关于Runtime的概念网上很多资料可供参考,本文不做介绍。文章将重点放在核心源码的分析及梳理消息转发机制,所以本文需要一定的Runtime基础。
一、 对象及方法本质
1. 首先我们用最简单的对象调用方法来一步一步深入解析:
#import
#include
#import "Person.h"
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
Person*p = [[Person alloc]init];
[p run];
return 0;
}
}
2. 通过下面的命令将.m文件转换为C++文件:
clang -rewrite-objc main.m -o test.c++
3. 编译的文件有98906行,最终main的核心文件如下:
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) {
/* @autoreleasepool */ { __AtAutoreleasePool __autoreleasepool;
Person*p = ((Person *(*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)((Person *(*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)objc_getClass("Person"), sel_registerName("alloc")), sel_registerName("init"));
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)p, sel_registerName("run"));
return 0;
}
}
- 3.1 由此可得,对象调用方法的本质是发送消息:
((void (*)(id, SEL))(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)p, sel_registerName("run"));
//(void *)objc_msgSend)((id)p 消息接受者
// sel_registerName("run") 方法编号
- 3.2 对象的本质是结构体:
#ifndef _REWRITER_typedef_Person
#define _REWRITER_typedef_Person
typedef struct objc_object Person;
typedef struct {} _objc_exc_Person;
#endif
struct Person_IMPL {
struct NSObject_IMPL NSObject_IVARS;
};
二、Runtime核心源码解析
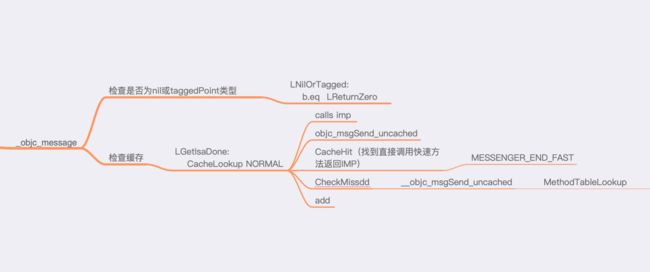
1. 通过在objc源码中搜索arm64架构下的_objc_msgSend,在ENTRY _objc_msgSend,首先会进行缓存检查和类型判断,LNilOrTagged此处会判断是否为nil或taggedPoint类型,如果是,则直接返回。taggedPoint是用来存储小值类型,其地址中包含值和类型数据,可以进行快速的访问数据,提高性能。
LGetIsaDone:
CacheLookup NORMAL
LNilOrTagged:
b.eq LReturnZero // nil check
// tagged
mov x10, #0xf000000000000000
cmp x0, x10
b.hs LExtTag
adrp x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_classes@PAGE
add x10, x10, _objc_debug_taggedpointer_classes@PAGEOFF
ubfx x11, x0, #60, #4
ldr x16, [x10, x11, LSL #3]
b LGetIsaDone
2. 如果不为nil,通过汇编指令b LGetIsaDone跳转到CacheLookup,来对缓存进行快速的查找,如果有缓存就直接返回,由于这一步是通过汇编执行,所以是快速查找,效率很高,查找过程如下图:
3. 如果缓存没有,将会进入慢速查找过程,核心方法为MethodTableLookup
STATIC_ENTRY __objc_msgSend_uncached
UNWIND __objc_msgSend_uncached, FrameWithNoSaves
// THIS IS NOT A CALLABLE C FUNCTION
// Out-of-band x16 is the class to search
//方法列表
MethodTableLookup
br x17
END_ENTRY __objc_msgSend_uncached
4. 通过MethodTableLookup方法的调用,会从汇编跳转到C/C++,所以说runtime是由汇编,C/C++组成的一套API
IMP _class_lookupMethodAndLoadCache3(id obj, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
return lookUpImpOrForward(cls, sel, obj,
YES/*initialize*/, NO/*cache*/, YES/*resolver*/);
}
5. 接下来看下lookUpImpOrForward核心代码:
retry:
runtimeLock.assertReading();
// 如果缓存中有IMP,直接返回
imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel);
if (imp) goto done;
// 如果没有,先找自己的IMP,找到加入方法缓存
{
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(cls, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, cls);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
// 自己没有,找父类,一直找到NSObject,因为NSObject的父类为nil,下面的条件是curClass != nil
{
unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();
for (Class curClass = cls->superclass;
curClass != nil;
curClass = curClass->superclass)
{
// 内存溢出相关
if (--attempts == 0) {
_objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list.");
}
// 先从父类缓存中找IMP
imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel);
if (imp) {
if (imp != (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) {
// 在父类中找到IMP,加入缓存
log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass);
goto done;
}
else {
// Found a forward:: entry in a superclass.
// Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method
// resolver for this class first.
break;
}
}
// Superclass method list.
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
log_and_fill_cache(cls, meth->imp, sel, inst, curClass);
imp = meth->imp;
goto done;
}
}
}
// 没有IMP,调用一次resolver动态方法解析,通过triedResolver变量来控制该方法只走一次
if (resolver && !triedResolver) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_resolveMethod(cls, sel, inst);
runtimeLock.read();
// Don't cache the result; we don't hold the lock so it may have
// changed already. Re-do the search from scratch instead.
triedResolver = YES;
goto retry;
}
// 没有IMP,也没有resolver,调用forwarding进行消息转发
imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
cache_fill(cls, sel, imp, inst);
done:
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
return imp;
- 5.1 过程就是先找自己,如果自己没有IMP,然后找父类的缓存,如果没有,循环查找父类的IMP,一直找到NSObject,如果还是没有,接下来就开始动态方法解析,如果动态方法解析没有实现,接下来再调用消息转发,流程如下图:
6. 动态方法解析调用如下
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel{
if (sel == @selector(run)) {
NSLog(@"===== 对象方法解析 ========");
SEL myRunSEL = @selector(myRun);
Method myRunSELM= class_getInstanceMethod(self, myRunSEL);
IMP myRunImp = method_getImplementation(myRunSELM);
const char *type = method_getTypeEncoding(myRunSELM);
return class_addMethod(self, sel, myRunImp, type);
}
return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel];
}
+ (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel{
if (sel == @selector(run)) {
NSLog(@" ====== 类方法解析 =======");
SEL myRunSEL = @selector(myRun);
//打印hellowordM1和hellowordM会发现地址一样
//说明类方法在元类中是以实例方法的形式存在的
// Method hellowordM1= class_getClassMethod(self, hellowordSEL);
Method myRunM= class_getInstanceMethod(object_getClass(self), myRunSEL);
IMP myRunImp = method_getImplementation(myRunM);
const char *type = method_getTypeEncoding(myRunM);
NSLog(@"%s",type);
return class_addMethod(object_getClass(self), sel, myRunImp, type);
}
return [super resolveClassMethod:sel];
}
7. 消息转发调用如下:
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
// if (aSelector == @selector(run)) {
// return [Person new];
// }
return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
if (aSelector == @selector(run)) {
// forwardingTargetForSelector 没有实现 就只能方法签名了
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod(object_getClass(self), @selector(readBook));
const char *type = method_getTypeEncoding(method);
return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@:@"];
}
return [super methodSignatureForSelector:aSelector];
}
- (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation{
NSLog(@"%s",__func__);
NSLog(@"------%@-----",anInvocation);
anInvocation.selector = @selector(readBook);
[anInvocation invoke];
}
8. 消息转发流程图如下:
三、使用runtime实现万能跳转
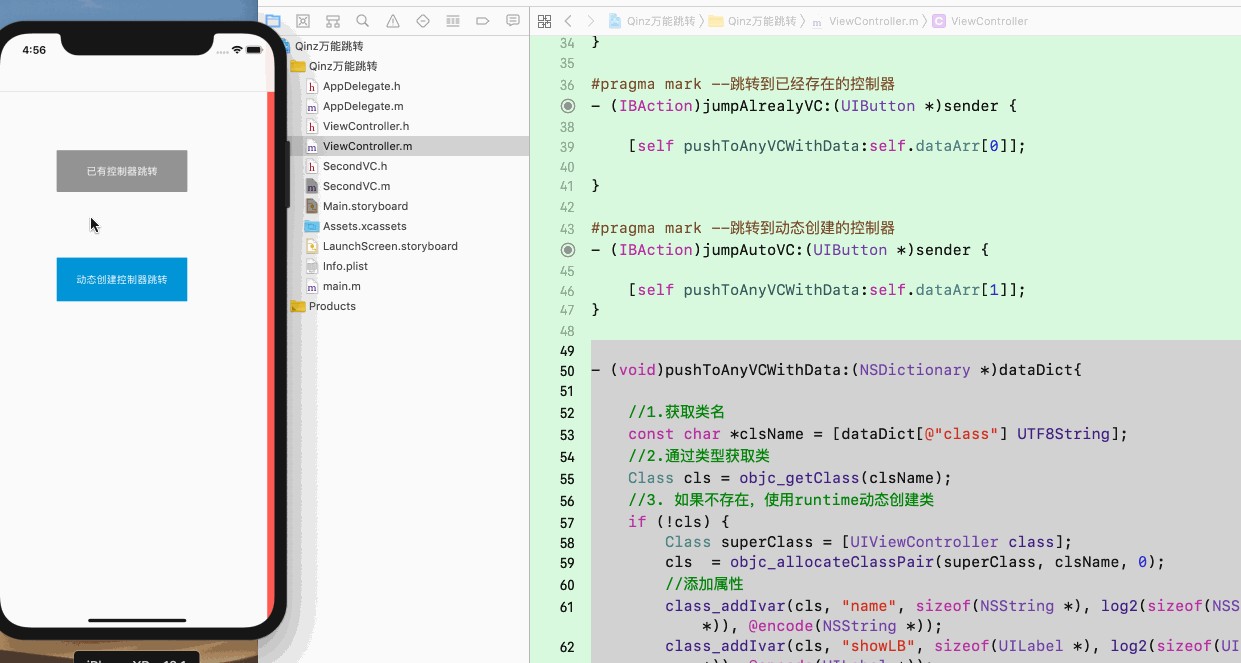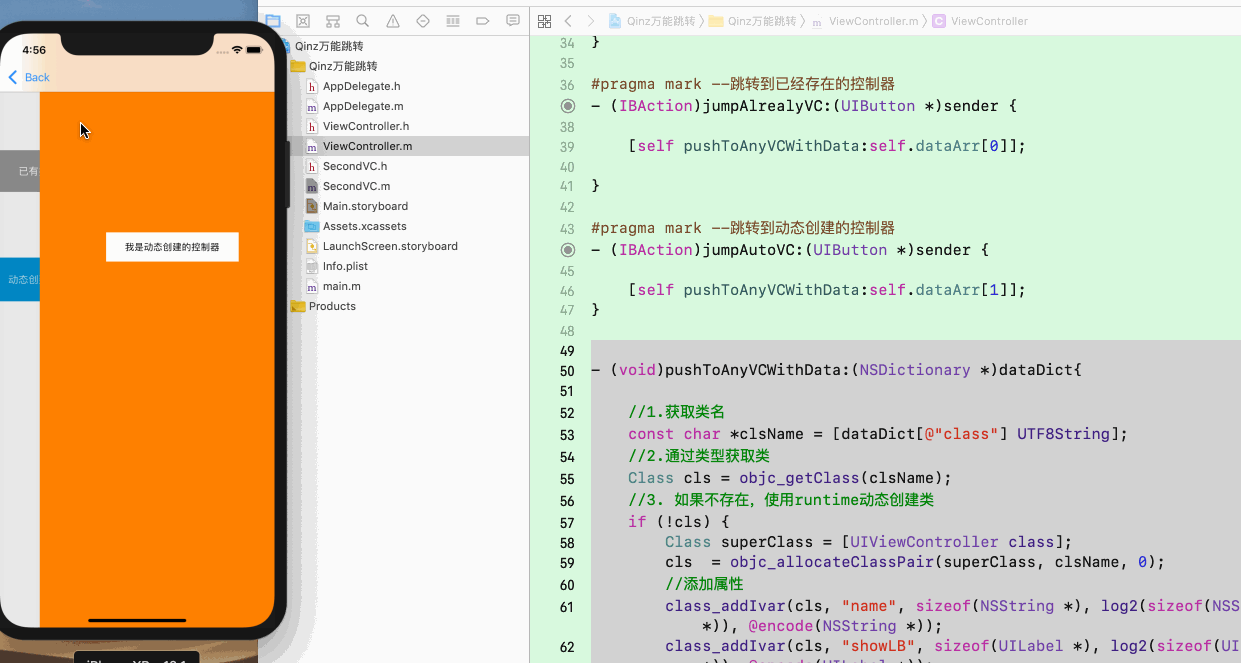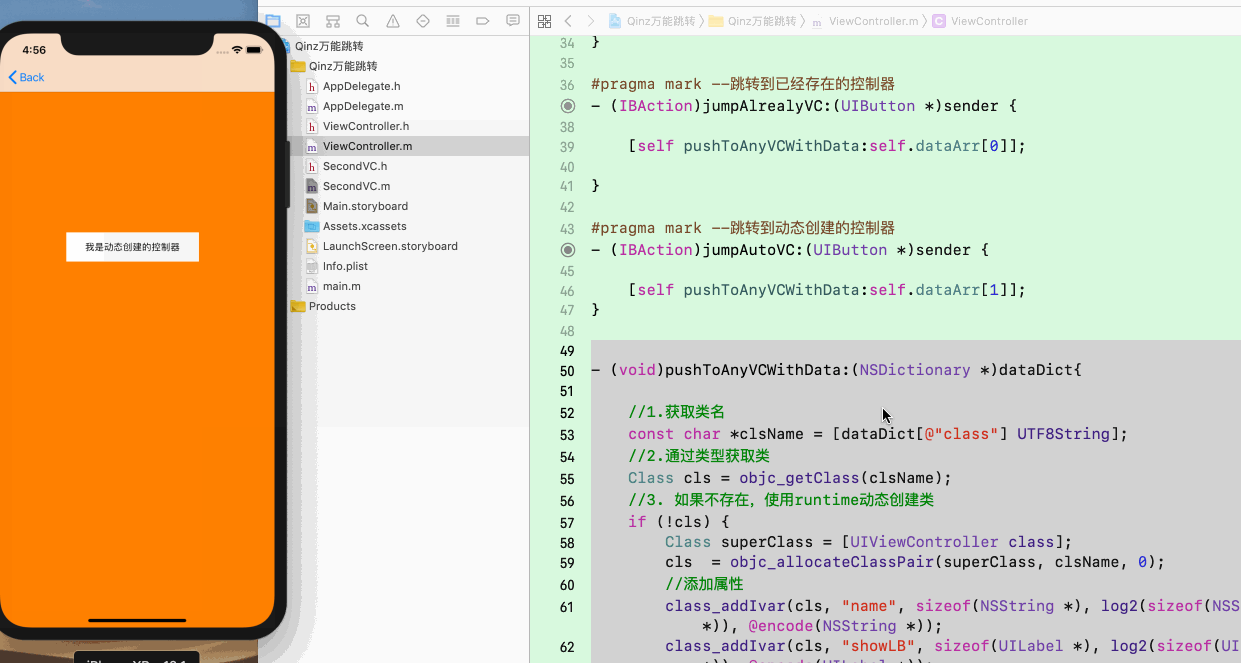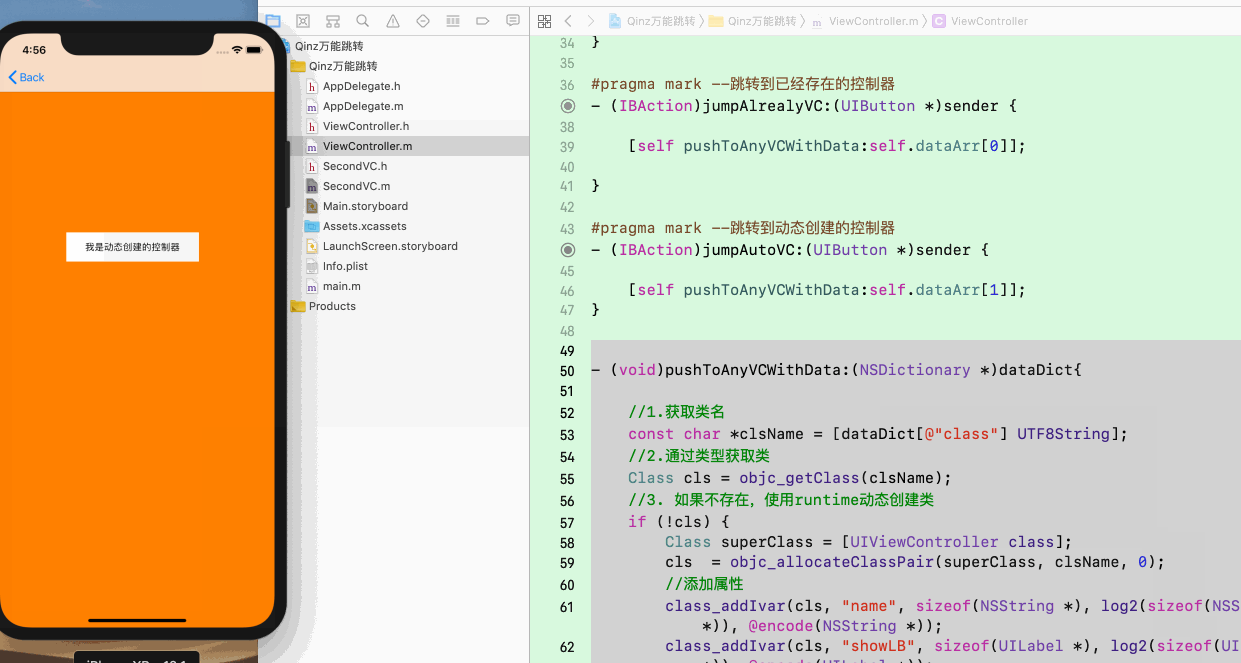
1. 首先模拟简单的后台返回数据,下面的QinzVC为项目中不存在的控制器:
self.dataArr = @[
@{@"class":@"SecondVC",
@"data":@{@"name":@"小明"}},
@{@"class":@"QinzVC",
@"data":@{@"name":@"我是动态创建的控制器"}},
];
2. 针对存在的控制器和不存在的控制器进行跳转,下面代码中有详细注释:
- (void)pushToAnyVCWithData:(NSDictionary *)dataDict{
//1.获取类名
const char *clsName = [dataDict[@"class"] UTF8String];
//2.通过类型获取类
Class cls = objc_getClass(clsName);
//3. 如果不存在,使用runtime动态创建类
if (!cls) {
Class superClass = [UIViewController class];
cls = objc_allocateClassPair(superClass, clsName, 0);
//添加属性
class_addIvar(cls, "name", sizeof(NSString *), log2(sizeof(NSString *)), @encode(NSString *));
class_addIvar(cls, "showLB", sizeof(UILabel *), log2(sizeof(UILabel *)), @encode(UILabel *));
//注册类
objc_registerClassPair(cls);
//添加方法
Method method = class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(myInstancemethod));
IMP methodIMP = method_getImplementation(method);
const char *types = method_getTypeEncoding(method);
BOOL result = class_addMethod(cls, @selector(viewDidLoad), methodIMP, types);
if (result) {
NSLog(@"=== 方法添加成功 =====");
}
}
// 实例化对象
id instance = nil;
@try {
//先尝试从SB中加载
UIStoryboard *sb = [UIStoryboard storyboardWithName:@"Main" bundle:[NSBundle mainBundle]];
instance = [sb instantiateViewControllerWithIdentifier:dataDict[@"class"]];
} @catch (NSException *exception) {
//SB中没有直接初始化
instance = [[cls alloc] init];
} @finally {
NSLog(@"控制器实例化完成");
}
//获取后台返回的数据,给属性赋值
NSDictionary *dict = dataDict[@"data"];
[dict enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:^(id _Nonnull key, id _Nonnull obj, BOOL * _Nonnull stop) {
// 检测是否存在key的属性
if (class_getProperty(cls, [key UTF8String])) {
[instance setValue:obj forKey:key];
}
// 检测是否存在key的变量
else if (class_getInstanceVariable(cls, [key UTF8String])){
[instance setValue:obj forKey:key];
}
}];
[self.navigationController pushViewController:instance animated:YES];
}
- (void)myInstancemethod {
[super viewDidLoad];
[self setValue:[UIColor orangeColor] forKeyPath:@"view.backgroundColor"];
[self setValue:[[UILabel alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(100, 300, 200, 44)] forKey:@"showLB"];
UILabel *showTextLB = [self valueForKey:@"showLB"];
[[self valueForKey:@"view"] addSubview:showTextLB];
//设置属性
showTextLB.text = [self valueForKey:@"name"];
showTextLB.font = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:14];
showTextLB.textColor = [UIColor blackColor];
showTextLB.textAlignment = NSTextAlignmentCenter;
showTextLB.backgroundColor = [UIColor whiteColor];
}
3. 实现万能界面跳转的演示如下:
总结:runtime是由汇编,C/C++组成的一套API,苹果在发送消息做了很多优化处理,目的是使消息的发送更加有效率,同时runtime的应用也很广泛,如实现上面的万能跳转,当然还可以使用runtime实现页面统计,全局改变字体大小,逆向中进行Hook等。
我是Qinz,希望我的文章对你有帮助。