仅以此文,祭奠线上无限crash的61位用户。
恩,先放重点:
中文字符串比较,请使用-localizedCompare:方法。这一个系统方法足矣!
-localizedCompare:方法。这一个系统方法足矣!2017.05.24更新
-localizedCompare:这个方法能保证排序结果与系统通讯录排序结果相同,基本符合拼音顺序,但偶尔有偏差。
感谢 @半江瑟瑟 提供的测试数据立冬、李东、李Dong
想做到与系统排序方式保持一致请使用-localizedCompare:方法,想做到完美拼音排序请使用老司机文中提到的逐字比较方式。
恩,重点说完开始讲故事,这篇文章主要用来总结几种中文字符串比较的方法,以防以后我那次遇到什么特殊的需求。
这个故事中你将会看到:
- 字符串转拼音
- -caseInsensitiveCompare:
- UILocalizedIndexedCollation
- 逐字比较
- GB_18030编码
- -localizedCompare:
然而知识点只有:
- 字符串转拼音
- -localizedCompare:
那个手机浏览的同志注意了,看到字符串转拼音后就可以打住了,下面的内容多图杀猫费流量=。=
事情是这样的,需求要求自定义通讯录选择流程,故无法直接调用系统通讯录。老司机自告奋勇的接下了活,毕竟脑袋一想还不难,可老司机低估了中文排序的坑=。=
1.最初的想法
最开始老司机想,首先所有联系人都会按姓名首字母分组,似乎需要转拼音。有了拼音就可以根据拼音排序,很顺畅的思路。Too young,Too naive。
///汉字转拼音
-(NSString *)transferChineseToPinYin:(NSString *)string {
NSMutableString *mutableString = [NSMutableString stringWithString:string];
CFStringTransform((CFMutableStringRef)mutableString, NULL, kCFStringTransformToLatin, false);
return [mutableString stringByFoldingWithOptions:NSDiacriticInsensitiveSearch locale:[NSLocale currentLocale]];
}
转拼音老司机没有引用第三方库,用了三行代码就搞定了。(这样的方式转换出来的拼音是没有音调的,如果想要带着音调,请将NSDiacriticInsensitiveSearch替换为NSCaseInsensitiveSearch)。
