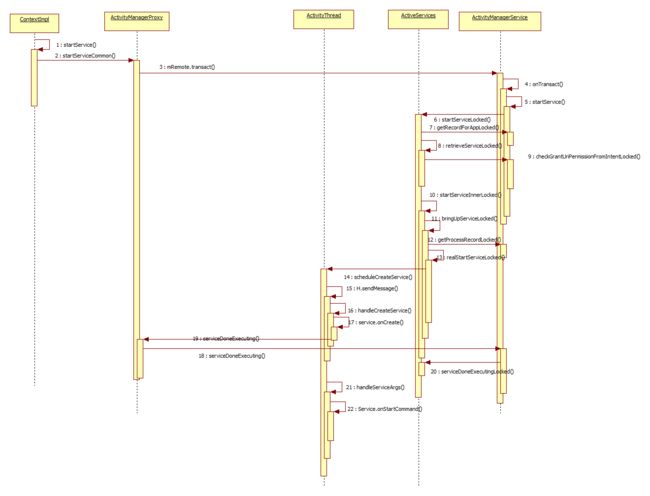
概述:
Ams在整个流程中充当server端的作用, ActivityManagerNative两次调用AMS,第一次调用创建service运行的process,第二次调用创建具体的service
一.从主进程调用到ActivityManagerService进程中,完成新进程的创建;
二. 从新进程调用到ActivityManagerService进程中,获取要在新进程启动的服务的相关信息;
三. 从ActivityManagerService进程又回到新进程中,最终将服务启动起来。
一.从contextimpl的startServiceCommon方法进入到ActivityManangerService的startService方法.
ComponentName res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, userId);
二.从AMS进入到ActivityServices中的startServiceLocked方法
在该方法中首先确定该服务是前台服务还是后台服务,
final boolean callerFg;
if (caller != null) {
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
if (callerApp == null) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Unable to find app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid()
+ ") when starting service " + service);
}
callerFg = callerApp.setSchedGroup != Process.THREAD_GROUP_BG_NONINTERACTIVE;
} else {
callerFg = true;
}
取出一个ServiceLookupResult对象
ServiceLookupResult res =
retrieveServiceLocked(service, resolvedType,
callingPid, callingUid, userId, true, callerFg);
ServiceLookupResult对象包括一个ServiceRecord对象和一个permission字符串
private final class ServiceLookupResult {
final ServiceRecord record;
final String permission;
ServiceLookupResult(ServiceRecord _record, String _permission) {
record = _record;
permission = _permission;
}
}
三.如果ActiveServices中没有存储service的引用,会生成一个新的ServiceRecord进行存储,并将service从PendingServices队列中去除,并且重新开始这个service.
if (r == null && createIfNeeded) {
Intent.FilterComparison filter
= new Intent.FilterComparison(service.cloneFilter());
ServiceRestarter res = new ServiceRestarter();
BatteryStatsImpl.Uid.Pkg.Serv ss = null;
BatteryStatsImpl stats = mAm.mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics();
synchronized (stats) {
ss = stats.getServiceStatsLocked(
sInfo.applicationInfo.uid, sInfo.packageName,
sInfo.name);
}
r = new ServiceRecord(mAm, ss, name, filter, sInfo, callingFromFg, res);
res.setService(r);
smap.mServicesByName.put(name, r);
smap.mServicesByIntent.put(filter, r);
// Make sure this component isn't in the pending list.
for (int i=mPendingServices.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ServiceRecord pr = mPendingServices.get(i);
if (pr.serviceInfo.applicationInfo.uid == sInfo.applicationInfo.uid
&& pr.name.equals(name)) {
mPendingServices.remove(i);
}
}
如果callerApp运行在后台,service有可能因为后台启动队列已满而暂缓启动,但如果callerApp运行在前台则没有这种情况
if (r.delayed) {
// This service is already scheduled for a delayed start; just leave
// it still waiting.
if (DEBUG_DELAYED_STARTS) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Continuing to delay: " + r);
return r.name;
}
if (smap.mStartingBackground.size() >= mMaxStartingBackground) {
// Something else is starting, delay!
Slog.i(TAG_SERVICE, "Delaying start of: " + r);
smap.mDelayedStartList.add(r);
r.delayed = true;
return r.name;
}
四,进入startServiceInnerLocked函数
如果此时
if (r.app != null && r.app.thread != null) {
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, false);
return null;
}
ServiceRecord对象中的app和app对象中的thread均不为null,则调用bringUpServiceLocked()函数,并返回null值,也就是service已经启动的情况
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false);
在bringUpServiceLocked()函数中:
1>
首先会调用
sendServiceArgsLocked函数
在这里出现一个StartItem的数据结构,这个类记录了一次service的启动过程的相关参数
final ArrayList pendingStarts = new ArrayList();
// start() arguments that haven't yet been delivered.
