简述
所在的组织 华工小灯神 需要为用户提供方便地获取成绩单的服务,于是需要爬取本科生的教务系统,识别验证码时使用tesseract正确率太低,于是选择mnist_cnn里的卷积神经网络模型进行预测,正确率约98%。代码见github。
基本爬虫流程
- 本科生教务系统是经典的方正系统,网上已有不少不错的爬虫实现,如python爬虫实战之模拟正方教务系统登录查询成绩、python爬虫正方教务系统。
- 但是不同学校可能还是会有点区别,为了弄清具体的请求过程还是借了个账号走了下请求流程,即登录、查看历史成绩,并用fiddler分析网络请求的具体细节,fiddler在分析这种http请求时非常好用(chrome控制台还是差点)。所有请求头、cookies、表单内容等都一览无余,在使用python模拟请求时也可以用fiddler方便地查看返回页面内容。
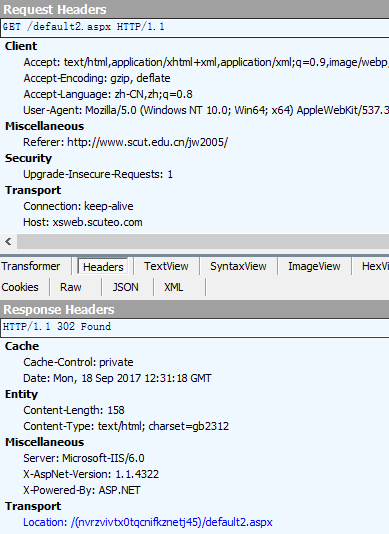
- 可以看到在访问教务处主页
http://www.scut.edu.cn/jw2005/时,实际上访问的是http://xsweb.scuteo.com/default2.aspx,而它为我们自动跳转到另一个路由,形式是/(20位标识符)/default2.aspx(即下面代码中用到的url_login),其中20位唯一标识符就是用来标志此次会话,某种程度上它相当于cookies。
- 请求时要注意先get访问一遍获取
csrf_token(即表单中的__VIEWSTATE参数),然后再连同其它参数一起post请求,其中中文参数是以gbk编码。登录时的post请求如下:
login_data = {
'__VIEWSTATE': csrf_token,
'txtUserName': student_id,
'TextBox2': password,
'txtSecretCode': veri_code,
'RadioButtonList1': '学生'.encode('gbk'), # 表示学生登录
'Button1': '',
'lbLanguage': '',
'hidPdrs': '',
'hidsc': '',
}
res = requests.post(url_login, data=login_data)
- 其中veri_code表示验证码,目前来看
/default3.aspx、/default5.aspx等其他版本登录页面的可以绕过验证码的bug已经被修复,只能访问http://xsweb.scuteo.com/(20位标识符)/CheckCode.aspx获取验证码,最直接的解决方案就是采用显示图片,人工输入的方式:
# 获取验证码
import requests
base_url = 'http://xsweb.scuteo.com/(wmyrw345umteq0e0sh5rayez)/'
res = requests.get(base_url + 'CheckCode.aspx')
from PIL import Image
import io
# 1. 外部工具显示
image_file = io.BytesIO(res.content) # import io
image = Image.open(image_file) # from PIL import Image
image.show()
veri_code = input('请输入看到的验证码:')
# 2. ipython内嵌显示
# from IPython.display import Image
# Image(data=res.content)
- 登录后就能获取成绩了,获取所有成绩的路由为
http://xsweb.scuteo.com/(20位标识符)/xscjcx.aspx?xh=学生账户名&xm=学生姓名&gnmkdm=N121605,学生姓名需要编码,post表单内容直接将fiddler中看到的表单数据复制过来即可,当然有些参数也可不要。此处的请求头中的referer参数必须要有,我使用的是http://xsweb.scuteo.com/(20位标识符)/xs_main.aspx?xh=学生账户名。 - 在获取到所有成绩页面后,查找到成绩所在的表格,简单解析后就可以得到需要的成绩信息了。
soup = BeautifulSoup(res.text, "lxml") # res为requests.post返回对象
table = soup.select_one('.datelist')
keys = [i.text for i in table.find('tr').find_all('td')]
scores = [
dict(zip(
keys, [i.text.strip() for i in tr.find_all('td')]))
for tr in table.find_all('tr')[1:]]
print(sorted([i['成绩'], i['课程名称']] for i in scores))
验证码处理
- 在识别之前我们可以对验证码做一定的处理(可用参考为:虫数据 - Lesson 1: 如何做文本行和文字分割),简单说来就是灰度、二值、滤波、强化等操作。(图片格式)
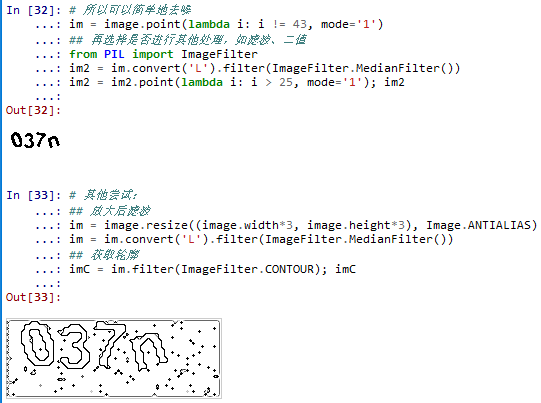
