这次接触到记忆化DFS,不过还需要多加练习
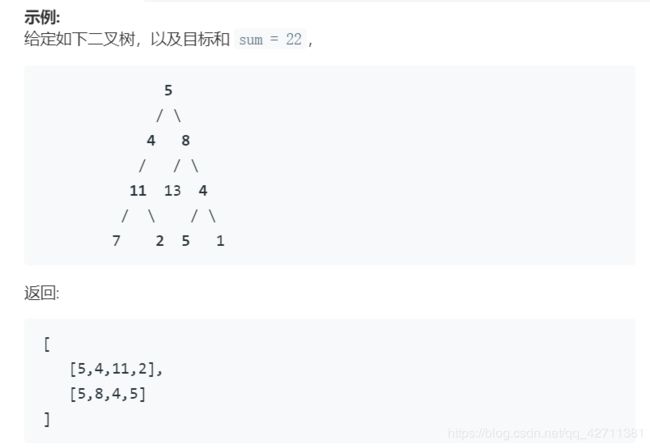
113. 路径总和 II - (根到叶子结点相关信息记录)
"""
思路:
本题 = 根到叶子结点的路径记录 + 根到叶子结点的值记录
"""
class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
def DFS(root, s, tmp):
if not root:
return
if not root.left and not root.right and s-root.val == 0:
res.append(tmp+[root.val].copy())
DFS(root.left, s - root.val, tmp + [root.val])
DFS(root.right, s - root.val, tmp + [root.val])
DFS(root, sum, [])
return res114. 二叉树展开为链表
"""
思路:
树的前序遍历再重新建树
需要主要的点是本题要求的是 !原地! 展开,所以建树的时候原始根结点不动。
"""
class Solution:
def flatten(self, root: TreeNode) -> None:
"""
Do not return anything, modify root in-place instead.
"""
if not root:
return
res = []
# 前序遍历
def Preorder(root):
if not root:
return
res.append(root.val)
Preorder(root.left)
Preorder(root.right)
Preorder(root)
res = res[1:]
treeNode = [root]
# 重新建树,左节点为空,右节点为其先序遍历的下一个。
while len(res) != 0:
tree = treeNode.pop(0)
rightChild = TreeNode(res.pop(0))
tree.right = rightChild
# 不要忘了将左边置为空
tree.left = None
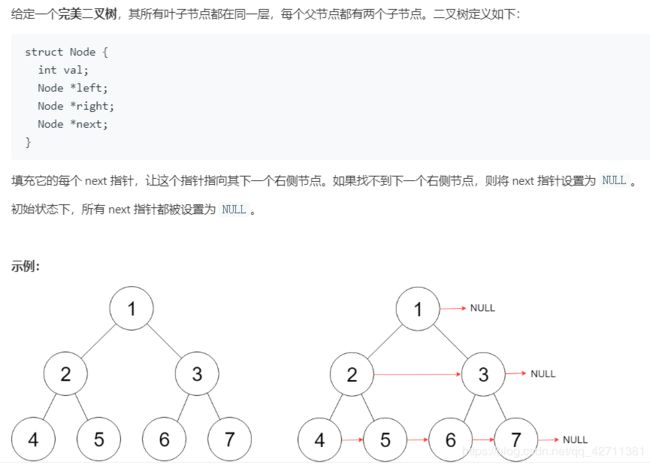
treeNode.append(rightChild)116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 / 117. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针 II
"""
树的层次遍历,每一个的next指向同层的下一个即可。
"""
class Solution:
def connect(self, root: 'Node') -> 'Node':
if not root:
return
Q = [(root, 0)]
pre = []
tmp = []
res = []
level = set()
level.add(0)
# 对树进行层次遍历
while len(Q) != 0:
node, deepth = Q.pop(0)
if deepth not in level:
res.append(tmp.copy())
tmp.clear()
level.add(deepth)
tmp.append(node)
if node.left:
Q.append((node.left, deepth+1))
if node.right:
Q.append((node.right, deepth+1))
res.append(tmp.copy())
# 每一个的next都是同层的下一个
for i in range(1, len(res)):
for j in range(len(res[i])-1):
res[i][j].next = res[i][j+1]
return root1020. 飞地的数量
"""
从边界的1开始出发(对可以到达的1进行染色),最后剩下的1就是飞地
"""
class Solution:
def numEnclaves(self, A) -> int:
# print(A)
vis = set()
directx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
directy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
def DFS(x, y):
A[x][y] = 2
for i in range(4):
newx, newy = x + directx[i], y + directy[i]
if -1 < newx < len(A) and -1 < newy < len(A[0]):
if (newx, newy) not in vis and A[newx][newy] == 1:
vis.add((newx, newy))
if DFS(newx, newy):
return True
return False
# 对第一行和最后一行的1
for i in range(len(A[0])):
if A[0][i] == 1 and (0, i) not in vis:
DFS(0, i)
if A[len(A) - 1][i] == 1 and (len(A) - 1, i) not in vis:
DFS(len(A) - 1, i)
# 对第一列和最后一列的1
for i in range(len(A)):
if A[i][0] == 1 and (i, 0) not in vis:
DFS(i, 0)
if A[i][len(A[0]) - 1] == 1 and (i, len(A[0]) - 1) not in vis:
DFS(i, len(A[0]) - 1)
res = 0
for i in A:
for j in i:
if j == 1:
res += 1
return reslru_cache装饰器
from functools import lru_cache
@lru_cache(None)使用时候需要注意什么是可以被记忆的?
