- YOLO各版本原理和优缺点解析
Ash Butterfield
计算机视觉
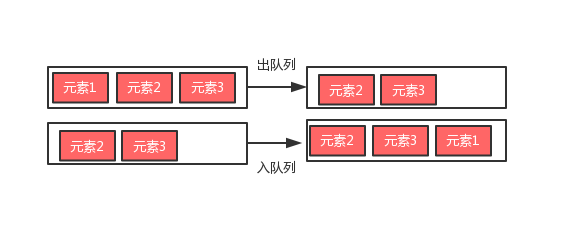
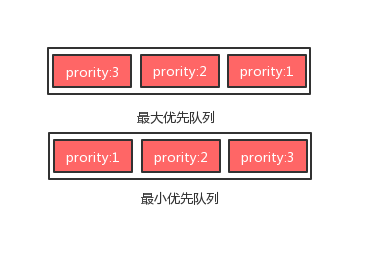
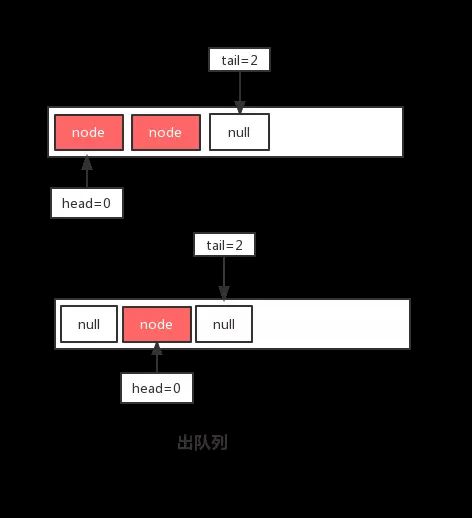
YOLO(YouOnlyLookOnce)是一种实时目标检测算法,以其高速度和较高精度著称。以下是各版本的详细介绍及优缺点分析:1.YOLOv1(2016年)原理:将输入图像划分为S×SS\timesSS×S的网格,每个网格预测多个边界框和类别置信度。使用单个神经网络直接对图像进行前向传播预测边界框和类别标签。优点:速度快,适合实时应用。模型结构简单,易于实现和训练。缺点:对小目标检测效果差,容易
- vue页面导出为pdf文件
weixin_45907435
vue.jspdf前端
在后台管理项目中,想到把页面导出为pdf格式的文件,可以使用html2canvas和jspdf插件实现1、安装'html2canvas''jspdf'npminstallhtml2canvas--savenpminstalljspdf--save2、util.js文件中封装导出方法//引入依赖importhtml2canvasfrom'html2canvas'importJsPDFfrom'jsp
- Linux操作系统管理System V标准中三种资源的方式
柯懒不是柯南
Linuxlinux运维服务器c++开发语言
操作系统管理SystemV标准中三种资源的方式前面介绍了四种进程间通信的方式,其中共享内存、消息队列和信号量属于SystemV标准的通信方式,在使用这三种进程间通信方式时可以发现其中的接口都比较类似,如下表所示:操作\通信方式共享内存消息队列信号量申请资源shmgetmsggetsemget操作资源常规读写操作msgsnd和msgrcvsemop释放资源shmctlmsgctlsemctl从应用层
- 设计模式(一):设计原则、常用设计模式
lercent
设计模式设计模式
1.设计原则SOLID原则-SRP单一职责原则:一个类或者模块只负责完成一个职责(或者功能)。SOLID原则-OCP开闭原则:如果要添加一个新的功能,能够在已有代码基础上直接扩展代码,而不用修改已有代码就能实现,那么就符合“扩展开放、对修改关闭”原则。SOLID原则-LSP里式替换原则:子类对象能够替换程序中父类对象出现的任何地方,并且保证原来程序的逻辑行为不变及正确性不被破坏。SOLID原则-I
- 前瞻技术:改变未来的关键趋势与应用
jiemidashi
经验分享
物联网IoT)在智能家居中的应用越来越广泛。智能家居通过互联网连接各种设备,使日常生活更加便捷。例如,智能灯泡可以通过手机控制。用户可以在外出时远程关灯,节约电量。这种智能化控制不仅提高了家居安全性,还提升了用户的生活质量。实现智能家居设备的控制需要几个步骤。首先,用户需要下载相关的智能家居应用。其次,设备如智能插座、安防摄像头等,需连接到同一网络。通过应用,用户可以轻松管理这些设备。比如,设定定
- 信息技术革新引领社会变革
JiYan_yellow
业界资讯
信息技术革新引领社会变革一、信息技术推动数字化转型随着信息技术的迅猛发展,我们正处在一个数字化的时代。信息技术在推动产业数字化转型方面发挥着重要作用。云计算、大数据、人工智能等先进技术的应用,使得企业能够实现更高效的生产和运营。例如,在制造业领域,智能制造技术能够提高生产效率和质量,降低运营成本。此外,信息技术还在促进供应链管理、市场营销等环节的数字化转型,为企业提供更广阔的发展空间。信息技术还深
- 单调栈和单调队列
累加
算法c++
单调栈定义单调栈是一种栈,栈内元素(通常是元素的值或者元素对应的索引)具有单调性,分为单调递增栈和单调递减栈:单调递增栈:从栈底到栈顶元素的值是单调递增的,即栈底元素是最小的,栈顶元素是最大的。在向栈中插入元素时,如果新元素小于栈顶元素,则将栈顶元素弹出,直到新元素大于等于栈顶元素,再将新元素入栈。单调递减栈:从栈底到栈顶元素的值是单调递减的,即栈底元素是最大的,栈顶元素是最小的。在向栈中插入元素
