原文发布于:wenghengcong.com
YYModel,相当精简,一个YYClassInfo类,一个NSObject+YYModel的分类。
YYClassInfo是YYModel对类中属性、成员变量、方法和类属性做的一层封装,后面详解会提到。
NSObject+YYModel工作,就是YYModel的主体工作——JSON转模型。
从实例开始
下面是一个实例:
YYBook *book = [YYBook modelWithJSON:@" \
{ \
\"name\": \"Harry Potter\", \
\"pages\": 512, \
\"publishDate\": \"2010-01-01\" \
}"];
NSObject (YYModel)中,-(instancetype)modelWithJSON:(id)json分两步:
+ (instancetype)modelWithJSON:(id)json {
NSDictionary *dic = [self _yy_dictionaryWithJSON:json];
return [self modelWithDictionary:dic];
}
- 将JSON转换为字典;
_yy_dictionaryWithJSON:将JSON转换为字典。
+ (NSDictionary *)_yy_dictionaryWithJSON:(id)json {
if (!json || json == (id)kCFNull) return nil;
NSDictionary *dic = nil;
NSData *jsonData = nil;
if ([json isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) {
dic = json;
} else if ([json isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) {
jsonData = [(NSString *)json dataUsingEncoding : NSUTF8StringEncoding];
} else if ([json isKindOfClass:[NSData class]]) {
jsonData = json;
}
if (jsonData) {
dic = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:jsonData options:kNilOptions error:NULL];
if (![dic isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) dic = nil;
}
return dic;
}
-
kCFNull
const
CFNullRefkCFNull; // the singleton null instance其中:
/*A reference to a CFNull object. */
typedef const struct CF_BRIDGED_TYPE(NSNull) __CFNull* CFNullRef;
-
JSONObjectWithData:jsonData
-
关于该方法,需要传options,关于options,API说明如下:
//允许json最外层不是NSArray或者NSDictionary NSJSONReadingMutableContainers = (1UL << 0), //容器是可变的,解析json返回可变的NSArray和NSDictionary NSJSONReadingMutableLeaves = (1UL << 1), //叶子节点是可变的,解析json返回可变的字符串类型 NSJSONReadingAllowFragments = (1UL << 2) 此处用kNilOptions,即0,表示的是返回的对象是不可变的,NSDictionary或NSArray。
如果解析失败,就返回nil;
data参数:支持五种编码格式:UTF-8, UTF-16LE, UTF-16BE, UTF-32LE。效率最高的是UTF-8,所以在此也是用该编码。
-
-
将字典转换为模型。
+ (instancetype)modelWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dictionary { if (!dictionary || dictionary == (id)kCFNull) return nil; if (![dictionary isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) return nil; /*!!!忽略 这部分不是转model的过程,只是在自定义了转化为自定义类时,需要获取该自定义的类。 Class cls = [self class]; //cls:YYBook _YYModelMeta *modelMeta = [_YYModelMeta metaWithClass:cls]; if (modelMeta->_hasCustomClassFromDictionary) { cls = [cls modelCustomClassForDictionary:dictionary] ?: cls; } */ NSObject *one = [cls new]; if ([one modelSetWithDictionary:dictionary]) return one; return nil; }
字典转模型过程如下:
-
第一步,假如用户实现了
modelCustomClassForDictionary,那么先获取类信息。modelCustomClassForDictionary方法提供了我们在字典转模型的过程中创建不同类型对象的途径:
比如,要初始化一个Shape类对象,根据是否有对应字段来生成不同的子类:
@class YYCircle, YYRectangle, YYLine;
@implementation YYShape
+ (Class)modelCustomClassForDictionary:(NSDictionary*)dictionary {
if (dictionary[@"radius"] != nil) {
return [YYCircle class];
} else if (dictionary[@"width"] != nil) {
return [YYRectangle class];
} else if (dictionary[@"y2"] != nil) {
return [YYLine class];
} else {
return [self class];
}
}
@end
- 第二步,才是真正的给属性赋值
NSObject *one = [cls new];
if ([one modelSetWithDictionary:dictionary]) return one;
字典转模型
- (BOOL)modelSetWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dic方法是NSObject+YYModel的一个方法,支持所有继承自NSObject对象的类。
在这里,作了省略,因为我们在给模型赋值,需要先对这个类进行大解剖。之后我们再看如何赋值。
//NSObject(YYModel)
- (BOOL)modelSetWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dic {
//!!!下面我们着重看这部分
//1. 获取类信息
_YYModelMeta *modelMeta = [_YYModelMeta metaWithClass:object_getClass(self)];
//2. 给模型赋值
....
