下面是对于request config的官方说明,更多信息请移步axios官网
{
// `url` is the server URL that will be used for the request
url: '/user',
// `method` is the request method to be used when making the request
method: 'get', // default
// `baseURL` will be prepended to `url` unless `url` is absolute.
// It can be convenient to set `baseURL` for an instance of axios to pass relative URLs
// to methods of that instance.
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
// `transformRequest` allows changes to the request data before it is sent to the server
// This is only applicable for request methods 'PUT', 'POST', and 'PATCH'
// The last function in the array must return a string or an instance of Buffer, ArrayBuffer,
// FormData or Stream
// You may modify the headers object.
transformRequest: [function (data, headers) {
// Do whatever you want to transform the data
return data;
}],
// `transformResponse` allows changes to the response data to be made before
// it is passed to then/catch
transformResponse: [function (data) {
// Do whatever you want to transform the data
return data;
}],
// `headers` are custom headers to be sent
headers: {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'},
// `params` are the URL parameters to be sent with the request
// Must be a plain object or a URLSearchParams object
params: {
ID: 12345
},
// `paramsSerializer` is an optional function in charge of serializing `params`
// (e.g. https://www.npmjs.com/package/qs, http://api.jquery.com/jquery.param/)
paramsSerializer: function(params) {
return Qs.stringify(params, {arrayFormat: 'brackets'})
},
// `data` is the data to be sent as the request body
// Only applicable for request methods 'PUT', 'POST', and 'PATCH'
// When no `transformRequest` is set, must be of one of the following types:
// - string, plain object, ArrayBuffer, ArrayBufferView, URLSearchParams
// - Browser only: FormData, File, Blob
// - Node only: Stream, Buffer
data: {
firstName: 'Fred'
},
// `timeout` specifies the number of milliseconds before the request times out.
// If the request takes longer than `timeout`, the request will be aborted.
timeout: 1000,
// `withCredentials` indicates whether or not cross-site Access-Control requests
// should be made using credentials
withCredentials: false, // default
// `adapter` allows custom handling of requests which makes testing easier.
// Return a promise and supply a valid response (see lib/adapters/README.md).
adapter: function (config) {
/* ... */
},
// `auth` indicates that HTTP Basic auth should be used, and supplies credentials.
// This will set an `Authorization` header, overwriting any existing
// `Authorization` custom headers you have set using `headers`.
auth: {
username: 'janedoe',
password: 's00pers3cret'
},
// `responseType` indicates the type of data that the server will respond with
// options are 'arraybuffer', 'blob', 'document', 'json', 'text', 'stream'
responseType: 'json', // default
// `xsrfCookieName` is the name of the cookie to use as a value for xsrf token
xsrfCookieName: 'XSRF-TOKEN', // default
// `xsrfHeaderName` is the name of the http header that carries the xsrf token value
xsrfHeaderName: 'X-XSRF-TOKEN', // default
// `onUploadProgress` allows handling of progress events for uploads
onUploadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// Do whatever you want with the native progress event
},
// `onDownloadProgress` allows handling of progress events for downloads
onDownloadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// Do whatever you want with the native progress event
},
// `maxContentLength` defines the max size of the http response content allowed
maxContentLength: 2000,
// `validateStatus` defines whether to resolve or reject the promise for a given
// HTTP response status code. If `validateStatus` returns `true` (or is set to `null`
// or `undefined`), the promise will be resolved; otherwise, the promise will be
// rejected.
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status >= 200 && status < 300; // default
},
// `maxRedirects` defines the maximum number of redirects to follow in node.js.
// If set to 0, no redirects will be followed.
maxRedirects: 5, // default
// `socketPath` defines a UNIX Socket to be used in node.js.
// e.g. '/var/run/docker.sock' to send requests to the docker daemon.
// Only either `socketPath` or `proxy` can be specified.
// If both are specified, `socketPath` is used.
socketPath: null, // default
// `httpAgent` and `httpsAgent` define a custom agent to be used when performing http
// and https requests, respectively, in node.js. This allows options to be added like
// `keepAlive` that are not enabled by default.
httpAgent: new http.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
httpsAgent: new https.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
// 'proxy' defines the hostname and port of the proxy server
// Use `false` to disable proxies, ignoring environment variables.
// `auth` indicates that HTTP Basic auth should be used to connect to the proxy, and
// supplies credentials.
