深度学习图像分类:植物幼苗图像分类入门(Plant Seedlings Classification)
前言:深度学习考试期末的题目,植物幼苗分类,可以帮助农业领域的进步。
题目介绍:kaggle原题:可以下载数据集,查看一些参与者的思路等。
易用的深度学习框架Keras简介及使用
部分图片如下:


思路:
由于是图像分类问题,tensorflow官网提供了深度学习做图片分类的入门教材都是MNIST或者CIFAR-10的例子。但这里数据都是图片,还是需要自己读入和预处理,采用keras搭建的网络。
1.图片的读入和预处理
2.模型的搭建
3.训练
4.评价
一、数据的读入和预处理
数据的读入:用的cv2,每个文件夹的名字就是其标签,但是名字不可以当作lable,所以建立了name_dic 字典转换为数字;
数据集划分:数据集并没有帮我们划分数据集,所以我用的sklearn*的train_test_split()*函数;
矩阵的保存:由于每次加载数据很消耗时间,所以将四个文件(训练、测试集的特征和标签用numpy进行了保存)
数据的打乱:因为读取时是按照顺序读取的,直接按这个顺序训练,训练效果可能会受影响,hstack((a,b))的功能是将a和b以水平的方式连接,经过转置np.random.shuffle()方法进行乱序
数据的预处理:训练特征需要进行归一化处理,标签需要进行one-hot编码
由于图片数据过少,用到了图像增强:
# 30°旋转 0.1的随机平移 0.2随机缩放
aug = ImageDataGenerator(rotation_range=180, width_shift_range=0.3,
height_shift_range=0.3, shear_range=0.2, zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True, fill_mode="nearest")# 获取文件路径和标签
def get_files(file_dir):
# file_dir: 文件夹路径
# return: 乱序后的图片和标签
# 直接读取数据,会节约时间
if (os.path.exists('train_image_list1.csv.npy')
& os.path.exists('test_image_list1.csv.npy')
& os.path.exists('test_label_list.csv.npy')
&os.path.exists('train_label_list.csv.npy')
&os.path.exists('hunxiao.csv.npy')):
train_image_list_1 = np.load('train_image_list1.csv.npy')
train_label_list_1 = np.load('train_label_list.csv.npy')
test_image_list_1 = np.load('test_image_list1.csv.npy')
test_label_list_1 = np.load('test_label_list.csv.npy')
test_label_list = np.load('hunxiao.csv.npy')
print("训练集一共有%d张图\n" % len(train_label_list_1))
print("测试集一共有%d张图\n" % len(test_label_list_1))
return train_image_list_1, train_label_list_1, test_image_list_1, test_label_list_1,test_label_list
image_list = []
label_list = []
name_dic = {'Black-grass': 0, 'Charlock': 1, 'Cleavers': 2, 'Common Chickweed': 3, 'Common wheat': 4,
'Fat Hen': 5, 'Loose Silky-bent': 6, 'Maize': 7, 'Scentless Mayweed': 8, 'Shepherds Purse': 9,
'Small-flowered Cranesbill': 10, 'Sugar beet': 11}
# 载入数据路径并写入标签值
for file in os.listdir(file_dir):
name = str(file)
name_count = 0
for key in os.listdir(file_dir + file):
name_count+=1
image_list.append(file_dir + '\\' + file + '\\' + key)
label_list.append(name_dic[file])
print(name+"种类有"+str(name_count)+"张图片")
print("一共有%d张图\n" % len(image_list))
image_list = np.hstack(image_list)
label_list = np.hstack(label_list)
temp = np.array([image_list, label_list])
temp = temp.transpose() # 转置
np.random.shuffle(temp)
train_img, test_img = train_test_split(temp, train_size=0.7)
train_image_list = list(train_img[:, 0])
test_image_list = list(test_img[:, 0])
train_label_list = list(train_img[:, 1])
train_label_list = [int(i) for i in train_label_list]
test_label_list = list(test_img[:, 1])
test_label_list = [int(i) for i in test_label_list]
train_image_list1 = []
test_image_list1 = []
for m in range(len(train_image_list)):
image = cv2.imread(train_image_list[m])
# print(image.shape) # 查看部分图片的shape
image = cv2.resize(image, (norm_size, norm_size))
image = img_to_array(image)
train_image_list1.append(image)
for m in range(len(test_image_list)):
image1 = cv2.imread(test_image_list[m])
image1 = cv2.resize(image1, (norm_size, norm_size))
image1 = img_to_array(image1)
test_image_list1.append(image1)
# 标准化:提高模型预测精准度,加快收敛
train_image_list1 = np.array(train_image_list1, dtype="float") / 255.0
