在原先代码设计中,我们为了方便,喜欢在一个模块中组织数据包的协议头,然后将要发送的数据融合在一起,并调用网卡将数据发送出去,这种偷懒的做法将多种逻辑融合在一起。这种做法一旦遇到复杂的数据发送需求时,系统逻辑的复杂性会呈现出爆炸性的增长,最后超出我们的控制范围。
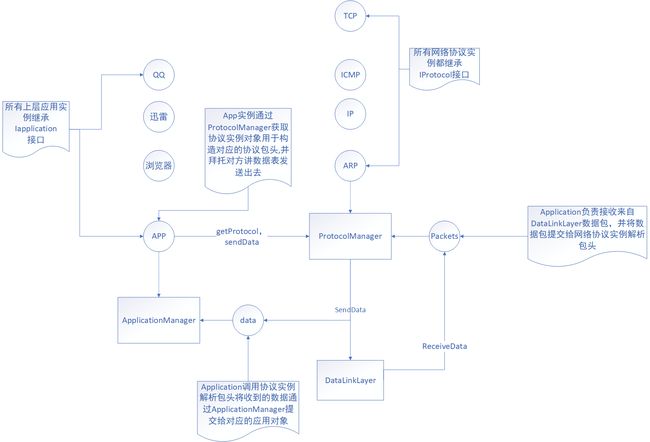
为了实现体系的层次化,将各种功能剥离成单独模块,实现系统的可理解性,我将体系结构改动为以下模式:
从上图看,所有的应用实例,也就是调用网络协议,实现数据收发功能的应用都继承IApplication接口和继承Application类,其内容如下:
package Application;
import java.util.HashMap;
public interface IApplication {
public int getPort();
public boolean isClosed();
public void handleData(HashMap data);
}
package Application;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Application implements IApplication{
protected int port = 0;
private boolean closed = false;
public Application() {
ApplicationManager manager = ApplicationManager.getInstance();
manager.addApplication(this);
}
@Override
public int getPort() {
return port;
}
@Override
public void handleData(HashMap data) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public boolean isClosed() {
return closed;
}
}
所有应用对象都要导出getPort()接口,每个port对应唯一一个应用对象,如果数据包到达后,协议会根据port寻找应该接受数据的应用对象。应用对象全部接受ApplicationManager的管理,当网络协议部分有数据需要提交给对应的应用时,需要通过ApplicationManager查询相应应用对象,它的代码如下:
package Application;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ApplicationManager {
private static ArrayList application_list = new ArrayList();
private static ApplicationManager instance = null;
private ApplicationManager() {
}
public static ApplicationManager getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new ApplicationManager();
}
return instance;
}
public static void addApplication(IApplication app) {
application_list.add(app);
}
public IApplication getApplicationByPort(int port) {
for (int i = 0; i < application_list.size(); i++) {
IApplication app = application_list.get(i);
if (app.getPort() == port) {
return app;
}
}
return null;
}
}
实现网络协议的模块单独形成一个独立部分,实现具体网络协议的对象都继承统一的接口IProtocol:
package protocol;
import java.util.HashMap;
import jpcap.packet.Packet;
public interface IProtocol {
public byte[] createHeader(HashMap headerInfo);
public HashMap handlePacket(Packet packet);
}
所有协议对象都接受ProtocolManager的统一管理,当应用对象需要调用某个协议对象创建包头时,需要经过ProtocolManager获取相应对象,同时它是唯一一个从网卡接收数据的对象,当网卡把数据包传递给它后,它通过解析网络包的以太太包头,决定把数据包转交给对应的网络协议对象解析,它的代码如下:
package protocol;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import Application.ApplicationManager;
import Application.IApplication;
import datalinklayer.DataLinkLayer;
import jpcap.PacketReceiver;
import jpcap.packet.EthernetPacket;
import jpcap.packet.IPPacket;
import jpcap.packet.Packet;
public class ProtocolManager implements PacketReceiver{
private static ProtocolManager instance = null;
private static ARPProtocolLayer arpLayer = null;
private static DataLinkLayer dataLinkInstance = null;
private static HashMap ipToMacTable = null;
private static HashMap dataWaitToSend = null;
private static byte[] broadcast=new byte[]{(byte)255,(byte)255,(byte)255,(byte)255,(byte)255,(byte)255};
private ProtocolManager() {}
public static ProtocolManager getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new ProtocolManager();
dataLinkInstance = DataLinkLayer.getInstance();
ipToMacTable = new HashMap();
dataWaitToSend = new HashMap();
dataLinkInstance.registerPacketReceiver(instance);
arpLayer = new ARPProtocolLayer();
}
return instance;
}
public IProtocol getProtocol(String name) {
