今天看cisco的文档,发现一条命令,bgp client-to-client reflection。这两天在实验室学习BGP,发现好多属性自己研究的都不够透彻。回来翻翻TCP/IP路由技术,发现以前在这个知识带你还划过重点,怎么又忘了。看来还是要多做试验才能深刻认识,温故知新,又学到了新东西。
下面是TCP/IP路由技术上对client-to-client的试验。
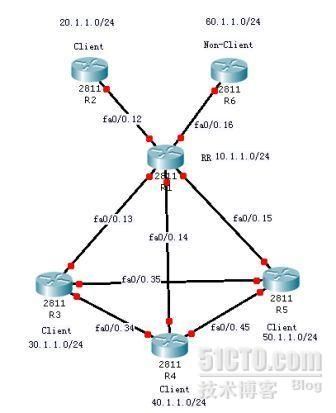
拓扑如下:
所有路由器都处于同一个AS1中。R1,R3,R4,R6建立full-mesh的对等体关系。R3,R4,R5,R6作为R1的客户端,R2为非客户端,R1为RR。
所有路由器建立IGP(ospf)互联,每个路由器的loopback0口宣告进ospf。
每个路由器的loopback1口宣告进BGP。
基本配置如下:
R1
R1#sh ip int b
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 unassigned YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.12 12.1.1.1 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.13 13.1.1.1 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.14 14.1.1.1 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.15 15.1.1.1 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.16 16.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Loopback0 1.1.1.1 YES manual up up
Loopback1 10.1.1.1 YES manual up up
。。。(omit)
R1#sh run | b router
router ospf 10
router-id 1.1.1.1
log-adjacency-changes
network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 13.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 14.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 15.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 16.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router bgp 1
no synchronization
bgp router-id 1.1.1.1
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 12.1.1.2 remote-as 1
neighbor 13.1.1.3 remote-as 1
neighbor 13.1.1.3 route-reflector-client
neighbor 14.1.1.4 remote-as 1
neighbor 14.1.1.4 route-reflector-client
neighbor 15.1.1.5 remote-as 1
neighbor 15.1.1.5 route-reflector-client
neighbor 16.1.1.6 remote-as 1
neighbor 16.1.1.6 route-reflector-client
no auto-summary
R3.
R3#sh ip int b
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 unassigned YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.13 13.1.1.3 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.23 23.1.1.3 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.34 34.1.1.3 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.35 35.1.1.3 YES manual up up
Loopback0 3.3.3.3 YES manual up up
Loopback1 30.1.1.1 YES manual up up
。。。。。(omit)
R3#sh run | b router
router ospf 10
router-id 3.3.3.3
log-adjacency-changes
network 3.3.3.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 13.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 34.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 35.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router bgp 1
no synchronization
bgp router-id 3.3.3.3
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 30.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 13.1.1.1 remote-as 1
neighbor 34.1.1.4 remote-as 1
neighbor 35.1.1.5 remote-as 1
no auto-summary
R2.
R2#sh ip int b
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 unassigned YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.12 12.1.1.2 YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.23 23.1.1.2 YES manual up up
Loopback0 2.2.2.2 YES manual up up
Loopback1 20.1.1.1 YES manual up up
。。。。。(omit)
R2#sh run | b router
router ospf 10
router-id 2.2.2.2
log-adjacency-changes
network 2.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 12.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router bgp 1
no synchronization
bgp router-id 2.2.2.2
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 20.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 12.1.1.1 remote-as 1
no auto-summary
R6.
R6#sh ip int b
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 unassigned YES manual up up
FastEthernet0/0.16 16.1.1.6 YES manual up up
Loopback1 60.1.1.1 YES manual up up
。。。。。(omit)
R6#sh run | b router
router ospf 10
router-id 6.6.6.6
log-adjacency-changes
network 6.6.6.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 16.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router bgp 1
no synchronization
bgp router-id 6.6.6.6
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 60.1.1.0 mask 255.255.255.0
neighbor 16.1.1.1 remote-as 1
no auto-summary
下面看看R3的BGP路由表
R3#sh ip b
。。。。。(omit)
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i10.1.1.0/24 13.1.1.1 0 100 0 i
*>i20.1.1.0/24 12.1.1.2 0 100 0 i
*> 30.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i40.1.1.0/24 14.1.1.4 0 100 0 i
*>i 34.1.1.4 0 100 0 i
* i50.1.1.0/24 15.1.1.5 0 100 0 i
*>i 35.1.1.5 0 100 0 i
*>i60.1.1.0/24 16.1.1.6 0 100 0 i
在看看R1向R3发送了那些路由
R1#sh ip b nei 13.1.1.3 ad
R1#sh ip b nei 13.1.1.3 advertised-routes
。。。。(omit)
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i20.1.1.0/24 12.1.1.2 0 100 0 i
*>i40.1.1.0/24 14.1.1.4 0 100 0 i
*>i50.1.1.0/24 15.1.1.5 0 100 0 i
*>i60.1.1.0/24 16.1.1.6 0 100 0 i
R1#
因为R3,R4.R5建立了full-mesh的路由关系,所以除了RR向其传送40/50.1.1.0的路由外,他自己也是可以从对等体学到这些路由的。这样就存在一点浪费。
下面在R1的BGP进程下敲上这条命令:no bgp client-to-client reflection
再来看看R1向R3发送了那些路由。
R1#sh ip b nei 13.1.1.3 ad
。。。。(omit)
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*>i20.1.1.0/24 12.1.1.2 0 100 0 i
如上所示,他总发送了自己和非客户端R2的路由,其他客户端对等体的路由都没有发送。这就是这条命令的作用。
敲上这条命令的前提是所有客户端都建立了full-mesh的邻接关系!RR不会在客户之间反射路由,但仍然可以把客户端的路由反射给非客户端,也将非客户端的路由反射给客户端。
如本例,R6并没有与所有的客户端建立full-mesh的邻接关系,因此,打上这条命令后它将学不到其他对等体客户端的路由。
R6#sh ip b
BGP table version is 18, local router ID is 6.6.6.6
Status codes: s suppressed, d damped, h history, * valid, > best, i - internal,
r RIB-failure, S Stale
Origin codes: i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i10.1.1.0/24 16.1.1.1 0 100 0 i
*>i20.1.1.0/24 12.1.1.2 0 100 0 i
*> 60.1.1.0/24 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i