return YES;
}
- 获取类信息
- 给模型赋值
获取类信息
方法调用链
_YYModelMeta,简单看一下这个类,这个类的目的是存储一个类的所有信息,包括属性、方法和成员变量等。
而我们能进行JSON转模型(即类对象)则依赖于如何获取该类对象中所有信息,才能对类型赋值。
/// Returns the cached model class meta
+ (instancetype)metaWithClass:(Class)cls {
if (!cls) return nil;
static CFMutableDictionaryRef cache;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
static dispatch_semaphore_t lock; //信号量,保持只有一个线程在获取cache
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
cache = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), 0, &kCFTypeDictionaryKeyCallBacks, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
lock = dispatch_semaphore_create(1);
});
dispatch_semaphore_wait(lock, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
_YYModelMeta *meta = CFDictionaryGetValue(cache, (__bridge const void *)(cls));
dispatch_semaphore_signal(lock);
if (!meta || meta->_classInfo.needUpdate) {
meta = [[_YYModelMeta alloc] initWithClass:cls];
if (meta) {
dispatch_semaphore_wait(lock, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
CFDictionarySetValue(cache, (__bridge const void *)(cls), (__bridge const void *)(meta));
dispatch_semaphore_signal(lock);
}
}
return meta;
}
这里有两个知识点:
- Core Foundation字典
static CFMutableDictionaryRef cache = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), 0, &kCFTypeDictionaryKeyCallBacks, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
_YYModelMeta *meta = CFDictionaryGetValue(cache, (__bridge const void *)(cls));
CFDictionarySetValue(cache, (__bridge const void *)(cls), (__bridge const void *)(meta));
其中关于创建CF字典的,更多可以参考Objective-C语言(五)系统框架
- 信号量机制
-
创建一个信号量:
static dispatch_semaphore_t lock; //信号量,保持只有一个线程在获取cache lock = dispatch_semaphore_create(1); -
信号量控制
dispatch_semaphore_wait(lock, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER); dispatch_semaphore_signal(lock);
dispatch_semaphore_wait等待信号,当信号总量少于0的时候就会一直等待,否则就可以正常的执行,并让信号总量-1。
dispatch_semaphore_signal信号量+1,表示增加一个可用资源。
更多关于信号量的内容可以参考 多线程编程(五)信号量与锁
在上面代码中,我们看到了两个加锁过程:
分别是CFDictionaryGetValue和CFDictionarySetValue,即在读写是都进行了加锁控制。
类信息的初始化
根据上面调用,进入到类信息的初始化:
meta = [[_YYModelMeta alloc] initWithClass:cls];
- (instancetype)initWithClass:(Class)cls;
我们来看这个方法中做了哪些工作(为体现主要流程,做了删减):
- (instancetype)initWithClass:(Class)cls {
YYClassInfo *classInfo = [YYClassInfo classInfoWithClass:cls];
//黑名单
//白名单
.....
//类对象属性又是个类,即嵌套对象
// 黑、白名单属性处理
// 自定义属性与json字段的映射关系
// 其他属性等的处理
.....
return self;
}
在这个方法里主要做了以下动作:
- 读取类信息:*YYClassInfo classInfo = [YYClassInfo classInfoWithClass:cls];
- class info包装成_YYModelMeta对象;
1. 读取类信息
首先来看:_YYModelMeta类中initWithClass方法里的第一行代码就是调用YYClassInfo的classInfoWithClass。
追溯下去:
+ (instancetype)classInfoWithClass:(Class)cls {
if (!cls) return nil;
static CFMutableDictionaryRef classCache;
static CFMutableDictionaryRef metaCache;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
static dispatch_semaphore_t lock;
//获取classCache、classCache的缓存
dispatch_semaphore_wait(lock, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
YYClassInfo *info = CFDictionaryGetValue(class_isMetaClass(cls) ? metaCache : classCache, (__bridge const void *)(cls));
if (info && info->_needUpdate) {
[info _update];
}
dispatch_semaphore_signal(lock);
if (!info) {
info = [[YYClassInfo alloc] initWithClass:cls];
if (info) {
//设置classCache、classCache的缓存
}
}
return info;
}
我们这里先忽略缓存的策略。关注:
info = [[YYClassInfo alloc] initWithClass:cls];
下面是YYClassInfo类的initWithClass方法:
- (instancetype)initWithClass:(Class)cls {
//比如:cls:YYBook
if (!cls) return nil;
self = [super init];
_cls = cls;
_superCls = class_getSuperclass(cls); //supercls:NSObject
_isMeta = class_isMetaClass(cls); //是否为元类,NO
if (!_isMeta) {
_metaCls = objc_getMetaClass(class_getName(cls));
}
_name = NSStringFromClass(cls); //类名
[self _update];
_superClassInfo = [self.class classInfoWithClass:_superCls];
return self;
}
根据YYModel对YYClassInfo的设定,该类是存储一个类对象所有信息的类,其声明:
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class cls; ///< class object
@property (nullable, nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class superCls; ///< super class object
@property (nullable, nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class metaCls; ///< class's meta class object
@property (nonatomic, readonly) BOOL isMeta; ///< whether this class is meta class
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; ///< class name
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) YYClassInfo *superClassInfo; ///< super class's class info
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSDictionary *ivarInfos; ///< ivars /*成员变量*/
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSDictionary *methodInfos; ///< methods /*方法*/
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSDictionary *propertyInfos; ///< properties /*属性*/
从上面的方法中以及YYClassInfo可以看出,获取了父类、元类以及类名等信息。其中关键的方法在_update方法中,以下做简单分析。
- (void)_update {
_ivarInfos = nil;
_methodInfos = nil;
_propertyInfos = nil;
Class cls = self.cls;
.....
