C++ 重载
C++ 允许在同一作用域中的某个函数和运算符指定多个定义,分别称为函数重载和运算符重载。重载声明是指一个与之前已经在该作用域内声明过的函数或方法具有相同名称的声明,但是它们的参数列表和定义(实现)不相同。当调用一个重载函数或重载运算符时,编译器通过把您所使用的参数类型与定义中的参数类型进行比较,决定选用最合适的定义。选择最合适的重载函数或重载运算符的过程,称为重载决策。
运算符重载:
运算符重载可以分为两部分:“运算符”和“重载”。重载一种编译时多态,重载实际上可以分为函数重载和操作符重载。运算符重载和函数重载的不同之处在于运算符重载重载的一定是操作符。一下是重载运算符的例子:
#include
using namespace std;
class point
{
double x;
double y;
public:
double get_x()
{
return x;
}
double get_y()
{
return y;
}
point(double X = 0.0 , double Y = 0.0):x(X),y(Y){};
point operator +(point p);
};
//重载操作符“+”
point point::operator +(point p)
{
double x = this->x + p.x;
double y = this->y + p.y;
point tmp_p(x,y);
return tmp_p;
}
int main()
{
point p1(1.2,3.1);
point p2(1.1,3.2);
point p3 = p1+p2;
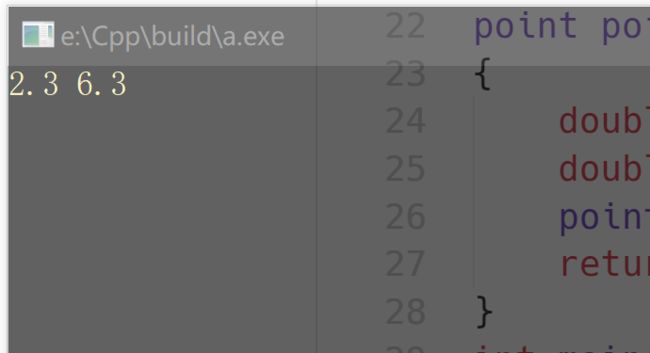
cout< 运行结果:
实现方式:
实现运算符重载一般用友元函数和类成员函数
例子:
#include
using std::endl;
using std::cout;
class point
{
double x;
double y;
public:
double get_x()
{
return x;
}
double get_y()
{
return y;
}
point(double X = 0.0 , double Y = 0.0):x(X),y(Y){};
friend point operator -(point p1,point p2);
point operator +(point p);
};
//重载操作符“-”
point operator -(point p1,point p2)
{
double x = p1.get_x() - p2.get_x();
double y = p1.get_y() - p2.get_y();
point p3(x,y);
return p3;
}
//重载操作符“+”
point point::operator +(point p)
{
double x = this->x + p.x;
double y = this->y + p.y;
point tmp_p(x,y);
return tmp_p;
}
int main()
{
point p1(1.2,3.2);
point p2(1.1,3.1);
point p3 = p1+p2;
point p4 = operator-(p1,p2);
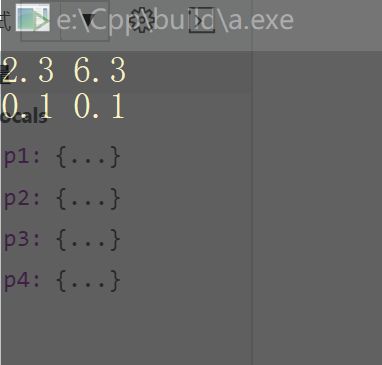
cout< 运行结果:
总结:
1.除了成员访问运算符.,作用域运算符::,c++绝大多数操作符可以重载
2.C++中只能对已有的C++运算符进行重载,不允许用户自己定义新的运算符。
3.运算符重载后不能改变运算符的操作对象(操作数)的个数。如:"+"是实现两个操作数的运算符,重载后仍然为双目运算符。