- 功能测试的范畴与目标
机器视觉小小测试员
测试手动测试功能测试
功能测试的范畴与目标在软件开发与质量检测的流程中,功能测试扮演着极为重要的角色。它着重于检验软件产品是否能够依据设计要求及用户期望,精准地实现既定的功能。简而言之,功能测试的核心任务是确认软件的各项特性与功能是否准确无误、全面且符合预期,确保软件在交付给用户之前具备可靠的可用性与稳定性。一、功能测试的范畴功能覆盖测试:功能测试的关键在于对软件的各个功能模块进行全面且细致的验证。测试人员会依据需求规
- 【AI系列】从零开始学习大模型GPT (2)- Build a Large Language Model (From Scratch)
Tasfa
AI人工智能教程人工智能学习gpt
前序文章【AI系列】从零开始学习大模型GPT(1)-BuildaLargeLanguageModel(FromScratch)BuildaLargeLanguageModel背景第1章:理解大型语言模型第2章:处理文本数据第3章:编码Attention机制什么是Attention机制?Attention机制的基本原理数学表示应用总结为什么要使用注意力机制如何实现?简单注意力机制带训练权重的注意力机
- 设计模式-外观模式
管大虾
设计模式设计模式外观模式
一、定义外观模式提供了一个统一的接口,用来访问子系统中的一群接口。外观定义了一个高层的接口,让子系统更容易使用。外观模式其实和适配器模式很像,只不过适配器模式转化接口是为了实现接口的兼容,把每个接口都做了转化,而外观模式改变接口的原因是为了简化接口,把复杂的一切都隐藏,只对外暴露出一个干净的外观,而且外观模式不只是简单得简化解耦,也实现了将客户从众多子组件中解耦。其实这个模式,我们在日常开发中会不
- 技术革新让生活更便捷
巴巴郭海鹄
生活量子计算经验分享
量子通信是一种利用量子力学原理进行信息传递的技术。它的基本原理是量子纠缠和量子密钥分发。量子纠缠指两个粒子即使相隔很远,一个粒子的状态改变会立刻引起另一个粒子状态的相应变化。量子密钥分发则是通过量子态传输实现加密密钥的安全交换。在信息安全领域,量子通信具有显著优势。传统加密方法依赖于复杂的数学问题,但未来可能被量子计算机解密。而量子通信利用量子力学的不确定性,提供了一种理论上无法被窃听的安全通信方
- Dify基础:windows下如何学习Linux系统?wsl相关基本概念的介绍
几道之旅
Dify:智能体(Agent)工作流知识库全搞定linuxwindowsdocker
文章目录前言首先,WSL到底是个什么东西?在WSL之前,有个hyperV,又是个啥?WSL和HyperV的关系是什么?我来总结一下吧,有了wsl,就相当于在你的windows上有了一个可以运行linux的虚拟机。这和Dify有啥关系?前言为了实现本文效果,我直接下血本把自己的wsl给卸载了。就说这个牺牲精神,希望大伙儿多多关注、多多点赞、多多评论。首先,WSL到底是个什么东西?在很久以前,有一个叫
- k8s worker 节点使用kubectl 命令
岳来
#kubeneteskubernetes容器kubectlworker节点
通常,kubectl命令在master节点使用,但为了方便,想要在worker节点使用该命令,如何操作?具体实现如下:$kubectlgetpodTheconnectiontotheserverlocalhost:8080wasrefused-didyouspecifytherighthostorport?#worker节点无法使用拷贝master节点文件scp/etc/kubernetes/ad
- Vue3笔记_<入门基础篇>
我的白银时代
Vue2进阶Vue3笔记Vue3零到一实战笔记vue.js前端