//读取类中的method
//读取类中的property
//读取类中的ivar
....
if (!_ivarInfos) _ivarInfos = @{};
if (!_methodInfos) _methodInfos = @{};
if (!_propertyInfos) _propertyInfos = @{};
_needUpdate = NO;
}
从上面可以看到,读取每一部分信息后,保存在了字典内,我们选取成员变量的读取来作解析:
unsigned int methodCount = 0;
//methods是method链表的首地址,methodCount是method数组的数目
Method *methods = class_copyMethodList(cls, &methodCount);
if (methods) {
NSMutableDictionary *methodInfos = [NSMutableDictionary new];
_methodInfos = methodInfos;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < methodCount; i++) {
YYClassMethodInfo *info = [[YYClassMethodInfo alloc] initWithMethod:methods[i]];
if (info.name) methodInfos[info.name] = info;
}
free(methods);
}
这一段的方法的重点在:class_copyMethodList,该方法是runtime中获取class method的方法。
@param cls The class you want to inspect.
@param outCount On return, contains the length of the returned array. If outCount is NULL, the length is not returned.
Method * class_copyMethodList(Class cls, unsigned int * outCount)
针对每一部分的信息,都有对应的类,分别为:YYClassMethodInfo,YYClassPropertyInfo,YYClassIvarInfo,而且每个类中都有对应的初始化方法。
其中关于这三部分信息,可以参考下面Method信息、Property信息、Ivar信息的部分,以及从runtime.h 读取的Class获取更多的基础知识。
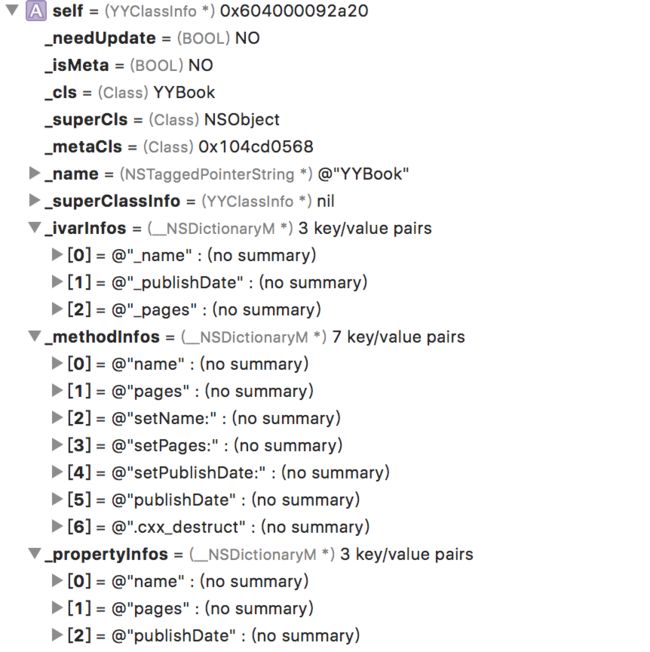
经过上面处理之后,我们可以得到如下YYBook类的Class Info:
2.class info包装成_YYModelMeta对象
等上面的class info处理完成之后,回到[_YYModelMeta initWithClass:]方法中,该方法将class info,对各种YYModel对外提供的接口进行整合处理。比如黑名单、白名单、自定义mapper等接口。
处理完成之后的_YYModelMeta对象才是我们之后进行赋值任务的主要承载着。
那么来看下这部分处理,有点长:
- (instancetype)initWithClass:(Class)cls {
YYClassInfo *classInfo = [YYClassInfo classInfoWithClass:cls];
if (!classInfo) return nil;
self = [super init];
// Get black list
NSSet *blacklist = nil;
if ([cls respondsToSelector:@selector(modelPropertyBlacklist)]) {
NSArray *properties = [(id)cls modelPropertyBlacklist];
if (properties) {
blacklist = [NSSet setWithArray:properties];
}
}
// Get white list
NSSet *whitelist = nil;
if ([cls respondsToSelector:@selector(modelPropertyWhitelist)]) {
NSArray *properties = [(id)cls modelPropertyWhitelist];
if (properties) {
whitelist = [NSSet setWithArray:properties];
}
}
//上面是黑白名单
//黑名单,是该名单里的属性都不作处理
//白名单,是除了该名单中的之外都不作处理
// Get container property's generic class
// 处理容器类中的类型
NSDictionary *genericMapper = nil;
if ([cls respondsToSelector:@selector(modelContainerPropertyGenericClass)]) {
genericMapper = [(id)cls modelContainerPropertyGenericClass];
if (genericMapper) {
NSMutableDictionary *tmp = [NSMutableDictionary new];
[genericMapper enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:^(id key, id obj, BOOL *stop) {
if (![key isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) return;
Class meta = object_getClass(obj);
if (!meta) return;
if (class_isMetaClass(meta)) {
//是否是元类,是元类就添加到字典
tmp[key] = obj;
} else if ([obj isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) {
//是以字符串形式提供的
Class cls = NSClassFromString(obj);
if (cls) {
tmp[key] = cls;
}
}
}];
genericMapper = tmp;
}
}
// Create all property metas.
// 创建所有属性的元数据字典
NSMutableDictionary *allPropertyMetas = [NSMutableDictionary new];
YYClassInfo *curClassInfo = classInfo;
while (curClassInfo && curClassInfo.superCls != nil) {
// recursive parse super class, but ignore root class (NSObject/NSProxy)
// 递归解析父类,但是忽略了根类
