gRPC学习记录(四)--官方Demo
标签(空格分隔): javaWEB
了解proto3后,接下来看官方Demo作为训练,这里建议看一遍之后自己动手搭建出来,一方面巩固之前的知识,一方面是对整个流程更加熟悉.
官方Demo地址: https://github.com/grpc/grpc-java
例子是一个简单的路由映射的应用,它允许客户端获取路由特性的信息,生成路由的总结,以及交互路由信息,如服务器和其他客户端的流量更新.
1.1定义服务
也就是写proto文件
//指定proto3格式
syntax = "proto3";
//一些生成代码的设置
option java_multiple_files = true;//以外部类模式生成
option java_package = "cn.mrdear.route";//所在包名
option java_outer_classname = "RouteProto";//最外层类名称
//定义服务
service RouteGuide{
//得到指定点的feature
//一个 简单 RPC , 客户端使用存根发送请求到服务器并等待响应返回,就像平常的函数调用一样。
rpc GetFeature(Point) returns (Feature) {}
//获取一个矩形内的点
//一个 服务器端流式 RPC , 客户端发送请求到服务器,拿到一个流去读取返回的消息序列。 客户端读取返回的流,
//直到里面没有任何消息。从例子中可以看出,通过在 响应 类型前插入 stream 关键字,可以指定一个服务器端的流方法。
rpc ListFeatures(Rectangle) returns (stream Feature){}
//记录该点
//一个 客户端流式 RPC , 客户端写入一个消息序列并将其发送到服务器,同样也是使用流。一旦客户端完成写入消息,
//它等待服务器完成读取返回它的响应。通过在 请求 类型前指定 stream 关键字来指定一个客户端的流方法。
rpc RecordRoute(stream Point) returns (RouteSummary){}
//路由交流
//一个 双向流式 RPC 是双方使用读写流去发送一个消息序列。两个流独立操作,因此客户端和服务器
//可以以任意喜欢的顺序读写:比如, 服务器可以在写入响应前等待接收所有的客户端消息,或者可以交替 的读取和写入消息,
//或者其他读写的组合。每个流中的消息顺序被预留。你可以通过在请求和响应前加 stream 关键字去制定方法的类型。
rpc RouteChat(stream RouteNote) returns (stream RouteNote){}
}
//代表经纬度
message Point {
int32 latitude = 1;
int32 longitude = 2;
}
//由两个点确定的一个方块
message Rectangle{
Point lo = 1;
Point hi = 2;
}
//某一位置的名称
message Feature {
string name = 1;
Point location = 2;
}
// Not used in the RPC. Instead, this is here for the form serialized to disk.
message FeatureDatabase {
repeated Feature feature = 1;
}
//给某一点发送消息
message RouteNote{
Point location = 1;
string message = 2;
}
//记录收到的信息
message RouteSummary{
int32 point_count = 1;
int32 feture_count = 2;
int32 distance = 3;
int32 elapsed_time = 4;
}
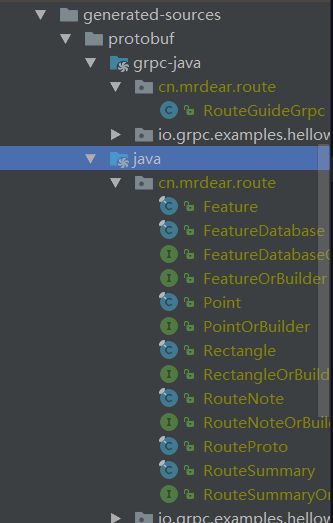
执行mvn compile生成如下代码:
1.2编写RouteGuideService
该类就是这个项目所提供给外部的功能.该类需要继承RouteGuideGrpc.RouteGuideImplBase,这个类提供了我们所定义分服务接口,继承后覆盖需要实现的自定义方法.
简单 RPC
简单RPC和普通方法调用形式差不多,客户端传来一个实体,服务端返回一个实体.
@Override
public void getFeature(Point request, StreamObserver responseObserver) {
System.out.println("getFeature得到的请求参数: " + request.toString());
// responseObserver.onError(); 代表请求出错
responseObserver.onNext(checkFeature(request));//包装返回信息
responseObserver.onCompleted();//结束一次请求
}
//找到复核的feature
private Feature checkFeature(Point location) {
for (Feature feature : features) {
if (feature.getLocation().getLatitude() == location.getLatitude()
&& feature.getLocation().getLongitude() == location.getLongitude()) {
return feature;
}
}
// No feature was found, return an unnamed feature.
return Feature.newBuilder().setName("").setLocation(location).build();
}
其中StreamObserver是一个应答观察者,用于封装返回的信息,服务器把该信息传给客户端.请求结束要调用onCompleted()方法.
