TensorFlow Object Detection API 超详细教程和踩坑过程(数据准备和训练)
1.准备数据
object detection的数据是需要tfrecord格式的,但是一般我们还是先制作voc格式的数据更加方便。
1.voc格式数据的准备:github上下载一个label-img:
然后选择VOC格式,开始漫长的数据标注过程,标注之后的数据会多一个xml文档,一般在标注之前就按照VOC2012的标准建立文件,你可以去下载VOC2012数据集看一下,如果不想我把数据文件的构成截图发出来,很详细了:
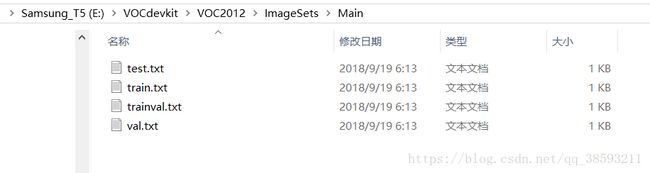
建立VOCdevkit文件,里面建立一个VOC2012文件夹,里面放三个文件:
这三个文件分别放XML、txt、和图像:
至此,VOC2012的数据已经准备完毕了,现在我们要把它转换成tfrecord。
当然如果你需要修改xml中的路径我这也有相应的代码:
# coding=utf-8
import os
import os.path
import xml.dom.minidom
path = "E:\VOCdevkit\VOC2012\Annotations"
files = os.listdir(path) # 得到文件夹下所有文件名称
s = []
count = 0
for xmlFile in files: # 遍历文件夹
if not os.path.isdir(xmlFile): # 判断是否是文件夹,不是文件夹才打开
name1 = xmlFile.split('.')[0]
dom = xml.dom.minidom.parse(path + '\\' + xmlFile)
root = dom.documentElement
newfolder = root.getElementsByTagName('folder')
newpath = root.getElementsByTagName('path')
newfilename = root.getElementsByTagName('filename')
newfolder[0].firstChild.data = 'VOCdevkit\VOC2012\JPEGImages'
newpath[0].firstChild.data = 'VOCdevkit\VOC2012\JPEGImages' + '\\' + name1 + '.jpg'
newfilename[0].firstChild.data = name1 + '.jpg'
with open(os.path.join(path, xmlFile), 'w') as fh:
dom.writexml(fh)
print('写入name/pose OK!')
count = count + 12.数据格式转换:数据转换为tfrecord有两种办法。
第一种:先将xml转换为csv,然后把cvs转换为tfrecord
xml到csv的代码:
import os
import glob
import pandas as pd
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def xml_to_csv(path):
xml_list = []
for xml_file in glob.glob(path + '/*.xml'):
tree = ET.parse(xml_file)
root = tree.getroot()
for member in root.findall('object'):
value = (root.find('filename').text,
int(root.find('size')[0].text),
int(root.find('size')[1].text),
member[0].text,
int(member[4][0].text),
int(member[4][1].text),
int(member[4][2].text),
int(member[4][3].text)
)
xml_list.append(value)
column_name = ['filename', 'width', 'height', 'class', 'xmin', 'ymin', 'xmax', 'ymax']
xml_df = pd.DataFrame(xml_list, columns=column_name)
return xml_df
def main():
for directory in ['train', 'test']:
project_path = '/home/lyf/tensorflow-tutorial/models/research/Annotations'
image_path = os.path.join(project_path, directory)
xml_df = xml_to_csv(image_path)
xml_df.to_csv('project_data/{}_labels.csv'.format(directory), index=None)
print('Successfully converted xml to csv.')
