操作系统实验——矩阵乘法
实验任务
在windows操作系统上,利用Windows API编写程序用多线程实现矩阵乘法。实现A、B两个矩阵的乘法,并输出计算结果。
该实验相对比较简单,可先看实验报告的实验步骤,然后需要了解一下几个关于pthread里的函数使用:
(1)pthread_join函数:
函数pthread_join用来等待一个线程的结束。
函数定义: int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval);
描述 :
pthread_join()函数,以阻塞的方式等待thread指定的线程结束。当函数返回时,被等待线程的资源被收回。如果进程已经结束,那么该函数会立即返回。并且thread指定的线程必须是joinable的。
参数 :
thread: 线程标识符,即线程ID,标识唯一线程。
retval: 用户定义的指针,用来存储被等待线程的返回值。
返回值 : 0代表成功。 失败,返回的则是错误号。
看下面一段程序:
#include
#include
#include
void *thread(void *str)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
sleep(2);
printf( "This in the thread : %d\n" , i );
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t pth;
int i;
int ret = pthread_create(&pth, NULL, thread, (void *)(i));
pthread_join(pth, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < 10; ++i)
{
sleep(1);
printf( "This in the main : %d\n" , i );
}
return 0;
} 如果我们注释掉”pthread_join(pth, NULL);”这一行: 运行结果如下:
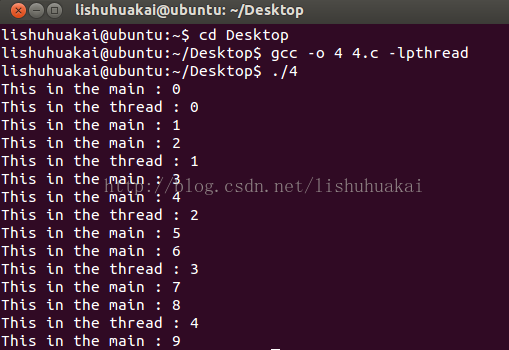
也就是说:子线程还没有执行完毕,main函数已经退出,那么子线程也就退出了!
如果我们不注释掉那一行,那么运行结果如下:
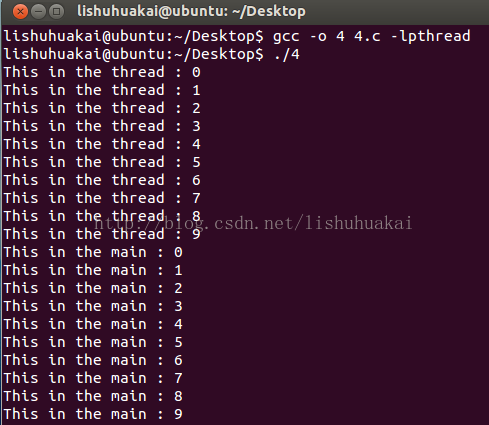
这说明:pthread_join函数的调用者在等待子线程退出后才继续执行!
(2)pthread_create函数:
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread,
const pthread_attr_t *restrict_attr,
void*(*start_rtn)(void*),
void *restrict arg);第一个参数*thread为指向线程标识符的指针。
第二个参数*restrict_attr用来设置线程属性,上面也可以用NULL,表示使用默认的属性。
第三个参数是线程运行函数的起始地址。
最后一个参数是运行函数的参数,NULL表示无参数。
(3)pthread_t:
pthread_t用于声明线程ID!
类型定义:
typedef unsigned long int pthread_t;
//come from /usr/include/bits/pthread.h
sizeof (pthread_t) =4;
(4)pthread_attr_init函数
声明:int pthread_attr_init(pthread_attr_t*attr);
返回值:返回0,表示函数初始化对象成功。失败时返回一个错误代码。
参数:指向一个线程属性的指针。
直接贴上带解释的代码:
#include