消费者的使用
按照前面分析生产者的流程,首先看看消费者怎么使用吧
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, MQClientException {
// 使用consumer group初始化DefaultMQPushConsumer
DefaultMQPushConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPushConsumer("please_rename_unique_group_name");
// 指定namesrv
consumer.setNamesrvAddr("localhost:9876");
// 订阅topic
consumer.subscribe("TopicTest", "*");
// 注册消费消息的回调
consumer.registerMessageListener(new MessageListenerConcurrently() {
@Override
public ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus consumeMessage(List msgs,
ConsumeConcurrentlyContext context) {
System.out.printf("%s Receive New Messages: %s %n", Thread.currentThread().getName(), msgs);
return ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus.CONSUME_SUCCESS;
}
});
// 启动consumer
consumer.start();
System.out.printf("Consumer Started.%n");
}
}
很简单,初始化DefaultMQPushConsumer,订阅topic,注册消息消费Listener就完成了
这里初始化的是DefaultMQPushConsumer,那么自然我们会想到会有DefaultMQPullConsumer
DefaultMQPushConsumer启动流程
我们首先拿DefaultMQPushConsumer开刀吧
public class DefaultMQPushConsumer extends ClientConfig implements MQPushConsumer {
}
public interface MQPushConsumer extends MQConsumer {
void start() throws MQClientException;
void shutdown();
@Deprecated
void registerMessageListener(MessageListener messageListener);
void registerMessageListener(final MessageListenerConcurrently messageListener);
void registerMessageListener(final MessageListenerOrderly messageListener);
void subscribe(final String topic, final String subExpression) throws MQClientException;
@Deprecated
void subscribe(final String topic, final String fullClassName,
final String filterClassSource) throws MQClientException;
void subscribe(final String topic, final MessageSelector selector) throws MQClientException;
void unsubscribe(final String topic);
void updateCorePoolSize(int corePoolSize);
void suspend();
void resume();
}
public interface MQConsumer extends MQAdmin {
@Deprecated
void sendMessageBack(final MessageExt msg, final int delayLevel) throws RemotingException,
MQBrokerException, InterruptedException, MQClientException;
void sendMessageBack(final MessageExt msg, final int delayLevel, final String brokerName)
throws RemotingException, MQBrokerException, InterruptedException, MQClientException;
Set fetchSubscribeMessageQueues(final String topic) throws MQClientException;
}
DefaultMQPushConsumer继承ClientConfig,并实现了MQPushConsumer接口,MQPushConsumer接口又继承MQConsumer和MQAdmin
这里的ClientConfig和MQAdmin在分析生产者的时候都出现过了,并且MQAdmin中定义的方法同Producer的实现一样,都被官方标记为过时的方法了,Consumer的实现里面也被标识为过了,MQPullConsumer中主要是定义了一些pull方法
了解了接口定义了那些功能的方法后,我们就来看DefaultMQPushConsumer的构造函数
public DefaultMQPushConsumer(final String namespace, final String consumerGroup, RPCHook rpcHook,
AllocateMessageQueueStrategy allocateMessageQueueStrategy, boolean enableMsgTrace, final String customizedTraceTopic) {
this.consumerGroup = consumerGroup;
this.namespace = namespace;
this.allocateMessageQueueStrategy = allocateMessageQueueStrategy;
defaultMQPushConsumerImpl = new DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl(this, rpcHook);
if (enableMsgTrace) {
try {
AsyncTraceDispatcher dispatcher = new AsyncTraceDispatcher(customizedTraceTopic, rpcHook);
dispatcher.setHostConsumer(this.getDefaultMQPushConsumerImpl());
traceDispatcher = dispatcher;
this.getDefaultMQPushConsumerImpl().registerConsumeMessageHook(
new ConsumeMessageTraceHookImpl(traceDispatcher));
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("system mqtrace hook init failed ,maybe can't send msg trace data");
}
}
}
和Producer相似,还是交给了DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl去干活
public DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl(DefaultMQPushConsumer defaultMQPushConsumer, RPCHook rpcHook) {
this.defaultMQPushConsumer = defaultMQPushConsumer;
this.rpcHook = rpcHook;
}
相对于DefaultMQProducerImpl的构造函数就比较简单干净了,只是简单地赋值,连初始化都没有,接下来就是subscribe()方法
public void subscribe(String topic, String subExpression) throws MQClientException {
this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.subscribe(withNamespace(topic), subExpression);
}
还是直接丢给DefaultMQProducerImpl
public void subscribe(String topic, String subExpression) throws MQClientException {
try {
// 解析subExpression
SubscriptionData subscriptionData = FilterAPI.buildSubscriptionData(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(),
topic, subExpression);
// 解析出来的数据丢给RebalanceImpl的subscriptionInner这个Map保存
this.rebalanceImpl.getSubscriptionInner().put(topic, subscriptionData);
if (this.mQClientFactory != null) { // 没有调用start()方法,mQClientFactory == null
this.mQClientFactory.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new MQClientException("subscription exception", e);
}
}
可以发现subscribe()方法也没有做啥事,只是解析一些subExpression,将解析得到的SubscriptionData保存到RebalanceImpl中
public void registerMessageListener(MessageListenerOrderly messageListener) {
this.messageListener = messageListener;
this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.registerMessageListener(messageListener);
}
public void registerMessageListener(MessageListener messageListener) {
this.messageListenerInner = messageListener;
}
registerMessageListener也很简单,也是赋值
最后start()方法,也是调用DefaultMQProducerImpl#start()方法
public void start() throws MQClientException {
setConsumerGroup(NamespaceUtil.wrapNamespace(this.getNamespace(), this.consumerGroup));
this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.start();
