大家都知道,系统要展示一个 UIView ,必须要知道它的位置和大小。
在不使用 AutoLayout 的时候,我们通过设置 frame 属性来告诉系统这个 UIView 的位置和大小。
如果使用了 AutoLayout ,则需要我们为 UIView 添加一些约束来让系统自己计算 UIView 的位置和大小。
为什么会产生约束冲突
想要解决约束冲突,首先我们要先知道为什么会产生约束冲突。
场景一
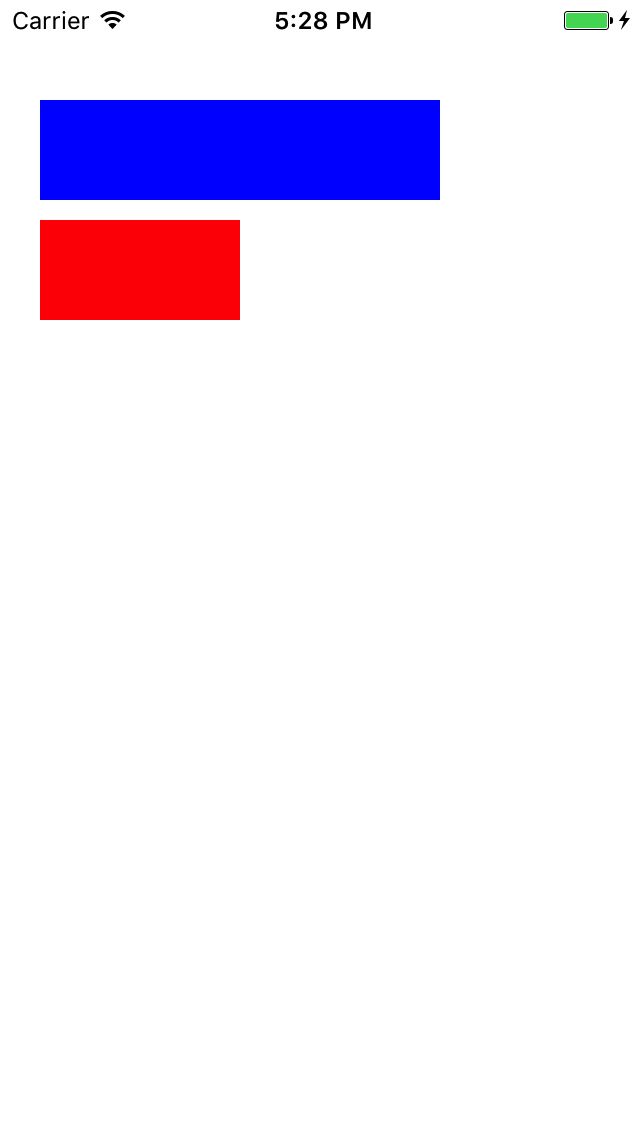
假设我有两个 UIView ,分别为 view1 和 view2 , view1 的位置和大小确定, view2 的顶部距离 view1 的底部距离固定, view2 的左边距、大小和 view1 相等。如以下代码:
[view1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.mas_equalTo(50);
make.left.mas_equalTo(20);
make.width.mas_equalTo(200);
make.height.mas_equalTo(50);
}];
[view2 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(view1.mas_bottom).offset(10);
make.left.height.width.equalTo(view1);
}];
这时,运行后的结果如下图:
这是一个最简单的使用 Masonry 布局例子。
场景二
如果我要给 view2 增加一个约束:宽度不能大于100,也就是如果 view1 的宽度小于100时,我要让 view2 的宽度等于 view1 的宽度,而如果 view1 的宽度大于100时, view2 的宽度等于100。如果直接这样设置 view2 的约束:
[view2 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(view1.mas_bottom).offset(10);
make.left.height.width.equalTo(view1);
make.width.mas_lessThanOrEqualTo(100);
}];
那么系统会报警告,提示约束冲突:
Unable to simultaneously satisfy constraints.
Probably at least one of the constraints in the following list is one you don't want.
Try this:
(1) look at each constraint and try to figure out which you don't expect;
(2) find the code that added the unwanted constraint or constraints and fix it.
(
"",
"",
""
)
Will attempt to recover by breaking constraint
Make a symbolic breakpoint at UIViewAlertForUnsatisfiableConstraints to catch this in the debugger.
The methods in the UIConstraintBasedLayoutDebugging category on UIView listed in may also be helpful.