for (YYClassPropertyInfo *propertyInfo in curClassInfo.propertyInfos.allValues) {
if (!propertyInfo.name) continue;
if (blacklist && [blacklist containsObject:propertyInfo.name]) continue; //黑名单包括该属性,继续下一个循环
if (whitelist && ![whitelist containsObject:propertyInfo.name]) continue; //白名单不包括该属性,继续下一个循环
_YYModelPropertyMeta *meta = [_YYModelPropertyMeta metaWithClassInfo:classInfo
propertyInfo:propertyInfo
generic:genericMapper[propertyInfo.name]];
if (!meta || !meta->_name) continue;
if (!meta->_getter || !meta->_setter) continue;
if (allPropertyMetas[meta->_name]) continue;
allPropertyMetas[meta->_name] = meta;
}
curClassInfo = curClassInfo.superClassInfo;
}
// 所有用户默认未进行 属性<->自定义 映射的数组都在这里面,此时先将所有的属性放在这,下面一步mapper中会将用户自定义对应的属性移除出去
if (allPropertyMetas.count) _allPropertyMetas = allPropertyMetas.allValues.copy;
// create mapper
// 创建json 与 model 属性的隐射关系
//只存储通过modelCustomPropertyMapper方法实现的[key:_YYModelPropertyMeta]键值对
NSMutableDictionary *mapper = [NSMutableDictionary new];
//该model中有key path 对应的属性对象_YYModelPropertyMeta数组中
NSMutableArray *keyPathPropertyMetas = [NSMutableArray new];
//一个属性对应多个key的_YYModelPropertyMeta数组,即modelCustomPropertyMapper中有key对应一个数组时
NSMutableArray *multiKeysPropertyMetas = [NSMutableArray new];
if ([cls respondsToSelector:@selector(modelCustomPropertyMapper)]) {
// 用户自定义mapper
NSDictionary *customMapper = [(id )cls modelCustomPropertyMapper];
[customMapper enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSString *propertyName, NSString *mappedToKey, BOOL *stop) {
//propertyName,model属性的名字
//从上面获取到所有属性对应的model字典里,取出propertyName对应的_YYModelPropertyMeta。
_YYModelPropertyMeta *propertyMeta = allPropertyMetas[propertyName];
if (!propertyMeta) return;
//mappedToKey:可能是自定义的值,如:name<->@"n",name<->user.name,或者数组:id<->[@"id",@"ID",@"user_id"]
//移除该propertyName的键值对,因为后面会建立[mappedToKey:propertyMeta]的键值对
[allPropertyMetas removeObjectForKey:propertyName];
if ([mappedToKey isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) {
//key 如果是 String,这个String有两种情况
//1. key
//2. key path
if (mappedToKey.length == 0) return;
propertyMeta->_mappedToKey = mappedToKey; //该propertyMeta对应的key
NSArray *keyPath = [mappedToKey componentsSeparatedByString:@"."];
for (NSString *onePath in keyPath) {
if (onePath.length == 0) {
NSMutableArray *tmp = keyPath.mutableCopy;
[tmp removeObject:@""];
keyPath = tmp;
break;
}
}
if (keyPath.count > 1) {
propertyMeta->_mappedToKeyPath = keyPath; //该propertyMeta对应的key path
[keyPathPropertyMetas addObject:propertyMeta]; //将propertyMeta添加到数组
}
propertyMeta->_next = mapper[mappedToKey] ?: nil; //如果有多个key对应同一个属性的话,那么next指向下一个meta property对象,否则为nil
mapper[mappedToKey] = propertyMeta; //将该propertyMeta添加到mapper
} else if ([mappedToKey isKindOfClass:[NSArray class]]) {
/*
+ (NSDictionary *)modelCustomPropertyMapper {
return @{
@"name" : @"n",
@"page" : @"p",
@"desc" : @"ext.desc",
@"bookID": @[@"id", @"ID", @"book_id"]};
}
*/
//如果key是个数组
NSMutableArray *mappedToKeyArray = [NSMutableArray new];
for (NSString *oneKey in ((NSArray *)mappedToKey)) {
if (![oneKey isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) continue;
if (oneKey.length == 0) continue;
NSArray *keyPath = [oneKey componentsSeparatedByString:@"."];