if (null != traceDispatcher) {
try {
traceDispatcher.start(this.getNamesrvAddr(), this.getAccessChannel());
} catch (MQClientException e) {
log.warn("trace dispatcher start failed ", e);
}
}
}
public synchronized void start() throws MQClientException {
switch (this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
log.info("the consumer [{}] start beginning. messageModel={}, isUnitMode={}", this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(),
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel(), this.defaultMQPushConsumer.isUnitMode());
this.serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED;
this.checkConfig();
this.copySubscription();
// 如果是集群模式,将InstanceName改成IP+PID
if (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel() == MessageModel.CLUSTERING) {
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.changeInstanceNameToPID();
}
// 创建MQClientInstance,和Producer一样的
this.mQClientFactory = MQClientManager.getInstance().getAndCreateMQClientInstance(this.defaultMQPushConsumer, this.rpcHook);
// RebalanceImpl设置,负载均衡相关实现
this.rebalanceImpl.setConsumerGroup(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
this.rebalanceImpl.setMessageModel(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel());
this.rebalanceImpl.setAllocateMessageQueueStrategy(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getAllocateMessageQueueStrategy());
this.rebalanceImpl.setmQClientFactory(this.mQClientFactory);
// 初始化PullAPIWrapper,消息拉取API封装类
this.pullAPIWrapper = new PullAPIWrapper(
mQClientFactory,
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(), isUnitMode());
// 注册过滤器
this.pullAPIWrapper.registerFilterMessageHook(filterMessageHookList);
// 设置offsetStore,消费进度存储,如果是集群模式,使用远程存储 RemoteBrokerOffsetStore,如果是广播模式,则使用本地存储LocalFileOffsetStore
if (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getOffsetStore() != null) {
this.offsetStore = this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getOffsetStore();
} else {
switch (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel()) {
case BROADCASTING:
this.offsetStore = new LocalFileOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
case CLUSTERING:
this.offsetStore = new RemoteBrokerOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
default:
break;
}
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.setOffsetStore(this.offsetStore);
}
// 加载消息消费进度
this.offsetStore.load();
// 是否保证顺序消费,初始化不同的ConsumeMessageService
if (this.getMessageListenerInner() instanceof MessageListenerOrderly) {
this.consumeOrderly = true;
this.consumeMessageService =
new ConsumeMessageOrderlyService(this, (MessageListenerOrderly) this.getMessageListenerInner());
} else if (this.getMessageListenerInner() instanceof MessageListenerConcurrently) {
this.consumeOrderly = false;
this.consumeMessageService =
new ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService(this, (MessageListenerConcurrently) this.getMessageListenerInner());
}
// 启动ConsumeMessageService
this.consumeMessageService.start();
// MQClientInstance的逻辑和Producer的一样
boolean registerOK = mQClientFactory.registerConsumer(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(), this);
if (!registerOK) {
this.serviceState = ServiceState.CREATE_JUST;
this.consumeMessageService.shutdown();
throw new MQClientException("The consumer group[" + this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup()
+ "] has been created before, specify another name please." + FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.GROUP_NAME_DUPLICATE_URL),
null);
}
mQClientFactory.start();
log.info("the consumer [{}] start OK.", this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
break;
case RUNNING:
case START_FAILED:
case SHUTDOWN_ALREADY:
throw new MQClientException("The PushConsumer service state not OK, maybe started once, "
+ this.serviceState
+ FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.CLIENT_SERVICE_NOT_OK),
null);
default:
break;
}
// 更新Topic的路由信息
this.updateTopicSubscribeInfoWhenSubscriptionChanged();
// 检测broker状态。
this.mQClientFactory.checkClientInBroker();
// 发送心跳包
this.mQClientFactory.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
// 重新负载
this.mQClientFactory.rebalanceImmediately();
}
start()方法中有几个比较重要的组件RebalanceImpl,PullAPIWrapper和ConsumeMessageService
RebalanceImpl实现重平衡
先来看一下RebalanceImpl,看名字就知道它的功能(重平衡),那么问题来了重平衡是个啥?
在说重平衡之前,有需要插播一点知识点了
RocketMQ的消费模式
我们都知道,消费者会从消息队列拉消息,在分布式环境下,我们的消费者不止1个实例,可能会有很多个消费者在消费共一个消息队列,消费者消费消息也得分情况的,1条消息只能在其中1个消费者中消费还是所有消费者都消费呢?这个就是消息队列的消费模式
在RocketMQ中有Group的概念,一个Group代表的是逻辑相同的一组实例,最可以表达这个概念的是我们将一个项目部署多个实例,那么这个项目的集群就可以称之为一个Group。在RocketMQ中存在2中消费模式:广播消费和集群消费
public enum MessageModel {
/**
* 广播
*/
BROADCASTING("BROADCASTING"),
/**
* 集群
*/
CLUSTERING("CLUSTERING");
}
- 广播消费:Rocketmq会将消息发送给Group中的每一个消费者
- 集群消费:同一条消息,只能被Group中的任意一个消费者消费,这个概念很重要,这是与广播消费的最明显区别。
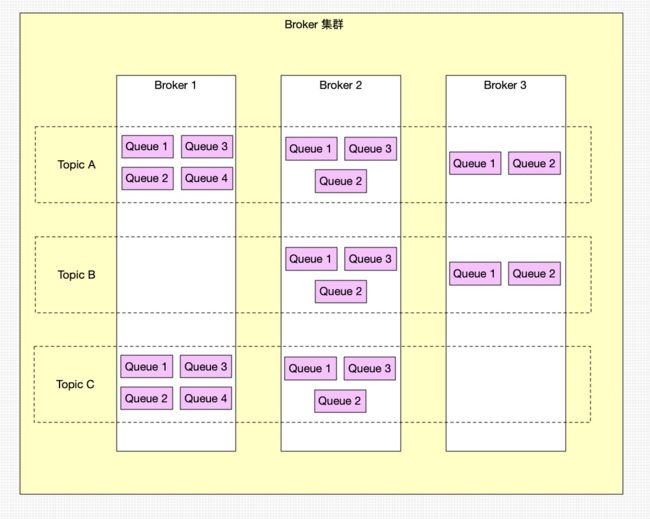
Broker中Topic的存储模型
我们都知道在RocketMQ中都是通过Topic来发送和消费消息的,但是Topic也仅仅是逻辑上的一个概念,而1个Topic下又包含了若干个逻辑队列,即消息队列,消息内容实际是存放在队列中的(保存的消息数据实际上不是真正的消息数据,而是指向commit log的消息索引),而队列又存储在Broker中的,下图展示了Topic的存储模型
插播知识结束了,再回来说什么是再平衡?首先我们来看看再平衡解决的是什么问题吧
大家可以想一下,消费者消费的事Topic中的各个Queue,那么可能会出现一些情况
- Broker 宕机了一台
- 消费者扩容了
- 其他情况
在广播消费的情况下,消费者扩容和Broker宕机不会有很大的影响,消费者扩容时,新的消费者会根据指定规则消费消息,不影响其他的消费者,broker宕机时,消费者从已经宕机的broker拉取消息会失败,所以消费者需要感知broker宕机。
在集群消费的情况下,消费者扩容和Broker宕机相对影响就比较大了,这2种情况都会导致消费者消费消息不平衡,所以就需要再平衡机制。不平衡怎么体现的呢?
当消费者扩容时,新的消费者该消费Topic的Queue呢?在新的消费者加入之前,所有的Queue都被别的消费者消费着呢?