// This will set an `Proxy-Authorization` header, overwriting any existing
// `Proxy-Authorization` custom headers you have set using `headers`.
proxy: {
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 9000,
auth: {
username: 'mikeymike',
password: 'rapunz3l'
}
},
// `cancelToken` specifies a cancel token that can be used to cancel the request
// (see Cancellation section below for details)
cancelToken: new CancelToken(function (cancel) {
})
}特别注意:
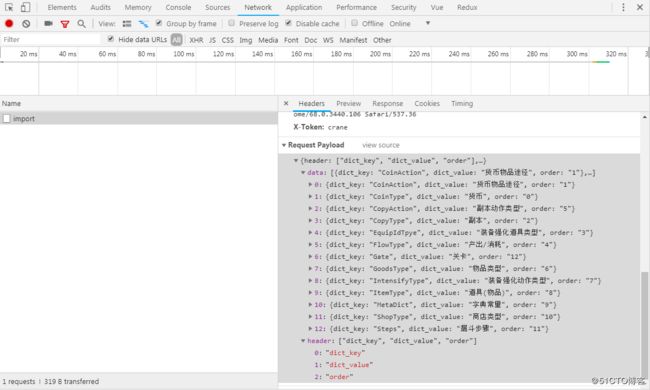
1.在使用axios时,有一个params作为传递参数,一个是data,这两个参数是有区别的。
params:是一定会拼接在url上的参数,不管你是不是post方式
data: 是对post方式,放在body里的数据
如下图:2.在使用post方式请求api时,关于后台接口无法获取axios传递的参数问题:
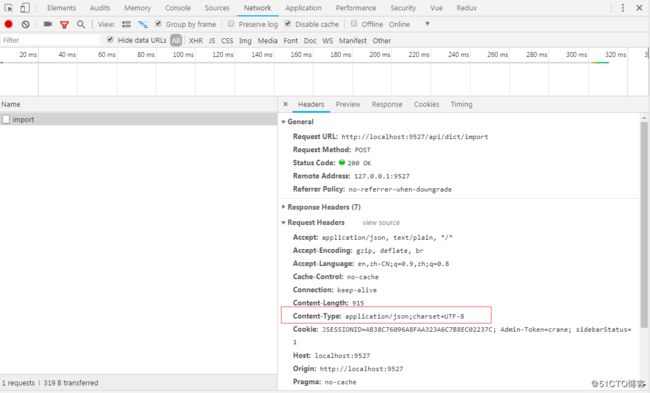
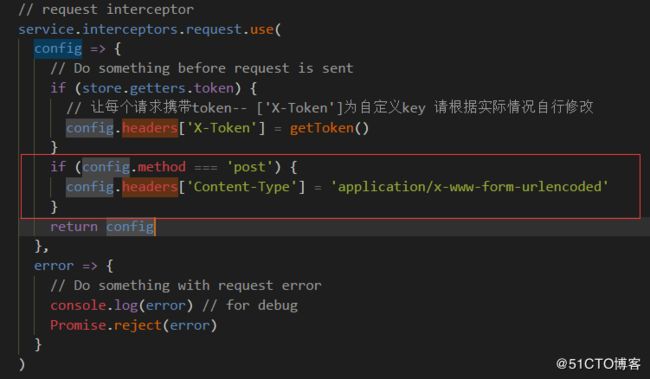
这是因为axios的默认请求头中Content-Type是text/plain,application/json格式,可查看:我们需要通过设置Content-Type就可以解决这个问题:
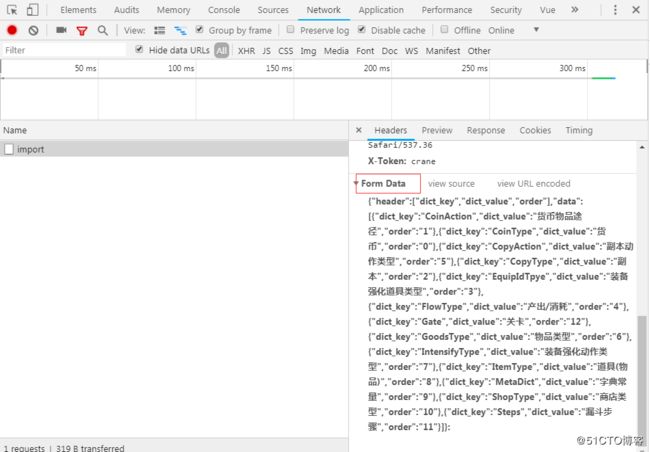
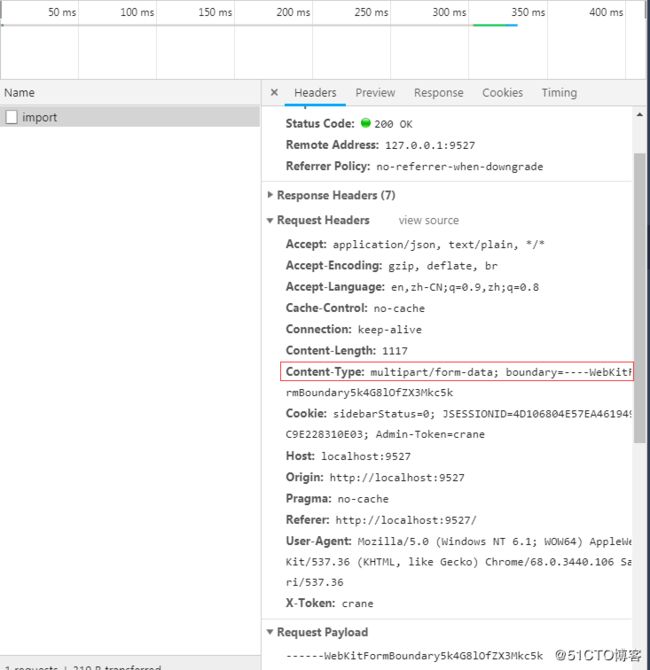
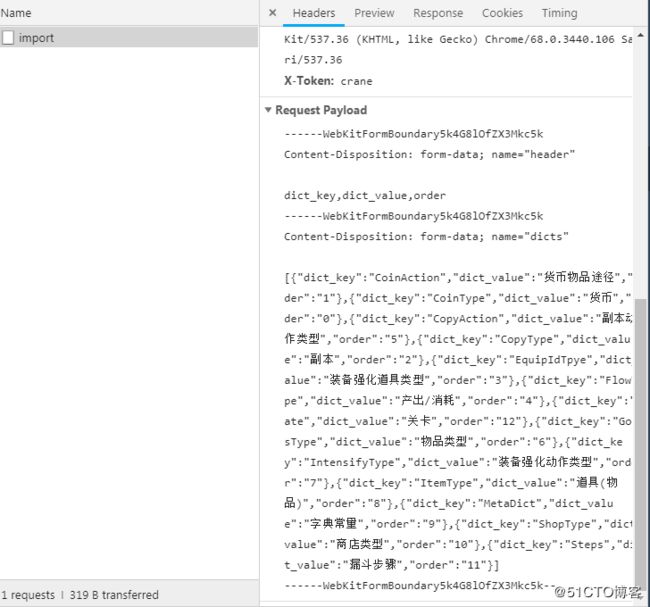
axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded';这个第三个图片就可以看到,原来在没有设置content-type时,Request payload,这是一个流,而设置完以后,这个数据就变为了Form Data,更多详细说明请看官方文档。
其实在formData是错误的解释,这里他依然采用的是key-value的形式给后台传值,因为我在传递data时:直接就是如下:
const data = {
header: ['dict_key','dict_value','order'],
data: [
{
'dict_key': '字典key',
'dict_value: 'dictkey',