目录Setup语法糖ref:定义一个数据的响应式reactive:定义一个对象类型的响应式数据toRef()toRefs()计算属性watchEffect函数生命周期Vue3获取DomPropsVue3自定义事件Setup语法糖setup是一个专门用于组合式API的特殊钩子函数,只在初始化时执行一次。setup有两种返回值:对象。对象中的属性,方法在模板中都可以直接使用函数。自定义渲染内容,覆盖模
- DeepSeek与ChatGPT正在改写学历规则?2025教育革命深度解析
笑傲江湖2023
人工智能chatgpt
一、颠覆性现状:AI如何解构学历价值1.知识获取民主化随着AI技术的不断进步,知识获取的方式正在发生翻天覆地的变化:DeepSeek-R1通过仅10%的训练成本,实现了与GPT-4o相当的性能,技术文档的生成效率提升了70%。这种高效的知识生成方式,使得人人都可以轻松获取和应用知识。斯坦福大学的研究显示,使用ChatGPT的大学生平均GPA提升了0.43分,但课程通过率却下降了11%(2024)。
- opencascade 标注-直线标注、半径标准、角度标注
一只小小汤圆
Opencascadec++c++
opencascade直线标注在OpenCascade(OCCT)中实现标注功能主要涉及使用其交互服务模块(AIS)和尺寸标注类。以下是关键步骤和示例代码:显示精度(小数点后几位)SetDimensionAspect设置显示颜色SetCommonColor1.创建尺寸标注对象使用AIS_LengthDimension等类创建线性尺寸标注:#include//定义两个点或边gp_PntP1(0,0,
- 【语义分割专题文章】
BoostingIsm
Segmentationpython
本栏聚焦在语义分割的相关算法,专栏内文章的代码均已实现。一、数据篇【遥感】【道路】篇:【语义分割】【专题系列】一、MassachusettsRoadsDataset马萨诸塞州道路数据集获取二、CNN篇Unet(2015):【语义分割】【专题系列】二、Unet语义分割代码实战PSPNet(2017):【语义分割】【专题系列】三、PSPNet语义分割代码实战Linknet(2017)FPN(Featu
- Flutter 简化线程Isolate的使用
CodeOfCC
flutterflutter开发语言dart多线程
文章目录前言一、完整代码二、使用示例1、通过lambda启动线程2、获取线程返回值3、线程通信4、结束isolate总结前言flutter的线程是数据独立的,每个线程一般通过sendport来传输数据,这样使得线程调用没那么方便,本文将提供一种支持lambda启动isolate的方法,且支持捕获值类型变量,以及支持返回值。一、完整代码由于代码量较少,原理就不介绍了,直接给出完整实现。isolate
- 分布式数据库面试整理
Necther
数据库面试分布式
5.3.1redis面试专题1、redis和memcached什么区别?为什么高并发下有时单线程的redis比多线程的memcached效率要高?区别:mc可缓存图片和视频。rd支持除k/v更多的数据结构;rd可以使用虚拟内存,rd可持久化和aof灾难恢复,rd通过主从支持数据备份;3.rd可以做消息队列。原因:mc多线程模型引入了缓存一致性和锁,加锁带来了性能损耗。2、redis主从复制如何实现
- win32汇编环境,对线程的创建与操作示例二
一品人家
汇编
;运行效果;win32汇编环境,对线程的创建与操作示例二;本文主要是实现用CreateThread创建线程时,如何把参数传入进去;以下举3个例子说明,如何把数值、字符串和自定义结构传入线程之中;下面为asm文件;>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>.386.modelflat,stdcallopti
- Web3 的虚实融合之路:从虚拟交互到元宇宙构建
dingzd95
web3web3交互
在这个数字技术日新月异的时代,我们正站在Web3的门槛上,见证着互联网的又一次革命。Web3不仅仅是技术的迭代,它代表了一种全新的交互方式和价值创造模式。本文将探讨Web3如何推动虚拟交互的发展,并最终实现元宇宙的构建,揭示这一技术演进背后的关键理念与现实意义。Web3:去中心化的新交互方式Web3,即第三代互联网,是一个去中心化、用户主权、数据自主的网络环境。它依托于区块链、分布式存储等技术,实
- Stable Diffusion 教程基础篇: 如何写出好的prompt,一些技巧和原则
AI想象家
stablediffusionpromptmidjourney人工智能openAIAI作画
StableDiffusion教程-中文AskAIforART·Originaltxt2imgandimg2imgmodes·基础模式之文生图/图生图点击可放大基础入门部分输入一段话,生成一张图。这是AI绘画的核心。入门就是那么简单,不过,这段话怎么写,其实也是有窍门的。在StableDiffusion里面,这段描述也就是Prompt,我们称之为AI的魔法咒语。那么,最开始我们需要怎么做呢?当然是
- SpringCloud—— eureka+feign实现声明式服务治理
2501_90225989
springcloudeurekaspring
为什么要使用Eureka,因为在一个完整的系统架构中,任何单点的服务都不能保证不会中断,因此我们需要服务发现机制,在某个节点中断后,其它的节点能够继续提供服务,从而保证整个系统是高可用的。服务发现有两种模式:一种是客户端发现模式,一种是服务端发现模式。Erueka采用的是客户端发现模式。feign:Feign是一个声明式的Web服务客户端,使用Feign可使得Web服务客户端的写入更加方便。它具有
- 笔记(四)
故里人间165
html前端
(一)定位1.给元素设置position:relative即可实观相对定位。可以用left,right,top,bottom四个属性位置。相对定位的参考点相对自己原来的位置2.绝对定位设置:给元素设置position:absolute即可实现绝对定位可以使用left,right,top,bottom四个属性调整位置3.固定定位设置:给元素设置position:fixed即可可以使用left,rig
- 国内靠谱的docker镜像源
zwjapple
docker容器运维
阿里云镜像源特点:阿里云提供的镜像加速服务,为每个用户分配专属的镜像源地址,稳定性高、速度快,能有效提升拉取镜像的效率。它依托阿里云强大的基础设施,覆盖全国多个地域的数据中心,能根据用户的地理位置智能分配节点,实现快速响应。获取方式:登录阿里云容器镜像服务控制台,在“镜像加速器”板块查看专属地址,格式类似https://xxxxxx.mirror.aliyuncs.com。华为云镜像源特点:华为云
- Java微服务技术栈(2)
Z-H-J
Java笔记随录java微服务开发语言
写在前面高级篇里的很多知识我都没有去实践过,只是知道相关的原理,主要原因是:应用场景在多数情况下难以碰见(高并发)对于运行的要求过高(如果是单节点进行模拟,那么就必须有很大的运行内存)所以这部分记录更多是一个思路的梳理,可能无法作为各位全面掌握该部分知识的条目,望见谅7.微服务的保护技术:Sentinelsentiel分为sentinel控制台和sentinel客户端,具体的规则过滤都由配置在微服
- Go语言输入输出
凉城未暖夜微凉
Golanggolang
packagefmtfmt包实现了类似C语言printf和scanf的格式化I/O。主要分为向外输出内容和获取输入内容两大部分。Go语言输入输出01、获取输入1、fmt.Scan2、fmt.Scanf3、fmt.Scanln4、bufio.NewReader5、Fscan系列6、Sscan系列02、输出数据1、fmt.Print2、fmt.Printf3、fmt.Println4、Fprint5、
- Python.pyecharts.charts折线图新旧版本对比详解!