当Broker宕机时,消费这台宕机Broker中的Queue的消费者会因为Broker宕机了导致消费的消息变少,压力变小,而生产者感知到这台Broker宕机,不再向这台Broker发送消息,导致消费发送给集群总其他的Broker,那么其他的消费者消费的消息就变多了
所以,在集群消费的情况下,因为一些原因导致Broker和消费者出现数量变化,出现了消费不均衡的情况
那么再平衡机制怎么解决这个问题呢?那我们就来看看RebalanceImpl是怎么做的吧
在看RebalanceImpl之前,我们还需要清除RebalanceImpl的触发机制,要不然你都不知道它在什么时候运行的
RebalanceImpl是DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl中的属性,并在
private final RebalanceImpl rebalanceImpl = new RebalancePushImpl(this);
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl中初始化了MQClientInstance对象,并在DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#start()方法中调用了MQClientInstance#start()方法,在MQClientInstance#start()方法中调用了RebalanceService#start()方法
public void start() throws MQClientException {
synchronized (this) {
switch (this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
...
this.rebalanceService.start();
...
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
break;
case RUNNING:
break;
case SHUTDOWN_ALREADY:
break;
case START_FAILED:
throw new MQClientException("The Factory object[" + this.getClientId() + "] has been created before, and failed.", null);
default:
break;
}
}
}
RebalanceService其实是一个线程的封装,那么看看这个线程执行的逻辑吧
@Override
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
this.waitForRunning(waitInterval);
this.mqClientFactory.doRebalance();
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
这个线程就是隔一段时间执行以下MQClientInstance#doRebalance()方法
看吧,又绕回到MQClientInstance了
public void doRebalance() {
for (Map.Entry entry : this.consumerTable.entrySet()) {
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
if (impl != null) {
try {
impl.doRebalance();
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("doRebalance exception", e);
}
}
}
}
MQClientInstance#doRebalance()方法中循环调用了consumerTable中MQConsumerInner#doRebalance()方法
consumerTable就是在DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#start()方法中通过MQClientInstance#registerConsumer() put值的
boolean registerOK = mQClientFactory.registerConsumer(this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup(), this);
所以consumerTable的key就是ConsumerGroup,Value就是DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl
public void doRebalance() {
if (!this.pause) {
this.rebalanceImpl.doRebalance(this.isConsumeOrderly());
}
}
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#doRebalance()方法最后才调用RebalanceImpl#doRebalance()方法
好了,饶了一大圈终于回到了最初的起点
public void doRebalance(final boolean isOrder) {
// getSubscriptionInner()返回的就是通过DefaultMQPushConsumer#subscribe()指定的Topic
Map subTable = this.getSubscriptionInner();
if (subTable != null) {
for (final Map.Entry entry : subTable.entrySet()) {
final String topic = entry.getKey();
try {
this.rebalanceByTopic(topic, isOrder);
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (!topic.startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) {
log.warn("rebalanceByTopic Exception", e);
}
}
}
}
// 再平衡后可能会导致当前消费者正在消费的Topic不再被当前消费者消费,需要移除
this.truncateMessageQueueNotMyTopic();
}
在RebalanceImpl#doRebalance()方法中,对每个订阅了的Topic调用RebalanceImpl#rebalanceByTopic()方法,最后会调用RebalanceImpl#truncateMessageQueueNotMyTopic()方法,移除不在当前消费者订阅Topic的Queue
private void rebalanceByTopic(final String topic, final boolean isOrder) {
switch (messageModel) {
case BROADCASTING: {
Set mqSet = this.topicSubscribeInfoTable.get(topic);
if (mqSet != null) {
boolean changed = this.updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance(topic, mqSet, isOrder);
if (changed) {
this.messageQueueChanged(topic, mqSet, mqSet);
log.info("messageQueueChanged {} {} {} {}",
consumerGroup,
topic,
mqSet,
mqSet);
}
} else {
log.warn("doRebalance, {}, but the topic[{}] not exist.", consumerGroup, topic);
}
break;
}
case CLUSTERING: {
// 获取topic的路由信息(Queue列表)
Set mqSet = this.topicSubscribeInfoTable.get(topic);
// 根据topic和consumerGroup从namesrv获取有哪些消费者
List cidAll = this.mQClientFactory.findConsumerIdList(topic, consumerGroup);
if (null == mqSet) {
if (!topic.startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) {
log.warn("doRebalance, {}, but the topic[{}] not exist.", consumerGroup, topic);
}
}
if (null == cidAll) {
log.warn("doRebalance, {} {}, get consumer id list failed", consumerGroup, topic);
}
if (mqSet != null && cidAll != null) {
List mqAll = new ArrayList();
mqAll.addAll(mqSet);
Collections.sort(mqAll);
Collections.sort(cidAll);
AllocateMessageQueueStrategy strategy = this.allocateMessageQueueStrategy;
// 使用AllocateMessageQueueStrategy进行将Queue分配给consumer,返回的结果allocateResult就是分配给当前消费者的Queue
List allocateResult = null;
try {
allocateResult = strategy.allocate(
this.consumerGroup,
this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(),
mqAll,
cidAll);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("AllocateMessageQueueStrategy.allocate Exception. allocateMessageQueueStrategyName={}", strategy.getName(),
e);
return;
}
Set allocateResultSet = new HashSet();
if (allocateResult != null) {
allocateResultSet.addAll(allocateResult);
}
// 这里和广播消费的逻辑一样
boolean changed = this.updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance(topic, allocateResultSet, isOrder);
if (changed) {
log.info(
"rebalanced result changed. allocateMessageQueueStrategyName={}, group={}, topic={}, clientId={}, mqAllSize={}, cidAllSize={}, rebalanceResultSize={}, rebalanceResultSet={}",
strategy.getName(), consumerGroup, topic, this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(), mqSet.size(), cidAll.size(),
allocateResultSet.size(), allocateResultSet);
// 如果Queue列表发生了变动,RebalancePushImpl#messageQueueChanged()的实现是修改了拉去消息的数量和消息大小的阈值
this.messageQueueChanged(topic, mqSet, allocateResultSet);
}
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}
前面说过,广播消费和集群消费区别很大,广播消费只需要感知Topic的Queue的变化信息,逻辑相对比较简单,而且集群消费的处理逻辑包含了广播消费的逻辑,集群消费逻辑更加的复杂,所以我们看集群消费的重平衡实现
在上面代码的注释中说明了处理逻辑,大概就是
- 获取Topic的路由信息,也就是Topic的Queue列表
- 从namesrv获取当前Topic和ConsumerGroup的所有消费者列表
- 使用AllocateMessageQueueStrategy,根据Queue列表和消费者列表重新分配Queue
- 重平衡后,当前消费和消费的Queue可能会发生变动,变动逻辑的处理在updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance()和messageQueueChanged()中
第1,2步不需要多解释,我们注重看第3,4步
AllocateMessageQueueStrategy是一个接口,可以实现这个接口自定义自己的重平衡逻辑,这里我们只看默认实现AllocateMessageQueueAveragely