# 备用尝试1: 先灰度化,然后利用point函数对每个像素点操作来二值化,再中值滤波,最后锐化图像
from PIL import ImageFilter, ImageEnhance
imageL = image.convert("L").point(
lambda i: i > 25, mode='1').filter(
ImageFilter.MedianFilter(3)).convert('L')
imageS = ImageEnhance.Sharpness(imageL).enhance(2.0)
# 备用尝试2: 由于验证码图片是palette格式,所以要先转换成RGB格式再滤波,然后增强,最后灰度、二值
im = image.convert('RGB').filter(ImageFilter.MedianFilter())
enhancer = ImageEnhance.Contrast(im)
im = enhancer.enhance(2)
im = im.convert("L").point(lambda i: i > 25, mode='1')
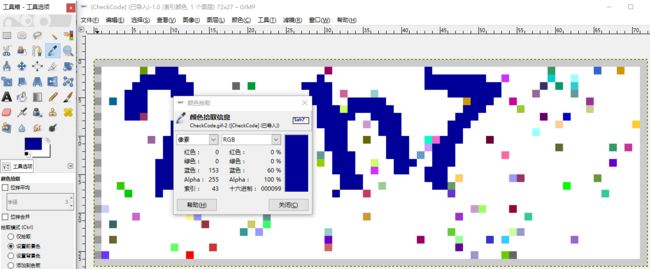
- 在尝试获取一定数量的验证码后,发现其固定用RGB(0,0,153)做验证字符颜色,利用该特征可以很方便地去噪。
# 查看像素分布
import numpy as np
from collections import Counter
a = np.concatenate(np.array(image))
# 将图片转为矩阵,再从二维矩阵降为一维
unique, counts = np.unique(a, return_counts=True)
# 对像素值索引计数,也可使用Counter(a).most_common()
print(sorted(list(zip(counts, unique)), reverse=True)[:10])
# 对出现次数排序,并输出前十个最多出现的
## 可以看到白色像素值索引255的出现最多
## 其次就是验证码的深蓝色索引值为43
## 因为该验证码没有模糊边缘,直接取所有像素值索引为43的点就可拿到字符信息
# 所以可以简单地去噪
im = image.point(lambda i: i != 43, mode='1')
## 再选择是否进行其他处理,如滤波、二值
from PIL import ImageFilter
im2 = im.convert('L').filter(ImageFilter.MedianFilter())
im2 = im2.point(lambda i: i > 25, mode='1'); im2
# 其他尝试:
## 放大后滤波
im = image.resize((image.width*3, image.height*3), Image.ANTIALIAS)
im = im.convert('L').filter(ImageFilter.MedianFilter())
## 获取轮廓
imC = im.filter(ImageFilter.CONTOUR); imC
## 更多的处理可使用scipy
## 可参考
## https://stackoverflow.com/questions/24687760/numpy-pil-python-crop-image-on-whitespace-or-crop-text-with-histogram-threshol
## http://www.scipy-lectures.org/advanced/image_processing/
## from scipy import ndimage
验证码识别
- 在简单的图像处理后,就可以拿OCR工具来尝试效果了。先试试开源的字符识别工具tesseract-ocr。(tesseract参数列表)(注意修改下面的路径为为自己的tesseract安装路径)
# 下载tesseract-ocr-setup.exe 安装
# pip install pytesseract
import pytesseract
pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = 'D:\\Tesseract-OCR\\tesseract'
tessdata_dir_config = '--tessdata-dir "D:\\Tesseract-OCR\\tessdata"' # or TESSDATA_PREFIX
from functools import partial
convert = partial(pytesseract.image_to_string, lang='eng', config=tessdata_dir_config)
# 可以尝试使用pip install tesserocr
# 使用下行代码转换
veri_code = convert(image) # image 为验证码 (PIL.Image)
# 去掉识别出的奇怪的字符
import re
veri_code_ = re.sub('[^0-9a-zA-Z]+', '', veri_code)