服务器端流式 RPC
在proto文件中声明了stream,但是从接口上看不出来和简单RPC的区别,代码中最主要的区别是多次调用responseObserver.onNext()的方法,最后完成时写回数据.
@Override
public void listFeatures(Rectangle request, StreamObserver responseObserver) {
int left = min(request.getLo().getLongitude(), request.getHi().getLongitude());
int right = max(request.getLo().getLongitude(), request.getHi().getLongitude());
int top = max(request.getLo().getLatitude(), request.getHi().getLatitude());
int bottom = min(request.getLo().getLatitude(), request.getHi().getLatitude());
for (Feature feature : features) {
//如果不存在则继续
if (!RouteGuideUtil.exists(feature)) {
continue;
}
int lat = feature.getLocation().getLatitude();
int lon = feature.getLocation().getLongitude();
if (lon >= left && lon <= right && lat >= bottom && lat <= top) {
//找到符合的就写入
responseObserver.onNext(feature);
}
}
//最后标识完成
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
客户端流式 RPC
服务端就需要一直监控客户端写入情况,因此需要一个StreamObserver接口,其中onNext方法会在客户端每次写入时调用,当写入完毕时调用onCompleted()方法.具体还要到后面客户端调用分析.
@Override
public StreamObserver recordRoute(StreamObserver responseObserver) {
return new StreamObserver() {
int pointCount;
int featureCount;
int distance;
Point previous;
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
//客户端每写入一个Point,服务端就会调用该方法
@Override
public void onNext(Point point) {
System.out.println("recordRoute得到的请求参数: " + point.toString());
pointCount++;
if (RouteGuideUtil.exists(checkFeature(point))) {
featureCount++;
}
if (previous != null) {
distance += calcDistance(previous, point);
}
previous = point;
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
System.err.println("Encountered error in recordRoute");
}
//客户端写入结束时调用
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
long seconds = NANOSECONDS.toSeconds(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
responseObserver.onNext(RouteSummary.newBuilder().setPointCount(pointCount)
.setFetureCount(featureCount)
.setDistance(distance)
.setElapsedTime((int) seconds).build());
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
};
}
双向流式 RPC
和客户端流式RPC差不多.
@Override
public StreamObserver routeChat(StreamObserver responseObserver) {
return new StreamObserver() {
@Override
public void onNext(RouteNote note) {
List notes = getOrCreateNotes(note.getLocation());
for (RouteNote prevNote : notes.toArray(new RouteNote[0])) {
responseObserver.onNext(prevNote);
}
notes.add(note);
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
System.err.println("Encountered error in routeChat");
}
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
responseObserver.onCompleted();
}
};
}
1.3创建服务端
和Helloworld一样的形式,最主要的是addService(new RouteGuideService(features)),这里把需要注册的服务给注册上.
public class RouteGuideServer {
private final int port;//服务端端口
private final Server server;//服务器
public RouteGuideServer(int port) throws IOException {
this.port = port;
//获取初始化数据
List features = RouteGuideUtil.parseFeatures(RouteGuideUtil.getDefaultFeaturesFile());
//初始化Server参数
server = ServerBuilder.forPort(port)
//添加指定服务
.addService(new RouteGuideService(features))
.build();
}
/**
* 启动服务
*/
public void start() throws IOException {
server.start();
System.out.println("Server started, listening on " + port);
//程序退出时关闭资源
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> {
System.err.println("*** shutting down gRPC server since JVM is shutting down");
RouteGuideServer.this.stop();
System.err.println("*** server shut down");
}));
}
/**
* 关闭服务
*/
public void stop() {
if (server != null) {
server.shutdown();
}
}
/**
* 使得server一直处于运行状态
*/
private void blockUntilShutdown() throws InterruptedException {
if (server != null) {
server.awaitTermination();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
RouteGuideServer server = new RouteGuideServer(50051);
server.start();
server.blockUntilShutdown();
}
}
1.4编写客户端
客户端需要一个channel和一个存根blockingStub或者asyncStub根据业务需要选择同步或者异步.
private final ManagedChannel channel;//grpc信道,需要指定端口和地址
private final RouteGuideGrpc.RouteGuideBlockingStub blockingStub;//阻塞/同步存根
private final RouteGuideGrpc.RouteGuideStub asyncStub;//非阻塞,异步存根
public RouteGuideClient(String host,int port) {
//创建信道
channel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress(host, port)
.usePlaintext(true)
.build();
//创建存根
blockingStub = RouteGuideGrpc.newBlockingStub(channel);
asyncStub = RouteGuideGrpc.newStub(channel);
}
/**
* 关闭方法
*/
public void shutdown() throws InterruptedException {
channel.shutdown().awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
简单grpc
和调用普通方法形式差不多.
public void getFeature(int lat,int lon){
System.out.println("start getFeature");
Point request = Point.newBuilder()
.setLatitude(lat)
.setLongitude(lon)
.build();
Feature feature;
try {
//同步阻塞调用
feature = blockingStub.getFeature(request);
System.out.println("getFeature服务端返回 :" + feature);
} catch (StatusRuntimeException e) {
System.out.println("RPC failed " +e.getStatus());
}
}
调用代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
RouteGuideClient client = new RouteGuideClient("localhost", 50051);
try {
client.getFeature(409146138, -746188906);//成功案例
client.getFeature(0, 0);//失败案例
} finally {
client.shutdown();
}
}
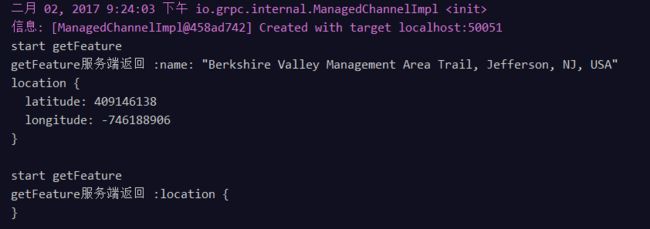
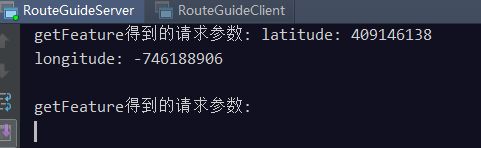
客户端日志
服务端日志(参数都为0的时候,这边并没拿到参数)
服务器端流式 RPC
和简单RPC差不多,只不过返回的是一个集合类.
//2.服务端流式RPC
public void listFeatures(int lowLat, int lowLon, int hiLat, int hiLon){
System.out.println("start listFeatures");
Rectangle request =
Rectangle.newBuilder()
.setLo(Point.newBuilder().setLatitude(lowLat).setLongitude(lowLon).build())
.setHi(Point.newBuilder().setLatitude(hiLat).setLongitude(hiLon).build()).build();
Iterator features;
try {
features = blockingStub.listFeatures(request);
for (int i = 1; features.hasNext(); i++) {
Feature feature = features.next();
System.out.println("getFeature服务端返回 :" + feature);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("RPC failed " +e.getMessage());
}
}
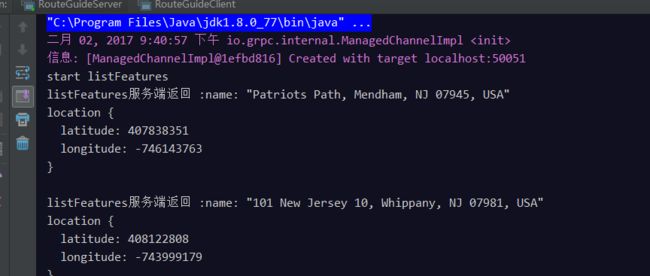
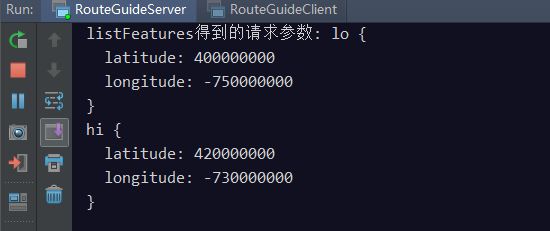
客户端日志:
服务端日志:
客户端流式 RPC
该种方式两遍都是异步操作,所以需要互相监听,也因此需要使用阻塞存根.服务端监听Point的写入,客户端监听RouteSummary的写回.
public void recordRoute(List features, int numPoints) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("start recordRoute");
final CountDownLatch finishLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
//建一个应答者接受返回数据
StreamObserver responseObserver = new StreamObserver() {
@Override
public void onNext(RouteSummary summary) {
System.out.println("recordRoute服务端返回 :" + summary);
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable t) {
System.out.println("RecordRoute Failed");
finishLatch.countDown();
}
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
System.out.println("RecordRoute finish");
finishLatch.countDown();
}
};
//客户端写入操作
StreamObserver requestObserver = asyncStub.recordRoute(responseObserver);
Random random = new Random();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < numPoints; ++i) {
int index = random.nextInt(features.size());
Point point = features.get(index).getLocation();
System.out.println("客户端写入point:" + point);
requestObserver.onNext(point);
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(1000) + 500);
if (finishLatch.getCount() == 0) {
return;
}
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
requestObserver.onError(e);
throw e;
}
//标识已经写完
requestObserver.onCompleted();
// Receiving happens asynchronously
if (!finishLatch.await(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES)) {
System.out.println("recordRoute can not finish within 1 minutes");
}
}
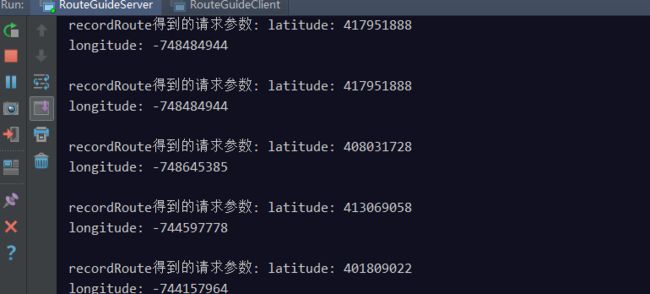
客户端日志:
服务端日志:
双向流式 RPC
和客户端流式RPC比较接近,同样都需要双方监控.
public CountDownLatch routeChat() {
System.out.println("start routeChat");
final CountDownLatch finishLatch = new CountDownLatch(1);
//写入监听
StreamObserver requestObserver =
//写回监听
asyncStub.routeChat(new StreamObserver() {
//服务端每写回一个操作就调用
@Override
public void onNext(RouteNote note) {
System.out.println("服务端写回: " + note);
}
@Override
public void onError(Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("RouteChat Failed:");
finishLatch.countDown();
}
@Override
public void onCompleted() {
System.out.println("Finished RouteChat");
finishLatch.countDown();
}
});
try {
RouteNote[] requests =
{newNote("First message", 0, 0), newNote("Second message", 0, 1),
newNote("Third message", 1, 0), newNote("Fourth message", 1, 1)};
for (RouteNote request : requests) {
System.out.println("客户端写入:" + request);
requestObserver.onNext(request);
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
requestObserver.onError(e);
throw e;
}
//标识写完
requestObserver.onCompleted();
return finishLatch;
}
这里调用需要特殊处理下;
CountDownLatch finishLatch = client.routeChat();
if (!finishLatch.await(1, TimeUnit.MINUTES)) {
System.out.println("routeChat can not finish within 1 minutes");
}
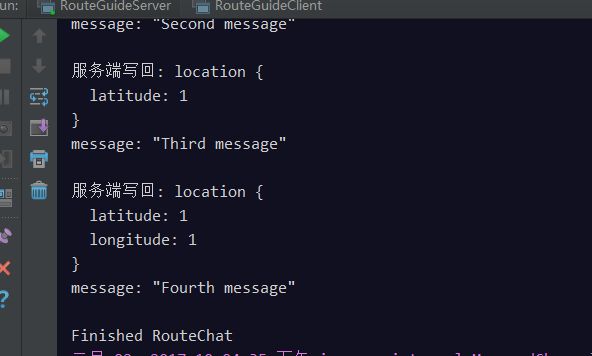
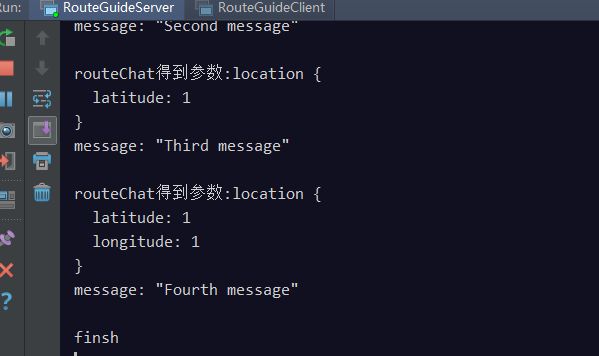
客户端日志:
服务端日志:
官方Demo之后,入门算结束,接下来就要看详细的官方文档,然后在项目中使用,这个过程会遇到不少问题,解决这些问题就是对这个技术的熟练.
附录:
相关代码: https://github.com/nl101531/JavaWEB