public interface AllocateMessageQueueStrategy {
List allocate(
final String consumerGroup,
final String currentCID,
final List mqAll,
final List cidAll
);
String getName();
}
public class AllocateMessageQueueAveragely implements AllocateMessageQueueStrategy {
private final InternalLogger log = ClientLogger.getLog();
@Override
public List allocate(String consumerGroup, String currentCID, List mqAll,
List cidAll) {
if (currentCID == null || currentCID.length() < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("currentCID is empty");
}
if (mqAll == null || mqAll.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("mqAll is null or mqAll empty");
}
if (cidAll == null || cidAll.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("cidAll is null or cidAll empty");
}
List result = new ArrayList();
if (!cidAll.contains(currentCID)) {
log.info("[BUG] ConsumerGroup: {} The consumerId: {} not in cidAll: {}",
consumerGroup,
currentCID,
cidAll);
return result;
}
int index = cidAll.indexOf(currentCID);
int mod = mqAll.size() % cidAll.size();
int averageSize =
mqAll.size() <= cidAll.size() ? 1 : (mod > 0 && index < mod ? mqAll.size() / cidAll.size()
+ 1 : mqAll.size() / cidAll.size());
int startIndex = (mod > 0 && index < mod) ? index * averageSize : index * averageSize + mod;
int range = Math.min(averageSize, mqAll.size() - startIndex);
for (int i = 0; i < range; i++) {
result.add(mqAll.get((startIndex + i) % mqAll.size()));
}
return result;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "AVG";
}
}
这段逻辑,我觉得很复杂,我就分析了,反正就是让Queue平均分配给每个consumer。大家可以和这个问题类比:n个人平均分m个苹果?
好了虽然我不太理解这段代码逻辑,但是需要强调一些点
- 由于分布式环境下有多个consumer,AllocateMessageQueueStrategy是在consumer本地执行的,所以在实现AllocateMessageQueueStrategy时需要保证在Queue和consumer不变得情况下,多次调用AllocateMessageQueueStrategy,consumer分配到的Queue列表应该尽量不变
- AllocateMessageQueueStrategy的参数mqAll,cidAll是排序了的
另外,我觉得这里只考虑了Consumer和Queue数量之间的平均,其实Consumer和Queue之间还有一层Broker的概念,还可以把Broker的因素考虑进来
好了,AllocateMessageQueueStrategy#allocate()执行完成后返回的结果是分配给当前消费者的Queue列表
获取到重平衡后的Queue列表,需要和平衡前的Queue列表进行比较,这段逻辑就是在RebalanceImpl#updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance()方法中
private boolean updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance(final String topic, final Set mqSet,
final boolean isOrder) {
boolean changed = false;
// 重平衡前的Queue列表
Iterator> it = this.processQueueTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry next = it.next();
MessageQueue mq = next.getKey();
ProcessQueue pq = next.getValue();
// 同一个Topic才处理
if (mq.getTopic().equals(topic)) {
// 重平衡后不再消费这个Queue了
if (!mqSet.contains(mq)) {
pq.setDropped(true);
if (this.removeUnnecessaryMessageQueue(mq, pq)) {
it.remove();
changed = true;
log.info("doRebalance, {}, remove unnecessary mq, {}", consumerGroup, mq);
}
} else if (pq.isPullExpired()) { // 如果Queue已经很久没有从Broker拉消息了,Push模式也会移除
switch (this.consumeType()) {
case CONSUME_ACTIVELY:
break;
case CONSUME_PASSIVELY:
pq.setDropped(true);
if (this.removeUnnecessaryMessageQueue(mq, pq)) {
it.remove();
changed = true;
log.error("[BUG]doRebalance, {}, remove unnecessary mq, {}, because pull is pause, so try to fixed it",
consumerGroup, mq);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
// 重平衡后有新的Queue要消费,构建新Queue的PullRequest从Broker拉消息
List pullRequestList = new ArrayList();
for (MessageQueue mq : mqSet) {
if (!this.processQueueTable.containsKey(mq)) {
if (isOrder && !this.lock(mq)) {
log.warn("doRebalance, {}, add a new mq failed, {}, because lock failed", consumerGroup, mq);
continue;
}
this.removeDirtyOffset(mq);
ProcessQueue pq = new ProcessQueue();
long nextOffset = this.computePullFromWhere(mq);
if (nextOffset >= 0) {
ProcessQueue pre = this.processQueueTable.putIfAbsent(mq, pq);
if (pre != null) {
log.info("doRebalance, {}, mq already exists, {}", consumerGroup, mq);
} else {
log.info("doRebalance, {}, add a new mq, {}", consumerGroup, mq);
PullRequest pullRequest = new PullRequest();
pullRequest.setConsumerGroup(consumerGroup);
pullRequest.setNextOffset(nextOffset);
pullRequest.setMessageQueue(mq);
pullRequest.setProcessQueue(pq);
pullRequestList.add(pullRequest);
changed = true;
}
} else {
log.warn("doRebalance, {}, add new mq failed, {}", consumerGroup, mq);
}
}
}
// 发送PullRequest
this.dispatchPullRequest(pullRequestList);
return changed;
}
这段逻辑别看这么长,但是很好理解,简单来说就是重平衡后Queue列表发生变动了,多了就是添加,少了就移除
到这里,重平衡机制就完了,看完之后是不是比较好理解了。
- 如果没有重平衡机制,会出现消费者不能均衡的消费Topic的消息
- 重平衡机制主要是在集群消费的情况下起作用,就是根据Consumer和Queue列表,定时更新当前消费者需要消费的Queue列表
PullAPIWrapper和PullMessageService实现消息拉取
接下来就是PullAPIWrapper这个组件了,PullAPIWrapper从名字就知道它干什么事,和RebalanceImpl一样我们也需要知道在哪使用了PullAPIWrapper。既然PullAPIWrapper是拉消息的实现,我们可以猜想一下,我们要拉去消息的话,肯定是从Topic的Queue拉,那么我们可以顺着RebalanceImpl的逻辑,在RebalanceImpl重平衡后,可能会消费新的Queue,我们顺着这个应该就是找到PullAPIWrapper了
在前面我们知道消费了新Queue会创建一个PullRequest对象,方法到pullRequestList这个队列里面,然后调用RebalanceImpl#dispatchPullRequest()方法发送请求
我们看看RebalancePushImpl#dispatchPullRequest()中这个方法的实现
@Override
public void dispatchPullRequest(List pullRequestList) {
for (PullRequest pullRequest : pullRequestList) {
this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
log.info("doRebalance, {}, add a new pull request {}", consumerGroup, pullRequest);
}
}
可以看到调用了DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#executePullRequestImmediately(),继续深入
public void executePullRequestImmediately(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
this.mQClientFactory.getPullMessageService().executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
}
又调用MQClientInstance#PullMessageService#executePullRequestImmediatel()方法
public void executePullRequestImmediately(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
try {
this.pullRequestQueue.put(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("executePullRequestImmediately pullRequestQueue.put", e);
}
}
最后将PullRequest保存到了PullMessageService#pullRequestQueue这个队列中,注意到PullMessageService也是一个线程的封装,并且和RebalanceService一样是在MQClientInstance#start()方法中启动的
public void start() throws MQClientException {
synchronized (this) {
switch (this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
...
