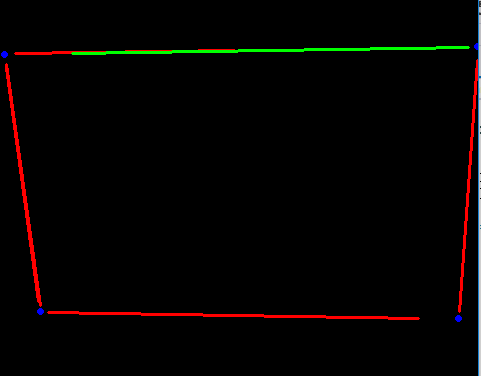
参考贾志刚的opencv图像处理方法,对一张倾斜图片进行矫正。条条大路通罗马,对一张倾斜图片进,有很多方法,这是最复杂的一种,通过求四个倾斜角点的位置,再设置目标点的位置,通过仿射变换进行图片矫正。
与PS方法的优势就是可以通过代码批量处理图片。
图片:
只能说这种方法确实比较好,特别是在进行图片批处理的时候,虽然复杂了点,但是能保证对大部分图片效果较好。
主要流程:
1 . 二值化
- 形态学操作,去噪点
- 进行轮廓查找, 通过 矩形的长款过滤较小和图片的大边框
- 霍夫直线变换,查找直线
- 过滤直线,通过直线位置和长度确定上下左右四条直线
- 求出四条直线
- 得到四条直线的交点,这就是物体原始四个角点
- 把原始的四个角点,变换到图片的四个角落,透视变换会把相对位置的像素通过线性插值填充
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Mat src, dst, gray_src;
char input_image[] = "input image";
char output_image[] = "output image";
int main(int argc, char ** argv){
src = imread("case5.jpg");
if (src.empty()){
printf("colud not load image ..\n");
return -1;
}
namedWindow(input_image, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
namedWindow(output_image, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow(input_image, src);
// 二值化处理
Mat binary;
cvtColor(src, gray_src, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
threshold(gray_src, binary, 0, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY_INV | THRESH_OTSU);
imshow("binary image", binary);
// 腐蚀操作
Mat structureElement = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(5, 5), Point(-1, -1));
dilate(binary, binary, structureElement); //腐蚀
imshow("erode", binary);
// 形态学操作
Mat kernel = getStructuringElement(MORPH_RECT, Size(3, 3), Point(-1, -1));
morphologyEx(binary, dst, MORPH_OPEN, kernel, Point(-1, -1), 3);
imshow("morphology", dst);
// 轮廓发现
bitwise_not(dst, dst, Mat());
vector> contours;
vector hireachy;
int width = src.cols;
int height = src.rows;
Mat drawImage = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3);
findContours(dst, contours, hireachy, CV_RETR_TREE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point());
for (size_t t = 0; t < contours.size(); t++){
Rect rect = boundingRect(contours[t]);
printf("rect.width : %d, src.cols %d \n ", rect.width, src.cols);
if (rect.width > (src.cols / 2) && rect.width < (src.cols - 5))
{
drawContours(drawImage, contours, static_cast(t), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, hireachy, 0, Point());
}
}
imshow("contours", drawImage);
// 绘制直线
vector lines;
Mat contoursImg;
int accu = min(width * 0.5, height *0.5);
cvtColor(drawImage, contoursImg, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Mat linesImage = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3);
HoughLinesP(contoursImg, lines, 1, CV_PI / 180.0, accu, accu, 0);
for (size_t t = 0; t < lines.size(); t++){
Vec4i ln = lines[t];
line(linesImage, Point(ln[0], ln[1]), Point(ln[2], ln[3]), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
}
printf("number of lines : %d", lines.size());
imshow("lines image :", linesImage);
// 定位直线
int deltah = 0;
Vec4i topLine, bottomLine, leftLine, rightLine;
for (int i = 0; i < lines.size(); i++){
Vec4i ln = lines[i];
deltah = abs(ln[3] - ln[1]);
if (ln[3] < height / 2.0 && ln[1] < height / 2.0 && deltah < accu - 1){
topLine = lines[i];
}
if (ln[3] > height / 2.0 && ln[1] > height / 2.0 && deltah < accu - 1){
bottomLine = lines[i];
}
if (ln[0] < width / 2.0 && ln[2] < width / 2.0 ){
leftLine = lines[i];
}
if (ln[0] > width / 2.0 && ln[2] > width / 2.0){
rightLine = lines[i];
}
}
cout << "topLine : " << topLine << endl;
cout << "bottomLine : " << bottomLine << endl;
cout << "leftLine : " << leftLine << endl;
cout << "rightLine : " << rightLine << endl;
// 拟合四条直线方程
float k1, c1;
k1 = float(topLine[3] - topLine[1]) / float(topLine[2] - topLine[0]);
c1 = topLine[1] - k1*topLine[0];
float k2, c2;
k2 = float(bottomLine[3] - bottomLine[1]) / float(bottomLine[2] - bottomLine[0]);
c2 = bottomLine[1] - k2*bottomLine[0];
float k3, c3;
k3 = float(leftLine[3] - leftLine[1]) / float(leftLine[2] - leftLine[0]);
c3 = leftLine[1] - k3*leftLine[0];
float k4, c4;
k4 = float(rightLine[3] - rightLine[1]) / float(rightLine[2] - rightLine[0]);
c4 = rightLine[1] - k4*rightLine[0];
// 四条直线交点
Point p1; // 左上角
p1.x = static_cast((c1 - c3) / (k3 - k1));
p1.y = static_cast(k1*p1.x + c1);
Point p2; // 右上角
p2.x = static_cast((c1 - c4) / (k4 - k1));
p2.y = static_cast(k1*p2.x + c1);
Point p3; // 左下角
p3.x = static_cast((c2 - c3) / (k3 - k2));
p3.y = static_cast(k2*p3.x + c2);
Point p4; // 右下角
p4.x = static_cast((c2 - c4) / (k4 - k2));
p4.y = static_cast(k2*p4.x + c2);
cout << "p1(x, y)=" << p1.x << "," << p1.y << endl;
cout << "p2(x, y)=" << p2.x << "," << p2.y << endl;
cout << "p3(x, y)=" << p3.x << "," << p3.y << endl;
cout << "p4(x, y)=" << p4.x << "," << p4.y << endl;
// 显示四个点坐标
circle(linesImage, p1, 2, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0);
circle(linesImage, p2, 2, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0);
circle(linesImage, p3, 2, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0);
circle(linesImage, p4, 2, Scalar(255, 0, 0), 2, 8, 0);
line(linesImage, Point(topLine[0], topLine[1]), Point(topLine[2], topLine[3]), Scalar(0, 255, 0), 2, 8, 0);
imshow("four corners", linesImage);
// 透视变换
vector src_corners(4); // 原来的点
src_corners[0] = p1;
src_corners[1] = p2;
src_corners[2] = p3;
src_corners[3] = p4;
vector dst_corners(4); // 目标点位
dst_corners[0] = Point(0,0);
dst_corners[1] = Point(width, 0);
dst_corners[2] = Point(0, height);
dst_corners[3] = Point(width , height);
// 获取变换矩阵
Mat reslutImg;
Mat warpmatrix = getPerspectiveTransform(src_corners, dst_corners);
warpPerspective(src, reslutImg, warpmatrix, reslutImg.size(), INTER_LINEAR);
imshow(output_image, reslutImg);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
二值化
形态学操作
轮廓查找
霍夫变换
求直线交点
透视变换
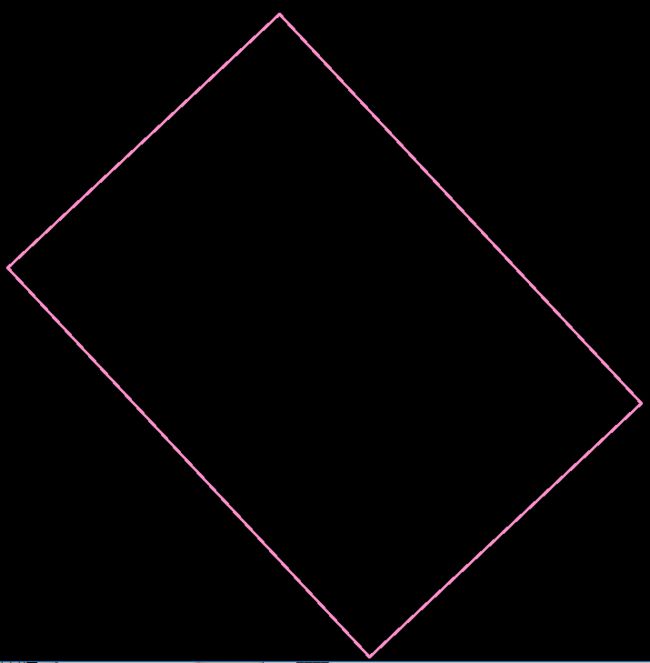
另种比较简单的方法
如图:
操作和以前的方法类似,处理比较简单。
- 二值化
- 使用canny进行轮廓检测,把轮廓进行显著化
- 查找轮廓,得到旋转的角度
- 进行仿射变换
#include
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
Mat src, dst, gray_src;
char input_image[] = "input image";
char output_image[] = "output image";
int threshold_value = 100;
int threshold_max = 255;
void FindROI(int, void*);
void Check_Skew(int, void *);
int main(int argc, char ** argv){
src = imread("case12.jpg");
if (src.empty()){
printf("colud not load image ..\n");
return -1;
}
namedWindow(input_image, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
namedWindow(output_image, CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
imshow(input_image, src);
createTrackbar("Threshold", output_image, &threshold_value, threshold_max, Check_Skew);
Check_Skew(0, 0);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
void Check_Skew(int, void *){
Mat canny_output;
cvtColor(src, gray_src, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
Canny(gray_src, canny_output, threshold_value, threshold_value * 2, 3, false);
vector> contours;
vector hireachy;
findContours(canny_output, contours, hireachy, RETR_TREE, CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE, Point(0, 0));
Mat drawImg = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3);
float maxw = 0;
float maxh = 0;
double degree = 0;
for (size_t t = 0; t < contours.size(); t++){
RotatedRect minRect = minAreaRect(contours[t]);
degree = abs(minRect.angle);
if (degree > 0){
maxw = max(maxw, minRect.size.width);
maxh = max(maxh, minRect.size.height);
}
}
RNG rng(12345);
for (size_t t = 0; t < contours.size(); t++){
RotatedRect minRect = minAreaRect(contours[t]);
if (maxw == minRect.size.width && maxh == minRect.size.height){
degree = minRect.angle;
Point2f pts[4];
minRect.points(pts);
Scalar color = Scalar(rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255), rng.uniform(0, 255));
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
line(drawImg, pts[i], pts[(i + 1) % 4], color, 2, 8, 0);
}
}
}
imshow("roi", drawImg);
printf("max contours width: %f\n", maxw);
printf("max contours heigh: %f\n", maxh);
printf("max contours angle: %f\n", degree);
Point2f center(src.cols / 2, src.rows / 2);
Mat rotm = getRotationMatrix2D(center, degree, 1.0);
warpAffine(src, dst, rotm, src.size(), INTER_LINEAR, 0, Scalar(255, 255, 255));
imshow(output_image, dst);
}