唔使般若
python
旧版本(0.5.10)实现frompyechartsimportLineline=Line("美国邮费阶梯图")datax=[1995,1996,1997,1998,1999,2001,2002,2003,2004,2005,2006,2007,2008,2009]datay=[0.32,0.32,0.32,0.32,0.33,0.33,0.34,0.37,0.37,0.37,0.37,0.39,
- unity引擎包含哪些核心组件
你一身傲骨怎能输
商业化游戏开发技术专栏unity游戏引擎
Unity引擎的核心组件构成了其强大的游戏开发和运行时环境。以下是一些主要的核心组件:SceneManagement:场景管理器允许开发者创建、加载和切换游戏中的不同场景。RenderingEngine:渲染引擎支持2D和3D图形,提供了多种渲染路径和着色器,以实现各种视觉效果。PhysicsEngine:物理引擎(基于NVIDIAPhysX)模拟真实世界的物理行为,包括碰撞检测和刚体动力学。Sc
- SpringBoot+vue 创建CRM财务系统,根据用户登录的注册号,动态判断属于哪个数据库连接,使用sqlserver odbc驱动
战族狼魂
数据库springbootvue.js
使用SpringBoot和Vue构建CRM财务系统时,基于用户登录时的注册号动态选择数据库连接,并使用SQLServerODBC驱动进行数据库操作,可以通过以下几个步骤来实现。目录1.配置SpringBoot动态数据源1.1.引入依赖1.2.配置动态数据源1.3.数据源上下文持有类1.4.配置多个数据源1.5.在登录时设置数据源2.配置Vue前端3.连接SQLServerODBC驱动4.总结1.配
- 插入表主键冲突做更新
a-john
有以下场景:
用户下了一个订单,订单内的内容较多,且来自多表,首次下单的时候,内容可能会不全(部分内容不是必须,出现有些表根本就没有没有该订单的值)。在以后更改订单时,有些内容会更改,有些内容会新增。
问题:
如果在sql语句中执行update操作,在没有数据的表中会出错。如果在逻辑代码中先做查询,查询结果有做更新,没有做插入,这样会将代码复杂化。
解决:
mysql中提供了一个sql语
- Android xml资源文件中@、@android:type、@*、?、@+含义和区别
Cb123456
@+@?@*
一.@代表引用资源
1.引用自定义资源。格式:@[package:]type/name
android:text="@string/hello"
2.引用系统资源。格式:@android:type/name
android:textColor="@android:color/opaque_red"
- 数据结构的基本介绍
天子之骄
数据结构散列表树、图线性结构价格标签
数据结构的基本介绍
数据结构就是数据的组织形式,用一种提前设计好的框架去存取数据,以便更方便,高效的对数据进行增删查改。正确选择合适的数据结构,对软件程序的高效执行的影响作用不亚于算法的设计。此外,在计算机系统中数据结构的作用也是非同小可。例如常常在编程语言中听到的栈,堆等,就是经典的数据结构。
经典的数据结构大致如下:
一:线性数据结构
(1):列表
a
- 通过二维码开放平台的API快速生成二维码
一炮送你回车库
api
现在很多网站都有通过扫二维码用手机连接的功能,联图网(http://www.liantu.com/pingtai/)的二维码开放平台开放了一个生成二维码图片的Api,挺方便使用的。闲着无聊,写了个前台快速生成二维码的方法。
html代码如下:(二维码将生成在这div下)
? 1
&nbs
- ImageIO读取一张图片改变大小
3213213333332132
javaIOimageBufferedImage
package com.demo;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
/**
* @Description 读取一张图片改变大小
* @author FuJianyon
- myeclipse集成svn(一针见血)
7454103
eclipseSVNMyEclipse
&n
- 装箱与拆箱----autoboxing和unboxing
darkranger
J2SE
4.2 自动装箱和拆箱
基本数据(Primitive)类型的自动装箱(autoboxing)、拆箱(unboxing)是自J2SE 5.0开始提供的功能。虽然为您打包基本数据类型提供了方便,但提供方便的同时表示隐藏了细节,建议在能够区分基本数据类型与对象的差别时再使用。
4.2.1 autoboxing和unboxing
在Java中,所有要处理的东西几乎都是对象(Object)
- ajax传统的方式制作ajax
aijuans
Ajax
//这是前台的代码
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme()+
- 只用jre的eclipse是怎么编译java源文件的?
avords
javaeclipsejdktomcat
eclipse只需要jre就可以运行开发java程序了,也能自动 编译java源代码,但是jre不是java的运行环境么,难道jre中也带有编译工具? 还是eclipse自己实现的?谁能给解释一下呢问题补充:假设系统中没有安装jdk or jre,只在eclipse的目录中有一个jre,那么eclipse会采用该jre,问题是eclipse照样可以编译java源文件,为什么呢?