switch (name.toLowerCase()) {
case "icmp":
return new ICMPProtocolLayer();
case "ip":
return new IPProtocolLayer();
}
return null;
}
public void sendData(byte[] data, byte[] ip) throws Exception {
/*
* 发送数据前先检查给定ip的mac地址是否存在,如果没有则先让ARP协议获取mac地址
*/
byte[] mac = ipToMacTable.get(Arrays.toString(ip));
if (mac == null) {
HashMap headerInfo = new HashMap();
headerInfo.put("sender_ip", ip);
byte[] arpRequest = arpLayer.createHeader(headerInfo);
if (arpRequest == null) {
throw new Exception("Get mac adress header fail");
}
dataLinkInstance.sendData(arpRequest, broadcast, EthernetPacket.ETHERTYPE_ARP);
//将要发送的数据存起,等待mac地址返回后再发送
dataWaitToSend.put(Arrays.toString(ip), data);
} else {
//如果mac地址已经存在则直接发送数据
dataLinkInstance.sendData(data, mac, IPPacket.IPPROTO_IP);
}
}
@Override
public void receivePacket(Packet packet) {
if (packet == null) {
return;
}
//确保收到数据包是arp类型
EthernetPacket etherHeader = (EthernetPacket)packet.datalink;
/*
* 数据链路层在发送数据包时会添加一个802.3的以太网包头,格式如下
* 0-7字节:[0-6]Preamble , [7]start fo frame delimiter
* 8-22字节: [8-13] destination mac, [14-19]: source mac
* 20-21字节: type
* type == 0x0806表示数据包是arp包, 0x0800表示IP包,0x8035是RARP包
*/
if (etherHeader.frametype == EthernetPacket.ETHERTYPE_ARP) {
//调用ARP协议解析数据包
ARPProtocolLayer arpLayer = new ARPProtocolLayer();
HashMap info = arpLayer.handlePacket(packet);
byte[] senderIP = (byte[])info.get("sender_ip");
byte[] senderMac = (byte[])info.get("sender_mac");
ipToMacTable.put(Arrays.toString(senderIP), senderMac);
//一旦有mac地址更新后,查看缓存表是否有等待发送的数据
sendWaitingData(senderIP);
}
//处理IP包头
if (etherHeader.frametype == EthernetPacket.ETHERTYPE_IP) {
handleIPPacket(packet);
}
}
private void handleIPPacket(Packet packet) {
IProtocol ipProtocol = new IPProtocolLayer();
HashMap info = ipProtocol.handlePacket(packet);
if (info == null) {
return ;
}
byte protocol = 0;
if (info.get("protocol") != null) {
protocol = (byte)info.get("protocol");
//设置下一层协议的头部
packet.header = (byte[])info.get("header");
System.out.println("receive packet with protocol: " + protocol);
}
if (protocol != 0) {
switch(protocol) {
case IPPacket.IPPROTO_ICMP:
handleICMPPacket(packet);
break;
default:
return;
}
}
}
private void handleICMPPacket(Packet packet) {
IProtocol icmpProtocol = new ICMPProtocolLayer();
HashMap headerInfo = icmpProtocol.handlePacket(packet);
short identifier = (short)headerInfo.get("identifier");
IApplication app = ApplicationManager.getInstance().getApplicationByPort(identifier);
if (app != null && app.isClosed() != true) {
app.handleData(headerInfo);
}
}
private void sendWaitingData(byte[] destIP) {
byte[] data = dataWaitToSend.get(Arrays.toString(destIP));
byte[] mac = ipToMacTable.get(Arrays.toString(destIP));
if (data != null && mac != null) {
dataLinkInstance.sendData(data, mac, EthernetPacket.ETHERTYPE_IP);
}
}
}
从代码我们看到,一旦数据包到来时,它的receivePacket接口会被调用,它通过嗅探以太包头判断数据包应该提交给哪种网络协议,在代码中目前我们只实现了对两种网络数据包的处理,一种是ARP包,一种是IP包。
它也负责发送数据,当应用或者协议需要把数据包发送出去时,需要调用它的sendData接口。它会先检查接收者IP对应的mac地址是否在缓存表中,如果没有,它会调用ARPProtocolLayer对象,通过ARP协议获取给定IP的mac地址。然后再调用其他协议对象,结合获得的mac地址去发送数据。
如果接收到的数据包是IP包,它会调用IPProtocolLayer对象解析协议包头,根据解析后返回的字段采取下一步行动,IP包头下面往往会跟着其他协议,由于我们本节实现ICMP ping应用,因此在代码中它监控IP处理后接下来是否要走ICMP协议,这些逻辑都在接口handleIPPacket中实现。如果所有协议处理完毕,需要把数据提交给对应的应用时,它会通过ApplicationManager把数据提交过去,这个逻辑在handleICMPPacket调用中有实现。