main()
修改path路径, 运行代码,就可以进行转换:生成两个csv文件。这两个csv一个是train,一个是test,然后把他们转换为tfrecord,运行代码是每次需要在pycharm里设置参数,或者在linux中执行如下命令:
# Create train data:
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/train_labels.csv --output_path=train.record
# Create test data:
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/test_labels.csv --output_path=test.record
"""
Usage:
# From tensorflow/models/
# Create train data:
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/train_labels.csv --output_path=train.record
# Create test data:
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=data/test_labels.csv --output_path=test.record
"""
from __future__ import division
from __future__ import print_function
from __future__ import absolute_import
import os
import io
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from PIL import Image
from research.object_detection.utils import dataset_util
from collections import namedtuple, OrderedDict
flags = tf.app.flags
flags.DEFINE_string('csv_input', '', 'Path to the CSV input')
flags.DEFINE_string('output_path', '', 'Path to output TFRecord')
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
# TO-DO replace this with label map
def class_text_to_int(row_label):
if row_label == 'Y':
return 1
if row_label== 'N':
return 2
else:
return None
def split(df, group):
data = namedtuple('data', ['filename', 'object'])
gb = df.groupby(group)
return [data(filename, gb.get_group(x)) for filename, x in zip(gb.groups.keys(), gb.groups)]
def create_tf_example(group, path):
with tf.gfile.GFile(os.path.join(path, '{}'.format(group.filename)), 'rb') as fid:
encoded_jpg = fid.read()
encoded_jpg_io = io.BytesIO(encoded_jpg)
image = Image.open(encoded_jpg_io)
width, height = image.size
filename = group.filename.encode('utf8')
image_format = b'jpg'
xmins = []
xmaxs = []
ymins = []
ymaxs = []
classes_text = []
classes = []
for index, row in group.object.iterrows():
xmins.append(row['xmin'] / width)
xmaxs.append(row['xmax'] / width)
ymins.append(row['ymin'] / height)
ymaxs.append(row['ymax'] / height)
classes_text.append(row['class'].encode('utf8'))
classes.append(class_text_to_int(row['class']))
tf_example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/height': dataset_util.int64_feature(height),
'image/width': dataset_util.int64_feature(width),
'image/filename': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/source_id': dataset_util.bytes_feature(filename),
'image/encoded': dataset_util.bytes_feature(encoded_jpg),
'image/format': dataset_util.bytes_feature(image_format),
'image/object/bbox/xmin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmins),
'image/object/bbox/xmax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(xmaxs),
'image/object/bbox/ymin': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymins),
'image/object/bbox/ymax': dataset_util.float_list_feature(ymaxs),
'image/object/class/text': dataset_util.bytes_list_feature(classes_text),
'image/object/class/label': dataset_util.int64_list_feature(classes),
}))
return tf_example
def main(_):
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(FLAGS.output_path)
path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'images')
examples = pd.read_csv(FLAGS.csv_input)
grouped = split(examples, 'filename')
for group in grouped:
tf_example = create_tf_example(group, path)
writer.write(tf_example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
output_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), FLAGS.output_path)
print('Successfully created the TFRecords: {}'.format(output_path))
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()
也可以用object detection 里内置的函数把csv转换为tfrecord,调用generate_tfrecord.py,注意要改变--csv_input与--output_path这两个参数:
python generate_tfrecord.py --csv_input=sunglasses_test_labels.csv --output_path=sunglass_test.record第二种:
执行:
mkdir object_detection/ssd_model把数据放到这个路径中:
./object_detection/ssd_model/VOCdevkit/
执行这个配置文件,这个是github的官方教程给的:
python ./object_detection/dataset_tools/create_pascal_tf_record.py --label_map_path=object_detection/data/pascal_label_map.pbtxt --data_dir=object_detection/ssd_model/VOCdevkit/ --year=VOC2012 --set=train --output_path=object_detection/ssd_model/pascal_train.record
python ./object_detection/dataset_tools/create_pascal_tf_record.py --label_map_path=object_detection/data/pascal_label_map.pbtxt --data_dir=object_detection/ssd_model/VOCdevkit/ --year=VOC2012 --set=val --output_path=object_detection/ssd_model/pascal_val.record至此,所需要的数据已经全部准备好。