&nb
- 前端模块化
bee1314
模块化
背景: 前端JavaScript模块化,其实已经不是什么新鲜事了。但是很多的项目还没有真正的使用起来,还处于刀耕火种的野蛮生长阶段。 JavaScript一直缺乏有效的包管理机制,造成了大量的全局变量,大量的方法冲突。我们多么渴望有天能像Java(import),Python (import),Ruby(require)那样写代码。在没有包管理机制的年代,我们是怎么避免所
- 处理百万级以上的数据处理
bijian1013
oraclesql数据库大数据查询
一.处理百万级以上的数据提高查询速度的方法: 1.应尽量避免在 where 子句中使用!=或<>操作符,否则将引擎放弃使用索引而进行全表扫描。
2.对查询进行优化,应尽量避免全表扫描,首先应考虑在 where 及 o
- mac 卸载 java 1.7 或更高版本
征客丶
javaOS
卸载 java 1.7 或更高
sudo rm -rf /Library/Internet\ Plug-Ins/JavaAppletPlugin.plugin
成功执行此命令后,还可以执行 java 与 javac 命令
sudo rm -rf /Library/PreferencePanes/JavaControlPanel.prefPane
成功执行此命令后,还可以执行 java
- 【Spark六十一】Spark Streaming结合Flume、Kafka进行日志分析
bit1129
Stream
第一步,Flume和Kakfa对接,Flume抓取日志,写到Kafka中
第二部,Spark Streaming读取Kafka中的数据,进行实时分析
本文首先使用Kakfa自带的消息处理(脚本)来获取消息,走通Flume和Kafka的对接 1. Flume配置
1. 下载Flume和Kafka集成的插件,下载地址:https://github.com/beyondj2ee/f
- Erlang vs TNSDL
bookjovi
erlang
TNSDL是Nokia内部用于开发电信交换软件的私有语言,是在SDL语言的基础上加以修改而成,TNSDL需翻译成C语言得以编译执行,TNSDL语言中实现了异步并行的特点,当然要完整实现异步并行还需要运行时动态库的支持,异步并行类似于Erlang的process(轻量级进程),TNSDL中则称之为hand,Erlang是基于vm(beam)开发,
- 非常希望有一个预防疲劳的java软件, 预防过劳死和眼睛疲劳,大家一起努力搞一个
ljy325
企业应用
非常希望有一个预防疲劳的java软件,我看新闻和网站,国防科技大学的科学家累死了,太疲劳,老是加班,不休息,经常吃药,吃药根本就没用,根本原因是疲劳过度。我以前做java,那会公司垃圾,老想赶快学习到东西跳槽离开,搞得超负荷,不明理。深圳做软件开发经常累死人,总有不明理的人,有个软件提醒限制很好,可以挽救很多人的生命。
相关新闻:
(1)IT行业成五大疾病重灾区:过劳死平均37.9岁
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-原型模式
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
/**
* Effective Java 建议使用copy constructor or copy factory来代替clone()方法:
* 1.public Product copy(Product p){}
* 2.publi
- 配置管理---svn工具之权限配置
chenyu19891124
SVN
今天花了大半天的功夫,终于弄懂svn权限配置。下面是今天收获的战绩。
安装完svn后就是在svn中建立版本库,比如我本地的是版本库路径是C:\Repositories\pepos。pepos是我的版本库。在pepos的目录结构
pepos
component
webapps
在conf里面的auth里赋予的权限配置为
[groups]
- 浅谈程序员的数学修养
comsci
设计模式编程算法面试招聘
浅谈程序员的数学修养
- 批量执行 bulk collect与forall用法
daizj
oraclesqlbulk collectforall
BULK COLLECT 子句会批量检索结果,即一次性将结果集绑定到一个集合变量中,并从SQL引擎发送到PL/SQL引擎。通常可以在SELECT INTO、
FETCH INTO以及RETURNING INTO子句中使用BULK COLLECT。本文将逐一描述BULK COLLECT在这几种情形下的用法。
有关FORALL语句的用法请参考:批量SQL之 F
- Linux下使用rsync最快速删除海量文件的方法
dongwei_6688
OS
1、先安装rsync:yum install rsync
2、建立一个空的文件夹:mkdir /tmp/test
3、用rsync删除目标目录:rsync --delete-before -a -H -v --progress --stats /tmp/test/ log/这样我们要删除的log目录就会被清空了,删除的速度会非常快。rsync实际上用的是替换原理,处理数十万个文件也是秒删。