转完拼音后,就可以调用-caseInsensitiveCompare:进行比较了,老司机当时真是美滋滋。
与-caseInsensitiveCompare:效果相同的还有一个专门为了TableView而存在的排序的类,叫做UILocalizedIndexedCollation。他也可以用来排序,使用起来也挺简单:
NSArray *arr = [self getName];///只是将几个字符串分别包装成对象
UILocalizedIndexedCollation *localized = [UILocalizedIndexedCollation currentCollation];
NSArray *temparr = [localized sortedArrayFromArray:arr collationStringSelector:@selector(fullName)];
不过他是基于对象的,你要把字符串当做某个对象的属性才能排序。并且它存在下面两个问题中的第一个问题。
不过有两个问题:
- 同音不同字
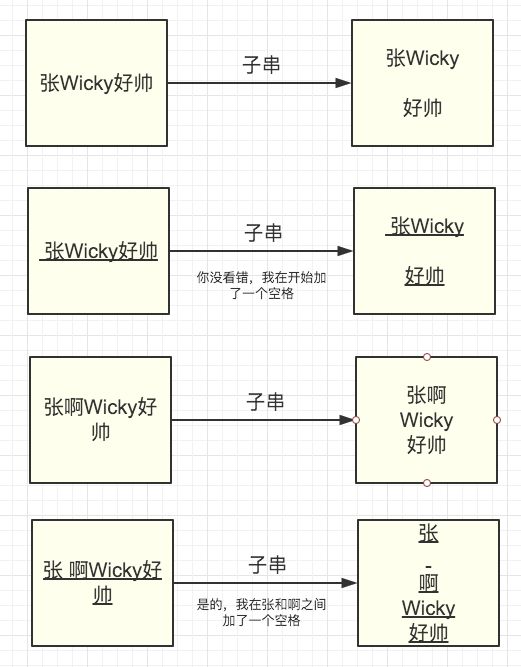
表现是什么呢?比如说三个人,请看图示:
这个结果明显是不我们可以接受的。
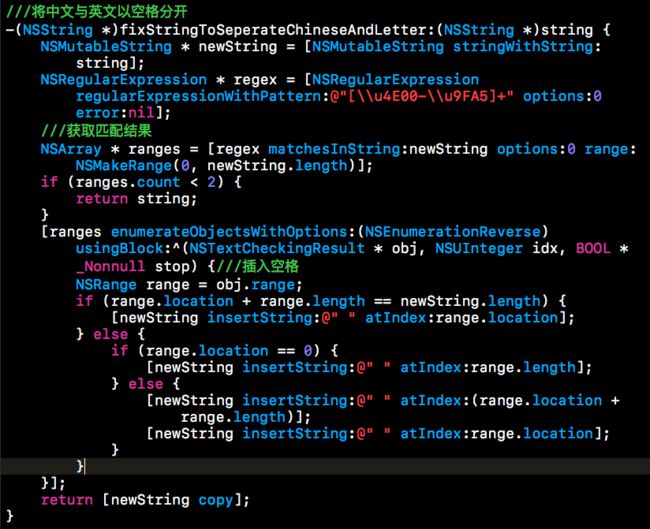
恩,上面转拼音的方法会在两个字之间自动加上一个空格。所以老司机发现可以把拼音分开。所以老司机在这里的想法是逐字比较。
这样的话,结果就是理想结果了。不过还有第二个问题。。
- 中英结合的字符串
中英结合的字符串转换成拼音以后效果跟预想的有一定偏差。什么表现呢?
为什么这样呢?我们看到转拼音的时候中英结合的是没有空格的。
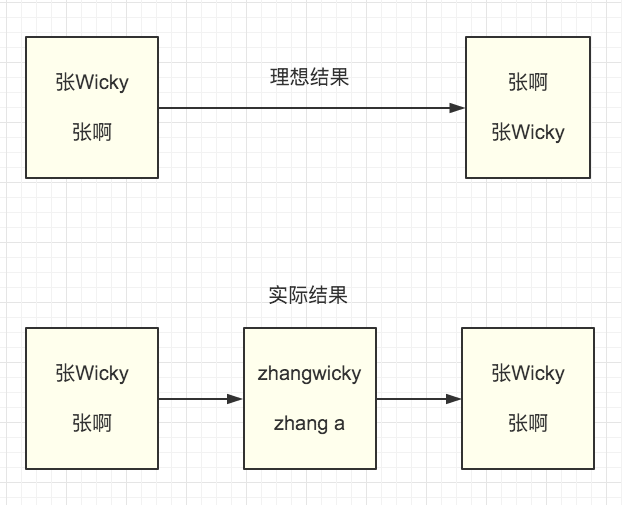
老司机遇到错误平错误,想到因为中英结合有问题,我处理一下字符串把中英文分开不就好了么?
这样的话张Wicky就变成张 Wicky转成拼音就变成zhang wicky。排序完成。
然而我的61位用户就是因为我这一时大意而受到了无限crash的折磨。。。
矛盾点在这,比如用户本来存的名字叫做张 啊。没错,就是名字里面本身就有一个空格(这61位用户你们为毛要存空格啊。。。其他用户怎么就不存呢。。一定是你不会用),经过上面的添加空格就会变成张 啊(名字中间变成了3个空格)。其实到这里还好,最可气的是-componentsSeparatedByString:这个方法的行为跟老司机想的不一致啊。(敲黑板,重点了啊)
同学们,张 啊这个字符串调用-componentsSeparatedByString:这个方法,传参@" ",你们的理想结果是什么?