test_image_list1 = np.array(test_image_list1, dtype="float") / 255.0
# convert the labels from integers to vectors one-hot编码
train_label_list1 = to_categorical(train_label_list, num_classes=CLASS_NUM)
test_label_list1 = to_categorical(test_label_list, num_classes=CLASS_NUM)
# 第一运行 把处理好的数据保存下来
np.save('train_image_list1.csv',train_image_list1)
np.save('test_image_list1.csv',test_image_list1)
np.save('test_label_list.csv',test_label_list1)
np.save('train_label_list.csv',train_label_list1)
np.save('hunxiao.csv',test_label_list)
return train_image_list1,train_label_list1,test_image_list1,test_label_list1,np.array(test_label_list)二、模型的搭建
卷积神经网络CNN经典模型
用深度学习做图片分类选的网络肯定是卷积神经网络,但是现在CNN的种类这么多,哪一个会在我们这个标志分类任务表现最好?在实验之前,没有人会知道。一般而言,先选一个最简单又最经典的网络跑一下看看分类效果是的策略是明智的选择,那么LeNet肯定是最符合以上的要求啦,实现简单,又相当经典。
选取了cnn中最简单LeNet网络,只有七层,参数相对较少,可以在本机上运行。
LeNet如下:由两个卷积层,两个池化层,以及两个全连接层组成。 卷积都是5*5的模板,stride=1,池化都是MAX。注意:图片上的参数和我的模型不一致,借助于理解。

如下为LeNet模型的摘要:
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
conv2d_1 (Conv2D) (None, 32, 32, 20) 1520 kernel_size=(5, 5)
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 32, 32, 20) 0 (0.25)
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_1 (MaxPooling2 (None, 16, 16, 20) 0 pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)
_________________________________________________________________
conv2d_2 (Conv2D) (None, 16, 16, 50) 25050 kernel_size=(5, 5)
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_2 (Dropout) (None, 16, 16, 50) 0 (0.25)
_________________________________________________________________
max_pooling2d_2 (MaxPooling2 (None, 8, 8, 50) 0
_________________________________________________________________pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)
flatten_1 (Flatten) (None, 3200) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 500) 1600500
_________________________________________________________________
activation_1 (Activation) (None, 500) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_3 (Dropout) (None, 500) 0
_________________________________________________________________(0.25)
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 12) 6012
_________________________________________________________________
activation_2 (Activation) (None, 12) 0
=================================================================
Total params: 1,633,082
Trainable params: 1,633,082
Non-trainable params: 0代码里增加了Dropout用于解决过拟合,激活函数relu函数
class LeNet:
def build(width, height, depth, classes):
'''参数分别为:长 宽 高 分类'''
# initialize the model
model = Sequential() # 建立线性堆叠模型
inputShape = (height, width, depth)
# if we are using "channels last", update the input shape
if K.image_data_format() == "channels_first": #for tensorflow
inputShape = (depth, height, width)
# first set of CONV => RELU => POOL layers
# 卷积1 过滤器大小为 5 * 5,会产生20个图像,卷积不会改变图像大小,起到了滤镜效果,设置ReLU激活函数
model.add(Conv2D(filters=20,kernel_size=(5, 5),padding="same",input_shape=inputShape,activation='relu'))
# 添加激活层
# model.add(Activation("relu"))
# 加入Dropout避免过拟合。
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
# 最大池化1 过滤器大小为 2 * 2,长和宽的步长均为2,不会改变图像的数量(仍旧是20),会改变大小(32*32变成16*16)
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)))
