它向后移,这样就提高了效率。
8.
id="iframe_0.659547650488298" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050109.png?_=0.5699711636544809%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.659547650488298',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 645px; height: 189px;">
怎么做到这一点呢?可以针对搜索词,算出一张《部分匹配表》(Partial Match Table)。这张表是如何产生的,后面再介绍,这里只要会用就可以了。
9.
id="iframe_0.34475657506183577" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050107.png?_=0.20329084582154144%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.34475657506183577',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 577px; height: 130px;">
已知空格与D不匹配时,前面六个字符"ABCDAB"是匹配的。查表可知,最后一个匹配字符B对应的"部分匹配值"为2,因此按照下面的公式算出向后移动的位数:
移动位数 = 已匹配的字符数 - 对应的部分匹配值
因为 6 - 2 等于4,所以将搜索词向后移动4位。
10.
id="iframe_0.5957260200607213" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050110.png?_=0.7354852018145288%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.5957260200607213',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 581px; height: 137px;">
因为空格与C不匹配,搜索词还要继续往后移。这时,已匹配的字符数为2("AB"),对应的"部分匹配值"为0。所以,移动位数 = 2 - 0,结果为 2,于是将搜索词向后移2位。
11.
id="iframe_0.08412048278597295" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050111.png?_=0.13359138844694618%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.08412048278597295',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 569px; height: 136px;">
因为空格与A不匹配,继续后移一位。
12.
id="iframe_0.7837952986011545" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050112.png?_=0.9328778492219196%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.7837952986011545',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 590px; height: 142px;">
逐位比较,直到发现C与D不匹配。于是,移动位数 = 6 - 2,继续将搜索词向后移动4位。
13.
id="iframe_0.6526957728631779" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050113.png?_=0.8136109916758352%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.6526957728631779',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 576px; height: 135px;">
逐位比较,直到搜索词的最后一位,发现完全匹配,于是搜索完成。如果还要继续搜索(即找出全部匹配),移动位数 = 7 - 0,再将搜索词向后移动7位,这里就不再重复了。
14.
id="iframe_0.16213974754295513" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050114.png?_=0.0424338042955672%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.16213974754295513',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 551px; height: 202px;">
下面介绍《部分匹配表》是如何产生的。
首先,要了解两个概念:"前缀"和"后缀"。 "前缀"指除了最后一个字符以外,一个字符串的全部头部组合;"后缀"指除了第一个字符以外,一个字符串的全部尾部组合。
15.
id="iframe_0.16148818086754835" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050109.png?_=0.6703231792241651%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.16148818086754835',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 645px; height: 189px;">
"部分匹配值"就是"前缀"和"后缀"的最长的共有元素的长度。以"ABCDABD"为例,
- "A"的前缀和后缀都为空集,共有元素的长度为0;
- "AB"的前缀为[A],后缀为[B],共有元素的长度为0;
- "ABC"的前缀为[A, AB],后缀为[BC, C],共有元素的长度0;
- "ABCD"的前缀为[A, AB, ABC],后缀为[BCD, CD, D],共有元素的长度为0;
- "ABCDA"的前缀为[A, AB, ABC, ABCD],后缀为[BCDA, CDA, DA, A],共有元素为"A",长度为1;
- "ABCDAB"的前缀为[A, AB, ABC, ABCD, ABCDA],后缀为[BCDAB, CDAB, DAB, AB, B],共有元素为"AB",长度为2;
- "ABCDABD"的前缀为[A, AB, ABC, ABCD, ABCDA, ABCDAB],后缀为[BCDABD, CDABD, DABD, ABD, BD, D],共有元素的长度为0。
16.