那么为什么会产生这样的冲突呢?原因很简单,view1 的宽度等于200,而 view2 的宽度等于 view1 的宽度,所以它的宽度也应为200,但 view2 的宽度不能大于100,所以系统不知道 view2 的宽度到底是多少。
解决约束冲突
通过上面这个例子,就引出了我们解决约束冲突的方法:设置优先级。
当两个约束产生冲突时,iOS会弃用优先级低的约束,而选择优先级较高的约束,达到正确布局的效果。
所以,针对上面那种情况,我们只需将 view2 的约束写为以下这种就行了:
[view2 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.equalTo(view1.mas_bottom).offset(10);
make.left.height.equalTo(view1);
make.width.equalTo(view1).priorityLow();
make.width.mas_lessThanOrEqualTo(100);
}];
效果如下图:
延伸--IntrinsicContentSize
大家可能有时会发现,我们在设置 UILabel 的约束时,可以不设置它的大小约束,这样它就会根据自己的内容(文字)来确定它的大小。如一下场景:
场景三
两个 UILabel,分别为 label1 和 label2 ,其中 label1 左边距和上边距确定, label2 的上边距和 label1 相同,左边距离 label1 的右边距离确定,如以下约束:
[label1 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.top.mas_equalTo(200);
make.left.mas_equalTo(20);
}];
[label2 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.left.equalTo(label1.mas_right).offset(10);
make.top.equalTo(label1);
}];
我们并没有设置两个 UILabel 的大小约束,运行效果如下:
可以发现,两个 UILabel 的宽度和高度都根据它们的内容来设置了。而这是为什么呢?原来 UIView 具有一个属性: CGSize intrinsicContentSize ,含义如下:
Intrinsic Content Size:固有大小。
顾名思义,在AutoLayout中,如果没有指定大小,那么 UIView 的大小就按照 intrinsicContentSize 来设置。
所以,虽然我们没有设置这两个 UILabel 的大小约束,它们还是根据自己的内容设置好了大小,展示出来。
CGSize intrinsicContentSize 这个属性是 readOnly 的,所以如果我们要修改它,需要定义一个子类,重写这个属性的 getter 方法。
值得一提的是如果我们不想使用这个属性,则可以在重写的 getter 方法中直接返回 return CGSizeMake(UIViewNoIntrinsicMetric, UIViewNoIntrinsicMetric); 就行了。
场景四
现在,我要增加一个 label2 的约束:让它的右边距距离父视图的最右边20px,如下:
[label2 mas_makeConstraints:^(MASConstraintMaker *make) {
make.left.equalTo(label1.mas_right).offset(10);
make.top.equalTo(label1);
make.right.equalTo(self.view.mas_right).offset(-20);
}];
此时,就产生了一个问题:正常情况下, label2 的最右边是不可能只距离父视图20px的,这就使得肯定有一个 UILabel 不能使用它的 intrinsicContentSize 了,那么应该修改哪个 UILabel 的宽度来让 label2 满足这个约束呢?
解决方案还是设置优先级,但这次我们需要设置的是两种约束的优先级: contentHugging 和 contentCompressionResistance。
contentHugging(不想变大约束):如果组件的此属性优先级比另一个组件此属性优先级高的话,那么这个组件就保持不变,另一个可以在需要拉伸的时候拉伸。
contentCompressionResistance (不想变小约束):如果组件的此属性优先级比另一个组件此属性优先级高的话,那么这个组件就保持不变,另一个可以在需要压缩的时候压缩。
所以,如果我们需要 label1 不使用 intrinsicContentSize , label2 使用 intrinsicContentSize ,则可以将 label1 的contentHugging 优先级设为低优先级,反之,如果我们需要 label1 使用 intrinsicContentSize ,则可以将其 contentHugging 的优先级设为高优先级。
那么怎么设置它们这两个约束的优先级呢?
UIView 提供了两个方法给我们设置它的这两个约束的优先级:
- (void)setContentHuggingPriority:(UILayoutPriority)priority forAxis:(UILayoutConstraintAxis)axis;
- (void)setContentCompressionResistancePriority:(UILayoutPriority)priority forAxis:(UILayoutConstraintAxis)axis;
其中,第一个参数为优先级,具体有以下几种:
static const UILayoutPriority UILayoutPriorityRequired NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(6_0) = 1000; // A required constraint. Do not exceed this.
static const UILayoutPriority UILayoutPriorityDefaultHigh NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(6_0) = 750; // This is the priority level with which a button resists compressing its content.
static const UILayoutPriority UILayoutPriorityDefaultLow NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(6_0) = 250; // This is the priority level at which a button hugs its contents horizontally.
static const UILayoutPriority UILayoutPriorityFittingSizeLevel NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(6_0) = 50;
当然,你也可以自己通过数字来设置它们的优先级。
第二个参数代表你要设置约束优先级的方向,分为横向和纵向:
typedef NS_ENUM(NSInteger, UILayoutConstraintAxis) {
UILayoutConstraintAxisHorizontal = 0,
UILayoutConstraintAxisVertical = 1
};
以上场景,我们可以通过以下代码来让 label1 使用 intrinsicContentSize , label2 不使用 intrinsicContentSize :
[label1 setContentHuggingPriority:UILayoutPriorityDefaultHigh forAxis:UILayoutConstraintAxisHorizontal];
效果如下图: