[Harfbuzz](http://harfbuzz.org/ 是一个 OpenType 文本整形引擎。当前的 Harfbuzz 代码库,之前被称为 harfbuzz-ng,版本号为 1.x.x,它是稳定的且处于活跃的维护之中。Harfbuzz 的使用非常广泛,在最新版本的 Firefox,GNOME,ChromeOS,Chrome,LibreOffice,XeTeX,Android,和 KDE 等项目中都有应用。Harfbuzz 的代码可以在 这里 下载,也可以通过 GitHub 访问。
老的 HarfBuzz 代码库,现在被称为 harfbuzz-old,它从 FreeType,Pango,和 Qt 派上而来,可以在 这里 下载。老的 HarfBuzz 代码库目前已经不再维护了。
Harfbuzz 在代码结构上,与 harfbuzz-old 的差别非常大。前面 Behdad Esfahbod 发的那篇名为 Harfbuzz API 设计(Harfbuzz API design) 的邮件,所描述的是新 Harfbuzz API 的设计。
本文来看一下 Harfbuzz API 的基本用法。学习一个开源库的 API 的用法最方便的途径,常常正是库本身包含的一些示例程序或这测试程序。下载当前最新的发布版本 1.7.5 的源码。将源码解压缩之后,通过如下命令编译它:
harfbuzz-1.7.5$ ./configure
harfbuzz-1.7.5$ make
编译过程将产生 Harfbuzz 的二进制库文件,和一些测试程序的可执行文件,位于 harfbuzz-1.7.5/src/test.cc 的即是其中一个测试程序。这个测试程序编译之后产生的可执行文件为 harfbuzz-1.7.5/src/test,通过如下方式执行:
harfbuzz-1.7.5$ src/test font-file.ttf
即需要唯一的参数,字库文件的路径。我们对这个测试程序做一点简单的修改,让它处理泰语和缅甸语,字库文件我们使用 Android 7.1.1 代码库中,external/noto-fonts/other/ 下的 NotoSansThai-Regular.ttf 和 NotoSansMyanmar-Regular.ttf:
harfbuzz-1.7.5$ src/test ~/Androids/android_7.1.1/external/noto-fonts/other/NotoSansThai-Regular.ttf
Opened font file ~/Androids/android_7.1.1/external/noto-fonts/other/NotoSansThai-Regular.ttf: 21380 bytes long
cluster 0 glyph 0x4 at (0,0)+(1264,0)
cluster 0 glyph 0x4e at (7,0)+(0,0)
cluster 0 glyph 0x5e at (127,0)+(0,0)
cluster 0 glyph 0x37 at (0,0)+(994,0)
cluster 3 glyph 0x25 at (0,0)+(1315,0)
cluster 4 glyph 0x26 at (0,0)+(1225,0)
cluster 5 glyph 0x27 at (0,0)+(1301,0)
cluster 6 glyph 0x30 at (0,0)+(1320,0)
cluster 7 glyph 0x31 at (0,0)+(1379,0)
cluster 8 glyph 0x33 at (0,0)+(1195,0)
harfbuzz-1.7.5$ src/test ~/Androids/android_7.1.1/external/noto-fonts/other/NotoSansMyanmar-Regular.ttf
Opened font file ~/Androids/android_7.1.1/external/noto-fonts/other/NotoSansMyanmar-Regular.ttf: 108160 bytes long
cluster 0 glyph 0x9 at (0,0)+(1381,0)
cluster 0 glyph 0x196 at (0,0)+(993,0)
cluster 2 glyph 0x5 at (0,0)+(1384,0)
cluster 2 glyph 0x195 at (0,0)+(547,0)
cluster 4 glyph 0x22 at (0,0)+(2308,0)
cluster 4 glyph 0x197 at (-42,0)+(0,0)
cluster 6 glyph 0x4 at (0,0)+(2302,0)
cluster 6 glyph 0xd5 at (-19,-50)+(0,0)
cluster 6 glyph 0x196 at (0,0)+(993,0)
cluster 10 glyph 0x22 at (0,0)+(2308,0)
cluster 11 glyph 0x16 at (0,0)+(1311,0)
cluster 11 glyph 0x104 at (-4,-50)+(0,0)