print(veri_code, '->', veri_code_)
- 可惜识别率太低,只有8%。看来还是使用卷积神经网络好了。
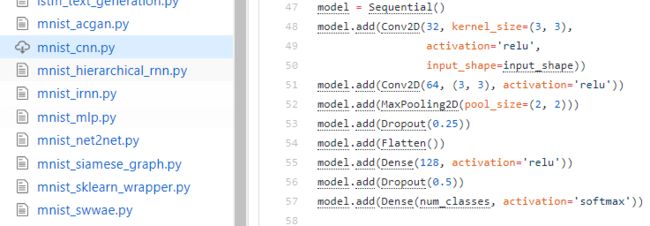
- 使用Keras构建神经网络模型非常简单,且在github上可以方便地找到Keras的官方样例,最经典的就是手写字符识别了,即mnist_cnn.py,和此次任务目标非常一致,直接拿来用,稍作修改即可。(另外还有简单有趣的mnist_transfer_cnn.py)
(一些基本概念可参考:卷积神经网络CNN基本概念笔记)
- 再简单搜索下,找到这两篇可以参考的不错的博文:
TensorFlow练习20: 使用深度学习破解字符验证码
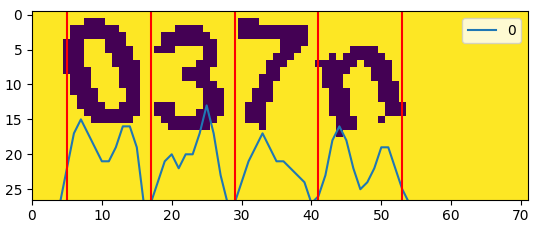
使用 Keras 来破解 captcha 验证码 - 下面的问题就是构建训练集了。由于正方教务系统返回的验证码格式固定,四个字符都是在固定的中心位置上进行了小范围的旋转,所以很好切割成单个字符,横坐标的分界点为
[5,17,29,41,53](单张验证码尺寸为72*27),至于字符之间有粘连影响的情况暂时不管,故可以考虑简单切割后识别单个字符。单个字符也便于自己生成训练集。
im = image.point(lambda i: i != 43, mode='1')
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
a = np.array(im)
pd.DataFrame(a.sum(axis=0)).plot.line() # 画出每列的像素累计值
plt.imshow(a) # 画出图像
split_lines = [5,17,29,41,53]
vlines = [plt.axvline(i, color='r') for i in split_lines] # 画出分割线
plt.show()
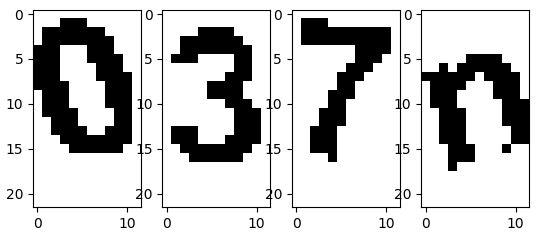
- 再去掉下面的一部分空白,将每个字符切割成
12*22(宽*高)的小块
im = image.point(lambda i: i != 43, mode='1')
y_min, y_max = 0, 22 # im.height - 1 # 26
split_lines = [5,17,29,41,53]
ims = [im.crop([u, y_min, v, y_max]) for u, v in zip(split_lines[:-1], split_lines[1:])]
for i in range(4):
plt.subplot(1,4,i+1)
plt.imshow(images[i], interpolation='none')
plt.show()
- 下面就是找一些字体,或直接利用windows系统自带的字体,利用PIL的draw函数并随机旋转一定角度,生成一批类似大小的单个字符的训练集,可惜没找到一样的字体效果的。
from PIL import Image
from PIL import ImageFont
from PIL import ImageDraw
from PIL import ImageFilter, ImageEnhance
import random
import string
CHRS = string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits # 小写字母+数字的字符串列表
t_size = (12, 22)
font_size = 20 # 即字体的高(大概值), 宽度约为一半
font_path = [ # 字体路径
r'E:/python/2017_9/Roboto-Regular.ttf',
r'C:/Windows/Fonts/VERDANA.TTF',
r'C:/Windows/Fonts/SIMKAI.TTF',
r'C:/Windows/Fonts/SIMSUNB.TTF',
r'C:/Windows/Fonts/REFSAN.TTF',
r'C:/Windows/Fonts/MSYH.TTC',
]
fonts = [ImageFont.truetype(fp, font_size) for fp in font_path]
# font = ImageFont.truetype('E:/python/2017_9/simhei.ttf', font_size)
def gen_fake_code(prefix, c, font):
txt = Image.new('L', t_size, color='black')
ImageDraw.Draw(txt).text((0, -2), c, fill='white', font=font)
w = txt.rotate(random.uniform(-20, 20), Image.BILINEAR) # center不指定,默认为中心点
img_ = w.point(lambda i: i < 10, mode='1')
# img_.show()
img_.save(prefix + '_' + c + '.png')
