最近在调试几个问题时,发现跟abort函数有关,以前只是简单使用,现在却发现不简单,就多留意了下。
简介
abort中止当前进程并返回错误代码。异常终止一个进程。中止当前进程,返回一个错误代码。错误代码的缺省值是3。
代码
/*** *abort.c - abort a program by raising SIGABRT * * Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. * *Purpose: * defines abort() - print a message and raise SIGABRT. * *******************************************************************************/ #include#include #include <internal.h> #include #include #include #include #include #include #ifdef _DEBUG #define _INIT_ABORT_BEHAVIOR _WRITE_ABORT_MSG #else /* _DEBUG */ #define _INIT_ABORT_BEHAVIOR _CALL_REPORTFAULT #endif /* _DEBUG */ unsigned int __abort_behavior = _INIT_ABORT_BEHAVIOR; /*** *void abort() - abort the current program by raising SIGABRT * *Purpose: * print out an abort message and raise the SIGABRT signal. If the user * hasn't defined an abort handler routine, terminate the program * with exit status of 3 without cleaning up. * * Multi-thread version does not raise SIGABRT -- this isn't supported * under multi-thread. * *Entry: * None. * *Exit: * Does not return. * *Uses: * *Exceptions: * *******************************************************************************/ void __cdecl abort ( void ) { _PHNDLR sigabrt_act = SIG_DFL; #ifdef _DEBUG if (__abort_behavior & _WRITE_ABORT_MSG) { /* write the abort message */ _NMSG_WRITE(_RT_ABORT); } #endif /* _DEBUG */ /* Check if the user installed a handler for SIGABRT. * We need to read the user handler atomically in the case * another thread is aborting while we change the signal * handler. */ sigabrt_act = __get_sigabrt(); if (sigabrt_act != SIG_DFL) { raise(SIGABRT); } /* If there is no user handler for SIGABRT or if the user * handler returns, then exit from the program anyway */ if (__abort_behavior & _CALL_REPORTFAULT) { #if defined (_M_ARM) || defined (_CRT_APP) __fastfail(FAST_FAIL_FATAL_APP_EXIT); #else /* defined (_M_ARM) || defined (_CRT_APP) */ if (IsProcessorFeaturePresent(PF_FASTFAIL_AVAILABLE)) __fastfail(FAST_FAIL_FATAL_APP_EXIT); _call_reportfault(_CRT_DEBUGGER_ABORT, STATUS_FATAL_APP_EXIT, EXCEPTION_NONCONTINUABLE); #endif /* defined (_M_ARM) || defined (_CRT_APP) */ } /* If we don't want to call ReportFault, then we call _exit(3), which is the * same as invoking the default handler for SIGABRT */ _exit(3); } /*** *unsigned int _set_abort_behavior(unsigned int, unsigned int) - set the behavior on abort * *Purpose: * *Entry: * unsigned int flags - the flags we want to set * unsigned int mask - mask the flag values * *Exit: * Return the old behavior flags * *Exceptions: * None * *******************************************************************************/ unsigned int __cdecl _set_abort_behavior(unsigned int flags, unsigned int mask) { unsigned int oldflags = __abort_behavior; __abort_behavior = oldflags & (~mask) | flags & mask; return oldflags; }