#second set of CONV => RELU => POOL layers
# 卷积2 过滤器大小为 5 * 5,会产生50个图像,卷积不会改变图像大小,起到了滤镜效果,设置ReLU激活函数
model.add(Conv2D(filters=50, kernel_size = (5, 5), padding="same",activation='relu'))
# 激活函数
# model.add(Activation("relu"))
# 加入Dropout避免过拟合。
# model.add(Dropout(0.25))
# 最大池化2 过滤器大小为2 * 2,长和宽的步长均为2,不会改变图像的数量(仍旧是50),会改变大小(16*16变成8*8)
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)))
# first (and only) set of FC => RELU layers
# Flatten层用来将输入“压平”
model.add(Flatten())
# Dense表示全连接层(500个神经元)
model.add(Dense(500))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
# 加入Dropout避免过拟合。
# model.add(Dropout(0.25))
# softmax classifier
# 建立输出层(分类数个神经元),softmax可以将输出预测为每一个图像的概率
model.add(Dense(classes,activation='softmax'))
# 多分类
model.add(Activation("softmax"))
# 查看模型的摘要
print(model.summary())
# return the constructed network architecture
return model其中conv2d表示执行卷积,maxpooling2d表示执行最大池化,Activation表示特定的激活函数类型,Flatten层用来将输入“压平”,用于卷积层到全连接层的过渡,Dense表示全连接层(500个神经元)。
三、训练
训练小技巧:每次训练都要记得保存模型,在模型未改变的基础上下载加载重新训练,可以分时分段训练,效果很好的。
混淆矩阵:

左边栏是数据的真实的类别,右栏是预测出的类别。简介一下TP,TN,FP,FN含义。
TP 就是 Ture Positive :原来是+,判别为 + 简记为—->“判对为正”
FP 就是 False Positive :原来是 -,判别为 + 简记为—-> “错判为正”
FN 就是False Negative :原来是 +,判别为 - 简记为—-> “错判成负”
TN 就是 True Negative:原来是 -,判别为 - 简记为—-> “判对为负”
很显然上述混淆矩阵适合而分类问题。
sensitivity: 正,判对的概率为 TP / (TP + FN)
specificity: 负,判对的概率为 TN/ (FP + TN)
precision : TP / (TP + FP) 在判为正的里面,判对的概率
recall :TP / (TP + FN) 正的里面判对的概率。== sensitivity
模型结果的混淆矩阵:
其中0行6列的12含义:准确的标签应该是0,但是模型预测是6.
predict 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
label
0 59 0 0 0 0 1 12 0 0 0 0 1
1 0 100 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
2 0 0 69 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
3 1 0 0 152 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0 54 2 2 0 0 0 0 0
5 1 1 0 1 0 114 1 0 0 0 0 0
6 14 0 0 0 1 0 174 0 0 0 1 0
7 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 61 1 0 0 0
8 1 1 6 1 0 0 0 1 142 3 0 0
9 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 55 0 0
10 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 131 0
11 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 0 0 1 105def train(aug, trainX, trainY, testX, testY,test_label_list):
# initialize the model
print("开始构建模型···")
model = LeNet.build(width=norm_size, height=norm_size, depth=3, classes=CLASS_NUM)
# 加载已经存在的模型
try:
model.load_weights('saveModel/plant_sign.model')
print("加载模型成功!继续训练模型")
except:
print("加载模型失败!开始训练一个新的模型")
print("定义训练方式···")
# 定义训练方式,三个参数,分别是loss:设置损失函数;optimizer:使用adam优化器收敛更快,metrics:设置评估模型的方式是准确率
opt = Adam(lr=INIT_LR, decay=INIT_LR / EPOCHS)
model.compile(loss="categorical_crossentropy", optimizer=opt,
metrics=["accuracy"])
# train the network,开始训练
print("开始训练网络···")
H = model.fit_generator(aug.flow(trainX, trainY, batch_size=BS),
validation_data=(testX, testY), steps_per_epoch=len(trainX) // BS,
epochs=EPOCHS, verbose=1)
# 输入训练数据集,划分方式是0.8+0.2 训练20个训练周期,每一个批次128项数据,verbose=2为显示训练过程
predY = model.predict_classes(testX)
# print(predY.shape)
# print(test_label_list.shape)
# 打印混淆矩阵
matrix = pd.crosstab(test_label_list,predY, rownames=['label'], colnames=['predict'])
print(matrix)
# save the model to disk
print("[INFO] serializing network...")
# model.save('saveModel/traffic_sign_result.model') # 保存模型
# 画出准确率执行结果
show_train_history(H)
# prediction_probability = model.predict(True_Train_X) # 预测可能性
# prediction = model.predict_classes(True_Train_X) # 直接预测分类结果在这里我们使用了Adam优化器,由于这个任务是一个多分类问题,可以使用类别交叉熵(categorical_crossentropy)。但如果执行的分类任务仅有两类,那损失函数应更换为二进制交叉熵损失函数(binary cross-entropy)
参数的定义
EPOCHS = 32 # 迭代次数
INIT_LR = 1e-3
BS = 32 # 总批次
CLASS_NUM = 12 #结果类数
norm_size = 32 # 图片统一大小输入我们还需要为训练设置一些参数,比如训练的epoches,batch_szie等。这些参数不是随便设的,比如batch_size的数值取决于你电脑内存的大小,内存越大,batch_size就可以设为大一点。又比如norm_size(图片归一化尺寸)是根据你得到的数据集,经过分析后得出的,因为我们这个数据集大多数图片的尺度都在这个范围内,所以我觉得32这个尺寸应该比较合适,但是不是最合适呢?那还是要通过实验才知道的,也许64的效果更好呢?
主函数
if __name__=='__main__':
train_file_path = "../dataset\\"
trainX,trainY,testX,testY,test_label_list = get_files(train_file_path) # 导入数据集
aug = ImageDataGenerator(rotation_range=30, width_shift_range=0.1,
height_shift_range=0.1, shear_range=0.2, zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True, fill_mode="nearest")
train(aug, trainX, trainY, testX, testY,test_label_list)四、评价
写了一个函数用来展示训练过程:
def show_train_history(H):
# plot the training loss and accuracy
plt.style.use("ggplot")
plt.figure()
N = EPOCHS # 训练周期数
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["loss"], label="train_loss")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["val_loss"], label="val_loss")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["acc"], label="train_acc")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["val_acc"], label="val_acc")
plt.title("Training Loss and Accuracy on traffic-sign classifier")
plt.xlabel("Epoch #")
plt.ylabel("Loss/Accuracy")
plt.legend(loc="lower left")
plt.savefig('plot.png')
plt.show()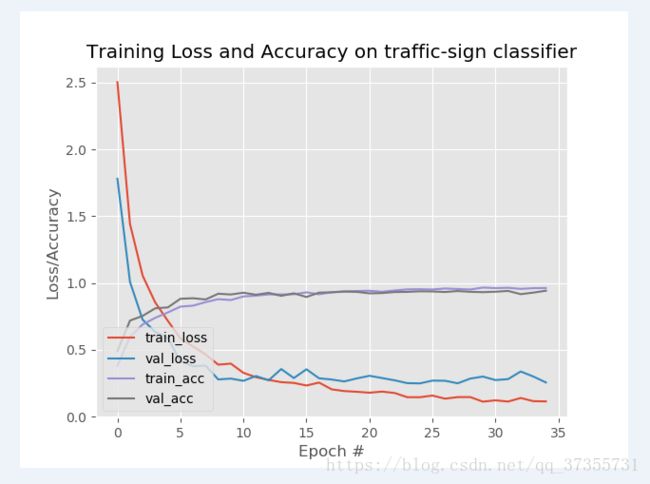
数据集中给出了15个样例文件,导入样例文件进行预测;
需要注意的是:对预测的图片必须处理和训练时一样,并且重新搭建模型,把模型载入,预测结果即可。代码如下:
import tensorflow as tf
import keras
import lenet_model
import os
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.utils import plot_model
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
def get_file(path):
test_list = []
test_name_list = []
for file in os.listdir(path):
image = cv2.imread(path+'/'+file )
image = cv2.resize(image, (norm_size, norm_size))
image = img_to_array(image)
test_list.append(image)
file_list_split = file.split(".")