id="iframe_0.5736068870628264" src="data:text/html;charset=utf8,%3Cimg%20id=%22img%22%20src=%22http://image.beekka.com/blog/201305/bg2013050112.png?_=0.529996294918659%22%20style=%22border:none;max-width:1520px%22%3E%3Cscript%3Ewindow.onload%20=%20function%20()%20%7Bvar%20img%20=%20document.getElementById('img');%20window.parent.postMessage(%7BiframeId:'iframe_0.5736068870628264',width:img.width,height:img.height%7D,%20'http://www.cnblogs.com');%7D%3C/script%3E" frameborder="0" scrolling="no" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; border-width: initial; border-style: none; width: 590px; height: 142px;">
"部分匹配"的实质是,有时候,字符串头部和尾部会有重复。比如,"ABCDAB"之中有两个"AB",那么它的"部分匹配值"就是2("AB"的长度)。搜索词移动的时候,第一个"AB"向后移动4位(字符串长度-部分匹配值),就可以来到第二个"AB"的位置。
kmp算法的理解与实现
一 kmp算法为什么比传统的字符串匹配算法快
假设文本T = y1y2y3....yn, 模式 P = p1p2p3...pm, 传统的匹配算法把位移为0,1,...n-m时的文本依次跟P比较,每次比较最多花费O(m)的时间,算法的复杂度为O((n-m+1)*m)。这种算法没有利用匹配过的信息,每次都从头开始比较,速度很慢。而kmp算法充分利用了之前的匹配信息,从而避免一些明显不合法的位移。加快匹配过程。来看一个例子:
#########000xxxx000###### 文本T
|<---- s ---->|000xxxx000~~~ 模式P
假设位移为s时,T和P匹配了红色部分的字符,即匹配到了模式P的前10个字符,如果按照传统的匹配方法,下一步就是从位移s+1开始比较,而kmp算法则直接从位移s+7开始比较,而且断定:位移s+7对应的串和模式P的前3个字符是相同的,可
以不用比较,直接从第4个字符开始比较,这种跳跃式的匹配是不是比传统匹配方法快很多,如下图所示:
#########000xxxx000###### 文本T
|<-------- s+7-------->| 000xxxx000~~~ 模式P
那么kmp是如何实现这种跳跃的呢?注意到红色部分的字符,即模式P的前10个字符,有一个特点:它的开始3个字符和末尾
3个字符是一样的,又已知文本T也存在红色部分的字符,我们把位移移动 10-3 = 7个位置,让模式P的开始3个字符对准文本
T红色部分的末尾3个字符,那么它们的前3个字符必然可以匹配。
二 构造前缀数组
上面的例子是文本T和模式P匹配了前面10个字符的情况下发生的,而且我们观察到模式P的前缀P10中,它的开始3个字符和末尾3个字符是一样的。如果对于模式P的所有前缀P1,P2...Pm,都能求出它们首尾有多少个字符是一样的,当然相同的字
符数越多越好,那么就可以按照上面的方法,进行跳跃式的匹配。
定义:
Pi表示模式P的前i个字符组成的前缀, next[i] = j表示Pi中的开始j个字符和末尾j个字符是一样的,而且对于前缀Pi来说,这样
的j是最大值。next[i] = j的另外一个定义是:有一个含有j个字符的串,它既是Pi的真前缀,又是Pi的真后缀
规定:
next[1] = next[0] = 0
next[i]就是前缀数组,下面通过1个例子来看如何构造前缀数组。
例子1:cacca有5个前缀,求出其对应的next数组。
前缀2为ca,显然首尾没有相同的字符,next[2] = 0
前缀3为cac,显然首尾有共同的字符c,故next[3] = 1
前缀4为cacc,首尾有共同的字符c,故next[4] = 1
前缀5为cacca,首尾有共同的字符ca,故next[5] = 2
如果仔细观察,可以发现构造next[i]的时候,可以利用next[i-1]的结果。假设模式已求得next[10] = 3,如下图所示:
000#xxx000 前缀P10
000 末尾3个字符
根据前缀函数的定义:next[10] = 3意味着末尾3个字符和P10的前3个字符是一样的
为求next[11],可以直接比较第4个字符和第11个字符,如下图所示:蓝色和绿色的#号所示,如果它们相等,则
next[11] = next[10]+1 = 4,这是因为next[10] = 3保证了前缀P11和末尾4个字符的前3个字符是一样的.
