1、@Entity与@Table
先看下栗子:
@Entity
@Table(name="tbl_user")
public class User implements Serializable{
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name="id")
private Integer id;
@Column(name="name")
private String name;
@Column(name="age")
private String age;
public String getAge() { return age; }
public void setAge(String age) { this.age= age; }
public String getName() { returnname; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name= name; }
public User() { }
public Integer getId() { return this.id; }
public void setId(Integer id) { this.id= id; }
}
@Entity注释指名这是一个实体Bean
@Table注释指定了Entity所要映射带数据库表;(如果缺省@Table注释,系统默认采用类名作为映射表的表名。)
@Column注释定义了将成员属性映射到关系表中的哪一列和该列的结构信息,属性如下:
1)name:映射的列名。如:映射tbl_user表的name列,可以在name属性的上面或getName方法上面加入;
2)unique:是否唯一;
3)nullable:是否允许为空;
4)length:对于字符型列,length属性指定列的最大字符长度;
5)insertable:是否允许插入;
6)updatetable:是否允许更新;
7)columnDefinition:定义建表时创建此列的DDL;
8)secondaryTable:从表名。如果此列不建在主表上(默认是主表),该属性定义该列所在从表的名字。
@Id注释指定表的主键,它可以有多种生成方式:
1)TABLE:容器指定用底层的数据表确保唯一;
2)SEQUENCE:使用数据库的SEQUENCE列来保证唯一(Oracle数据库通过序列来生成唯一ID);
3)IDENTITY:使用数据库的IDENTITY列来保证唯一;
4)AUTO:由容器挑选一个合适的方式来保证唯一;
5)NONE:容器不负责主键的生成,由程序来完成。
@GeneratedValue注释定义了标识字段生成方式。(strategy=GenerationType.AUTO)
@Temporal注释用来指定java.util.Date或java.util.Calender属性与数据库类型date、time或timestamp中的那一种类型进行映射。
@Temporal(value=TemporalType.TIME)
private Date birthday;
2、Lombok 之 Constructor( @NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor, @AllArgsContructor )
1)、@NoArgsConstructor : 生成一个无参数的构造方法,这个annotation在与其他的annotation配合起来使用的时候更加能凸显出他的重要性,例如在使用 hibernate这种框架的时候,如果有一个有参数的构造方法的时候,NoArgsConstructor会展示出他的作用。
2)、@RequiredArgsConstructor: 会生成一个包含常量,和标识了NotNull的变量 的构造方法。生成的构造方法是private,如何想要对外提供使用可以使用 staticName选项生成一个static方法。
3)、@AllArgsContructor: 会生成一个包含所有变量,同时如果变量使用了NotNull annotation , 会进行是否为空的校验
来看一个栗子:
import lombok.AccessLevel;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.NonNull;
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName ="of")
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
public class ConstructorExample {
private int x, y;
@NonNull private T description;
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class NoArgsExample {
@NonNull private String field;
}
}
上面的例子用Java代码翻译一下就是:
public class ConstructorExample {
private int x, y;
@NonNull private T description;
private ConstructorExample(T description) {
if(description ==null) throw new NullPointerException("description");
this.description = description;
}
public static ConstructorExample of(T description) {
return new ConstructorExample(description);
}
@java.beans.ConstructorProperties({"x","y","description"})
protected ConstructorExample(int x,int y, T description) {
if(description ==null) throw new NullPointerException("description");
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.description = description;
}
public static class NoArgsExample {
@NonNull private String field;
public NoArgsExample() {
}
}
}
3、SpringMVC的@Valid(详见链接)
@Valid注解进行数据验证
4、Spring Boot @ConfigurationProperties(详细说明)
通常,我们使用@Value注释来逐个注入.properties值,这对于小而简单的结构.properties文件很有用。
如下:
文件:global.properties
thread-pool=12
@Value示例
文件:GlobalProperties.java
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:global.properties")
public class GlobalProperties{
@Value("${thread-pool}")
private int threadPool;
@Value("${email}")
private String email;
//getters and setters
}
@ConfigurationProperties示例
文件: application.yml
logging:
level:
org.springframework.web:ERROR
com.yiibai:DEBUG
email:[email protected]
thread-pool:10
app:
menus:
-title:Home
name:Home
path:/
-title:Login
name:Login
path:/login
compiler:
timeout:5
output-folder:/temp/
error:/error/
文件: AppProperties.java