流程
从上面代码,我可以看到,abort的流程如下:
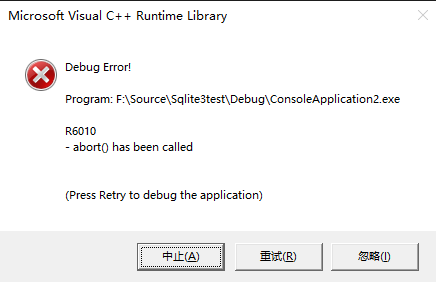
如果是调试版,且__abort_behavior为_WRITE_ABORT_MSG,则调用_NMSG_WRITE(_RT_ABORT);弹出crt异常提示框
点"中止"进程直接退出,点"忽略"后,就判断sigabrt_act的值,不等于SIG_DFL的话调用raise发送信号SIGABRT,然后调用_exit(3)退出
release版则会检测本机支不支持PF_FASTFAIL_AVAILABLE,支持就走windows快速失败机制,不支持就执行 _call_reportfault(_CRT_DEBUGGER_ABORT, STATUS_FATAL_APP_EXIT, EXCEPTION_NONCONTINUABLE);然后退出。
隐藏的秘密
上面讲的那些我相信大家都了解,但是,其实这个函数里,可能会引发多个异常。
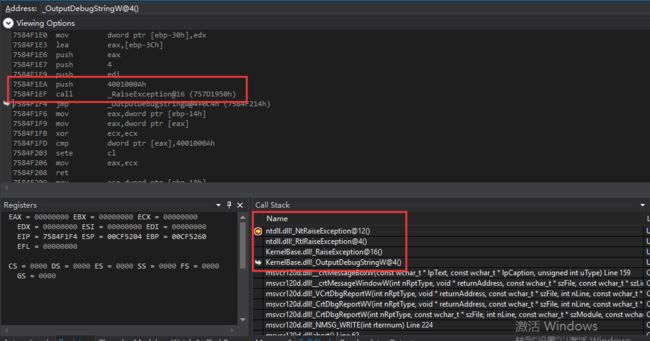
调用_NMSG_WRITE(_RT_ABORT),会引发异常0x4001000A或0x40010006:
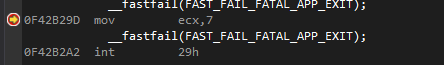
调用__fastfail(FAST_FAIL_FATAL_APP_EXIT);会引发异常0xc0000409子代码为FAST_FAIL_FATAL_APP_EXIT:
而调用_call_reportfault会引发异常STATUS_FATAL_APP_EXIT(0x40000015):
#if (defined (_M_IX86) || defined (_M_X64)) && !defined (_CRT_APP) void __cdecl _call_reportfault( int nDbgHookCode, DWORD dwExceptionCode, DWORD dwExceptionFlags ) { // Notify the debugger if attached. if (nDbgHookCode != _CRT_DEBUGGER_IGNORE) _CRT_DEBUGGER_HOOK(nDbgHookCode); /* Fake an exception to call reportfault. */ EXCEPTION_RECORD ExceptionRecord = {0}; CONTEXT ContextRecord; EXCEPTION_POINTERS ExceptionPointers = {&ExceptionRecord, &ContextRecord}; BOOL wasDebuggerPresent = FALSE; DWORD ret = 0; #if defined (_M_IX86) __asm { mov dword ptr [ContextRecord.Eax], eax mov dword ptr [ContextRecord.Ecx], ecx mov dword ptr [ContextRecord.Edx], edx mov dword ptr [ContextRecord.Ebx], ebx mov dword ptr [ContextRecord.Esi], esi mov dword ptr [ContextRecord.Edi], edi mov word ptr [ContextRecord.SegSs], ss mov word ptr [ContextRecord.SegCs], cs mov word ptr [ContextRecord.SegDs], ds mov word ptr [ContextRecord.SegEs], es mov word ptr [ContextRecord.SegFs], fs mov word ptr [ContextRecord.SegGs], gs pushfd pop [ContextRecord.EFlags] } ContextRecord.ContextFlags = CONTEXT_CONTROL; #pragma warning(push) #pragma warning(disable:4311) ContextRecord.Eip = (ULONG)_ReturnAddress(); ContextRecord.Esp = (ULONG)_AddressOfReturnAddress(); #pragma warning(pop) ContextRecord.Ebp = *((ULONG *)_AddressOfReturnAddress()-1); #elif defined (_M_X64) __crtCaptureCurrentContext(&ContextRecord); ContextRecord.Rip = (ULONGLONG) _ReturnAddress(); ContextRecord.Rsp = (ULONGLONG) _AddressOfReturnAddress()+8; #endif /* defined (_M_X64) */ ExceptionRecord.ExceptionCode = dwExceptionCode; ExceptionRecord.ExceptionFlags = dwExceptionFlags; ExceptionRecord.ExceptionAddress = _ReturnAddress(); wasDebuggerPresent = IsDebuggerPresent(); /* Raises an exception that bypasses all exception handlers. */ ret = __crtUnhandledException(&ExceptionPointers); // if no handler found and no debugger previously attached // the execution must stop into the debugger hook. if (ret == EXCEPTION_CONTINUE_SEARCH && !wasDebuggerPresent && nDbgHookCode != _CRT_DEBUGGER_IGNORE) { _CRT_DEBUGGER_HOOK(nDbgHookCode); } }