# if __name__ == '__main__':
import os
os.chdir(r'E:\python\2017_9\fakes_single')
for c in CHRS: # 对每一个字符的每一种字体生成200张
for n, font in enumerate(fonts):
for i in range(200):
gen_fake_code(str(n)+'-'+str(i), c, font)
- 对官方mnist-cnn样例做简单修改后就可以训练我们自己的模型了。
import keras
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Flatten
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D
from keras import backend as K
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import os
os.chdir(r'E:\python\2017_9\fakes_single') # 跳转到训练集目录
import string
CHRS = string.ascii_lowercase + string.digits # 字符列表
num_classes = 36 # 共要识别36个字符(所有小写字母+数字),即36类
batch_size = 128
epochs = 12
# 输入图片的尺寸
img_rows, img_cols = 12, 22
# 根据keras的后端是TensorFlow还是Theano转换输入形式
if K.image_data_format() == 'channels_first':
input_shape = (1, img_rows, img_cols)
else:
input_shape = (img_rows, img_cols, 1)
import glob
X, Y = [], []
for f in glob.glob('*.png')[:]: # 遍历当前目录下所有png后缀的图片
t = 1.0 * np.array(Image.open(f))
t = t.reshape(*input_shape) # reshape后要赋值
X.append(t) # 验证码像素列表
s = f.split('_')[1].split('.')[0] # 获取文件名中的验证码字符
Y.append(CHRS.index(s)) # 将字符转换为相应的0-35数值
X = np.stack(X) # 将列表转换为矩阵
Y = np.stack(Y)
# 此时Y形式为 array([26, 27, 28, ..., 23, 24, 25])
# 对Y值进行one-hot编码 # 可尝试 keras.utils.to_categorical(np.array([0,1,1]), 3) 理解
Y = keras.utils.to_categorical(Y, num_classes)
split_point = len(Y) - 720 # 简单地分割训练集与测试集
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = X[:split_point], Y[:split_point], X[split_point:], Y[split_point:]
# 以下模型和mnist-cnn相同
# 两层3x3窗口的卷积(卷积核数为32和64),一层最大池化(MaxPooling2D)
# 再Dropout(随机屏蔽部分神经元)并一维化(Flatten)到128个单元的全连接层(Dense),最后Dropout输出到36个单元的全连接层(全部字符为36个)
model = Sequential()
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3, 3),
activation='relu',
input_shape=input_shape))
model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2)))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(num_classes, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss=keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy,
optimizer=keras.optimizers.Adadelta(),
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
verbose=1,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test))
score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0)
print('Test loss:', score[0])
