TensorFlow实现MNIST的自编码网络
本篇博客将介绍基于无监督学习的一个简单应用———自编码器(autoencoder),并学习TensorFlow搭建一个自编码网络,并用它在MNIST数据集上训练。
自编码网络的作用是将输入样本压缩到隐藏层,然后解压,在输出端重建样本。最终输出层神经元数量等于输入层神经元的数量。这里面主要有两个过程:压缩和解压。压缩依靠的是输入数据(图像、文字、声音)本身存在不同程度的冗余信息,自动编码网络通过学习去掉这些冗余信息,把有用的特征输入到隐藏层中。
压缩过程一方面要限制隐藏神经元的数量,来学习到一些有意义的特征,另一方面还希望神经元大部分时间是被抑制的,当神经元的输出接近于1的时候是被激活,接近于0的时候认为是被抑制的。希望部分神经元处于被抑制的状态,这种规则称为稀疏性限制。
多个隐藏层的主要作用是,如果输入的数据是图像,第一层会学习如何识别边,第二层会学习如何去组合边,从而构建轮廓、角等。更高层会学习如何去组合更有意义的特征,例如,如果输入的是人脸的话,更高层会学习如何识别和组合眼睛、鼻子、嘴巴等人脸器官。
TensorFlow的自编码网络实现
(1)加载数据和设置超参数
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist=input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True)
learning_rate=0.01
training_epochs=20
batch_size=256
display_step=1
example_to_show=10(2)构建网络
#网络参数
n_hidden_1=256
n_hidden_2=128
n_input=784
#输入占位符
X=tf.placeholder('float',[None,n_input])
#定义权重和偏置
weights={'encoder_h1':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input,n_hidden_1])),
'encoder_h2':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1,n_hidden_2])),
'decoder_h1':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2,n_hidden_1])),
'decoder_h2':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1,n_input]))}
biases={'encoder_b1':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])),
'encoder_b2':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_2])),
'decoder_b1':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden_1])),
'decoder_b2':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_input]))}
#定义压缩函数
def encoder(x):
layer_1=tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(x,weights['encoder_h1']),biases['encoder_b1']))
layer_2=tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1,weights['encoder_h2']),biases['encoder_b2']))
return(layer_2)
#定义解压函数
def decoder(x):
layer_1=tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(x,weights['decoder_h1']),biases['decoder_b1']))
layer_2=tf.nn.sigmoid(tf.add(tf.matmul(layer_1,weights['decoder_h2']),biases['decoder_b2']))
return(layer_2)
(3)构建模型并定义损失和优化器
#构建模型
encoder_op=encoder(X)
decoder_op=decoder(encoder_op)
#预测值
y_pred=decoder_op
#真值
y_ture=X
#定义损失和优化器
cost=tf.reduce_mean(tf.pow(y_ture-y_pred,2))
optimizer=tf.train.RMSPropOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)(4)训练数据及评估模型
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
total_batch=int(mnist.train.num_examples/batch_size)
#开始训练
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys=mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
_,c=sess.run([optimizer,cost],feed_dict={X:batch_xs})
#每一轮打印一次损失
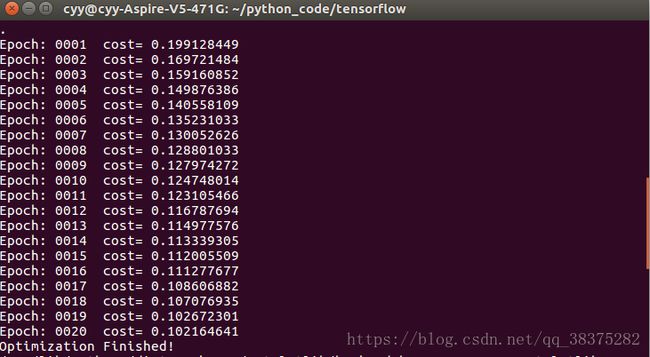
if epoch % display_step==0:
print('Epoch:', '%04d ' %(epoch+1),'cost=','{:.9f}'.format(c))
print('Optimization Finished!')
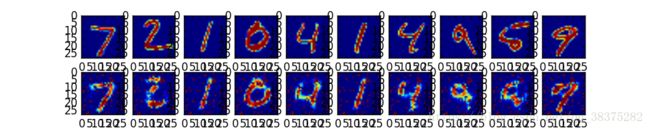
#对测试集中图像使用训练好的自编码网络
encode_decode=sess.run(y_pred,feed_dict={X:mnist.test.images[:example_to_show]})
#比较测试集原始图像和自编码的重建图像
f,a=plt.subplots(2,10,figsize=(10,2))
for i in range(example_to_show):
a[0][i].imshow(np.reshape(mnist.test.images[i],(28,28)))
a[1][i].imshow(np.reshape(encode_decode[i],(28,28)))
f.show()
plt.draw()
plt.waitforbuttonpress()输出每一轮的损失结果如下:
测试集的图片和进过自编码重建特征后的图像对比如下