接着调用
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "start");
在这个函数中主要对处于executing状态的service进行判断,看是否已经超时,前台service是20秒,后台servie是200s
之后会执行scheduleServiceArgs()函数,在该函数中跳转到handleServiceArgs函数中
handleServiceArgs((ServiceArgsData)msg.obj);
在handleServiceArgs中主要执行了onStartCommand和onTaskRemoved两个回调函数
res = s.onStartCommand(data.args, data.flags, data.startId);
s.onTaskRemoved(data.args);
通过binder通信回到AMS中执行serviceDoneExecuting()函数
2>
再回到bringUpServieLocked()函数中,判断该service是否处于正在准备restart的状态,或者service处在restart队列就强制把它移除该队列.再判断service是否处于延迟开始状态,
if (!whileRestarting && r.restartDelay > 0) {
// If waiting for a restart, then do nothing.
return null;
}
if (DEBUG_SERVICE) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "Bringing up " + r + " " + r.intent);
// We are now bringing the service up, so no longer in the
// restarting state.
if (mRestartingServices.remove(r)) {
r.resetRestartCounter();
clearRestartingIfNeededLocked(r);
}
// Make sure this service is no longer considered delayed, we are starting it now.
if (r.delayed) {
if (DEBUG_DELAYED_STARTS) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE, "REM FR DELAY LIST (bring up): " + r);
getServiceMap(r.userId).mDelayedStartList.remove(r);
r.delayed = false;
}
// Make sure that the user who owns this service is started. If not,
// we don't want to allow it to run.
if (mAm.mStartedUsers.get(r.userId) == null) {
String msg = "Unable to launch app "
+ r.appInfo.packageName + "/"
+ r.appInfo.uid + " for service "
+ r.intent.getIntent() + ": user " + r.userId + " is stopped";
Slog.w(TAG, msg);
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
3>之后判断该service是否要运行在一个单独的进程中,如果运行在当前进程并且进程已经启动,就直接调用realStartServiceLocked()方法:
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
如果要运行在单独的进程中,会调用startProcessLocked()方法开启一个新的进程.
观察startProcessLocked()方法:
如果service会运行在当前进程中,就会调用getProcessLocked()方法得到一个ProcessRecord对象。
下面代码中有一段逻辑,如果启动service的intent由后台发出,那么一旦判断目前的进程时bad进程就会直接返回一个null值.
badProcess是指在一段时间内发生两次以上crash的进程,AMS中有一个队列来存储这些bad进程,而一旦该进程被restart了,那么它就会从bad队列中去除掉.
if (!isolated) {
app = getProcessRecordLocked(processName, info.uid, keepIfLarge);
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: after getProcessRecord");
if ((intentFlags & Intent.FLAG_FROM_BACKGROUND) != 0) {
// If we are in the background, then check to see if this process
// is bad. If so, we will just silently fail.
if (mBadProcesses.get(info.processName, info.uid) != null) {
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG, "Bad process: " + info.uid
+ "/" + info.processName);
return null;
}
} else {
// When the user is explicitly starting a process, then clear its
// crash count so that we won't make it bad until they see at
// least one crash dialog again, and make the process good again
// if it had been bad.
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG, "Clearing bad process: " + info.uid
+ "/" + info.processName);
mProcessCrashTimes.remove(info.processName, info.uid);
if (mBadProcesses.get(info.processName, info.uid) != null) {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PROC_GOOD,
UserHandle.getUserId(info.uid), info.uid,
info.processName);
mBadProcesses.remove(info.processName, info.uid);
if (app != null) {
app.bad = false;
}
}
}
} else {
// If this is an isolated process, it can't re-use an existing process.
app = null;
}
最终进入到startProcessLocked()方法调用Process.start()方法开启一个新的进程.
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: asking zygote to start proc");
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, app.info.seinfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, entryPointArgs);
/ We don't have to do anything more if:
// (1) There is an existing application record; and
// (2) The caller doesn't think it is dead, OR there is no thread
// object attached to it so we know it couldn't have crashed; and
// (3) There is a pid assigned to it, so it is either starting or
// already running.
创建新新进程后,会把service加入到等待启动的队列中
if (!mPendingServices.contains(r)) {
mPendingServices.add(r);
}
当新进程启动后,会调用attachApplicationLocked方法调用ActiveService中的realStartService()方法启动该service,在方法内部继续调用ActivityThread的scheduleCreateService方法.
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);