this.pullMessageService.start();
...
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
break;
case RUNNING:
break;
case SHUTDOWN_ALREADY:
break;
case START_FAILED:
throw new MQClientException("The Factory object[" + this.getClientId() + "] has been created before, and failed.", null);
default:
break;
}
}
}
那么我们看看PullMessageService执行的逻辑
@Override
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
PullRequest pullRequest = this.pullRequestQueue.take();
this.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Pull Message Service Run Method exception", e);
}
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
private void pullMessage(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
final MQConsumerInner consumer = this.mQClientFactory.selectConsumer(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup());
if (consumer != null) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl impl = (DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl) consumer;
impl.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} else {
log.warn("No matched consumer for the PullRequest {}, drop it", pullRequest);
}
}
就是从刚才的那个队列里面取出PullRequest,交给对应的DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#pullMessage()处理
public void pullMessage(final PullRequest pullRequest) {
// 获取ProcessQueue,如果ProcessQueue已经不再处理了,就会忽略
final ProcessQueue processQueue = pullRequest.getProcessQueue();
if (processQueue.isDropped()) {
log.info("the pull request[{}] is dropped.", pullRequest.toString());
return;
}
// 更新ProcessQueue的pull时间,这个和前面提到的RebalanceImpl#updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance()方法中ProcessQueue#isPullExpired()判断有关
pullRequest.getProcessQueue().setLastPullTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
// 这里省略了一些check逻辑
// 获取当前缓存的消息的数量和大小
long cachedMessageCount = processQueue.getMsgCount().get();
long cachedMessageSizeInMiB = processQueue.getMsgSize().get() / (1024 * 1024);
// 如果缓存的消息的数量和大小超过了阈值会延时执行PullRequest
if (cachedMessageCount > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdForQueue()) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
}
if (cachedMessageSizeInMiB > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullThresholdSizeForQueue()) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
return;
}
// 下面也是一段检查各种信息的check
if (!this.consumeOrderly) {
if (processQueue.getMaxSpan() > this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeConcurrentlyMaxSpan()) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_FLOW_CONTROL);
return;
}
} else {
if (processQueue.isLocked()) {
if (!pullRequest.isLockedFirst()) {
final long offset = this.rebalanceImpl.computePullFromWhere(pullRequest.getMessageQueue());
boolean brokerBusy = offset < pullRequest.getNextOffset();
pullRequest.setLockedFirst(true);
pullRequest.setNextOffset(offset);
}
} else {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_EXCEPTION);
log.info("pull message later because not locked in broker, {}", pullRequest);
return;
}
}
final SubscriptionData subscriptionData = this.rebalanceImpl.getSubscriptionInner().get(pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic());
if (null == subscriptionData) {
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_EXCEPTION);
log.warn("find the consumer's subscription failed, {}", pullRequest);
return;
}
final long beginTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 拉去消息请求的回调
PullCallback pullCallback = new PullCallback() {
...
};
// 省略了一些参数的构造
try {
this.pullAPIWrapper.pullKernelImpl(
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
subExpression,
subscriptionData.getExpressionType(),
subscriptionData.getSubVersion(),
pullRequest.getNextOffset(),
this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullBatchSize(),
sysFlag,
commitOffsetValue,
BROKER_SUSPEND_MAX_TIME_MILLIS,
CONSUMER_TIMEOUT_MILLIS_WHEN_SUSPEND,
CommunicationMode.ASYNC,
pullCallback
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("pullKernelImpl exception", e);
this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest, PULL_TIME_DELAY_MILLS_WHEN_EXCEPTION);
}
}
可以看到这个方法比较长,尼玛,这个方法就有240行左右,阿里规范呢?这个方法大部分都是在各种check逻辑,最后我们找到了期待已久的PullAPIWrapper,调用了PullAPIWrapper#pullKernelImpl()方法拉去消息
PullAPIWrapper#pullKernelImpl()和其他发送请求的逻辑差不多,都是构造参数,然后通过MQClientAPIImpl发送请求,MQClientAPIImpl最后也是通过NettyRemotingClient发送请求的,我们在RocketMQ如何实现请求与响应分析了底层发送请求的逻辑
这里我们只关注部分参数就行了,pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),pullRequest.getNextOffset()和this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullBatchSize()通过这3个参数,Broker就知道该返回给消费者哪些消息了,就是offset+size,可以把Broker理解成数组,offset就是index,size就是从index开始取多少个数据。我们来看看请求返回的PullResult对象包含哪些信息
public class PullResult {
// 拉去的状态
private final PullStatus pullStatus;
// 下一次拉去的offset
private final long nextBeginOffset;
private final long minOffset;
private final long maxOffset;
// 这个拉取到的消息内容
private List msgFoundList;
}
可以看到PullResult的结构还是比较简单的,由于拉去消息时异步拉去的,所以处理PullResult是在PullCallback中处理的,现在再看看PullResult如何处理PullResult吧
PullCallback pullCallback = new PullCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(PullResult pullResult) {
if (pullResult != null) {
pullResult = DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.pullAPIWrapper.processPullResult(pullRequest.getMessageQueue(), pullResult,
subscriptionData);
switch (pullResult.getPullStatus()) {
case FOUND:
// 获取下次拉消息的offset
long prevRequestOffset = pullRequest.getNextOffset();
// 更新PullReques的NextOffset
pullRequest.setNextOffset(pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
long pullRT = System.currentTimeMillis() - beginTimestamp;
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.getConsumerStatsManager().incPullRT(pullRequest.getConsumerGroup(),
pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic(), pullRT);
long firstMsgOffset = Long.MAX_VALUE;
if (pullResult.getMsgFoundList() == null || pullResult.getMsgFoundList().isEmpty()) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
} else {
firstMsgOffset = pullResult.getMsgFoundList().get(0).getQueueOffset();
pullRequest.getMessageQueue().getTopic(), pullResult.getMsgFoundList().size());
// 将拉取的Message保存到ProcessQueue中
boolean dispatchToConsume = processQueue.putMessage(pullResult.getMsgFoundList());
// 使用ConsumeMessageServic消费ProcessQueue中的消息
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.consumeMessageService.submitConsumeRequest(
pullResult.getMsgFoundList(),
processQueue,
pullRequest.getMessageQueue(),
dispatchToConsume);
// 再次将PullReques对象放到队列中,进行下一次拉取
if (DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullInterval() > 0) {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestLater(pullRequest,
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getPullInterval());
} else {
DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl.this.executePullRequestImmediately(pullRequest);
}
}
break;
// 省略了其他的case逻辑
}
}
}
};
可以看到,一进来就是通过PullAPIWrapper.processPullResult()出来返回结果,这里就不贴代码了,PullAPIWrapper.processPullResult()方法主要完成了
- 过滤了一些不满足Tag要求的Message
- 反序列话Message的二进制数据为List
原来PullResult#msgFoundList返回时其实是空的,经过了PullAPIWrapper.processPullResult()方法后才赋值的,然后就是处理返回来的消息了,这里我们只关注PullStatus#FOUND的处理逻辑
- 更新了PullRequest的nextOffset
- 将拉取的Message保存到ProcessQueue中
- 使用ConsumeMessageServic消费ProcessQueue中的消息
- 再次将PullRequest放到队列中,进行下次拉取
这里我们可以返现PullRequest这个对象从RebalanceImpl中创建开始,就一直在复用这个对象,PullRequest#nextBeginOffset不断被更新,从而实现消息的不断拉取,这里我再多嘴一下,RebalanceImpl是隔一段时间才运行一次,难道Consumer刚启动时需要等一段时间才能消费到消息吗?那肯定是不可能的,那么我们再简单看一下Consumer启动的时候怎么触发RebalanceImpl开始执行的
在DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#start()方法最后会指定updateTopicSubscribeInfoWhenSubscriptionChanged()和rebalanceImmediately()方法
public synchronized void start() throws MQClientException {
...
// 更新路由信息
this.updateTopicSubscribeInfoWhenSubscriptionChanged();
this.mQClientFactory.checkClientInBroker();
this.mQClientFactory.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
// 立刻执行RebalanceImpl
this.mQClientFactory.rebalanceImmediately();
}
好了,我们再回来,拉取到消息后会保存到ProcessQueue中,我们看看≈的结构吧
public class ProcessQueue {
// 操作msgTreeMap时加的读写锁
private final ReadWriteLock lockTreeMap = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
// Message保存到这个TreeMap中
private final TreeMap msgTreeMap = new TreeMap();
// 统计当前Queue中Message的数量
private final AtomicLong msgCount = new AtomicLong();
// 统计当前Queue中Message的大小
private final AtomicLong msgSize = new AtomicLong();
// 重平衡时会修改dropped,标识当前消费者还需不需要继续消费这个Message
private volatile boolean dropped = false;
// 添加到这个Queue的Message的最大的offset
private volatile long queueOffsetMax = 0L;
}
这里列了我们现在关心的一些属性,ProcessQueue#putMessage()方法就是将拉取到的Message保存在msgTreeMap中,msgTreeMap的key是Message的offset,Value就是Message数据
ConsumeMessageService处理消息
Message保存到ProcessQueue后,会使用ConsumeMessageService消费消息,ConsumeMessageService也是一个接口,它有2个实现,分别是ConsumeMessageOrderlyService和ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService
public interface ConsumeMessageService {
void start();
void shutdown();
void updateCorePoolSize(int corePoolSize);
void incCorePoolSize();
void decCorePoolSize();
int getCorePoolSize();
ConsumeMessageDirectlyResult consumeMessageDirectly(final MessageExt msg, final String brokerName);
void submitConsumeRequest(
final List msgs,
final ProcessQueue processQueue,
final MessageQueue messageQueue,
final boolean dispathToConsume);
}
ConsumeMessageOrderlyService和顺序消费有关,这个后面我们单独写一篇文章分析,这里我们就看看ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService如何消费Message的吧
ConsumeMessageService最重要的就是submitConsumeRequest()方法,我们看看ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService是如何实现的吧
public void submitConsumeRequest(
final List msgs,
final ProcessQueue processQueue,
final MessageQueue messageQueue,
final boolean dispatchToConsume) {
final int consumeBatchSize = this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumeMessageBatchMaxSize();
if (msgs.size() <= consumeBatchSize) {
ConsumeRequest consumeRequest = new ConsumeRequest(msgs, processQueue, messageQueue);
try {
this.consumeExecutor.submit(consumeRequest);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
this.submitConsumeRequestLater(consumeRequest);
}
} else {
for (int total = 0; total < msgs.size(); ) {
List msgThis = new ArrayList(consumeBatchSize);
for (int i = 0; i < consumeBatchSize; i++, total++) {
if (total < msgs.size()) {
msgThis.add(msgs.get(total));
} else {
break;
}
}
// 提交到线程池中消费消息
ConsumeRequest consumeRequest = new ConsumeRequest(msgThis, processQueue, messageQueue);
try {
this.consumeExecutor.submit(consumeRequest);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
for (; total < msgs.size(); total++) {
msgThis.add(msgs.get(total));
}
this.submitConsumeRequestLater(consumeRequest);
}
}
}
}
逻辑计较简单,消费消息的时候做了一个分批,也就是将msgs根据批量消费阈值,将msgs分为多份,然后提交到线程池中消费
@Override
public void run() {
// 如果当前消费者已经不消费这个Queue了,直接放弃处理
if (this.processQueue.isDropped()) {
log.info("the message queue not be able to consume, because it's dropped. group={} {}", ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.consumerGroup, this.messageQueue);
return;
}
MessageListenerConcurrently listener = ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.messageListener;
ConsumeConcurrentlyContext context = new ConsumeConcurrentlyContext(messageQueue);
ConsumeConcurrentlyStatus status = null;
defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.resetRetryAndNamespace(msgs, defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
long beginTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
boolean hasException = false;
ConsumeReturnType returnType = ConsumeReturnType.SUCCESS;
try {
if (msgs != null && !msgs.isEmpty()) {
for (MessageExt msg : msgs) {
MessageAccessor.setConsumeStartTimeStamp(msg, String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()));
}
}
// 使用listener消费消息
status = listener.consumeMessage(Collections.unmodifiableList(msgs), context);
} catch (Throwable e) {
...