接下来我们看看ping应用的实现:
package Application;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Random;
import protocol.ICMPProtocolLayer;
import protocol.IProtocol;
import protocol.ProtocolManager;
public class PingApp extends Application{
private int echo_times = 0;
private short identifier = 0;
private short sequence = 0;
private byte[] destIP = null;
/*
* times: 连续发送多少次数据包
* destIP: ping的对象
*/
public PingApp(int times, byte[] destIP ) {
if (times > 0) {
echo_times = times;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("ehoc times must > 0");
}
Random rand = new Random();
identifier = (short) (rand.nextInt() & 0x0000FFFF);
this.destIP = destIP;
this.port = identifier;
}
public void startPing() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.echo_times; i++) {
try {
byte[] packet = createPackage(null);
ProtocolManager.getInstance().sendData(packet, destIP);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private byte[] createPackage(byte[] data) throws Exception {
byte[] icmpEchoHeader = this.createICMPEchoHeader();
if (icmpEchoHeader == null) {
throw new Exception("ICMP Header create fail");
}
byte[] ipHeader = this.createIP4Header(icmpEchoHeader.length);
//分别构建ip包头和icmp echo包头后,将两个包头结合在一起
byte[] packet = new byte[icmpEchoHeader.length + ipHeader.length];
ByteBuffer packetBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(packet);
packetBuffer.put(ipHeader);
packetBuffer.put(icmpEchoHeader);
return packetBuffer.array();
}
private byte[] createICMPEchoHeader() {
IProtocol icmpProto = ProtocolManager.getInstance().getProtocol("icmp");
if (icmpProto == null) {
return null;
}
//构造icmp echo 包头
HashMap headerInfo = new HashMap();
headerInfo.put("header", "echo");
headerInfo.put("identifier", identifier);
headerInfo.put("sequence_number", sequence);
sequence++;
//附带当前时间
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(Long.BYTES);
buffer.putLong(time);
byte[] timeBuffer = buffer.array();
headerInfo.put("data", timeBuffer);
byte[] icmpEchoHeader = icmpProto.createHeader(headerInfo);
return icmpEchoHeader;
}
private byte[] createIP4Header(int dataLength) {
IProtocol ip4Proto = ProtocolManager.getInstance().getProtocol("ip");
if (ip4Proto == null || dataLength <= 0) {
return null;
}
//创建IP包头默认情况下只需要发送数据长度,下层协议号,接收方ip地址
HashMap headerInfo = new HashMap();
headerInfo.put("data_length", dataLength);
ByteBuffer destIP = ByteBuffer.wrap(this.destIP);
headerInfo.put("destination_ip", destIP.getInt());
byte protocol = ICMPProtocolLayer.PROTOCL_ICMP;
headerInfo.put("protocol", protocol);
headerInfo.put("identification", (short)this.port);
byte[] ipHeader = ip4Proto.createHeader(headerInfo);
return ipHeader;
}
@Override
public void handleData(HashMap data) {
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
short sequence = (short)data.get("sequence");
byte[] time_buf = (byte[])data.get("data");
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.wrap(time_buf);
long send_time = buf.getLong();
System.out.println("receive reply for ping request " + sequence + "for " + (time - send_time) / 1000 + "secs");
}
}
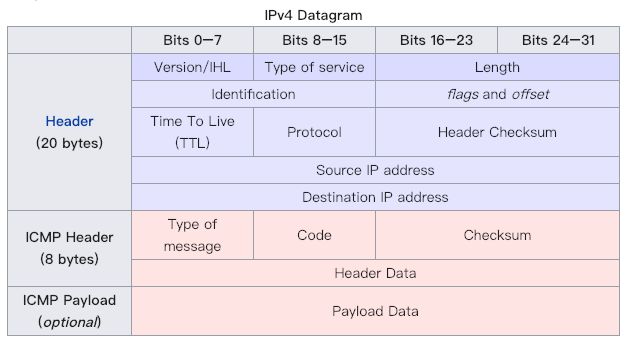
它通过调用IPProtocoalLayer和ICMPProtocolLayer组装包头,以便发生ping数据包,它所做的工作就是组装出如下格式的数据包:
从上图看,ping数据包分成两部分,一部分是上面的IP包头,它有20字节,第二部分是下面的ICMP header,有8字节,最后是payload,这部分由程序自己附带,收到ping包的对方会原封不动的把payload转发回来。在Ping应用实现中,我们附带的payload是当前数据包的组建时间,当下次接收到回应时,我们把这个时间拿到,再结合当前时间就可以知道数据传递的一个来回需要多久。
在ping应用中,createIP4Header调用IPProtocolLayer组装IP包头,createICMPEchoHeader调用ICMPProtocolLayer组装ICMP header。当数据包返回后,它的handleData被调用,它在该接口里对返回数据进行操作。我们看看IPProtocolLayer的实现:
package protocol;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.util.HashMap;
import datalinklayer.DataLinkLayer;
import jpcap.packet.Packet;
import utils.Utility;
public class IPProtocolLayer implements IProtocol{
private static int ETHERNET_FRAME_HEADER_LENGTH = 14;
private static byte IP_VERSION = 4;
private static int CHECKSUM_OFFSET = 10;
private static int HEADER_LENGTH_OFFSET = 0 + ETHERNET_FRAME_HEADER_LENGTH;
private static int TOTAL_LENGTH_OFFSET = 2 + ETHERNET_FRAME_HEADER_LENGTH;
private static int SOURCE_IP_OFFSET = 12 + ETHERNET_FRAME_HEADER_LENGTH;
private static int DEST_IP_OFFSET = 16 + ETHERNET_FRAME_HEADER_LENGTH;
private static int PROTOCOL_INDICATOR_OFFSET = 9 + ETHERNET_FRAME_HEADER_LENGTH;
@Override
public byte[] createHeader(HashMap headerInfo) {
byte version = (byte) (IP_VERSION & 0x0F);
byte internetHeaderLength = 5;
if (headerInfo.get("internet_header_length") != null) {
internetHeaderLength = (byte)headerInfo.get("internet_header_length");
}
byte[] buffer = new byte[internetHeaderLength * 4];
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(buffer);
byteBuffer.put((byte) (version << 4 | internetHeaderLength));
byte b = byteBuffer.get(0);
byte dscp = 0;
if (headerInfo.get("dscp") != null) {
dscp = (byte)headerInfo.get("dscp");
}
byte ecn = 0;
if (headerInfo.get("ecn") != null) {
ecn = (byte)headerInfo.get("ecn");
}
byteBuffer.put((byte)(dscp << 2 | ecn));
if (headerInfo.get("data_length") == null) {
return null;
}
/*
* 总长度等于IP数据包包头长度加上末尾option长度加上后续数据长度
*/
int optionLength = 0;
byte[] options = null;
if (headerInfo.get("options") != null) {
options = (byte[])headerInfo.get("options");
optionLength += options.length;
}
short totalLength = (short) ((int)headerInfo.get("data_length") + optionLength + internetHeaderLength*4);
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.putShort(totalLength);
short identification = 0;
if (headerInfo.get("identification") != null) {
identification = (short)headerInfo.get("identification");
}
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.putShort(identification);
short flagAndOffset = 0;
if (headerInfo.get("flag") != null) {
flagAndOffset = (short) (((short)headerInfo.get("flag")) << 13);
}
if (headerInfo.get("fragment_offset") != null) {
flagAndOffset |= ((short)headerInfo.get("fragment_offset"));
}
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.putShort(flagAndOffset);
byte timeToLive = 64;
if (headerInfo.get("time_to_live") != null) {
timeToLive = (byte)headerInfo.get("time_to_live");
}
byteBuffer.put(timeToLive);
byte protocol = 0;
if (headerInfo.get("protocol") == null) {
return null;
}
protocol = (byte)headerInfo.get("protocol");
byteBuffer.put(protocol);
short checkSum = 0;
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.putShort(checkSum);
//设置source ip
byte[] ipArr = DataLinkLayer.getInstance().deviceIPAddress();
ByteBuffer ip = ByteBuffer.wrap(ipArr);
int srcIP = ip.getInt();
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.putInt(srcIP);