print('Test accuracy:', score[1])
# model.save(r'E:\python\2017_9\model_test.h5')
- 可以看到很快就收敛了,下面接着上面的环境测试一下,获取新的验证码预测并将其保存
import requests
import io
os.chdir(r'E:\python\2017_9\modeltest')
def get_image():
'''
从教务处网站获取验证码
'''
extra_code = 'azuuwd2ijh40vlnfg1ajdhbn'
url_base = 'http://xsweb.scuteo.com/(%s)/' % extra_code
# url_base = requests.get('http://xsweb.scuteo.com/default2.aspx').url.replace('default2.aspx', '')
url_veri_img = url_base + 'CheckCode.aspx'
headers = {
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/60.0.3112.113 Safari/537.36',
}
res = requests.get(url_veri_img, headers=headers)
image_file = io.BytesIO(res.content)
image = Image.open(image_file)
return image
def handle_split_image(image):
'''
切割验证码,返回包含四个字符图像的列表
'''
im = image.point(lambda i: i != 43, mode='1')
y_min, y_max = 0, 22 # im.height - 1 # 26
split_lines = [5,17,29,41,53]
ims = [im.crop([u, y_min, v, y_max]) for u, v in zip(split_lines[:-1], split_lines[1:])]
# w = w.crop(w.getbbox()) # 切掉白边 # 暂不需要
return ims
def predict(images):
'''
使用模型对四个字符的列表对应的验证码进行预测
'''
Y = []
for i in range(4):
im = images[i]
test_input = np.concatenate(np.array(im))
test_input = test_input.reshape(1, *input_shape)
y_probs = model.predict(test_input)
Y.append(CHRS[y_probs[0].argmax(-1)])
return ''.join(Y)
def multi_process(x):
'''
获取预测并保存图片,图片名为预测值
'''
image = get_image()
images = handle_split_image(image)
image.save( predict(images) + '.png')
from multiprocessing.dummy import Pool
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now
start = now()
with Pool(30) as pool:
pool.map(multi_process, [i for i in range(300)])
print('耗时 -> %s' % (now()-start))
- 检查一下正确率,约在40%,一些相似字符如
f、t、l、1、i等比较容易混淆,大概是训练字体与实际获取的不太一样,且验证码切割时由于字符歪斜粘连会有某一字符的一部分出现在另一字符区域导致干扰。 -
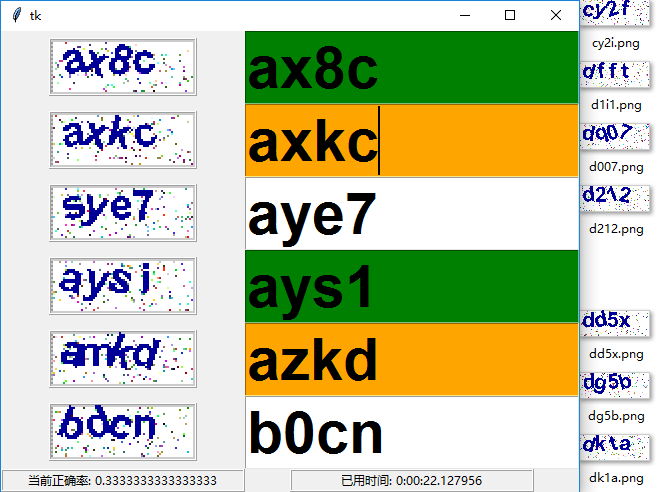
看来要提高正确率,还是得人工打码,继续获取预测1000多个验证码并保存,在此基础上进行人工打码。在windows文件系统下重命名太不方便,图片看着也太小,还是用python自带的GUI库tkinter做一个简单的打码助手,顺便统计之前预测的正确率和打码花费时间,有些小bug,不过也凑合用。
# 该文件命名为dama.py 命令行pyinstaller -w -F dama.py 生成exe文件(dist目录下)放入验证码所在文件夹执行
import os
import glob
image_files = glob.glob('*.png')
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
colours = ['green','orange','white']*2
labels = []
entrys = []
strvars = []
for r, c in enumerate(colours):
l = Label(root, text=c, relief=RIDGE, width=34)
