涉及源码(Android 4.4.2):
/dalvik/vm/Init.cpp
/dalvik/vm/oo/Class.cpp
在Dalvik虚拟机启动过程中,我们并没有对初始化并启动虚拟机的过程也就是dvmStartup函数展开分析,这里我们对其中BOOTCLASSPATH类加载过程进行分析,也就是dvmClassStartup函数,下面我们再来看看dvmStartup函数。
/dalvik/vm/Init.cpp
std::string dvmStartup(int argc, const char* const argv[],
bool ignoreUnrecognized, JNIEnv* pEnv)
{
...
ALOGV("VM init args (%d):", argc);
...
// 1、读取BOOTCLASSPATH
setCommandLineDefaults();
// 2、初始化bootstrap class loader
if (!dvmClassStartup()) {
return "dvmClassStartup failed";
}
}
1、读取BOOTCLASSPATH
static void setCommandLineDefaults()
{
const char* envStr = getenv("CLASSPATH");
if (envStr != NULL) {
gDvm.classPathStr = strdup(envStr);
} else {
gDvm.classPathStr = strdup(".");
}
// 读取到BOOTCLASSPATH环境变量,就可以拿到BOOTCLASSPATH路径
envStr = getenv("BOOTCLASSPATH");
if (envStr != NULL) {
gDvm.bootClassPathStr = strdup(envStr);
} else {
gDvm.bootClassPathStr = strdup(".");
}
...
}
从上面可以知道,BOOTCLASSPATH路径的值被保存到gDvm.bootClassPathStr中。
2、初始化bootstrap class loader
这个函数定义在文件dalvik/vm/oo/Class.c中,用来初始化启动类加载器(Bootstrap Class Loader),同时还会初始化java.lang.Class类。启动类加载器是用来加载Java核心类的,用来保证安全性,即保证加载的Java核心类是合法的。
/dalvik/vm/oo/Class.cpp
bool dvmClassStartup()
{
/* make this a requirement -- don't currently support dirs in path */
if (strcmp(gDvm.bootClassPathStr, ".") == 0) {
ALOGE("ERROR: must specify non-'.' bootclasspath");
return false;
}
gDvm.loadedClasses =
dvmHashTableCreate(256, (HashFreeFunc) dvmFreeClassInnards);
gDvm.pBootLoaderAlloc = dvmLinearAllocCreate(NULL);
if (gDvm.pBootLoaderAlloc == NULL)
return false;
if (false) {
linearAllocTests();
exit(0);
}
gDvm.classSerialNumber = INITIAL_CLASS_SERIAL_NUMBER;
gDvm.initiatingLoaderList = (InitiatingLoaderList*)
calloc(ZYGOTE_CLASS_CUTOFF, sizeof(InitiatingLoaderList));
// createInitialClasses加载了9大基本类型
if (!createInitialClasses()) {
return false;
}
/*
* Process the bootstrap class path. This means opening the specified
* DEX or Jar files and possibly running them through the optimizer.
*/
assert(gDvm.bootClassPath == NULL);
// 加载所有的Boot Class
processClassPath(gDvm.bootClassPathStr, true);
if (gDvm.bootClassPath == NULL)
return false;
return true;
}
下面来看看processClassPath方法加载所有的Boot Class的过程。
static ClassPathEntry* processClassPath(const char* pathStr, bool isBootstrap)
{
ClassPathEntry* cpe = NULL;
char* mangle;
char* cp;
const char* end;
int idx, count;
/*
* Allocate storage. We over-alloc by one so we can set an "end" marker.
*/
cpe = (ClassPathEntry*) calloc(count+1, sizeof(ClassPathEntry));
/*
* Set the global pointer so the DEX file dependency stuff can find it.
*/
// 初始化bootClassPath,它是以全局的指针,指向所有依赖的jar
gDvm.bootClassPath = cpe;
/*
* Go through a second time, pulling stuff out.
*/
cp = mangle;
idx = 0;
while (cp < end) {
if (*cp == '\0') {
/* leading, trailing, or doubled ':'; ignore it */
} else {
if (isBootstrap &&
dvmPathToAbsolutePortion(cp) == NULL) {
ALOGE("Non-absolute bootclasspath entry '%s'", cp);
free(cpe);
cpe = NULL;
goto bail;
}
ClassPathEntry tmp;
tmp.kind = kCpeUnknown;
tmp.fileName = strdup(cp);
tmp.ptr = NULL;
/*
* Drop an end marker here so DEX loader can walk unfinished
* list.