eg:为函数传入相同的一对参数其总是会返回相同的结果
494. 目标和 - 记忆化DFS
"""
思路:
利用DFS求出所有组合题型 -> DFS超时了(DFS不好好剪枝真的很容易超时)
每一个数字有两个符号+、-可以选择,DFS的参数为数组中的数字
"""
class Solution:
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums, S: int) -> int:
self.res = 0
nums = sorted(nums, reverse=True)
def DFS(numInd, sums):
if sums == S and numInd == len(nums):
self.res += 1
return
if numInd > len(nums)-1 or sums + sum(nums[numInd:]) < S or sums - sum(nums[numInd:]) > S:
return
DFS(numInd + 1, sums + nums[numInd])
DFS(numInd + 1, sums - nums[numInd])
DFS(0, 0)
return self.res"""
加上装饰器后,完美通过
"""
from functools import lru_cache
class Solution:
def findTargetSumWays(self, nums, S: int) -> int:
nums = sorted(nums, reverse=True)
@lru_cache(None)
def DFS(numInd, sums):
if sums == S and numInd == len(nums):
return 1
# 出界了 or (现在的和加上后面所有的和都小于目标 or 现在的和减去后面所有的和还大于目标)那么肯定无论怎么操作都不能得到
if numInd > len(nums)-1 or sums + sum(nums[numInd:]) < S or sums - sum(nums[numInd:]) > S:
return 0
# 要么加上、要么减去
return DFS(numInd + 1, sums + nums[numInd]) + DFS(numInd + 1, sums - nums[numInd])
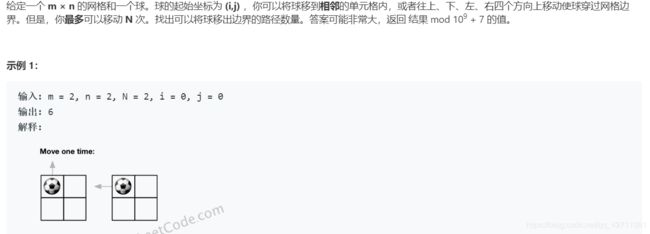
return DFS(0, 0)576. 出界的路径数 - 记忆化DFS
"""
思路
基本框架就是个DFS,相当于在m×n的矩阵外面再包一层,一旦来到这一层就是表示出来了。同时需要注意只有在原本m×n矩阵中才可以进行移动,出来了就不能移动了。
这里的重点是用到了lru_cache装饰器
"""
from functools import lru_cache
class Solution:
def findPaths(self, m: int, n: int, N: int, i: int, j: int) -> int:
directx = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
directy = [0, 0, -1, 1]
# 因为DFS是一个确定参数,所以可以使用lru_cache装饰器
@lru_cache(None)
def DFS(x, y, times):
if times > N:
return 0
# 已经出界了
if x < 1 or x > m or y < 1 or y > n:
return 1
cur = 0
if 0 < x < m+1 and 0 < y < n+1:
for i in range(4):
newx, newy = x + directx[i], y + directy[i]
cur += DFS(newx, newy, times+1)
return int(cur % (10**9 + 7))
return DFS(i+1, j+1, 0)688. “马”在棋盘上的概率 - (和 出界的路径数 相似)
"""
思路:
记忆化DFS,需要注意的是本题概率的计算
"""
from functools import lru_cache
class Solution:
def knightProbability(self, N: int, K: int, r: int, c: int) -> float:
directx = [-2, -2, -1, -1, 1, 2, 2, 1]
directy = [-1, 1, -2, 2, -2, -1, 1, 2]
@lru_cache(None)
def DFS(x, y, times):
if times > K:
return 0
# 出界了那么留在棋盘上的概率为0
if x < 0 or x > N-1 or y < 0 or y > N - 1:
return 0
# 指定步数仍然没有出界那么留在棋盘上的概率为1
if times == K and -1 < x < N and -1 < y < N:
return 1
cur = 0
if -1 < x < N and -1 < y < N:
for i in range(8):
newx, newy = x + directx[i], y + directy[i]
# 重点是这里的概率求法需要除以8
cur += (DFS(newx, newy, times + 1) / 8)
return cur
return DFS(r, c, 0)