是的,比预想的多了两个空字符串。。。问题很严重,原本张 啊字符串长度为3,拼音数组元素个数为4。然而后面有调用了-substringWithRange:方法。。。是的你没猜错,越界了。。。
到这想填坑其实还可以,只要在添加空格以后再检验是否有连续空格,替换成一个空格就好了。。。不过这种打补丁,让代码越来越失去可维护性的做法老司机觉得是个隐患。。。所以老司机不得不想出第二个方法。
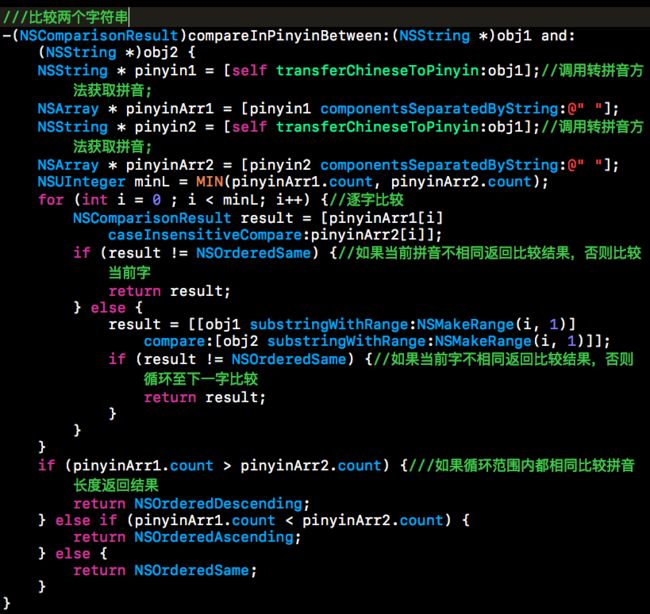
2.逐字比较时确保字与拼音一一对应
最初的想法因为越界出问题,那么我是否让字与拼音一一对应上就好了呢?
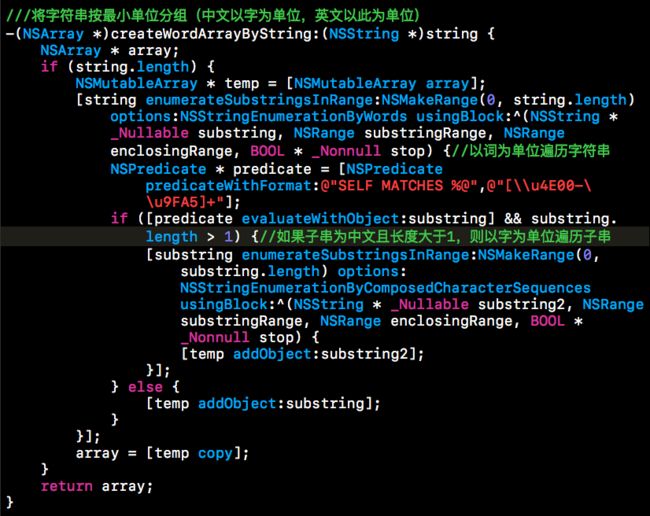
那么首先要把字符串分成一个字一个字的,但是单词还要保证是单词而不是字母。
事实上老司机到这已经有了些许抗拒,为什么一个字符串排序就这么难。。。
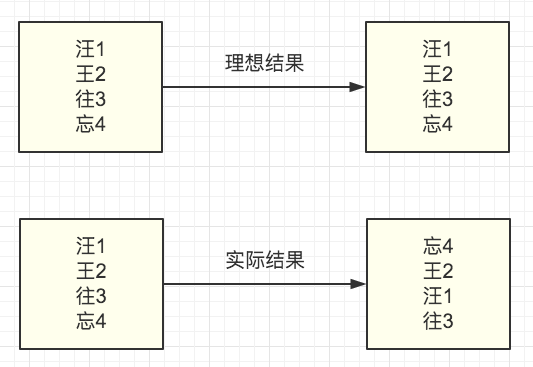
到了这里思路大概就是这个样子的:
到了这里,因为先拆字,所以不需要手动添加空格,也避免了-substringWithRange:方法,所以根本就不存在越界了。看起来似乎比最初的想法省了很多事,老司机心里美滋滋。
多说一嘴,-enumerateSubstringsInRange:这个方法的行为很诡异,不知道是bug还是什么原理,表现如下:
当第一个可见字符为汉字且紧跟着一个单词的时候,这里面的子串都中文和英文是不会分开的,且后面的子串不熟影响。其他情况下都可以正常返回子串。
2017.05.25更新
有同学问具体是怎么实现的?老司机将中文拼音比较写在了字符串的扩展中。以下是.m中相关代码:
#define replaceIfContain(string,target,replacement,tone) \
do {\
if ([string containsString:target]) {\
string = [string stringByReplacingOccurrencesOfString:target withString:replacement];\
string = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@%d",string,tone];\
}\
} while(0)
@interface NSString ()
@property (nonatomic ,strong) NSArray * wordArray;
@property (nonatomic ,copy) NSString * wordPinyinWithTone;
@property (nonatomic ,copy) NSString * wordPinyinWithoutTone;
@end
@implementation NSString (DWStringSortUtils)
-(NSComparisonResult)dw_ComparedInPinyinWithString:(NSString *)string considerTone:(BOOL)tone {
if ([self isEqualToString:string]) {
return NSOrderedSame;
}
NSArray * arr1 = self.wordArray;
NSArray * arr2 = string.wordArray;
NSUInteger minL = MIN(arr1.count, arr2.count);
for (int i = 0; i < minL; i ++) {
if ([arr1[i] isEqualToString:arr2[i]]) {
continue;
}
NSString * pinyin1 = [arr1[i] transferWordToPinYinWithTone:tone];
NSString * pinyin2 = [arr2[i] transferWordToPinYinWithTone:tone];
if (tone) {
pinyin1 = transformPinyinTone(pinyin1);
pinyin2 = transformPinyinTone(pinyin2);
}
NSComparisonResult result = [pinyin1 caseInsensitiveCompare:pinyin2];
if (result != NSOrderedSame) {
return result;
} else {
result = [arr1[i] localizedCompare:arr2[i]];
if (result != NSOrderedSame) {
return result;
}
}
}
if (arr1.count < arr2.count) {
return NSOrderedAscending;
} else if (arr1.count > arr2.count) {
return NSOrderedDescending;
} else {
return NSOrderedSame;
}
}
#pragma mark --- tool method ---
-(NSString *)transferWordToPinYinWithTone:(BOOL)tone {
if (tone && self.wordPinyinWithTone) {
return self.wordPinyinWithTone;
} else if (!tone && self.wordPinyinWithoutTone) {
return self.wordPinyinWithoutTone;
}
NSMutableString * mutableString = [[NSMutableString alloc] initWithString:self];
CFStringTransform((CFMutableStringRef)mutableString, NULL, kCFStringTransformToLatin, false);
NSStringCompareOptions toneOption = tone ?NSCaseInsensitiveSearch:NSDiacriticInsensitiveSearch;