//如果key path大于1,就是***.***,那么就讲整个添加到mappedToKeyArray
//否则,即添加key就行
if (keyPath.count > 1) {
[mappedToKeyArray addObject:keyPath];
} else {
[mappedToKeyArray addObject:oneKey];
}
if (!propertyMeta->_mappedToKey) {
//最后,将最后一个key座位propertyMeta的_mappedToKey
propertyMeta->_mappedToKey = oneKey;
propertyMeta->_mappedToKeyPath = keyPath.count > 1 ? keyPath : nil;
}
}
if (!propertyMeta->_mappedToKey) return;
//
propertyMeta->_mappedToKeyArray = mappedToKeyArray;
[multiKeysPropertyMetas addObject:propertyMeta];
propertyMeta->_next = mapper[mappedToKey] ?: nil;
mapper[mappedToKey] = propertyMeta;
}
}];
}
//上一步操作后,allPropertyMetas 不是用户自定义,根据model属性默认的,即name=property name的所有属性
[allPropertyMetas enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSString *name, _YYModelPropertyMeta *propertyMeta, BOOL *stop) {
//遍历allPropertyMetas,重新将其中的propertyMeta的_mappedToKey和_next
propertyMeta->_mappedToKey = name;
propertyMeta->_next = mapper[name] ?: nil;
//mapper经过此步骤之后,mapper包含了所有的映射关系
mapper[name] = propertyMeta;
}];
if (mapper.count) _mapper = mapper;
//以下两者处理都在上面自定义mapper中
if (keyPathPropertyMetas) _keyPathPropertyMetas = keyPathPropertyMetas;
if (multiKeysPropertyMetas) _multiKeysPropertyMetas = multiKeysPropertyMetas;
_classInfo = classInfo;
_keyMappedCount = _allPropertyMetas.count; //经过黑白名单筛选之后的属性数目
_nsType = YYClassGetNSType(cls); //获取Foundation type
//对应四个自定义方法
_hasCustomWillTransformFromDictionary = ([cls instancesRespondToSelector:@selector(modelCustomWillTransformFromDictionary:)]);
_hasCustomTransformFromDictionary = ([cls instancesRespondToSelector:@selector(modelCustomTransformFromDictionary:)]);
_hasCustomTransformToDictionary = ([cls instancesRespondToSelector:@selector(modelCustomTransformToDictionary:)]);
_hasCustomClassFromDictionary = ([cls respondsToSelector:@selector(modelCustomClassForDictionary:)]);
return self;
}
代码中作了详尽的注释,简而言之,得出如下等式:
类本身信息 + 用户自定义部分 = _YYModelMeta
其中,_YYModelMeta是后面model赋值的主要数据源。
Method信息
YYClassMethodInfo类的声明:
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Method method; ///< method
// method_name:方法名
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; ///< method name
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) SEL sel; ///< method's selector
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) IMP imp; ///< method's implementation
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *typeEncoding; ///< method's parameter and return types
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *returnTypeEncoding; ///< return value's type
@property (nullable, nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSArray *argumentTypeEncodings; ///< array of arguments' type
简单做一下说明:
-
Method类型
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
在objc-runtime-old.h文件中声明如下:
struct old_method {
SEL method_name; //方法SEL
char *method_types; //方法参数的类型
IMP method_imp; //该方法的具体实现的函数指针
};
那么我们就可以理解name,SEL,IMP属性了。
其中,对于SEL和IMP这两个概念,需要区别:
-
SEL
/// An opaque type that represents a method selector. typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
Objective-C是动态语言,动态体现在可以在运行的时候修改所执行的方法,可以把一个对象的所有方法看成一张表,SEL就可以看成表中每一条的索引,根据方法名来生成对应的SEL,所以OC中不同的方法名就对应不同的方法
SEL1 | SEL2 | SEL3 ...
IMP1 | IMP2 | IMP3 ...
-
IMP
A pointer to the function of a method implementation. typedef id (*IMP)(id, SEL, ...);
IMP是真正的函数指针,指向函数的实现
这里,我们用YYBook来说明其中的Method信息,如下为其声明文件:
@interface YYBook : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, assign) uint64_t pages;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSDate *publishDate;
@end
但是,我们并没有发现有任何方法声明,但是,我们需要注意的是在Objective-C 2.0中,属性会自动为我们生成属性对应成员变量的setter与getter方法,这些方法并不需要手动书写,但是却在编译时在类信息中。
我们选择属性的pages来一窥Method的信息:
首先,pages的getter/setter方法,其声明应该是:
- (int)pages; //1
- (void)setPages:(int)pages; //2
针对方法1,没有参数,有返回值,且返回值为int类型。方法2呢,没有返回值,但是包含一个int类型的参数。
下面,我们看YYClassMethodInfo的初始化方法:
- (instancetype)initWithMethod:(Method)method {
if (!method) return nil;
self = [super init];
_method = method;
_sel = method_getName(method); //Returns the name of a method
_imp = method_getImplementation(method); //Returns the implementation of a method.
const char *name = sel_getName(_sel); //Returns the name of the method specified by a given selector
if (name) {
_name = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:name];
}
//描述参数类型与返回类型的type encoding
const char *typeEncoding = method_getTypeEncoding(method); //Returns a string describing a method's parameter and return types
if (typeEncoding) {
_typeEncoding = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:typeEncoding];
}
//返回类型
char *returnType = method_copyReturnType(method); //Returns a string describing a method's return type
if (returnType) {
_returnTypeEncoding = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:returnType];
free(returnType);
}
unsigned int argumentCount = method_getNumberOfArguments(method); //参数的个数
if (argumentCount > 0) {
NSMutableArray *argumentTypes = [NSMutableArray new];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < argumentCount; i++) {
char *argumentType = method_copyArgumentType(method, i); //返回某一个参数对应的类型
NSString *type = argumentType ? [NSString stringWithUTF8String:argumentType] : nil;
[argumentTypes addObject:type ? type : @""];
if (argumentType) free(argumentType);
}
_argumentTypeEncodings = argumentTypes; //方法中所有参数的类型在该数组中
}
return self;
}
关注几个runtime的方法:
* OBJC_EXPORT SEL method_getName(Method m) //获取方法名
* OBJC_EXPORT IMP method_getImplementation(Method m) //获取方法实现首地址
* OBJC_EXPORT const char *sel_getName(SEL sel) //获取SEL名
* OBJC_EXPORT const char *method_getTypeEncoding(Method m) //获取返回参数的type encoding
* OBJC_EXPORT unsigned int method_getNumberOfArguments(Method m) //获取参数个数
* OBJC_EXPORT char *method_copyArgumentType(Method m, unsigned int index) //获取参数的type encoding
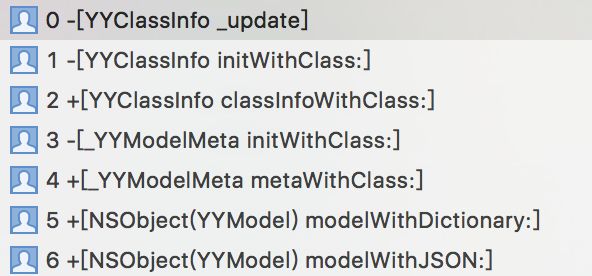
根据这些方法,我们能获取Method的大部分重要信息。对pages的getter方法:
图一
其中,需要关注的是:
unsigned int argumentCount = method_getNumberOfArguments(method); //参数的个数
if (argumentCount > 0) {
NSMutableArray *argumentTypes = [NSMutableArray new];
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < argumentCount; i++) {
char *argumentType = method_copyArgumentType(method, i); //返回某一个参数对应的类型
NSString *type = argumentType ? [NSString stringWithUTF8String:argumentType] : nil;
[argumentTypes addObject:type ? type : @""];
if (argumentType) free(argumentType);
}
_argumentTypeEncodings = argumentTypes; //方法中所有参数的类型在该数组中
}
这个代码,是处理方法参数类型的,在debug模式下,我们获取到的argumentCount=2,可是根据方法声明,
- (int)pages;并没有参数!
这就要从Objective-C中方法调用说起,在OC中,方法调用,也叫给对象发送消息,发送消息最后都会调用下面这个函数:
id objc_msgSend(id self, SEL op, ...)
可以看出来,除了真正的参数之外,还有两个参数是默认的,一个是对象本身self,另外一个是方法的SEL。所以刚才获取到的参数为2,是正确的。而在- (int)pages;中,参数的类型为:
[@"@",@":"]
前面@"@"指代该参数为self,即对象为id类型,@":",指代类型是SEL类型。关于type encoding,参考构建iOS-Model层(二)类型解析。
下面,看一下- (void)setPages:(int)pages;方法对应的初始化过程。
图二
这里有一点可以继续深挖的是,我们在YYBook中声明了三个属性,但是获取其方法却有七个,即:
Method *methods = class_copyMethodList(cls, &methodCount);
其中,methodCount为7,按道理应该是6。调试发现,还有一个方法如下:
图三
看方法名,是销毁方法。
Property信息
有了前面关于Method的铺垫,Property其实也是一致的。所以,下面是流水记录:
@interface YYClassPropertyInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) objc_property_t property; ///< property
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; ///< property's name
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) YYEncodingType type; ///< property's type
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *typeEncoding; ///< property's encoding value
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *ivarName; ///< property's ivar name
@property (nullable, nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class cls; ///< may be nil
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) SEL getter; ///< getter (nonnull)
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) SEL setter; ///< setter (nonnull)
@end
这部分,更多可以参考:
构建iOS Model层系列文章
Ivar信息
@interface YYClassIvarInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Ivar ivar; ///< ivar
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; ///< Ivar's name
//成员变量在类内存中是以一定的偏移量存放的
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) ptrdiff_t offset; ///< Ivar's offset
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *typeEncoding; ///< Ivar's type encoding
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) YYEncodingType type; ///< Ivar's type
在初始化过程中,依次:
- _name成员变量:
- _pages成员变量:
- _publishDate成员变量:
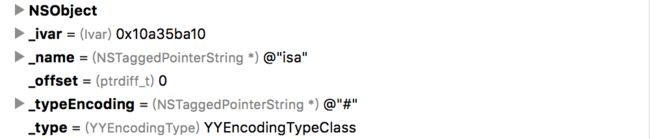
这里,又有一个可以深究的点,看下图:
发现,没有,这里还有一个特俗的成员变量isa。至于这个为何物,自己去寻吧。
给模型赋值
经过上面这些步骤之后拿到的类的所有信息,需要将这些信息用于字典转模型的过程中。
回到字典转模型NSObject+YYModel分类中调用的的方法- (BOOL)modelSetWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dic,这里,仍然会将部分细节省略,只关注主要节点流程:
- (BOOL)modelSetWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dic {
if (!dic || dic == (id)kCFNull) return NO;
if (![dic isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) return NO;
_YYModelMeta *modelMeta = [_YYModelMeta metaWithClass:object_getClass(self)]; //此时获取在内存中获取,几乎立即返回
if (modelMeta->_keyMappedCount == 0) return NO;
if (modelMeta->_hasCustomWillTransformFromDictionary) {
dic = [((id)self) modelCustomWillTransformFromDictionary:dic];
if (![dic isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) return NO;
}
ModelSetContext context = {0};
context.modelMeta = (__bridge void *)(modelMeta);
context.model = (__bridge void *)(self);
context.dictionary = (__bridge void *)(dic);
/*
+ (NSDictionary *)modelCustomPropertyMapper {
return @{@"messageId":@[@"id", @"ID", @"mes_id"],
@"time":@"t",
@"name":@"user.name"
};
}
*/
if (modelMeta->_keyMappedCount >= CFDictionaryGetCount((CFDictionaryRef)dic)) {
//下面函数无法设置key path的函数,因为model中属性是name,但mapper中的key则是user.name。然后dic中如果key则是user。所以无法设置key path
//同样,也无法设置multi keys,因为model中属性是id,但mapper中key则是@[@"id", @"ID", @"mes_id"],所以也无法设置
CFDictionaryApplyFunction((CFDictionaryRef)dic, ModelSetWithDictionaryFunction, &context);
//针对model中有key path的属性
if (modelMeta->_keyPathPropertyMetas) {