000#xxx000# 前缀P11
000# 末尾4个字符
所以只需验证第4个字符和第11个字符。但如果这两个字符不想等呢?那就继续迭代,利用next[next[10] = next[3]的值来求
next[11]。
代码如下:void compute_prefix(int *next, char *p)
{
int i, n, k;
n = strlen(p);
next[1] = next[0] = 0;
k = 0; /* 第i次迭代开始之前,k表示next[i-1]的值 */
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for (; k != 0 && p[k] != p[i-1]; k = next[k]);
if (p[k] == p[i-1]) k++;
next[i] = k;
}
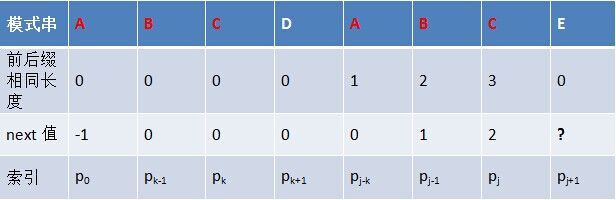
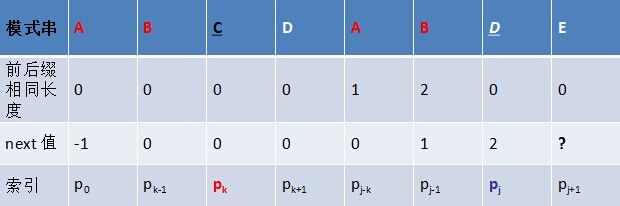
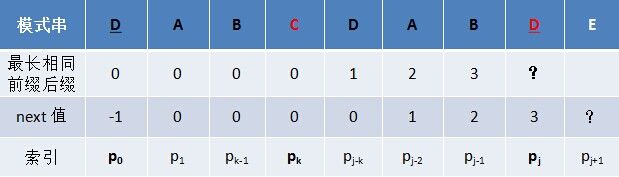
} - 2. 下面的问题是:已知next [0, ..., j],如何求出next [j + 1]呢?
对于P的前j+1个序列字符:
- 若p[k] == p[j],则next[j + 1 ] = next [j] + 1 = k + 1;
- 若p[k ] ≠ p[j],如果此时p[ next[k] ] == p[j ],则next[ j + 1 ] = next[k] + 1,否则继续递归前缀索引k = next[k],而后重复此过程。 相当于在字符p[j+1]之前不存在长度为k+1的前缀"p0 p1, …, pk-1 pk"跟后缀“pj-k pj-k+1, …, pj-1 pj"相等,那么是否可能存在另一个值t+1 < k+1,使得长度更小的前缀 “p0 p1, …, pt-1 pt” 等于长度更小的后缀 “pj-t pj-t+1, …, pj-1 pj” 呢?如果存在,那么这个t+1 便是next[ j+1]的值,此相当于利用已经求得的next 数组(next [0, ..., k, ..., j])进行P串前缀跟P串后缀的匹配。
模式串的后缀:ABDE
模式串的前缀:ABC
前缀右移两位: ABC
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void compute_prefix(int *next, char *p)
{
int n, k;
n = strlen(p);
next[0] = next[1] = 0;
k = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
while(k && p[k] != p[i-1])
k = next[k]; //其实求next数组就是求匹配的字符串前缀后缀相同的字符最大长度,其实与下面的字符一样的
if(p[k] == p[i-1])
k++;
next[i] = k;
}
}
int kmp_match(char *text, char *p, int *next)
{
int ans = 0, j = 0;
int text_len = strlen(text);
int p_len = strlen(p);
for(int i = 0; i < text_len; i++)
{
while(j && text[i] != p[j])
j = next[j];
if(text[i] == p[j])
j++;
if(j == p_len)
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int Case, ans;
char W[10005], T[1000005];
int next[10005];
cin >> Case;
while(Case--)
{
scanf("%s", W);
scanf("%s", T);
compute_prefix(next, W);
ans = kmp_match(T, W, next);
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}