*/
cpe[idx].kind = kCpeLastEntry;
cpe[idx].fileName = NULL;
cpe[idx].ptr = NULL;
if (!prepareCpe(&tmp, isBootstrap)) {
/* drop from list and continue on */
free(tmp.fileName);
} else {
/* copy over, pointers and all */
cpe[idx] = tmp;
idx++;
}
}
cp += strlen(cp) +1;
}
assert(idx <= count);
if (idx == 0 && !gDvm.optimizing) {
/*
* There's no way the vm will be doing anything if this is the
* case, so just bail out (reasonably) gracefully.
*/
ALOGE("No valid entries found in bootclasspath '%s'", pathStr);
gDvm.lastMessage = pathStr;
dvmAbort();
}
LOGVV(" (filled %d of %d slots)", idx, count);
/* put end marker in over-alloc slot */
cpe[idx].kind = kCpeLastEntry;
cpe[idx].fileName = NULL;
cpe[idx].ptr = NULL;
//dumpClassPath(cpe);
bail:
free(mangle);
gDvm.bootClassPath = cpe;
return cpe;
}
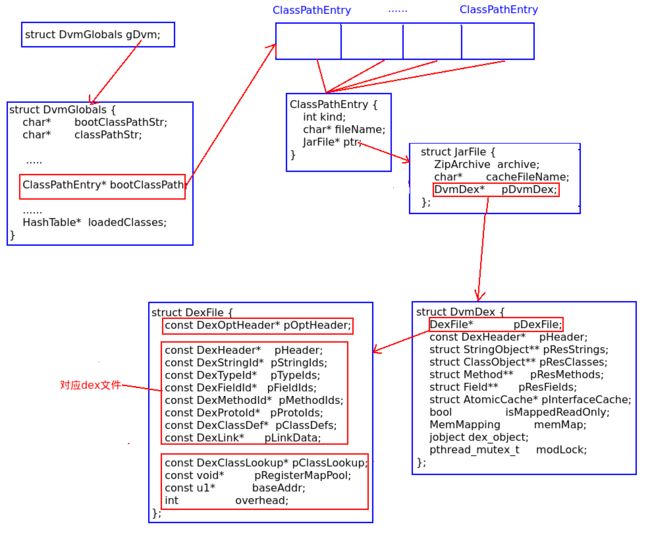
BOOTCLASSPATH包含多个文件,这里的处理方式就是将每一个jar都封装成一个ClassPathEntry对象,每一个ClassPathEntry对象都指向一个jar包。
static bool prepareCpe(ClassPathEntry* cpe, bool isBootstrap)
{
struct stat sb;
if (stat(cpe->fileName, &sb) < 0) {
ALOGD("Unable to stat classpath element '%s'", cpe->fileName);
return false;
}
if (S_ISDIR(sb.st_mode)) {
ALOGE("Directory classpath elements are not supported: %s", cpe->fileName);
return false;
}
char suffix[10];
getFileNameSuffix(cpe->fileName, suffix, sizeof(suffix));
if ((strcmp(suffix, "jar") == 0) || (strcmp(suffix, "zip") == 0) ||
(strcmp(suffix, "apk") == 0)) {
JarFile* pJarFile = NULL;
if (dvmJarFileOpen(cpe->fileName, NULL, &pJarFile, isBootstrap) == 0) {
cpe->kind = kCpeJar;
cpe->ptr = pJarFile;
return true;
}
} else if (strcmp(suffix, "dex") == 0) {
RawDexFile* pRawDexFile = NULL;
if (dvmRawDexFileOpen(cpe->fileName, NULL, &pRawDexFile, isBootstrap) == 0) {
cpe->kind = kCpeDex;
cpe->ptr = pRawDexFile;
return true;
}
} else {
ALOGE("Unknown type suffix '%s'", suffix);
}
ALOGD("Unable to process classpath element '%s'", cpe->fileName);
return false;
}
上面代码应该很熟悉了,就是加载dex或者jar的过程。在文章Dalvik虚拟机对dex的加载过程中分析过。
上面主要工作就是:
(1)对于.jar/.zip/.apk结尾的文件,则调用dvmJarFileOpen进行处理。
对于.dex结尾的文件则调用dvmRawDexFileOpen进行处理。
(2)处理成功后,则设置ClassPathEntry的kind为KCpeJar或者是KCpeDex,代表文件的类型是Jar还是Dex。并且设置cpe->ptr指针为对应的文件(jar文件则是JarFile,Dex文件这是RawDexFile)
整个过程的关系图如下:
参考文章:
http://www.cnblogs.com/jacobchen/p/3599483.html
http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/android-in-depth-dalvik
http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/8885792