}
...
if (!processQueue.isDropped()) {
// listener处理完消息后,processConsumeResult()方法会提交offset
ConsumeMessageConcurrentlyService.this.processConsumeResult(status, context, this);
} else {
log.warn("processQueue is dropped without process consume result. messageQueue={}, msgs={}", messageQueue, msgs);
}
}
这里我们只关注2个地方,这里会直接调用listener处理消息,然后会调用processConsumeResult()方法
public void processConsumeResult() {
...
long offset = consumeRequest.getProcessQueue().removeMessage(consumeRequest.getMsgs());
if (offset >= 0 && !consumeRequest.getProcessQueue().isDropped()) {
this.defaultMQPushConsumerImpl.getOffsetStore().updateOffset(consumeRequest.getMessageQueue(), offset, true);
}
}
在processConsumeResult()方法的最后会调用ProcessQueue#removeMessage()移除ProcessQueue中已经消费完的Message
public long removeMessage(final List msgs) {
long result = -1;
final long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.lockTreeMap.writeLock().lockInterruptibly();
this.lastConsumeTimestamp = now;
try {
if (!msgTreeMap.isEmpty()) {
result = this.queueOffsetMax + 1;
int removedCnt = 0;
for (MessageExt msg : msgs) {
MessageExt prev = msgTreeMap.remove(msg.getQueueOffset());
if (prev != null) {
removedCnt--;
msgSize.addAndGet(0 - msg.getBody().length);
}
}
msgCount.addAndGet(removedCnt);
// 如果msgTreeMap不为空,返回的事msgTreeMap的firstKey,也就是没有被消费消息的最小的offset
if (!msgTreeMap.isEmpty()) {
result = msgTreeMap.firstKey();
}
}
} finally {
this.lockTreeMap.writeLock().unlock();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("removeMessage exception", t);
}
return result;
}
removeMessage()逻辑也比较简单,直接从msgTreeMap中直接remove就行,但是我们需要关注这个方法的返回值,这个方法返回的当前Queue中还没有没处理消息的最小offset,这个offset很关键
返回的offset会被OffsetStore保存下来,OffsetStore也是一个接口,它有2个实现,分别是LocalFileOffsetStore和RemoteBrokerOffsetStore
public interface OffsetStore {
void load() throws MQClientException;
void updateOffset(final MessageQueue mq, final long offset, final boolean increaseOnly);
long readOffset(final MessageQueue mq, final ReadOffsetType type);
void persistAll(final Set mqs);
void persist(final MessageQueue mq);
void removeOffset(MessageQueue mq);
Map cloneOffsetTable(String topic);
void updateConsumeOffsetToBroker(MessageQueue mq, long offset, boolean isOneway) throws RemotingException,
MQBrokerException, InterruptedException, MQClientException;
}
OffsetStore管理消息的Offset
在DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#start()方法中,会根据MessageModel初始化这个OffsetStore,如果是广播消费OffsetStore就是LocalFileOffsetStore,如果是集群消费就是RemoteBrokerOffsetStore
switch (this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getMessageModel()) {
case BROADCASTING:
this.offsetStore = new LocalFileOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
case CLUSTERING:
this.offsetStore = new RemoteBrokerOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
default:
break;
}
这个就比较好理解了,广播模式下,每个消费者都会消费所有的Queue,所以他们只需要保存自己的offset就行了,所以本地就行;但是集群模式下,可能会消费者宕机,重启,扩容等情况,所以不能将offset保存到本地,使用RemoteBrokerOffsetStore的话,就可以将offset交给Broker保存,这样当消费者正常启动后,从Broker哪里获取这个offset就像了,这里我们看看RemoteBrokerOffsetStore的实现就行了
public void updateOffset(MessageQueue mq, long offset, boolean increaseOnly) {
if (mq != null) {
AtomicLong offsetOld = this.offsetTable.get(mq);
if (null == offsetOld) {
offsetOld = this.offsetTable.putIfAbsent(mq, new AtomicLong(offset));
}
if (null != offsetOld) {
if (increaseOnly) {
MixAll.compareAndIncreaseOnly(offsetOld, offset);
} else {
offsetOld.set(offset);
}
}
}
}
可以看到RemoteBrokerOffsetStore将每个Queue的消费完的offset保存到了offsetTable这个Map中,可以看到updateOffset()方法只是将offset保存到了内存,并没有交个Broker,交给Broker保存的方法是persistAll()
public void persistAll(Set mqs) {
if (null == mqs || mqs.isEmpty())
return;
final HashSet unusedMQ = new HashSet();
if (!mqs.isEmpty()) {
for (Map.Entry entry : this.offsetTable.entrySet()) {
MessageQueue mq = entry.getKey();
AtomicLong offset = entry.getValue();
if (offset != null) {
if (mqs.contains(mq)) {
try {
// 将offset交给Broker保存
this.updateConsumeOffsetToBroker(mq, offset.get());
log.info("[persistAll] Group: {} ClientId: {} updateConsumeOffsetToBroker {} {}",
this.groupName,
this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(),
mq,
offset.get());
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("updateConsumeOffsetToBroker exception, " + mq.toString(), e);
}
} else {
unusedMQ.add(mq);
}
}
}
}
if (!unusedMQ.isEmpty()) {
for (MessageQueue mq : unusedMQ) {
this.offsetTable.remove(mq);
log.info("remove unused mq, {}, {}", mq, this.groupName);
}
}
}
在MQClientInstance#start()方法中会启动一些定时任务,其中就包括定时执行persistAllConsumerOffset(),默认是5s执行一次,这个任务最终会调用OffsetStore#persistAll()方法
public void start() throws MQClientException {
...
this.startScheduledTask();
...