NSString * pinyin = [mutableString stringByFoldingWithOptions:toneOption locale:[NSLocale currentLocale]];
if (tone) {
self.wordPinyinWithTone = pinyin;
} else {
self.wordPinyinWithoutTone = pinyin;
}
return pinyin;
}
-(BOOL)dw_StringIsChinese {
if (self.length == 0) {
return NO;
}
NSPredicate * predicate = [NSPredicate predicateWithFormat:@"SELF MATCHES %@",@"[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5]+"];
return [predicate evaluateWithObject:self];
}
-(NSArray *)dw_TrimStringToWord {
if (self.length) {
NSMutableArray * temp = [NSMutableArray array];
[self enumerateSubstringsInRange:NSMakeRange(0, self.length) options:NSStringEnumerationByWords usingBlock:^(NSString * _Nullable substring, NSRange substringRange, NSRange enclosingRange, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
if (substring.length > 1 && temp.count == 0 && ![substring dw_StringIsChinese] && [substring dw_SubStringConfirmToPattern:@"[\\u4E00-\\u9FA5]+"].count > 0) {///为防止第一个字与英文连在一起
[temp addObject:[substring substringToIndex:1]];
[temp addObject:[substring substringFromIndex:1]];
} else {
if (substring.length > 1 && [substring dw_StringIsChinese]) {
[substring enumerateSubstringsInRange:NSMakeRange(0, substring.length) options:(NSStringEnumerationByComposedCharacterSequences) usingBlock:^(NSString * _Nullable substring2, NSRange substringRange, NSRange enclosingRange, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
[temp addObject:substring2];
}];
} else {
if (substring.length) {
[temp addObject:substring];
}
}
}
}];
return [temp copy];
}
return nil;
}
#pragma mark --- inline method ---
static inline NSString * transformPinyinTone(NSString * pinyin) {
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ā", @"a",1);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"á", @"a",2);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ǎ", @"a",3);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"à", @"a",4);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ō", @"o",1);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ó", @"o",2);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ǒ", @"o",3);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ò", @"o",4);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ē", @"e",1);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"é", @"e",2);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ě", @"e",3);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"è", @"e",4);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ī", @"i",1);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"í", @"i",2);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ǐ", @"i",3);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ì", @"i",4);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ū", @"u",1);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ú", @"u",2);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ǔ", @"u",3);