CFArrayApplyFunction((CFArrayRef)modelMeta->_keyPathPropertyMetas,
CFRangeMake(0, CFArrayGetCount((CFArrayRef)modelMeta->_keyPathPropertyMetas)),
ModelSetWithPropertyMetaArrayFunction,
&context);
}
//针对model中有multi keys的属性
if (modelMeta->_multiKeysPropertyMetas) {
CFArrayApplyFunction((CFArrayRef)modelMeta->_multiKeysPropertyMetas,
CFRangeMake(0, CFArrayGetCount((CFArrayRef)modelMeta->_multiKeysPropertyMetas)),
ModelSetWithPropertyMetaArrayFunction,
&context);
}
} else {
CFArrayApplyFunction((CFArrayRef)modelMeta->_allPropertyMetas,
CFRangeMake(0, modelMeta->_keyMappedCount),
ModelSetWithPropertyMetaArrayFunction,
&context);
}
if (modelMeta->_hasCustomTransformFromDictionary) {
return [((id)self) modelCustomTransformFromDictionary:dic];
}
return YES;
}
在这个方法里,调用的一个方法是:
//第一个参数是:对应的字典
//第二个参数是:该字典要执行的方法
//方法中携带的参数
CFDictionaryApplyFunction((CFDictionaryRef)dic, ModelSetWithDictionaryFunction, &context);
CFDictionaryApplyFunction方法会对字典每个元素执行一个自定义的方法。在这里,这个方法就是:
static void ModelSetWithDictionaryFunction(const void *_key, const void *_value, void *_context) {
ModelSetContext *context = _context;
__unsafe_unretained _YYModelMeta *meta = (__bridge _YYModelMeta *)(context->modelMeta);
__unsafe_unretained _YYModelPropertyMeta *propertyMeta = [meta->_mapper objectForKey:(__bridge id)(_key)];
__unsafe_unretained id model = (__bridge id)(context->model);
while (propertyMeta) {
if (propertyMeta->_setter) {
ModelSetValueForProperty(model, (__bridge __unsafe_unretained id)_value, propertyMeta);
}
propertyMeta = propertyMeta->_next;
};
}
以上就是给模型属性赋值的核心!
可以看到,所有的类的信息,都封装在结构体ModelSetContext中:
typedef struct {
void *modelMeta; ///< _YYModelMeta
void *model; ///< id (self)
void *dictionary; ///< NSDictionary (json)
} ModelSetContext;
剩下的,我们到了最后一步,方法ModelSetValueForProperty(model, (__bridge __unsafe_unretained id)_value, propertyMeta);这个方法里做的唯一工作,就是从字典取出值赋给Model。而且,直接使用了objc_msgSend方法来进行赋值。
下面是针对属性为NSDate类型的赋值:
case YYEncodingTypeNSDate: {
if ([value isKindOfClass:[NSDate class]]) {
((void (*)(id, SEL, id))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, value);
} else if ([value isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) {
((void (*)(id, SEL, id))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, YYNSDateFromString(value));
}
} break;
可以看到,
objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, value)中,model,即一步一步传导下来的即将要赋值的model对象,meta->_setter则是通过YYModel一步一步解析出来的setter方法,value则是通过JSON转为字典后对应该属性中的value。
如此,我们就完成了属性的赋值。
也许,你还有疑问:CFArrayApplyFunction这个函数调用在if分支中的作用,在这里简单作一下说明:
假如用户自定义mapper如下:
@interface YYMessage : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign) uint64_t messageId;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *content;
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSDate *time;
@property (nonatomic ,copy) NSString *name;
@end
//自定义mapper
+ (NSDictionary *)modelCustomPropertyMapper {
return @{@"messageId":@[@"id", @"ID", @"mes_id"],
@"time":@"t",
@"name":@"user.name"
};
}
这里,出现了以下两种情况:
- 属性对应了多个key,比如属性messageId,可以解析“id”,“ID”,“mes_id”三种key,即服务器返回的JSON中假如有这三种key之一,都支持解析。
- 属性是key path,如user.name。
关于这部分的信息,其实都在类信息的初始化-class info包装成_YYModelMeta对象中处理完成。
在自定义mapper下,我们YYMessage的类信息如下:
-
YYMessage类信息的_YYModelMeta
-
YYMessage class info
- YYMessage 自定义mapper中的key path。
- YYMessage 自定义mapper中的key path。
至此,我们完结了,这一篇摘要。
然而,YYModel还有许多特性,值得我们去摸索。
系列
- YYModel阅读摘要(一)基础
- YYModel阅读摘要(二)特性
- YYModel阅读摘要(三)参考