axios
请求配置
这些是用于发出请求的可用配置选项。 只有url是必需的。 如果未指定方法,请求将默认为GET。
{
// `url`是将用于请求的服务器URL
url: '/user',
// `method`是发出请求时使用的请求方法
method: 'get', // 默认
// `baseURL`将被添加到`url`前面,除非`url`是绝对的。
// 可以方便地为 axios 的实例设置`baseURL`,以便将相对 URL 传递给该实例的方法。
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
// `transformRequest`允许在请求数据发送到服务器之前对其进行更改
// 这只适用于请求方法'PUT','POST'和'PATCH'
// 数组中的最后一个函数必须返回一个字符串,一个 ArrayBuffer或一个 Stream
transformRequest: [function (data) {
// 做任何你想要的数据转换
return data;
}],
// `transformResponse`允许在 then / catch之前对响应数据进行更改
transformResponse: [function (data) {
// Do whatever you want to transform the data
return data;
}],
// `headers`是要发送的自定义 headers
headers: {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'},
// `params`是要与请求一起发送的URL参数
// 必须是纯对象或URLSearchParams对象
params: {
ID: 12345
},
// `paramsSerializer`是一个可选的函数,负责序列化`params`
paramsSerializer: function(params) {
return Qs.stringify(params, {arrayFormat: 'brackets'})
},
// `data`是要作为请求主体发送的数据(如果将headers修改为json格式不起作用,那么就需要把params改为data)
// 仅适用于请求方法“PUT”,“POST”和“PATCH”
// 当没有设置`transformRequest`时,必须是以下类型之一:
// - string, plain object, ArrayBuffer, ArrayBufferView, URLSearchParams
// - Browser only: FormData, File, Blob
// - Node only: Stream
data: {
firstName: 'Fred'
},
// `timeout`指定请求超时之前的毫秒数。
// 如果请求的时间超过'timeout',请求将被中止。
timeout: 1000,
// `withCredentials`指示是否跨站点访问控制请求
// should be made using credentials
withCredentials: false, // default
// `adapter'允许自定义处理请求,这使得测试更容易。
// 返回一个promise并提供一个有效的响应(参见[response docs](#response-api))
adapter: function (config) {
/* ... */
},
// `auth'表示应该使用 HTTP 基本认证,并提供凭据。
// 这将设置一个`Authorization'头,覆盖任何现有的`Authorization'自定义头,使用`headers`设置。
auth: {
username: 'janedoe',
password: 's00pers3cret'
},
// “responseType”表示服务器将响应的数据类型
// 包括 'arraybuffer', 'blob', 'document', 'json', 'text', 'stream'
responseType: 'json', // default
//`xsrfCookieName`是要用作 xsrf 令牌的值的cookie的名称
xsrfCookieName: 'XSRF-TOKEN', // default
// `xsrfHeaderName`是携带xsrf令牌值的http头的名称
xsrfHeaderName: 'X-XSRF-TOKEN', // default
// `onUploadProgress`允许处理上传的进度事件
onUploadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// 使用本地 progress 事件做任何你想要做的
},
// `onDownloadProgress`允许处理下载的进度事件
onDownloadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// Do whatever you want with the native progress event
},
// `maxContentLength`定义允许的http响应内容的最大大小
maxContentLength: 2000,
// `validateStatus`定义是否解析或拒绝给定的promise
// HTTP响应状态码。如果`validateStatus`返回`true`(或被设置为`null` promise将被解析;否则,promise将被
// 拒绝。
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status >= 200 && status < 300; // default
},
// `maxRedirects`定义在node.js中要遵循的重定向的最大数量。
// 如果设置为0,则不会遵循重定向。
maxRedirects: 5, // 默认
// `httpAgent`和`httpsAgent`用于定义在node.js中分别执行http和https请求时使用的自定义代理。
// 允许配置类似`keepAlive`的选项,
// 默认情况下不启用。
httpAgent: new http.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
httpsAgent: new https.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
// 'proxy'定义代理服务器的主机名和端口
// `auth`表示HTTP Basic auth应该用于连接到代理,并提供credentials。
// 这将设置一个`Proxy-Authorization` header,覆盖任何使用`headers`设置的现有的`Proxy-Authorization` 自定义 headers。
proxy: {
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 9000,
auth: : {
username: 'mikeymike',
password: 'rapunz3l'
}
},
// “cancelToken”指定可用于取消请求的取消令牌
// (see Cancellation section below for details)
cancelToken: new CancelToken(function (cancel) {
})
}
var instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
timeout: 1000,
headers: {'X-Custom-Header': 'foobar'}
});
//等价于
axios({
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
timeout: 1000,
headers: {'X-Custom-Header': 'foobar'}
})
使用 then 时,您将收到如下响应:
axios.get('/user/12345')
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response.data);
console.log(response.status);
console.log(response.statusText);
console.log(response.headers);
console.log(response.config);
});
目录搭建
一般项目都要在src下加一个api目录,里面封装你的接口。然后再建一个helpers目录里面有一个request.js是对你的接口进行操作的代码。
request.js
-
axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type']
用来设置post请求的文本类
axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
-
axios.defaults.baseURL
接口默认的基础路径,写这个后面我们对接口进行操作的时候就不需要传http....,只要需要传一个相对路径就可以了。
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://blog-server.hunger-vallery.com'
-
axios.defaults.withCredentials = true
默认情况下当接口和前台页面不在一个域名下,就会有跨域问题,我们可以对接口设置允许跨域,但是跨域操作不会带上你的cookie,这样就没法验证你的信息,所以需要我们设置axios.defaults.withCredentials = true也就是跨域情况下也带上cookie。
当前案例下的代码
import axios from 'axios'
import {Message} from 'element-ui'
axios.defaults.headers.post['Content-Type'] = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://blog-server.hunger-valley.com'
axios.defaults.withCredentials = true
export default function request(url,type='GET',data={}){
return new Promise((resolve, reject)=>{
let option = {
url,
method: type
}
if(type.toLowerCase() === 'get'){
option.params = data
}else {
option.data = data
}
axios(option).then(res=>{
if(res.data.status === 'ok'){
resolve(res.data)
}else {
Message.error(res.data.msg)
reject(res.data)
}
}).catch(err=>{
Message.error('网络异常')
reject({msg: '网络异常'})
})
})
}
在api文件下创建auth.js和blog.js
小窍门:在对接口进行封装操作的时候每个函数中都要写return,这样就都可以返回一个promise了
- atuh.js
import request from '@/helpers/request.js'
const url = {
Register: '/auth/register',
Login: '/auth/login',
Logout: '/auth/logout',
GetInfo: '/auth'
}
export default {
register({username,password}){
//这里之所以要return是因为request()调用后就是一个new Promise
//所以你return它,就可以继续.then
return request(url.Register,'POST',{username,password})
},
login({username,password}){
return request(url.Login, 'POST',{username,password})
},
logout(){
return request(url.Logout)
},
getInfo(){
return request(url.GetInfo)
}
}
通过上面的封装我们就可以直接引入这个文件,然后
auth.register({username:'wang',password:'123456'}).then(data=>{console.log(data)})
vuex的使用
使用vuex在state里声明一些全局都可以使用的属性,如isLogin和user
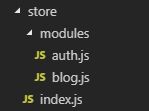
目录结构,在当前目录下建一个store里面有一个modules目录和index.js,modules目录下有auth.js和blog.js
auth.js主要是对用户的操作,如登录和注销,代码如下
import auth from '@/api/auth'
const state = {
user: null,
isLogin: false
}
//这里之所以在getters里又声明了一个user和isLogin
//是因为如果不声明你在其他地方使用都得是auth.user和auth.isLogin
//在getters里声明了我们就可以不用写auth.了
const getters = {
user:state=>state.user,
isLogin:state=>state.isLogin
}
const mutations = {
setUser(state,payload){
state.user = payload.user
},
setLogin(state,payload){
state.isLogin = payload.isLogin
}
}
//actions中都是异步操作也就是ajax和端口的请求都写这
const actions = {
//声明一个login函数,这是一个登录
//传入一个context.commit和我们需要传入的参数
login({commit},{username,password}){
return auth.login({username,password})
.then(res=>{
//成功后触发mutations里里的方法
commit('setUser',{user:res.data})
commit('setLogin',{isLogin: true})
})
},
//注册
async register({commit},{username,password}){
let res = await auth.register({username,password})
commit('setUser',{user:res.data})
commit('setLogin',{isLogin: true})
return res.data
},
//es6语法等同于上面的
//注销
async logout({commit}){
await auth.logout()
commit('setUser',{user: null})
commit('setLogin',{isLogin: false})
},
//检测是否登录
// async checkLogin({commit,state}){
// if(state.isLogin) return true
// let res = await auth.getInfo()
// commit('setLogin',{isLogin:res.isLogin})
// if(!res.isLogin) return false
// commit('setUser',{user: red.data})
// return true
// }
checkLogin({commit,state}){
return auth.getInfo()
.then(res=>{
//请求成功后isLogin就等于你res.isLogin
commit('setLogin',{isLogin:res.isLogin})
//如果是true说明登录了,就需要设置用户信息,也就是触发setUser
if(state.isLogin){
commit('setUser',{user:res.data})
//这里之所以还要return是因为我们是返回的一个promise.then()也就是下一次对它.then()的时候也就是对promise.then()的返回值进行处理,所以在.then()里要return要不然就是undefined
return true
}else{
return false
}
})
}
}
export default {
state,
getters,
mutations,
actions
}
在header.vue中写
Let's share
精品博客汇聚
立即登录 注册账号 Let's share
![]()
我的 - 注销
登录页面login.vue
用户名
密码
立即登录
没有账号?注册新用户
通过上面的代码我们可以实现简单的登录注册,但是这里的问题是有一些页面是只能登录后才可以看得,这里就需要通过路由守卫对权限进行验证,使用方法:在需要权限验证的路由里面写一个meta,里面一般写{requiresAuth: true}
在router里的index.js里面写
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Login from '@/pages/Login/login.vue'
import store from '@/store/index.js'
const Edit=()=>import('@/pages/Edit/edit.vue')
const Create=()=>import('@/pages/Create/create.vue')
const Index=()=>import('@/pages/Index/index.vue')
const My = ()=>import('@/pages/My/my.vue')
const Register = ()=>import('@/pages/Register/register.vue')
const User = ()=>import('@/pages/User/user.vue')
const Detail = ()=>import('@/pages/Detail/detail.vue')
Vue.use(Router)
const router = new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/login',
component: Login
},
{
path: '/edit/:blogId',
component: Edit,
meta: {requiresAuth: true}
},
{
path: '/detail/:blogId',
component: Detail,
meta: {requiresAuth: true}
},
{
path: '/create',
component: Create
},
{
path: '/',
component: Index
},
{
path: '/my',
component: My
},
{
path: '/user/:userId',
component: User,
meta: {requiresAuth: true}
},
{
path: '/register',
component: Register
}
]
})
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
//检查每一个路由里面是否有requiresAuth存在,
// 如果有就对权限进行验证,然后如果登录才能跳到指定目录,否则直接跳到登录
// 如果没有就直接跳到指定目录
if(to.matched.some(record=>record.meta.requiresAuth)){
//这里要注意因为isLogin是通过异步修改的,所以我们也要在异步方法中判断它是否登录
//触发actions里的checkLogin方法
store.dispatch('checkLogin')
.then(isLogin=>{
//如果没登录就直接跳到login并且带上当前的路径参数,然后登陆完会直接回到这个页面,所以这里需要对点击登录按钮的路由的路径做判断
//在login.js里修改为
//onlogin(){
//this.login({username:this.username,password:this.password})
// .then(res=>{
//this.$router.push({path:this.$route.query.redirect || '/'})
// })
// }
if(!isLogin){
next({
path: '/login',
query: {redirect: to.fullPath}
})
}else{
next()
}
})
}else{
next()
}
})
export default router
创建博客页面的实现create.vue
创建文章
文章标题
限30个字
内容简介
限30个字
文章内容
限30个字
确定
首页index.vue
![]()
{{blog.user.username}}
{{blog.title}} {{blog.updatedAt}}
{{blog.description}}
详情页detail.vue
自定义插件
如果很多组件中都会使用某一方法,我们可以把这个方法写成插件,也就是使用
//util.js
install(Vue,options){
Vue.prototype.定义的插件名=你的方法
}
之后我们只需要在mian.js里引入它,然后通过Vue.use(名字)使用它即可
这里以时间插件为例:
util.js
function friendlyDate(datsStr){
let dateObj = typeof datsStr === 'object' ? datsStr : new Date(datsStr)
let time = dateObj.getTime()
let now = Date.now()
let space = now - time
let str = ''
switch(true){
case space < 60000:
str = '刚刚'
break
case space < 1000 * 3600:
str = Math.floor(space/60000) + '分钟前'
break
case space < 1000*3600*24:
str = Math.floor(space/(1000*3600)) + '小时前'
break
default:
str = Math.floor(space/(1000*3600*24)) + '天前'
}
return str
}
export default {
install(Vue,options){
Vue.prototype.friendlyDate = friendlyDate
}
}
main.js
import Util from '@/helpers/util'
Vue.use(Util)
然后在其他组件中就可以使用了
//detail.vue
{{friendlyDate(createdAt)}}
我的页面my.vue
20
5月
2018
{{blog.title}}
{{blog.description}}
编辑
删除
编辑页面edit.vue
template>
编辑文章
文章标题
限30个字
内容简介
限30个字
文章内容
限30个字
确定