replaceIfContain(pinyin, @"ù", @"u",4);
return pinyin;
}
#pragma mark ---setter/getter ---
-(void)setWordPinyinWithTone:(NSString *)wordPinyinWithTone {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(wordPinyinWithTone), wordPinyinWithTone, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC);
}
-(NSString *)wordPinyinWithTone {
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, _cmd);
}
-(void)setWordPinyinWithoutTone:(NSString *)wordPinyinWithoutTone {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(wordPinyinWithoutTone), wordPinyinWithoutTone, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC);
}
-(NSString *)wordPinyinWithoutTone {
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, _cmd);
}
-(void)setWordArray:(NSArray *)wordArray {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(wordArray), wordArray, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
-(NSArray *)wordArray {
NSArray * array = objc_getAssociatedObject(self, _cmd);
if (!array) {
array = [self dw_TrimStringToWord];
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(wordArray), array, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
return array;
}
@end
3.带音调的拼音排序
上面的排序老司机都是在排没有音调的拼音。老司机在上面也有介绍过如果转换带音调的拼音方法,老司机又开始美滋滋的优化自己的代码了。想想不过是转拼音的时候转成带音调的然后源代码比较呗。结果。。。
系统这是什么鬼顺序,开始怀疑小学老师教的āáǎà是假的了都。。老司机都快疯了,妈妈,不要再让我给字符串排序了。。。
又开始翻阅博客如何排序啊。。。
之前考虑过这个方法 但问题是不能对首字母之后的拼音排序 而且需要引用额外的文件 比较麻烦。
后来查到gb编码本来就是用拼音排序的就hack了一下:在stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:后面用16位编码 将中文转为ascii来比较 更简洁。
引自按照拼音对数组中的中文字符串排序的算法中Lunar川小槑的回复
\#define GB18030_ENCODING CFStringConvertEncodingToNSStringEncoding(kCFStringEncodingGB_18030_2000)
// 其他代码...
NSComparator comparator = ^(NSString *obj1, NSString *obj2){
NSString *str1 = [obj1 stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:GB18030_ENCODING];
NSString *str2 = [obj2 stringByAddingPercentEscapesUsingEncoding:GB18030_ENCODING];
return [str1 compare:str2];
};
试了一下,诶,果然好使!顺序对的!也不用逐字比较了!一级棒!不过老司机真的有做测试的潜质,我也不知道为什么,我就随便改了一下数据,我都不知道怎么想的把往字改成了彺字结果就又错了。。。想想可能GB_18030这个标准也不都是按照拼音排的吧。。。
4.最后的,也是最简单的,系统放在那我就一直没用的。。。
最后的最后我又找到了这个方法,-localizedCompare:。真的是比什么都简单,又比什么都对啊。这个方法没什么bug也没什么风险。。。简单的不要不要的。。。
扣个题:
中文字符串比较,请使用-localizedCompare:方法。这一个系统方法足矣!
-localizedCompare:方法。这一个系统方法足矣!中文字符串比较,请使用-localizedCompare:方法。这一个系统方法足矣!
-localizedCompare:方法。这一个系统方法足矣!中文字符串比较,请使用-localizedCompare:方法。这一个系统方法足矣!
-localizedCompare:方法。这一个系统方法足矣!扣题改了,看下文章开头的更新
想想自己因为要按拼音分组所以转了拼音,之后就一直再以拼音排序,快要被自己蠢哭了。。。