下文均基于mysql-connector-java-5.1.43, mysql server version 5.6版本进行分析。
从刚开始接触JDBC开始,就学到使用PrepareStatement对sql进行预编译,不用每次语句都进行一次重新sql解析和编译,相较于使用Statement能够提高程序的性能,那么到底是用PrepareStatement对性能的提升有多大呢?
通过示例代码:
import java.sql.*;
/**
* Created by ZHUKE on 2017/8/18.
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/test", "root", "root");
String prepareSql = "select * from user_info where firstName = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(prepareSql);
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
String statementSql = "select * from user_info where firstName= 'zhuke'";
long nowTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
int count = 100000;
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
preparedStatement.setString(1, "zhuke");
preparedStatement.execute();
}
long nowTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("preparedStatement execute " + count + " times consume " + (nowTime1 - nowTime) + " ms");
long nowTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
statement.execute(statementSql);
}
long nowTime3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("statement execute " + count + " times consume " + (nowTime3 - nowTime2) + " ms");
}
}
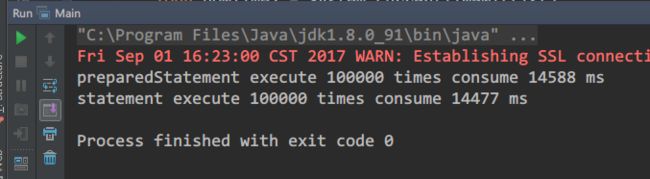
执行同样的语句100000次,得到的结果如下:
14588 : 14477,这就是我一直深信的性能提升???
一定是哪里出了问题,通过查找资料知道,PrepareStatement会将带有参数占位符?的sql语句提交到mysql服务器,服务器会对sql语句进行解析和编译,将编译后的sql id返回给客户端,客户端下次值需要将参数值和sql id发送到服务器即可。以此节省了服务器多次重复编译同一sql语句的开销,而且因为不用每次都发送完整sql内容,也一定程度上节省了网络开销。
那么为什么以上代码中,PrepareStatement没有实现性能提升呢?
通过开启mysql的详细日志,对PrepareStatement的执行来一探究竟。
preparedStatement.setString(1, "zhuke");
preparedStatement.execute();
mysql日志如下:
通过mysql日志我们可以看到,通过PrepareStatement的方式,每次执行发送给mysql服务器的依然是完整的参数拼接完成后的sql语句,并没有利用到上述的服务器预编译的特性。
通过mysql-connector-java(5.1.43版本)连接驱动的源码来查找原因。
public java.sql.PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
synchronized (getConnectionMutex()) {
……
if (this.useServerPreparedStmts && getEmulateUnsupportedPstmts()) {
canServerPrepare = canHandleAsServerPreparedStatement(nativeSql);
}
//如果useServerPreparedStmts配置为true,且服务器支持sql预编译优化,则执行服务器sql优化
if (this.useServerPreparedStmts && canServerPrepare) {
if (this.getCachePreparedStatements()) {
synchronized (this.serverSideStatementCache) {
……
} else {//否则执行本地预编译
……
}
return pStmt;
}
}
服务器支持预编译的情况下,那么就只由useServerPreparedStmts 控制是否进行服务器预编译了。而从源码中又知道其默认值为false。那么如果不显式配置useServerPreparedStmts =true,就不会进行服务器预编译,而只执行本地预编译。
Important change: Due to a number of issues with the use of server-side prepared statements, Connector/J 5.0.5 has disabled their use by default. The disabling of server-side prepared statements does not affect the operation of the connector in any way.
To enable server-side prepared statements, add the following configuration property to your connector string:
useServerPrepStmts=true
The default value of this property is false (that is, Connector/J does not use server-side prepared statements).
通过查找MySQL官网发现,驱动文件在版本 5.0.5后将设为了false,所以需要手动指定和开启服务器预编译功能。
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/relnotes/connector-j/5.1/en/news-5-0-5.html
通过在url链接中添加参数useServerPreparedStmts =true开启服务器预编译。
现在我们看到mysql日志信息如下:
此时我们看到,开启了服务器预编译后,mysql服务器会首先prepare
预编译
select * from user_info where firstName = ?
语句。
再次实验以上代码,看看性能提升了多少:
13312 : 14535,性能提升了8.4%.
与之对应的还有一个参数:cachePrepStmts表示服务器是否需要缓存prepare预编译对象。
// 关闭cachePrepStmts时新建两个preparedStatement
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/test?useServerPrepStmts=true", "root", "root");
String prepareSql = "select * from user_info where firstName = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(prepareSql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "zhuke");
preparedStatement.execute();
preparedStatement.close();
preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(prepareSql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "zhuke1");
preparedStatement.execute();
preparedStatement.close();
可以看到此时,针对完全相同的sql语句,服务器进行了两次预编译过程。
那么当我们开启cachePrepStmts的时候呢?
// 关闭cachePrepStmts时新建两个preparedStatement
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1/test?useServerPrepStmts=true&cachePrepStmts=true", "root", "root");
String prepareSql = "select * from user_info where firstName = ?";
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(prepareSql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "zhuke");
preparedStatement.execute();
preparedStatement.close();
preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(prepareSql);
preparedStatement.setString(1, "zhuke1");
preparedStatement.execute();
preparedStatement.close();
可以看到,开启cachePrepStmts时,mysql服务器只进行了一次预编译过程。
通过阅读源码发现,当开启cachePrepStmts时,客户端会以sql语句作为键,预编译完成后的对象PrepareStatement作为值,保存在Map中,以便下次可以重复利用和缓存。
//prepareStatement关闭时,将对象存入缓存中
public void close() throws SQLException {
MySQLConnection locallyScopedConn = this.connection;
if (locallyScopedConn == null) {
return; // already closed
}
synchronized (locallyScopedConn.getConnectionMutex()) {
if (this.isCached && isPoolable() && !this.isClosed) {
clearParameters();
this.isClosed = true;
//缓存预编译对象
this.connection.recachePreparedStatement(this);
return;
}
realClose(true, true);
}
}
public void recachePreparedStatement(ServerPreparedStatement pstmt) throws SQLException {
synchronized (getConnectionMutex()) {
if (getCachePreparedStatements() && pstmt.isPoolable()) {
synchronized (this.serverSideStatementCache) {
Object oldServerPrepStmt = this.serverSideStatementCache.put(makePreparedStatementCacheKey(pstmt.currentCatalog, pstmt.originalSql), pstmt);
if (oldServerPrepStmt != null) {
((ServerPreparedStatement) oldServerPrepStmt).isCached = false;
((ServerPreparedStatement) oldServerPrepStmt).realClose(true, true);
}
}
}
}
}
结论
使用mysql的预编译对象PrepateStatement时,一定需要设置useServerPrepStmts=true开启服务器预编译功能,设置cachePrepStmts=true开启客户端对预编译对象的缓存。
参考资料:
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/sql-syntax-prepared-statements.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/justfortaste/p/3920140.html