l.grid(row=r,column=0)
labels.append(l)
v = StringVar(root, value='predict')
strvars.append(v)
e = Entry(root, textvariable=v, bg=c, relief=SUNKEN, width=10,
font = "Helvetica 44 bold")
e.grid(row=r,column=1)
entrys.append(e)
info_label1 = Label(root, text='当前正确率', relief=RIDGE, width=34)
info_label1.grid(row=7,column=0)
info_label2 = Label(root, text='已用时间', relief=RIDGE, width=34)
info_label2.grid(row=7,column=1)
# ims = []
num = 0
cur_files = None
correct = 0
incorrect = 0
if not os.path.exists('new'):
os.mkdir('new')
import datetime
now = datetime.datetime.now
start = now()
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
def enter_callback(e):
global num, cur_files
global correct, incorrect
if cur_files:
for i in range(6):
name = strvars[i].get()
# print(name)
if cur_files[i].split('.')[0] == name:
correct += 1
else:
incorrect += 1
try:
os.rename(cur_files[i], ''.join(['new/', name, '.png']))
except Exception as e:
print(e)
info1 = '当前正确率: %s' % (correct/(correct+incorrect))
info2 = '已用时间: %s' % (now()-start)
info_label1.config(text=info1)
info_label2.config(text=info2)
else:
for i in range(6):
labels[i].config(width=144)
cur_files = image_files[num: num+6]
for i in range(6):
f = image_files[num+i]
im = Image.open(f).resize((144, 54))
im = ImageTk.PhotoImage(im)
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18369936/how-to-open-pil-image-in-tkinter-on-canvas
# im = PhotoImage(file=f)
labels[i].configure(image=im)
labels[i].image = im
strvars[i].set(f.split('.')[0])
num += 6
root.bind("", enter_callback)
root.mainloop()
- 打码了一千个后,利用上文模型继续进行训练
# 由人工打码得到的训练集进行训练
os.chdir(r'E:\python\2017_9\modeltest\new')
# 检查是否有打错码如打成3个字符的图片
file_names = glob.glob('*.png')
error = [i for i in file_names if len(i.split('.')[0])!=4]
if error:
print(error)
raise Exception('打码出错,请检查')
# 构造训练集
X, Y = [], []
for f in file_names:
image = Image.open(f)
ims = handle_split_image(image) # 打开并切割图片
name = f.split('.')[0]
# 将图片切割出的四个字符及其准确值依次放入列表
for i, im in enumerate(ims):
# 以下类同上文
t = 1.0 * np.array(im)
t = t.reshape(*input_shape)
X.append(t)
s = name[i]
Y.append(CHRS.index(s)) # 验证码字符
X = np.stack(X)
Y = np.stack(Y)
Y = keras.utils.to_categorical(Y, num_classes)
split_point = len(Y) - 1000
x_train, y_train, x_test, y_test = X[:split_point], Y[:split_point], X[split_point:], Y[split_point:]
model.fit(x_train, y_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
epochs=epochs,
verbose=1,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test))
score = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0)
print('Test loss:', score[0])
print('Test accuracy:', score[1])
# model.save('ok.h5') # 保存模型
-
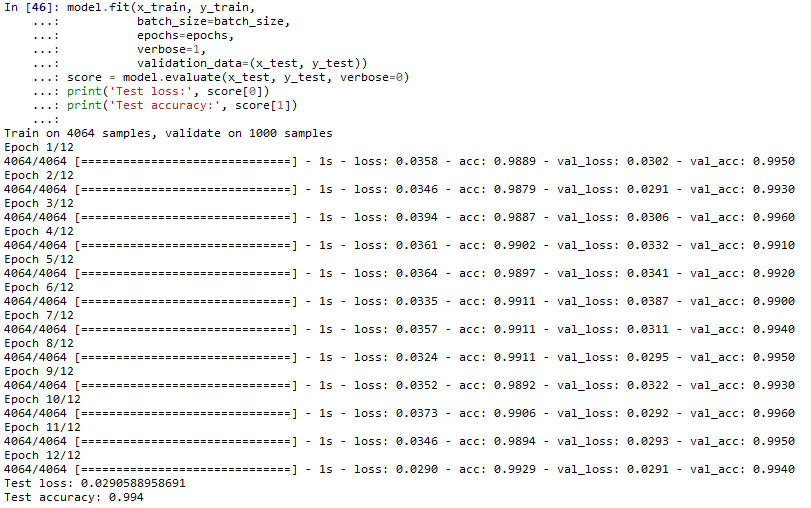
由于训练集很小,速度更快,多训练几回使得acc在0.99以上。
- 最后,再去访问新的教务处验证码进行测试,100张验证码大约有98张能完全识别对,这个正确率暂时足够使用了。
- 将以上内容简单的整合在一起,模型加载采用
keras.models.load_model方法获取,再抄点tkinter的UI,就可得到最终效果,代码见github:
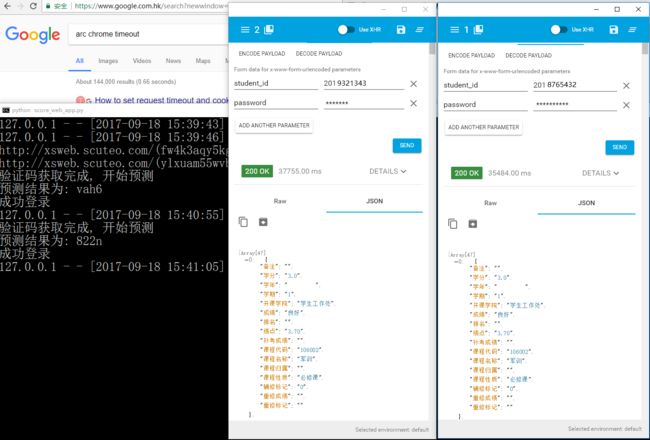
- 此外,利用flask和gevent可以构建一个简单的web服务,详见README:
其他资料
- 常见验证码的弱点与验证码识别
- Handwritten Digit Recognition using Convolutional Neural Networks in Python with Keras
- Keras Tutorial: The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide to Deep Learning in Python
- TensorFlow - MNIST For ML Beginners
- TensorFlow - Deep MNIST for Experts
- Keras as a simplified interface to TensorFlow: tutorial
- Neural Net for Handwritten Digit Recognition in JavaScript
- ptigas/simple-captcha-solver
- Multi-Class Classification Tutorial with the Keras Deep Learning Library
- fchollet/classifier_from_little_data_script_3.py
- Youtube - Neural Network Tutorial and Visualization (Python and PyQt - part 1)及其Github - PythonPyQtANN
- PIN-Identify-by-zhengfang与identifyZF - PHP实现,使用字典方式解决正方验证码-即将验证码中单个字符与字典中的字符一一计算距离,根据距离判断其值,类似Kmeans聚类
- 9 Ways to Get Help with Deep Learning in Keras
- issue - Is there a way in Keras to apply different weights to a cost function? #2115
- Keras backends 官方文档 - 中文
- issue - Custom loss function y_true y_pred shape mismatch #4781
- stackoverflow - Keras binary_crossentropy vs categorical_crossentropy performance?
- wassname/keras_weighted_categorical_crossentropy.py
- fchollet/deep-learning-with-python-notebooks
- Sequence Classification with LSTM Recurrent Neural Networks in Python with Keras
- Jupyter Tricks
- Issues using Keras np_utils.to_categorical
- Keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy
- Keras.optimizers.Adagrad
- Keras.metrics.categorical_accuracy
- Keras.backend.int_shape
- Python/Keras - Saving model weights after every N batches
- Scipy Lecture Notes
- Isolate greatest/smallest labeled patches from numpy array