}
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.persistAllConsumerOffset();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask persistAllConsumerOffset exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000 * 10, this.clientConfig.getPersistConsumerOffsetInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
private void persistAllConsumerOffset() {
Iterator> it = this.consumerTable.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Entry entry = it.next();
MQConsumerInner impl = entry.getValue();
impl.persistConsumerOffset();
}
}
@Override
public void persistConsumerOffset() {
try {
this.makeSureStateOK();
Set mqs = new HashSet();
Set allocateMq = this.rebalanceImpl.getProcessQueueTable().keySet();
mqs.addAll(allocateMq);
this.offsetStore.persistAll(mqs);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("group: " + this.defaultMQPushConsumer.getConsumerGroup() + " persistConsumerOffset exception", e);
}
}
到这里,DefaultMQPushConsumer消费者的内容也差不多完了,接下来就是DefaultMQPullConsumer了,是不是害怕了,写了这么多才分析完DefaultMQPushConsumer,难道DefaultMQPullConsumer还搞这么长,使不得,使不得
简单了解DefaultMQPullConsumer的启动流程
再看DefaultMQPullConsumer之前,可以想一想,再DefaultMQPushConsumer中我们初始化了一个组件是PullAPIWrapper,看到没有DefaultMQPushConsumer其实通过PullAPIWrapper进行封装的,这下是不是恍然大悟了,DefaultMQPushConsumer我们都分析完了,DefaultMQPullConsumer岂不就是小事了,那我就快速过一下DefaultMQPullConsumer吧
首先呢,还是得看一下怎么使用DefaultMQPullConsumer
public class MQPullConsumer {
private static final Map OFFSE_TABLE = new HashMap();
public static void main(String[] args) throws MQClientException {
DefaultMQPullConsumer consumer = new DefaultMQPullConsumer("groupName");
consumer.setNamesrvAddr("name-serverl-ip:9876;name-server2-ip:9876");
consumer.start();
// 从指定topic中拉取所有消息队列
Set mqs = consumer.fetchSubscribeMessageQueues("order-topic");
for(MessageQueue mq:mqs){
try {
// 获取消息的offset,指定从store中获取
long offset = consumer.fetchConsumeOffset(mq,true);
System.out.println("consumer from the queue:"+mq+":"+offset);
while(true){
PullResult pullResult = consumer.pullBlockIfNotFound(mq, null,
getMessageQueueOffset(mq), 32);
putMessageQueueOffset(mq,pullResult.getNextBeginOffset());
switch(pullResult.getPullStatus()){
case FOUND:
List messageExtList = pullResult.getMsgFoundList();
for (MessageExt m : messageExtList) {
System.out.println(new String(m.getBody()));
}
break;
case NO_MATCHED_MSG:
break;
case NO_NEW_MSG:
break;
case OFFSET_ILLEGAL:
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
consumer.shutdown();
}
// 保存上次消费的消息下标
private static void putMessageQueueOffset(MessageQueue mq,
long nextBeginOffset) {
OFFSE_TABLE.put(mq, nextBeginOffset);
}
// 获取上次消费的消息的下标
private static Long getMessageQueueOffset(MessageQueue mq) {
Long offset = OFFSE_TABLE.get(mq);
if(offset != null){
return offset;
}
return 0l;
}
}
接下来就是DefaultMQPullConsumer的源码了,DefaultMQPullConsumer的初始也很简单,只是这里初始化的是DefaultMQPullConsumerImpl对象,DefaultMQPullConsumerImpl也很简单,没啥说的
public DefaultMQPullConsumer(final String namespace, final String consumerGroup, RPCHook rpcHook) {
this.namespace = namespace;
this.consumerGroup = consumerGroup;
defaultMQPullConsumerImpl = new DefaultMQPullConsumerImpl(this, rpcHook);
}
public DefaultMQPullConsumerImpl(final DefaultMQPullConsumer defaultMQPullConsumer, final RPCHook rpcHook) {
this.defaultMQPullConsumer = defaultMQPullConsumer;
this.rpcHook = rpcHook;
}
然后是DefaultMQPullConsumer#start()方法,也是调用DefaultMQPullConsumerImpl#start()方法
public void start() throws MQClientException {
this.setConsumerGroup(NamespaceUtil.wrapNamespace(this.getNamespace(), this.consumerGroup));
this.defaultMQPullConsumerImpl.start();
}
public synchronized void start() throws MQClientException {
switch (this.serviceState) {
case CREATE_JUST:
this.serviceState = ServiceState.START_FAILED;
this.checkConfig();
this.copySubscription();
if (this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getMessageModel() == MessageModel.CLUSTERING) {
this.defaultMQPullConsumer.changeInstanceNameToPID();
}
this.mQClientFactory = MQClientManager.getInstance().getAndCreateMQClientInstance(this.defaultMQPullConsumer, this.rpcHook);
this.rebalanceImpl.setConsumerGroup(this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
this.rebalanceImpl.setMessageModel(this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getMessageModel());
this.rebalanceImpl.setAllocateMessageQueueStrategy(this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getAllocateMessageQueueStrategy());
this.rebalanceImpl.setmQClientFactory(this.mQClientFactory);
this.pullAPIWrapper = new PullAPIWrapper(
mQClientFactory,
this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getConsumerGroup(), isUnitMode());
this.pullAPIWrapper.registerFilterMessageHook(filterMessageHookList);
if (this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getOffsetStore() != null) {
this.offsetStore = this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getOffsetStore();
} else {
switch (this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getMessageModel()) {
case BROADCASTING:
this.offsetStore = new LocalFileOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
case CLUSTERING:
this.offsetStore = new RemoteBrokerOffsetStore(this.mQClientFactory, this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
break;
default:
break;
}
this.defaultMQPullConsumer.setOffsetStore(this.offsetStore);
}
this.offsetStore.load();
boolean registerOK = mQClientFactory.registerConsumer(this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getConsumerGroup(), this);
if (!registerOK) {
this.serviceState = ServiceState.CREATE_JUST;
throw new MQClientException("The consumer group[" + this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getConsumerGroup()
+ "] has been created before, specify another name please." + FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.GROUP_NAME_DUPLICATE_URL),
null);
}
mQClientFactory.start();
log.info("the consumer [{}] start OK", this.defaultMQPullConsumer.getConsumerGroup());
this.serviceState = ServiceState.RUNNING;
break;
case RUNNING:
case START_FAILED:
case SHUTDOWN_ALREADY:
throw new MQClientException("The PullConsumer service state not OK, maybe started once, "
+ this.serviceState
+ FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.CLIENT_SERVICE_NOT_OK),
null);
default:
break;
}
}
DefaultMQPullConsumerImpl#start()方法和DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#start()方法基本一样,DefaultMQPushConsumerImpl#start()方法的最后还多了几个方法调用,然后就没了,对,没了
因为pull需要使用方自己获取Topic的Queue列表,并且自己管理offset的信息,比使用Push麻烦多了,所以我们经常使用的是DefaultMQPushConsumer
总结
最后,总结一下,哎算了,太多了,不想总结了,反正DefaultMQPushConsumer和DefaultMQPullConsumer可以借用经典的一句话来总结,DefaultMQPushConsumer就是“xx不用动,xx自己动”,完美
欢迎关注我的公众号