cluster 11 glyph 0x195 at (0,0)+(547,0)
cluster 15 glyph 0xe at (0,0)+(2271,0)
cluster 15 glyph 0x197 at (-14,0)+(0,0)
cluster 15 glyph 0xd2 at (0,0)+(534,0)
cluster 18 glyph 0x15 at (0,0)+(2304,0)
cluster 18 glyph 0x19f at (-57,0)+(0,0)
cluster 18 glyph 0xd1 at (-31,0)+(0,0)
cluster 18 glyph 0x1a1 at (0,0)+(709,0)
harfbuzz-1.7.5/src/test.cc 的完整源码如下:
#include "hb-private.hh"
#include "hb.h"
#ifdef HAVE_GLIB
# include
# if !GLIB_CHECK_VERSION (2, 22, 0)
# define g_mapped_file_unref g_mapped_file_free
# endif
#endif
#include
#include
#ifdef HAVE_FREETYPE
#include "hb-ft.h"
#endif
int
main (int argc, char **argv)
{
hb_blob_t *blob = nullptr;
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf (stderr, "usage: %s font-file.ttf\n", argv[0]);
exit (1);
}
/* Create the blob */
{
const char *font_data;
unsigned int len;
hb_destroy_func_t destroy;
void *user_data;
hb_memory_mode_t mm;
#ifdef HAVE_GLIB
GMappedFile *mf = g_mapped_file_new (argv[1], false, nullptr);
font_data = g_mapped_file_get_contents (mf);
len = g_mapped_file_get_length (mf);
destroy = (hb_destroy_func_t) g_mapped_file_unref;
user_data = (void *) mf;
mm = HB_MEMORY_MODE_READONLY_MAY_MAKE_WRITABLE;
#else
FILE *f = fopen (argv[1], "rb");
fseek (f, 0, SEEK_END);
len = ftell (f);
fseek (f, 0, SEEK_SET);
font_data = (const char *) malloc (len);
if (!font_data) len = 0;
len = fread ((char *) font_data, 1, len, f);
destroy = free;
user_data = (void *) font_data;
fclose (f);
mm = HB_MEMORY_MODE_WRITABLE;
#endif
blob = hb_blob_create (font_data, len, mm, user_data, destroy);
}
printf ("Opened font file %s: %u bytes long\n", argv[1], hb_blob_get_length (blob));
/* Create the face */
hb_face_t *face = hb_face_create (blob, 0 /* first face */);
hb_blob_destroy (blob);
blob = nullptr;
unsigned int upem = hb_face_get_upem (face);
int textSize = 36;
uint16_t x_ppem, y_ppem;
int x_scale, y_scale;
x_ppem = y_ppem = textSize;
const int kDevicePixelFraction = 64;
const int kMultiplyFor16Dot16 = 1 << 16;
float emScale = kDevicePixelFraction * kMultiplyFor16Dot16 / (float)upem;
x_scale = emScale * textSize;
y_scale = emScale * textSize;
hb_font_t *font = hb_font_create (face);
hb_font_set_scale(font, x_scale, y_scale);
hb_font_set_ppem(font, x_ppem, y_ppem);
#ifdef HAVE_FREETYPE
hb_ft_font_set_funcs (font);
#endif