importorg.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
importorg.springframework.stereotype.Component;
importjava.util.ArrayList;
importjava.util.List;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties("app")// prefix app, find app.* values 可写成( prefix ="app")
public class AppProperties{
private String error;
private List menus=new ArrayList<>();
private Compiler compiler = new Compiler();
public static class Menu{
private String name;
private String path;
privateString title;
//getters and setters
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Menu{"+"name='"+name+'\''+", path='"+path+'\''+", title='"+title+'\''+'}';
}
}
public static class Compiler{
private String timeout;
private String outputFolder;
//getters and setters
@Override
public String toString(){
return "Compiler{"+"timeout='"+timeout+'\''+", outputFolder='"+outputFolder+'\''+'}';
}
}
//getters and setters
}
5、@PropertySource
@PropertySource注解用于指定目录,指定编码读取properties文件
如:
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:application.properties"},encoding="utf-8")
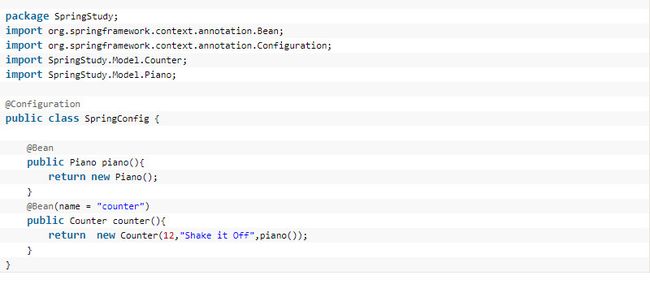
6、Spring中基于Java的配置@Configuration和@Bean用法(详细说明)
首先,需要xml中进行少量的配置来启动Java配置:
用@Configuration注解该类,等价 与XML中配置beans;用@Bean标注方法等价于XML中配置bean。
代码如下:
具体的使用
// 读取bean.xml中的内容
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/bean.xml");
//读取配置文件
ApplicationContext annotationContext =newAnnotationConfigApplicationContext("SpringStudy");
7、spring MVC @ModelAttribute(详细说明)
8、Spring @RestController
一直使用springmvc的时候就记得返回string或者json的话就直接用@RestController。如果想要页面跳转的话,就使用@Controller。一开始就有个疑问,就是我想在一个类中既能返回string或者json又能进行页面跳转怎么办。现在终于明白:点击打开链接。在这篇文章中介绍的非常详细,简单说来就是:
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody。
所以,以后定义controller的时候,可以直接使用@Controller,如果需要返回json可以直接在方法中添加@ResponseBody即可。
9、@ResponseBody和@RequestBody(详细说明)
@RequestBody
作用:
i) 该注解用于读取Request请求的body部分数据,使用系统默认配置的HttpMessageConverter进行解析,然后把相应的数据绑定到要返回的对象上;
ii) 再把HttpMessageConverter返回的对象数据绑定到 controller中方法的参数上。
使用时机:
A) GET、POST方式提时, 根据request header Content-Type的值来判断:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded, 可选(即非必须,因为这种情况的数据@RequestParam, @ModelAttribute也可以处理,当然@RequestBody也能处理);
multipart/form-data, 不能处理(即使用@RequestBody不能处理这种格式的数据);
其他格式, 必须(其他格式包括application/json, application/xml等。这些格式的数据,必须使用@RequestBody来处理);
B) PUT方式提交时, 根据request header Content-Type的值来判断:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded, 必须;
multipart/form-data, 不能处理;
其他格式, 必须;
说明:request的body部分的数据编码格式由header部分的Content-Type指定;
@ResponseBody
作用:
该注解用于将Controller的方法返回的对象,通过适当的HttpMessageConverter转换为指定格式后,写入到Response对象的body数据区。
使用时机:
返回的数据不是html标签的页面,而是其他某种格式的数据时(如json、xml等)使用;
10、@RequestParam(详细说明)
在SpringMVC后台控制层获取参数的方式主要有两种,一种是request.getParameter("name"),另外一种是用注解@RequestParam直接获取。
如下:
//不指定入参时,前端传入的就是inputStr
@RequestParam String inputStr
// 下面的对传入参数指定为aa,如果前端不传aa参数名,会报错
@RequestParam(value="aa") String inputStr
//可以通过required=false或者true来要求@RequestParam配置的前端参数是否一定要传
// required=false表示不传的话,会给参数赋值为null,required=true就是必须要有
@RequestMapping("testRequestParam")
public String filesUpload( @RequestParam(value="aa", required=true) String inputStr, HttpServletRequest request)
11、@ResponseEntity(详细说明)
@ResponseEntity可以定义返回的HttpHeaders和HttpStatus
12、@PathVariable
先看栗子:
/**
* @PathVariable 可以映射占位符到方法中的参数(类似赋值)
* @param id
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/testPathVariable/{id}")
public String testPathVariable( @PathVariable("id") Integer id){
System.out.println("PathVariable id="+id);
return "success";
}
SpringMVC中是不可以通过@PathVariable这个注解来传递对象的,原因其实很简单:@PathVariable是用来获得请求url中的动态参数的,所以该注解只能支持将参数放在请求url的GET提交方式,所以不管你如何进行设置,@PathVariable都是无法支持Post请求的。