- Yii CModel中rules验证规格
dcj3sjt126com
rulesyiivalidate
Yii cValidator主要用法分析:
yii验证rulesit 分类: Yii yii的rules验证 cValidator主要属性 attributes ,builtInValidators,enableClientValidation,message,on,safe,skipOnError
- 基于vagrant的redis主从实验
dcj3sjt126com
vagrant
平台: Mac
工具: Vagrant
系统: Centos6.5
实验目的: Redis主从
实现思路
制作一个基于sentos6.5, 已经安装好reids的box, 添加一个脚本配置从机, 然后作为后面主机从机的基础box
制作sentos6.5+redis的box
mkdir vagrant_redis
cd vagrant_
- Memcached(二)、Centos安装Memcached服务器
frank1234
centosmemcached
一、安装gcc
rpm和yum安装memcached服务器连接没有找到,所以我使用的是make的方式安装,由于make依赖于gcc,所以要先安装gcc
开始安装,命令如下,[color=red][b]顺序一定不能出错[/b][/color]:
建议可以先切换到root用户,不然可能会遇到权限问题:su root 输入密码......
rpm -ivh kernel-head
- Remove Duplicates from Sorted List
hcx2013
remove
Given a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such that each element appear only once.
For example,Given 1->1->2, return 1->2.Given 1->1->2->3->3, return&
- Spring4新特性——JSR310日期时间API的支持
jinnianshilongnian
spring4
Spring4新特性——泛型限定式依赖注入
Spring4新特性——核心容器的其他改进
Spring4新特性——Web开发的增强
Spring4新特性——集成Bean Validation 1.1(JSR-349)到SpringMVC
Spring4新特性——Groovy Bean定义DSL
Spring4新特性——更好的Java泛型操作API
Spring4新
- 浅谈enum与单例设计模式
247687009
java单例
在JDK1.5之前的单例实现方式有两种(懒汉式和饿汉式并无设计上的区别故看做一种),两者同是私有构
造器,导出静态成员变量,以便调用者访问。
第一种
package singleton;
public class Singleton {
//导出全局成员
public final static Singleton INSTANCE = new S
- 使用switch条件语句需要注意的几点
openwrt
cbreakswitch
1. 当满足条件的case中没有break,程序将依次执行其后的每种条件(包括default)直到遇到break跳出
int main()
{
int n = 1;
switch(n) {
case 1:
printf("--1--\n");
default:
printf("defa
- 配置Spring Mybatis JUnit测试环境的应用上下文
schnell18
springmybatisJUnit
Spring-test模块中的应用上下文和web及spring boot的有很大差异。主要试下来差异有:
单元测试的app context不支持从外部properties文件注入属性
@Value注解不能解析带通配符的路径字符串
解决第一个问题可以配置一个PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer的bean。
第二个问题的具体实例是:
- Java 定时任务总结一
tuoni
javaspringtimerquartztimertask
Java定时任务总结 一.从技术上分类大概分为以下三种方式: 1.Java自带的java.util.Timer类,这个类允许你调度一个java.util.TimerTask任务; 说明: java.util.Timer定时器,实际上是个线程,定时执行TimerTask类 &
- 一种防止用户生成内容站点出现商业广告以及非法有害等垃圾信息的方法
yangshangchuan
rank相似度计算文本相似度词袋模型余弦相似度
本文描述了一种在ITEYE博客频道上面出现的新型的商业广告形式及其应对方法,对于其他的用户生成内容站点类型也具有同样的适用性。
最近在ITEYE博客频道上面出现了一种新型的商业广告形式,方法如下:
1、注册多个账号(一般10个以上)。
2、从多个账号中选择一个账号,发表1-2篇博文