test_name_list.append(file_list_split[0])
test_list = np.array(test_list, dtype="float") / 255.0
return test_list,test_name_list
norm_size = 32
if __name__ == '__main__':
name_dic = {'0': 'Black-grass', '1': 'Charlock', '2': 'Cleavers',
'3': 'Common Chickweed', '4': 'Common wheat',
'5': 'Fat Hen', '6': 'Loose Silky-bent', '7': 'Maize',
'8': 'Scentless Mayweed', '9': 'Shepherds Purse',
'10': 'Small-flowered Cranesbill', '11': 'Sugar beet'}
path = "../dataset_test/test2"
test_list, test_name_list=get_file(path)
model = lenet_model.LeNet.build(width=32, height=32, depth=3, classes=12)
try:
model.load_weights('saveModel/traffic_sign_w.model')
print("加载模型成功!继续训练模型")
except:
print("加载模型失败!开始训练一个新的模型")
# 可视化模型
# plot_model(model, to_file='model.png')
aug = ImageDataGenerator(rotation_range=30, width_shift_range=0.1,
height_shift_range=0.1, shear_range=0.2, zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True, fill_mode="nearest")
aug.flow(test_list)
result = model.predict_classes(test_list)
name_list = []
for i in result:
name_list.append(name_dic[str(i)])
finally_result = pd.DataFrame({'file':test_name_list,'species':name_list})
print(finally_result)
finally_result.to_csv("../dataset_test/result.csv",index=False)
# print(finally_result1)最终结果200次迭代,线下90%,线上86%,效果有待提高。
下面贴出所有代码:
model.py
# import the necessary packages
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers.convolutional import Conv2D
from keras.layers.convolutional import MaxPooling2D
from keras.layers.core import Dense,Dropout,Activation,Flatten
from keras import backend as K
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.optimizers import Adam
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
from keras.utils import to_categorical # 用于one-hot编码
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
import pandas as pd
class LeNet:
def build(width, height, depth, classes):
'''参数分别为:长 宽 高 分类'''
# initialize the model
model = Sequential() # 建立线性堆叠模型
inputShape = (height, width, depth)
# if we are using "channels last", update the input shape
if K.image_data_format() == "channels_first": #for tensorflow
inputShape = (depth, height, width)
# first set of CONV => RELU => POOL layers
# 卷积1 过滤器大小为 5 * 5,会产生20个图像,卷积不会改变图像大小,起到了滤镜效果,设置ReLU激活函数
model.add(Conv2D(filters=20,kernel_size=(5, 5),padding="same",input_shape=inputShape,activation='relu'))
# 添加激活层
# model.add(Activation("relu"))
# 加入Dropout避免过拟合。
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
# 最大池化1 过滤器大小为 2 * 2,长和宽的步长均为2,不会改变图像的数量(仍旧是20),会改变大小(32*32变成16*16)
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)))
#second set of CONV => RELU => POOL layers
# 卷积2 过滤器大小为 5 * 5,会产生50个图像,卷积不会改变图像大小,起到了滤镜效果,设置ReLU激活函数
model.add(Conv2D(filters=50, kernel_size = (5, 5), padding="same",activation='relu'))
# 激活函数
# model.add(Activation("relu"))
# 加入Dropout避免过拟合。
# model.add(Dropout(0.25))
# 最大池化2 过滤器大小为2 * 2,长和宽的步长均为2,不会改变图像的数量(仍旧是50),会改变大小(16*16变成8*8)
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), strides=(2, 2)))
# first (and only) set of FC => RELU layers
# Flatten层用来将输入“压平”
model.add(Flatten())
# Dense表示全连接层(500个神经元)
model.add(Dense(500))
model.add(Activation("relu"))
# 加入Dropout避免过拟合。
# model.add(Dropout(0.25))
# softmax classifier
# 建立输出层(分类数个神经元),softmax可以将输出预测为每一个图像的概率
model.add(Dense(classes,activation='softmax'))
# 多分类
model.add(Activation("softmax"))
# 查看模型的摘要
print(model.summary())
# return the constructed network architecture
return model
# 获取文件路径和标签
def get_files(file_dir):