3.修改配置文件:
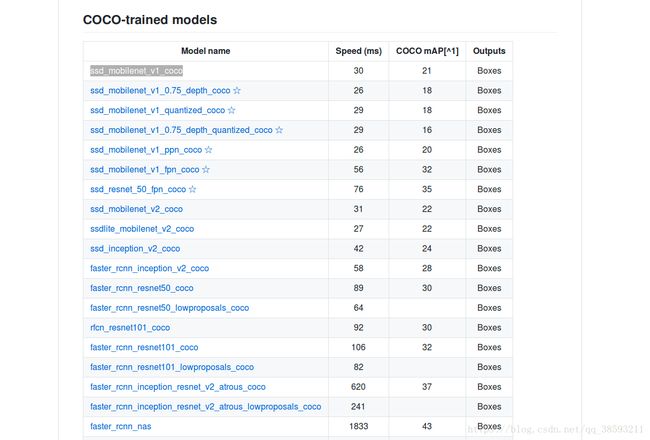
首先选择你所用的模型,我测了一下,带fpn层的模型用起来有点点问题,我用的ssd_mobilenet_v1_coco模型,你可以自己选择模型:
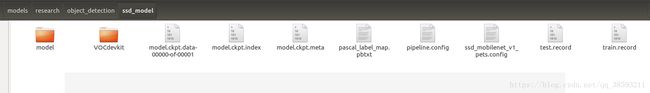
下载的模型解压后放到刚刚建立的ssd-model文件中,然后还得拷贝两个配置文件到ssd-model中:
cp object_detection/data/pascal_label_map.pbtxt object_detection/ssd_model/
cp object_detection/samples/configs/ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config object_detection/ssd_model/ssd-model中就是这样:
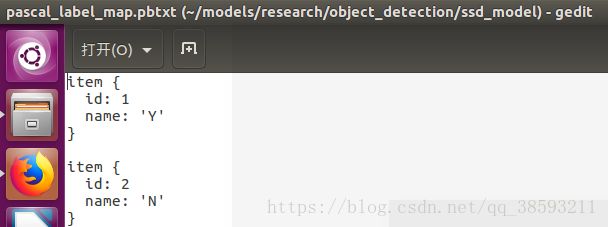
pascal_label_map.pbtxt中的信息需要根据自己的类别更改:
然后在ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config文件中将一些信息修改:
fine_tune_checkpoint: "/home/lyf/models/research/object_detection/ssd_model/model.ckpt"
train_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "/home/lyf/models/research/object_detection/ssd_model/pascal_train.record"
}
label_map_path: "/home/lyf/models/research/object_detection/ssd_model/pascal_label_map.pbtxt"
}
eval_input_reader: {
tf_record_input_reader {
input_path: "/home/lyf/models/research/object_detection/ssd_model/pascal_val.record"
}
label_map_path: "/home/lyf/models/research/object_detection/ssd_model/pascal_label_map.pbtxt"
shuffle: false
num_readers: 1
}至于其他的batch和迭代次数也要根据数据量调整一下。
4.开始训练:
执行下列命令:
python object_detection/legacy/train.py --train_dir object_detection/train --pipeline_config_path object_detection/ssd_model/ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config训练过程中可以打开tensorborder检测训练情况:
tensorboard --logdir=/home/lyf/models/research/object_detection/ssd_model
训练完成之后把训练文件转化为pb文件:
python object_detection/export_inference_graph.py --input_type image_tensor --pipeline_config_path object_detection/ssd_model/ssd_mobilenet_v1_pets.config --trained_checkpoint_prefix object_detection/train/model.ckpt-10000 --output_directory object_detection/ssd_model/model/5.模型测试:
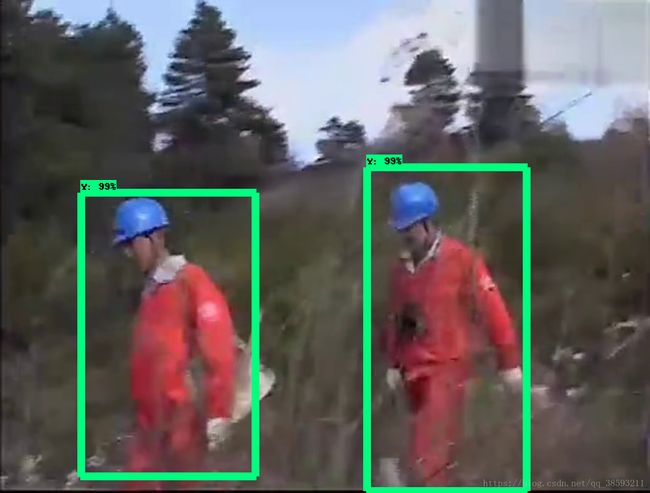
建立一个test.py,就可以用于测试了,记得pip intall python-opencv。
import cv2
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from object_detection.utils import label_map_util
from object_detection.utils import visualization_utils as vis_util
class TOD(object):
def __init__(self):
self.PATH_TO_CKPT = '/home/lyf/models/research/object_detection/ssd_model/model/frozen_inference_graph.pb'
self.PATH_TO_LABELS = '/home/lyf/models/research/object_detection/ssd_model/pascal_label_map.pbtxt'
self.NUM_CLASSES = 1
self.detection_graph = self._load_model()
self.category_index = self._load_label_map()
def _load_model(self):
detection_graph = tf.Graph()
with detection_graph.as_default():
od_graph_def = tf.GraphDef()
with tf.gfile.GFile(self.PATH_TO_CKPT, 'rb') as fid:
serialized_graph = fid.read()
od_graph_def.ParseFromString(serialized_graph)
tf.import_graph_def(od_graph_def, name='')
return detection_graph
def _load_label_map(self):
label_map = label_map_util.load_labelmap(self.PATH_TO_LABELS)
categories = label_map_util.convert_label_map_to_categories(label_map,
max_num_classes=self.NUM_CLASSES,
use_display_name=True)
category_index = label_map_util.create_category_index(categories)
return category_index
def detect(self, image):
with self.detection_graph.as_default():
with tf.Session(graph=self.detection_graph) as sess:
# Expand dimensions since the model expects images to have shape: [1, None, None, 3]
image_np_expanded = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
image_tensor = self.detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('image_tensor:0')
boxes = self.detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_boxes:0')
scores = self.detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_scores:0')
classes = self.detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('detection_classes:0')
num_detections = self.detection_graph.get_tensor_by_name('num_detections:0')
# Actual detection.
(boxes, scores, classes, num_detections) = sess.run(
[boxes, scores, classes, num_detections],
feed_dict={image_tensor: image_np_expanded})
# Visualization of the results of a detection.
vis_util.visualize_boxes_and_labels_on_image_array(
image,
np.squeeze(boxes),
np.squeeze(classes).astype(np.int32),
np.squeeze(scores),
self.category_index,
use_normalized_coordinates=True,
line_thickness=8)
cv2.namedWindow("detection", cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("detection", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
image = cv2.imread('/home/lyf/test/000084.jpg')
detecotr = TOD()
detecotr.detect(image)