hb_buffer_t *buffer = hb_buffer_create ();
uint16_t myanmarChars[] = {0x1005, 0x102C, 0x1001, 0x102B,
0x101E, 0x102D, 0x1000, 0x1039, 0x1001, 0x102C,
0x101E, 0x1012, 0x1039, 0x1013, 0x102B,
0x100A, 0x102D, 0x102F, 0x1011, 0x102F, 0x1036, 0x1038
};
uint16_t thaiChars[] = {
0xE01, 0xE49, 0xE33, 0xE20, 0xE21, 0xE22, 0xE2B, 0xE2C, 0xE2E
};
uint16_t *chars = myanmarChars;
// hb_buffer_add_utf8 (buffer, "\xe0\xa4\x95\xe0\xa5\x8d\xe0\xa4\xb0\xe0\xa5\x8d\xe0\xa4\x95", -1, 0, -1);
hb_buffer_add_utf16(buffer, chars, -1, 0, -1);
hb_buffer_guess_segment_properties (buffer);
hb_shape (font, buffer, nullptr, 0);
unsigned int count = hb_buffer_get_length (buffer);
hb_glyph_info_t *infos = hb_buffer_get_glyph_infos (buffer, nullptr);
hb_glyph_position_t *positions = hb_buffer_get_glyph_positions (buffer, nullptr);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
hb_glyph_info_t *info = &infos[i];
hb_glyph_position_t *pos = &positions[i];
printf ("cluster %d glyph 0x%x at (%d,%d)+(%d,%d)\n",
info->cluster,
info->codepoint,
pos->x_offset,
pos->y_offset,
pos->x_advance,
pos->y_advance);
}
hb_buffer_destroy (buffer);
hb_font_destroy (font);
hb_face_destroy (face);
return 0;
}
接着再来看前面那段code的结构,上面这段代码执行的步骤如下:
-
- 读取字库文件中的数据,然后创建
hb_blot_t。
- 读取字库文件中的数据,然后创建
-
- 利用前面创建的那个含有字库文件数据的
blob,创建一个face。
- 利用前面创建的那个含有字库文件数据的
-
- 利用前面创建的
face,创建一个font。然后把字体大小的信息(ppem)及字体设计空间向用户空间转换的系数(scale)设置给font。计算ppem及scale的那段代码借用了android 4.2TextLayoutCache.cpp的一些做法。
- 利用前面创建的
-
- 创建一个
buffer,把文本添加进去。这个地方用UTF-16编码,是因为就手动编码 Unicode 而言,对于许多复杂语系的 Unicode 范围,UTF-16 比 UTF-8 要方便的多,因而也使我们可以更方便地修改它。
- 创建一个
-
- 调用 Harfbuzz 的主
shape接口执行shape动作。
- 调用 Harfbuzz 的主
-
- 最后从
shape之后的buffer中,取出glyph和position相关信息。
- 最后从
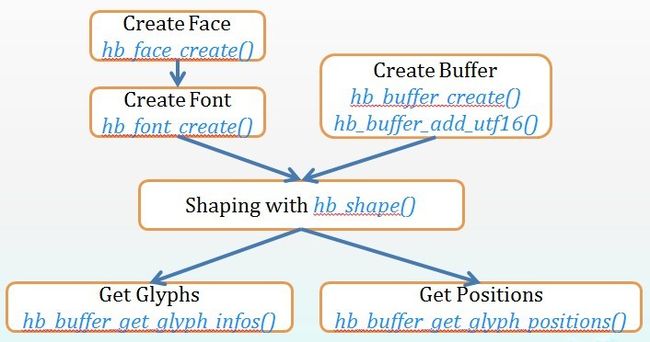
通常情况下对于 Harfbuzz API 的使用,大体上如上面所述。用一张图来简单说明上面的过程:
这样的用法,之所以称为基本用法,有如下这样一些原因:
- 前面的第 2、3 步中,在创建
face和font时,是直接通过字库文件的路径进行的。通常情况每个系统都会有自己的字库文件管理系统和 Glyph 管理系统,这种做法就完全没有考虑与现有系统的这些模块衔接的问题。在实际系统中,这两个对象应该通过相应有 callback 参数的那些接口来创建。 - 在 Harfbuzz API Design 中,我们看到有提到 Unicode callback 及 Script、Language 和 Direction 这些文本属性等,这些都是需要正确的设置给
buffer的,因而前面第 4 步所对应的这个测试程序的做法,所创建的buffer是不够完整的。 - 在打印位置信息时,我们看到有通过
HBFixedToFloat()这个函数来对 Harfbuzz 输出的位置信息做一个转换,转换为float格式的像素个数值。可以看到这个地方除了一个2048。这个系数在这个测试程序里用的是一个猜想的值。字体大小为36,所以猜想返回的advance值应该处于这一数量级。所以取了2048这个系数。
Done.