int destIP = 0;
if (headerInfo.get("destination_ip") == null) {
return null;
}
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
destIP = (int)headerInfo.get("destination_ip");
byteBuffer.putInt(destIP);
if (headerInfo.get("options") != null) {
byteBuffer.put(options);
}
checkSum = (short) Utility.checksum(byteBuffer.array(), byteBuffer.array().length);
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.putShort(CHECKSUM_OFFSET, checkSum);
return byteBuffer.array();
}
@Override
public HashMap handlePacket(Packet packet) {
/*
* 解析收到数据包的IP包头,暂时不做校验和检测,默认网络发送的数据包不会出错,
* 暂时忽略对option段的处理
*/
byte[] ip_data = new byte[packet.header.length + packet.data.length];
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(ip_data);
buffer.put(packet.header);
buffer.put(packet.data);
HashMap headerInfo = new HashMap();
//获取发送者IP
byte[] src_ip = new byte[4];
buffer.position(SOURCE_IP_OFFSET);
buffer.get(src_ip, 0, 4);
headerInfo.put("source_ip", src_ip);
//获取接受者IP
byte[] dest_ip = new byte[4];
buffer.position(DEST_IP_OFFSET);
buffer.get(dest_ip, 0, 4);
headerInfo.put("dest_ip", dest_ip);
//确保接受者是我们自己
byte[] ip = DataLinkLayer.getInstance().deviceIPAddress();
for (int i = 0; i < ip.length; i++) {
if (ip[i] != dest_ip[i]) {
return null;
}
}
//获得下一层协议编号
buffer.position(0);
byte protocol = buffer.get(PROTOCOL_INDICATOR_OFFSET);
headerInfo.put("protocol", protocol);
int k = 0;
if (protocol == 1) {
k = 2;
System.out.println("receive protocol 2");
}
byte headerLength = buffer.get(HEADER_LENGTH_OFFSET);
headerLength &= 0x0F;
//*4得到包头字节长度
headerLength *= 4;
short totalLength = buffer.getShort(TOTAL_LENGTH_OFFSET);
int dataLength = totalLength - headerLength;;
byte[] data = new byte[dataLength];
buffer.position(headerLength + ETHERNET_FRAME_HEADER_LENGTH);
buffer.get(data, 0, dataLength);
headerInfo.put("header", data);
return headerInfo;
}
}
它的目的很简单,就是根据上图包头的字段组装协议包头,如果有对应的数据包抵达,它根据协议包头字段对数据进行解析。我们再看看ICMPProtocolLayer的实现:
package protocol;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import jpcap.PacketReceiver;
import jpcap.packet.EthernetPacket;
import jpcap.packet.Packet;
public class ICMPProtocolLayer implements IProtocol{
public static byte PROTOCL_ICMP = 1;
private ArrayList protocol_header_list = new ArrayList();
private Packet packet;
public ICMPProtocolLayer() {
//增加icmp echo 协议包头创建对象
protocol_header_list.add(new ICMPEchoHeader());
}
//checkType针对的是IPV6
private HashMap analyzeICMPMessage() {
HashMap info = null;
info = handleICMPInfoMsg(this.packet);
return info;
}
private HashMap handleICMPInfoMsg(Packet packet) {
for (int i = 0; i < protocol_header_list.size(); i++) {
IProtocol handler = protocol_header_list.get(i);
HashMap info = handler.handlePacket(packet);
if (info != null) {
return info;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public byte[] createHeader(HashMap headerInfo) {
for (int i = 0; i < protocol_header_list.size(); i++) {
byte[] buff = protocol_header_list.get(i).createHeader(headerInfo);
if (buff != null) {
return buff;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public HashMap handlePacket(Packet packet) {
this.packet = packet;
return analyzeICMPMessage();
}
}
ICMPProtocolLayer 很简单,它只是一个框架,因为ICMP具体数据包的形式多样,因此我们依旧使用责任链模式把具体工作分发给具体对象,例如我们要组装ping数据包对应的echo包头,据需要下面具体的实现实例:
package protocol;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.ByteOrder;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Random;
import jpcap.packet.Packet;
import utils.Utility;
public class ICMPEchoHeader implements IProtocol{
private static int ICMP_EOCH_HEADER_LENGTH = 8;
private static byte ICMP_ECHO_TYPE = 8;
private static byte ICMP_ECHO_REPLY_TYPE = 0;
private static short ICMP_ECHO_IDENTIFIER_OFFSET = 4;
private static short ICMP_ECHO_SEQUENCE_NUM_OFFSET = 6;
private static short ICMP_ECHO_OPTIONAL_DATA_OFFSET = 8;
private static short ICMP_ECHO_ONLY_HEADER_LENGTH = 8;
@Override
public byte[] createHeader(HashMap headerInfo) {
String headerName = (String)headerInfo.get("header");
if (headerName != "echo" && headerName != "echo_reply") {
return null;
}
int bufferLen = ICMP_EOCH_HEADER_LENGTH;
int dataLen = ((byte[])headerInfo.get("data")).length;
if (headerInfo.get("data") != null) {
bufferLen += ((byte[])headerInfo.get("data")).length;
}
byte[] buffer = new byte[bufferLen ];
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(buffer);
byte type = ICMP_ECHO_TYPE;
if (headerName == "echo_reply") {
type = ICMP_ECHO_REPLY_TYPE;
}
byteBuffer.put(type);
byte code = 0;
byteBuffer.put(code);
short checkSum = 0;
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.putShort(checkSum);
short identifier = 0;
if (headerInfo.get("identifier") == null) {
Random ran = new Random();
identifier = (short) ran.nextInt();
headerInfo.put("identifier", identifier);
}
identifier = (short) headerInfo.get("identifier");
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.putShort(identifier);
System.out.println("ICMP echo header, identifier: " + String.format("0x%08x", identifier));
short sequenceNumber = 0;
if (headerInfo.get("sequence_number") != null) {
sequenceNumber = (short) headerInfo.get("sequence_number");
}
headerInfo.put("sequence_number", sequenceNumber);
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.putShort(sequenceNumber);
System.out.println("ICMP echo header, sequence: " + String.format("0x%08x", sequenceNumber));
if (headerInfo.get("data") != null) {
byte[] data = (byte[])headerInfo.get("data");
byteBuffer.put(data, 0, data.length);
}
checkSum = (short) Utility.checksum(byteBuffer.array(), byteBuffer.array().length);
byteBuffer.order(ByteOrder.BIG_ENDIAN);
byteBuffer.putShort(2, checkSum);
System.out.println("ICMP echo header, checksum: " + String.format("0x%08x", checkSum));
return byteBuffer.array();
}
@Override
public HashMap handlePacket(Packet packet) {
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(packet.header);
if (buffer.get(0) != ICMP_ECHO_REPLY_TYPE) {
return null;
}
HashMap header = new HashMap();
header.put("identifier", buffer.getShort(ICMP_ECHO_IDENTIFIER_OFFSET));
header.put("sequence", buffer.getShort(ICMP_ECHO_SEQUENCE_NUM_OFFSET));;
if (packet.header.length > ICMP_ECHO_ONLY_HEADER_LENGTH) {
header.put("data", packet.data);
}
return header;
}
}
上面协议对象负责组装ping协议包头,如果ping数据包返回,它也会根据相应的包头字段进行解读,解读后获得的数据就会提交给对应的应用对象。更加详细的代码讲解和调试演示请观看视频。
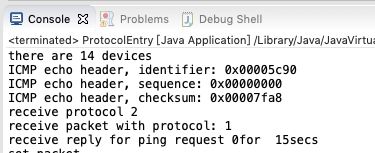
上面代码运行后,情况如下:
我们构造了一个ping数据包,发送给路由器,路由器收到后返回数据包给Ping应用,这一来回用时15秒,之所以那么久是因为我在代码中设置断点调试所致。
更详实的讲解以及抓包演示,请通过下面链接观看视频:
更详细的讲解和代码调试演示过程,请点击链接
更多技术信息,包括操作系统,编译器,面试算法,机器学习,人工智能,请关照我的公众号: