一、TensorBoard可视化工具
TensorBoard实现形式为web应用程序,这为提供分布式、跨系统的图形界面服务带来了便利。
1.使用流程
SummaryOps->Session--(input)-->FileWriter---(add)--->Event file---(load)-->TensorBoard
import tensorflow as tf with tf.name_scope('graph') as scope: matrix1 = tf.constant([[3., 3.]],name ='matrix1') #1 row by 2 column matrix2 = tf.constant([[2.],[2.]],name ='matrix2') # 2 row by 1 column product = tf.matmul(matrix1, matrix2,name='product') sess = tf.Session() writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("/data/logs/", sess.graph) #第一个参数指定生成文件的目录。 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init)
命令行执行 tensorboard --logdir=/data/logs
打开localhost:6006
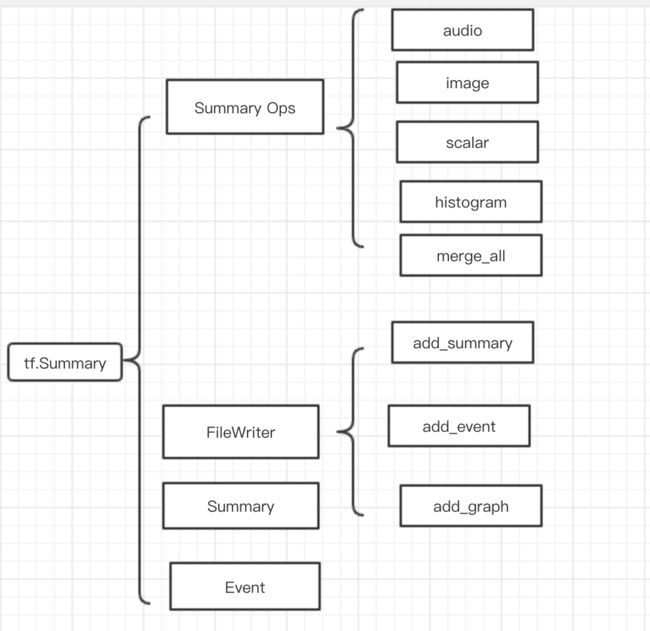
如图所示,tf.summary 模块的功能
2.可视化数据流图
通过with tf.name_scope('sc_name'):定义一个名字可以把一些列操作定义为一个节点,在图上展示为一个节点
点击加号可以展示节点内详情
from __future__ import absolute_import from __future__ import division from __future__ import print_function import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('/Users/quxiaoyuan/work/data/mnist',one_hot=True) with tf.name_scope('input'): x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x-input') y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y-input') with tf.name_scope('softmax_layer'): with tf.name_scope('weights'): weights = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10])) with tf.name_scope('biases'): biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10])) with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'): y = tf.matmul(x,weights) + biases with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy'): diff = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_,logits=y) with tf.name_scope('total'): cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(diff) tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy',cross_entropy) with tf.name_scope('train'): train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cross_entropy) with tf.name_scope('accuracy'): with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'): correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(y_,1)) with tf.name_scope('accuracy'): accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
3.ft.summary操作
add_summay生成折线图
with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy'): diff = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_,logits=y) with tf.name_scope('total'): cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(diff) tf.summary.scalar('cross_entropy',cross_entropy) with tf.name_scope('train'): train_step = tf.train.AdamOpimizer(0.01).minimize(cross_entropy) with tf.name_scope('accuracy'): with tf.name_scope('correct_prediction'): correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(y_,1)) with tf.name_scope('accuracy'): accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32)) tf.summary.scalar('accuracy',accuracy) merged = tf.summary.merge_all() for i in range(FLAGS.max_step): if i % FLAGS.max_step == 0: summary, acc = sess.run([merged,accuracy],feed_dict=feed_dict(False)) witer.add_summary(summary,i)
histogram生成数据分布图
with tf.name_scope('softmax_layer'): with tf.name_scope('weights'): weights = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10])) tf.summary.histogram('weights',weights)
tf.summary.image生成图像
with tf.name_scope('input'): x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784],name='x-input') y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10],name='y-input') with tf.name_scope('input_reshape'): image_shaped_input = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1]) tf.summary.image('input',image_shaped_input,10)