# file_dir: 文件夹路径
# return: 乱序后的图片和标签
# 直接读取数据,会节约时间
if (os.path.exists('train_image_list1.csv.npy')
& os.path.exists('test_image_list1.csv.npy')
& os.path.exists('test_label_list.csv.npy')
&os.path.exists('train_label_list.csv.npy')
&os.path.exists('hunxiao.csv.npy')):
train_image_list_1 = np.load('train_image_list1.csv.npy')
train_label_list_1 = np.load('train_label_list.csv.npy')
test_image_list_1 = np.load('test_image_list1.csv.npy')
test_label_list_1 = np.load('test_label_list.csv.npy')
test_label_list = np.load('hunxiao.csv.npy')
print("训练集一共有%d张图\n" % len(train_label_list_1))
print("测试集一共有%d张图\n" % len(test_label_list_1))
return train_image_list_1, train_label_list_1, test_image_list_1, test_label_list_1,test_label_list
image_list = []
label_list = []
name_dic = {'Black-grass': 0, 'Charlock': 1, 'Cleavers': 2, 'Common Chickweed': 3, 'Common wheat': 4,
'Fat Hen': 5, 'Loose Silky-bent': 6, 'Maize': 7, 'Scentless Mayweed': 8, 'Shepherds Purse': 9,
'Small-flowered Cranesbill': 10, 'Sugar beet': 11}
# 载入数据路径并写入标签值
for file in os.listdir(file_dir):
name = str(file)
name_count = 0
for key in os.listdir(file_dir + file):
name_count+=1
image_list.append(file_dir + '\\' + file + '\\' + key)
label_list.append(name_dic[file])
print(name+"种类有"+str(name_count)+"张图片")
print("一共有%d张图\n" % len(image_list))
image_list = np.hstack(image_list)
label_list = np.hstack(label_list)
temp = np.array([image_list, label_list])
temp = temp.transpose() # 转置
np.random.shuffle(temp)
train_img, test_img = train_test_split(temp, train_size=0.7)
train_image_list = list(train_img[:, 0])
test_image_list = list(test_img[:, 0])
train_label_list = list(train_img[:, 1])
train_label_list = [int(i) for i in train_label_list]
test_label_list = list(test_img[:, 1])
test_label_list = [int(i) for i in test_label_list]
train_image_list1 = []
test_image_list1 = []
for m in range(len(train_image_list)):
image = cv2.imread(train_image_list[m])
# print(image.shape) # 查看部分图片的shape
image = cv2.resize(image, (norm_size, norm_size))
image = img_to_array(image)
train_image_list1.append(image)
for m in range(len(test_image_list)):
image1 = cv2.imread(test_image_list[m])
image1 = cv2.resize(image1, (norm_size, norm_size))
image1 = img_to_array(image1)
test_image_list1.append(image1)
# 标准化:提高模型预测精准度,加快收敛
train_image_list1 = np.array(train_image_list1, dtype="float") / 255.0
test_image_list1 = np.array(test_image_list1, dtype="float") / 255.0
# convert the labels from integers to vectors one-hot编码
train_label_list1 = to_categorical(train_label_list, num_classes=CLASS_NUM)
test_label_list1 = to_categorical(test_label_list, num_classes=CLASS_NUM)
# 第一运行 把处理好的数据保存下来
np.save('train_image_list1.csv',train_image_list1)
np.save('test_image_list1.csv',test_image_list1)
np.save('test_label_list.csv',test_label_list1)
np.save('train_label_list.csv',train_label_list1)
np.save('hunxiao.csv',test_label_list)
return train_image_list1,train_label_list1,test_image_list1,test_label_list1,np.array(test_label_list)
def show_train_history(H):
# plot the training loss and accuracy
plt.style.use("ggplot")
plt.figure()
N = EPOCHS # 训练周期数
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["loss"], label="train_loss")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["val_loss"], label="val_loss")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["acc"], label="train_acc")
plt.plot(np.arange(0, N), H.history["val_acc"], label="val_acc")
plt.title("Training Loss and Accuracy on traffic-sign classifier")
plt.xlabel("Epoch #")
plt.ylabel("Loss/Accuracy")
plt.legend(loc="lower left")
plt.savefig('plot.png')
plt.show()
def train(aug, trainX, trainY, testX, testY,test_label_list):
# initialize the model
print("开始构建模型···")
model = LeNet.build(width=norm_size, height=norm_size, depth=3, classes=CLASS_NUM)
# 加载已经存在的模型
try:
model.load_weights('saveModel/plant_sign.model')
print("加载模型成功!继续训练模型")
except:
print("加载模型失败!开始训练一个新的模型")
print("定义训练方式···")
# 定义训练方式,三个参数,分别是loss:设置损失函数;optimizer:使用adam优化器收敛更快,metrics:设置评估模型的方式是准确率
opt = Adam(lr=INIT_LR, decay=INIT_LR / EPOCHS)
model.compile(loss="categorical_crossentropy", optimizer=opt,
metrics=["accuracy"])
# train the network,开始训练
print("开始训练网络···")
H = model.fit_generator(aug.flow(trainX, trainY, batch_size=BS),
validation_data=(testX, testY), steps_per_epoch=len(trainX) // BS,
epochs=EPOCHS, verbose=1)
# 输入训练数据集,划分方式是0.8+0.2 训练20个训练周期,每一个批次128项数据,verbose=2为显示训练过程
predY = model.predict_classes(testX)
# print(predY.shape)
# print(test_label_list.shape)
# 打印混淆矩阵
matrix = pd.crosstab(test_label_list,predY, rownames=['label'], colnames=['predict'])
print(matrix)
# save the model to disk
print("[INFO] serializing network...")
# model.save('saveModel/traffic_sign_result.model') # 保存模型
# 画出准确率执行结果
show_train_history(H)
# prediction_probability = model.predict(True_Train_X) # 预测可能性
# prediction = model.predict_classes(True_Train_X) # 直接预测分类结果
EPOCHS = 32 # 迭代次数
INIT_LR = 1e-3
BS = 32
CLASS_NUM = 12
norm_size = 32
if __name__=='__main__':
train_file_path = "../dataset\\"
trainX,trainY,testX,testY,test_label_list = get_files(train_file_path) # 导入数据集
aug = ImageDataGenerator(rotation_range=30, width_shift_range=0.1,
height_shift_range=0.1, shear_range=0.2, zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True, fill_mode="nearest")
train(aug, trainX, trainY, testX, testY,test_label_list)
predict.py
import tensorflow as tf
import keras
import lenet_model
import os
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras.utils import plot_model
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
def get_file(path):
test_list = []
test_name_list = []
for file in os.listdir(path):
image = cv2.imread(path+'/'+file )
image = cv2.resize(image, (norm_size, norm_size))
image = img_to_array(image)
test_list.append(image)
file_list_split = file.split(".")
test_name_list.append(file_list_split[0])
test_list = np.array(test_list, dtype="float") / 255.0
return test_list,test_name_list
norm_size = 32
if __name__ == '__main__':
name_dic = {'0': 'Black-grass', '1': 'Charlock', '2': 'Cleavers',
'3': 'Common Chickweed', '4': 'Common wheat',
'5': 'Fat Hen', '6': 'Loose Silky-bent', '7': 'Maize',
'8': 'Scentless Mayweed', '9': 'Shepherds Purse',
'10': 'Small-flowered Cranesbill', '11': 'Sugar beet'}
path = "../dataset_test/test2"
test_list, test_name_list=get_file(path)
model = lenet_model.LeNet.build(width=32, height=32, depth=3, classes=12)
try:
model.load_weights('saveModel/traffic_sign_w.model')
print("加载模型成功!继续训练模型")
except:
print("加载模型失败!开始训练一个新的模型")
# 可视化模型
# plot_model(model, to_file='model.png')
aug = ImageDataGenerator(rotation_range=30, width_shift_range=0.1,
height_shift_range=0.1, shear_range=0.2, zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True, fill_mode="nearest")
aug.flow(test_list)
result = model.predict_classes(test_list)
name_list = []
for i in result:
name_list.append(name_dic[str(i)])
finally_result = pd.DataFrame({'file':test_name_list,'species':name_list})
print(finally_result)
finally_result.to_csv("../dataset_test/result.csv",index=False)
# print(finally_result1)