'order': 12
},
........
]
}
// 这种方式传递到axios中的data时,他依然会以key-value给后台传值,实际上你在后台可以通过getParameterMap()获取到data的字符串key,但你没法通过getParameter("header"),浏览器返回的那个结果就能看出来,已经把data转为字符串,作为formdata的一个key,而对应的值就是一个“”。上面的方式可以通过getParamterMap()去遍历获取到key,但没法使用Spring Boot的那些映射方法,所以上面额方法不够好,也不算是formdata数据,那么如何做呢?如下:
// 构造formData数据,关键在这里
const data = new FormData()
data.append('header', this.tableHeader)
data.append('dicts', JSON.stringify(this.tableData))
// 调用导入接口,传入对象,表头和表数据
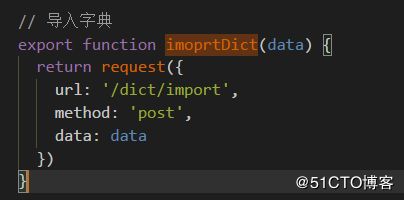
imoprtDict(data).then(response => {
if (response.data.success) {
this.$message({
message: '批量导入成功!',
type: 'success'
})
} else {
this.$message.error('批量导入失败!')
}
// api
export function imoprtDict(data) {
return request({
url: '/dict/import',
method: 'post',
data
})
}
总结:
1.params参数一定会在url后面显示拼接
2.data参数说明:
// `data` is the data to be sent as the request body
// Only applicable for request methods 'PUT', 'POST', and 'PATCH'
// When no `transformRequest` is set, must be of one of the following types:
// - string, plain object, ArrayBuffer, ArrayBufferView, URLSearchParams
// - Browser only: FormData, File, Blob
// - Node only: Stream, Buffer
3.通常我们不要自作聪明去设置headers
4.如果data是一个formData对象,那么Content-Type自动就是multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFo